Lin Wang
Refining the Information Bottleneck via Adversarial Information Separation
Feb 09, 2026Abstract:Generalizing from limited data is particularly critical for models in domains such as material science, where task-relevant features in experimental datasets are often heavily confounded by measurement noise and experimental artifacts. Standard regularization techniques fail to precisely separate meaningful features from noise, while existing adversarial adaptation methods are limited by their reliance on explicit separation labels. To address this challenge, we propose the Adversarial Information Separation Framework (AdverISF), which isolates task-relevant features from noise without requiring explicit supervision. AdverISF introduces a self-supervised adversarial mechanism to enforce statistical independence between task-relevant features and noise representations. It further employs a multi-layer separation architecture that progressively recycles noise information across feature hierarchies to recover features inadvertently discarded as noise, thereby enabling finer-grained feature extraction. Extensive experiments demonstrate that AdverISF outperforms state-of-the-art methods in data-scarce scenarios. In addition, evaluations on real-world material design tasks show that it achieves superior generalization performance.
MiniRec: Data-Efficient Reinforcement Learning for LLM-based Recommendation
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:The integration of reinforcement learning (RL) into large language models (LLMs) has opened new opportunities for recommender systems by eliciting reasoning and improving user preference modeling. However, RL-based LLM recommendation faces significant efficiency challenges, making full-data training costly. Existing data selection methods define sample value based on learnability or representativeness, yet their loss- or gradient-driven or dataset coverage-driven criteria often misalign with RL learning dynamics, resulting in suboptimal performance. To address this, we propose MiniRec, a data selection framework tailored for RL-based LLM recommendation. MiniRec evaluates sample learnability using key RL signals -- rewards -- pruning samples that are too easy (too high reward) or too difficult (consistently low reward). It assesses representativeness by aligning sample gradients with the approximated "ideal" global RL optimization trajectory, selecting samples that mainly drive model updates, and it also enforces diversity to reduce redundancy. Combined with a curriculum learning strategy from easy to hard samples, MiniRec significantly reduces training cost while largely preserving performance. Extensive experiments demonstrate MiniRec's effectiveness, highlighting the importance of reward-aligned, trajectory-informed data selection in RL-based LLM recommendation.
Cells on Autopilot: Adaptive Cell (Re)Selection via Reinforcement Learning
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:The widespread deployment of 5G networks, together with the coexistence of 4G/LTE networks, provides mobile devices a diverse set of candidate cells to connect to. However, associating mobile devices to cells to maximize overall network performance, a.k.a. cell (re)selection, remains a key challenge for mobile operators. Today, cell (re)selection parameters are typically configured manually based on operator experience and rarely adapted to dynamic network conditions. In this work, we ask: Can an agent automatically learn and adapt cell (re)selection parameters to consistently improve network performance? We present a reinforcement learning (RL)-based framework called CellPilot that adaptively tunes cell (re)selection parameters by learning spatiotemporal patterns of mobile network dynamics. Our study with real-world data demonstrates that even a lightweight RL agent can outperform conventional heuristic reconfigurations by up to 167%, while generalizing effectively across different network scenarios. These results indicate that data-driven approaches can significantly improve cell (re)selection configurations and enhance mobile network performance.
A Conditioned UNet for Music Source Separation
Dec 17, 2025Abstract:In this paper we propose a conditioned UNet for Music Source Separation (MSS). MSS is generally performed by multi-output neural networks, typically UNets, with each output representing a particular stem from a predefined instrument vocabulary. In contrast, conditioned MSS networks accept an audio query related to a stem of interest alongside the signal from which that stem is to be extracted. Thus, a strict vocabulary is not required and this enables more realistic tasks in MSS. The potential of conditioned approaches for such tasks has been somewhat hidden due to a lack of suitable data, an issue recently addressed with the MoisesDb dataset. A recent method, Banquet, employs this dataset with promising results seen on larger vocabularies. Banquet uses Bandsplit RNN rather than a UNet and the authors state that UNets should not be suitable for conditioned MSS. We counter this argument and propose QSCNet, a novel conditioned UNet for MSS that integrates network conditioning elements in the Sparse Compressed Network for MSS. We find QSCNet to outperform Banquet by over 1dB SNR on a couple of MSS tasks, while using less than half the number of parameters.
Fourier-KAN-Mamba: A Novel State-Space Equation Approach for Time-Series Anomaly Detection
Nov 19, 2025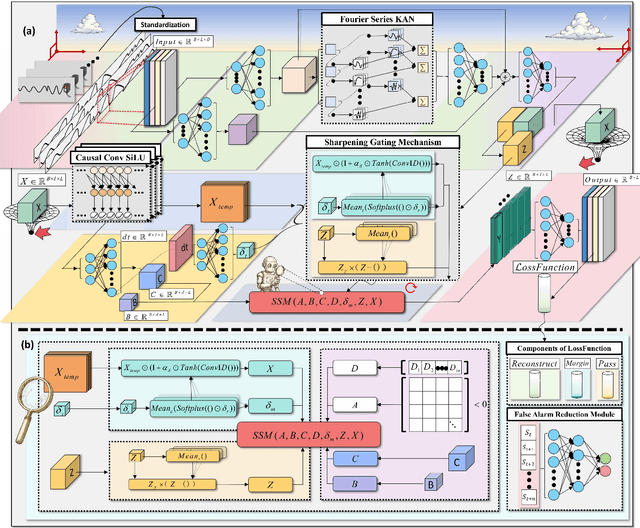
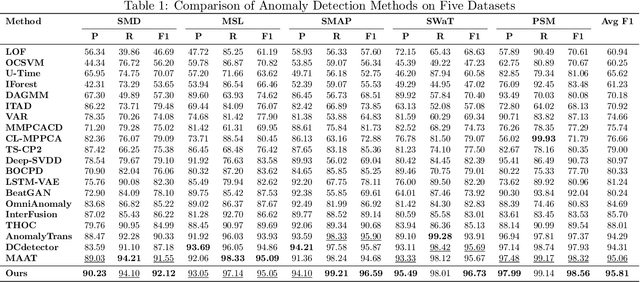
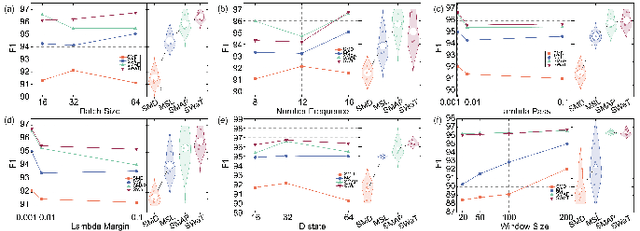

Abstract:Time-series anomaly detection plays a critical role in numerous real-world applications, including industrial monitoring and fault diagnosis. Recently, Mamba-based state-space models have shown remarkable efficiency in long-sequence modeling. However, directly applying Mamba to anomaly detection tasks still faces challenges in capturing complex temporal patterns and nonlinear dynamics. In this paper, we propose Fourier-KAN-Mamba, a novel hybrid architecture that integrates Fourier layer, Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks (KAN), and Mamba selective state-space model. The Fourier layer extracts multi-scale frequency features, KAN enhances nonlinear representation capability, and a temporal gating control mechanism further improves the model's ability to distinguish normal and anomalous patterns. Extensive experiments on MSL, SMAP, and SWaT datasets demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms existing state-of-the-art approaches. Keywords: time-series anomaly detection, state-space model, Mamba, Fourier transform, Kolmogorov-Arnold Network
OneOcc: Semantic Occupancy Prediction for Legged Robots with a Single Panoramic Camera
Nov 05, 2025Abstract:Robust 3D semantic occupancy is crucial for legged/humanoid robots, yet most semantic scene completion (SSC) systems target wheeled platforms with forward-facing sensors. We present OneOcc, a vision-only panoramic SSC framework designed for gait-introduced body jitter and 360{\deg} continuity. OneOcc combines: (i) Dual-Projection fusion (DP-ER) to exploit the annular panorama and its equirectangular unfolding, preserving 360{\deg} continuity and grid alignment; (ii) Bi-Grid Voxelization (BGV) to reason in Cartesian and cylindrical-polar spaces, reducing discretization bias and sharpening free/occupied boundaries; (iii) a lightweight decoder with Hierarchical AMoE-3D for dynamic multi-scale fusion and better long-range/occlusion reasoning; and (iv) plug-and-play Gait Displacement Compensation (GDC) learning feature-level motion correction without extra sensors. We also release two panoramic occupancy benchmarks: QuadOcc (real quadruped, first-person 360{\deg}) and Human360Occ (H3O) (CARLA human-ego 360{\deg} with RGB, Depth, semantic occupancy; standardized within-/cross-city splits). OneOcc sets new state-of-the-art (SOTA): on QuadOcc it beats strong vision baselines and popular LiDAR ones; on H3O it gains +3.83 mIoU (within-city) and +8.08 (cross-city). Modules are lightweight, enabling deployable full-surround perception for legged/humanoid robots. Datasets and code will be publicly available at https://github.com/MasterHow/OneOcc.
Learning Event-guided Exposure-agnostic Video Frame Interpolation via Adaptive Feature Blending
Oct 26, 2025Abstract:Exposure-agnostic video frame interpolation (VFI) is a challenging task that aims to recover sharp, high-frame-rate videos from blurry, low-frame-rate inputs captured under unknown and dynamic exposure conditions. Event cameras are sensors with high temporal resolution, making them especially advantageous for this task. However, existing event-guided methods struggle to produce satisfactory results on severely low-frame-rate blurry videos due to the lack of temporal constraints. In this paper, we introduce a novel event-guided framework for exposure-agnostic VFI, addressing this limitation through two key components: a Target-adaptive Event Sampling (TES) and a Target-adaptive Importance Mapping (TIM). Specifically, TES samples events around the target timestamp and the unknown exposure time to better align them with the corresponding blurry frames. TIM then generates an importance map that considers the temporal proximity and spatial relevance of consecutive features to the target. Guided by this map, our framework adaptively blends consecutive features, allowing temporally aligned features to serve as the primary cues while spatially relevant ones offer complementary support. Extensive experiments on both synthetic and real-world datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach in exposure-agnostic VFI scenarios.
Automated and Scalable SEM Image Analysis of Perovskite Solar Cell Materials via a Deep Segmentation Framework
Sep 30, 2025



Abstract:Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) is indispensable for characterizing the microstructure of thin films during perovskite solar cell fabrication. Accurate identification and quantification of lead iodide and perovskite phases are critical because residual lead iodide strongly influences crystallization pathways and defect formation, while the morphology of perovskite grains governs carrier transport and device stability. Yet current SEM image analysis is still largely manual, limiting throughput and consistency. Here, we present an automated deep learning-based framework for SEM image segmentation that enables precise and efficient identification of lead iodide, perovskite and defect domains across diverse morphologies. Built upon an improved YOLOv8x architecture, our model named PerovSegNet incorporates two novel modules: (i) Adaptive Shuffle Dilated Convolution Block, which enhances multi-scale and fine-grained feature extraction through group convolutions and channel mixing; and (ii) Separable Adaptive Downsampling module, which jointly preserves fine-scale textures and large-scale structures for more robust boundary recognition. Trained on an augmented dataset of 10,994 SEM images, PerovSegNet achieves a mean Average Precision of 87.25% with 265.4 Giga Floating Point Operations, outperforming the baseline YOLOv8x-seg by 4.08%, while reducing model size and computational load by 24.43% and 25.22%, respectively. Beyond segmentation, the framework provides quantitative grain-level metrics, such as lead iodide/perovskite area and count, which can serve as reliable indicators of crystallization efficiency and microstructural quality. These capabilities establish PerovSegNet as a scalable tool for real-time process monitoring and data-driven optimization of perovskite thin-film fabrication.The source code is available at:https://github.com/wlyyj/PerovSegNet/tree/master.
Mind Meets Space: Rethinking Agentic Spatial Intelligence from a Neuroscience-inspired Perspective
Sep 11, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in agentic AI have led to systems capable of autonomous task execution and language-based reasoning, yet their spatial reasoning abilities remain limited and underexplored, largely constrained to symbolic and sequential processing. In contrast, human spatial intelligence, rooted in integrated multisensory perception, spatial memory, and cognitive maps, enables flexible, context-aware decision-making in unstructured environments. Therefore, bridging this gap is critical for advancing Agentic Spatial Intelligence toward better interaction with the physical 3D world. To this end, we first start from scrutinizing the spatial neural models as studied in computational neuroscience, and accordingly introduce a novel computational framework grounded in neuroscience principles. This framework maps core biological functions to six essential computation modules: bio-inspired multimodal sensing, multi-sensory integration, egocentric-allocentric conversion, an artificial cognitive map, spatial memory, and spatial reasoning. Together, these modules form a perspective landscape for agentic spatial reasoning capability across both virtual and physical environments. On top, we conduct a framework-guided analysis of recent methods, evaluating their relevance to each module and identifying critical gaps that hinder the development of more neuroscience-grounded spatial reasoning modules. We further examine emerging benchmarks and datasets and explore potential application domains ranging from virtual to embodied systems, such as robotics. Finally, we outline potential research directions, emphasizing the promising roadmap that can generalize spatial reasoning across dynamic or unstructured environments. We hope this work will benefit the research community with a neuroscience-grounded perspective and a structured pathway. Our project page can be found at Github.
SAC-MIL: Spatial-Aware Correlated Multiple Instance Learning for Histopathology Whole Slide Image Classification
Sep 04, 2025



Abstract:We propose Spatial-Aware Correlated Multiple Instance Learning (SAC-MIL) for performing WSI classification. SAC-MIL consists of a positional encoding module to encode position information and a SAC block to perform full instance correlations. The positional encoding module utilizes the instance coordinates within the slide to encode the spatial relationships instead of the instance index in the input WSI sequence. The positional encoding module can also handle the length extrapolation issue where the training and testing sequences have different lengths. The SAC block is an MLP-based method that performs full instance correlation in linear time complexity with respect to the sequence length. Due to the simple structure of MLP, it is easy to deploy since it does not require custom CUDA kernels, compared to Transformer-based methods for WSI classification. SAC-MIL has achieved state-of-the-art performance on the CAMELYON-16, TCGA-LUNG, and TCGA-BRAC datasets. The code will be released upon acceptance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge