Jiahao Chen
Kimi K2.5: Visual Agentic Intelligence
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:We introduce Kimi K2.5, an open-source multimodal agentic model designed to advance general agentic intelligence. K2.5 emphasizes the joint optimization of text and vision so that two modalities enhance each other. This includes a series of techniques such as joint text-vision pre-training, zero-vision SFT, and joint text-vision reinforcement learning. Building on this multimodal foundation, K2.5 introduces Agent Swarm, a self-directed parallel agent orchestration framework that dynamically decomposes complex tasks into heterogeneous sub-problems and executes them concurrently. Extensive evaluations show that Kimi K2.5 achieves state-of-the-art results across various domains including coding, vision, reasoning, and agentic tasks. Agent Swarm also reduces latency by up to $4.5\times$ over single-agent baselines. We release the post-trained Kimi K2.5 model checkpoint to facilitate future research and real-world applications of agentic intelligence.
ProphetKV: User-Query-Driven Selective Recomputation for Efficient KV Cache Reuse in Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:The prefill stage of long-context Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is severely bottlenecked by computational overhead. To mitigate this, recent methods assemble pre-calculated KV caches of retrieved RAG documents (by a user query) and reprocess selected tokens to recover cross-attention between these pre-calculated KV caches. However, we identify a fundamental "crowding-out effect" in current token selection criteria: globally salient but user-query-irrelevant tokens saturate the limited recomputation budget, displacing the tokens truly essential for answering the user query and degrading inference accuracy. We propose ProphetKV, a user-query-driven KV Cache reuse method for RAG scenarios. ProphetKV dynamically prioritizes tokens based on their semantic relevance to the user query and employs a dual-stage recomputation pipeline to fuse layer-wise attention metrics into a high-utility set. By ensuring the recomputation budget is dedicated to bridging the informational gap between retrieved context and the user query, ProphetKV achieves high-fidelity attention recovery with minimal overhead. Our extensive evaluation results show that ProphetKV retains 96%-101% of full-prefill accuracy with only a 20% recomputation ratio, while achieving accuracy improvements of 8.8%-24.9% on RULER and 18.6%-50.9% on LongBench over the state-of-the-art approaches (e.g., CacheBlend, EPIC, and KVShare).
Unveiling Perceptual Artifacts: A Fine-Grained Benchmark for Interpretable AI-Generated Image Detection
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Current AI-Generated Image (AIGI) detection approaches predominantly rely on binary classification to distinguish real from synthetic images, often lacking interpretable or convincing evidence to substantiate their decisions. This limitation stems from existing AIGI detection benchmarks, which, despite featuring a broad collection of synthetic images, remain restricted in their coverage of artifact diversity and lack detailed, localized annotations. To bridge this gap, we introduce a fine-grained benchmark towards eXplainable AI-Generated image Detection, named X-AIGD, which provides pixel-level, categorized annotations of perceptual artifacts, spanning low-level distortions, high-level semantics, and cognitive-level counterfactuals. These comprehensive annotations facilitate fine-grained interpretability evaluation and deeper insight into model decision-making processes. Our extensive investigation using X-AIGD provides several key insights: (1) Existing AIGI detectors demonstrate negligible reliance on perceptual artifacts, even at the most basic distortion level. (2) While AIGI detectors can be trained to identify specific artifacts, they still substantially base their judgment on uninterpretable features. (3) Explicitly aligning model attention with artifact regions can increase the interpretability and generalization of detectors. The data and code are available at: https://github.com/Coxy7/X-AIGD.
Attributing and Exploiting Safety Vectors through Global Optimization in Large Language Models
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:While Large Language Models (LLMs) are aligned to mitigate risks, their safety guardrails remain fragile against jailbreak attacks. This reveals limited understanding of components governing safety. Existing methods rely on local, greedy attribution that assumes independent component contributions. However, they overlook the cooperative interactions between different components in LLMs, such as attention heads, which jointly contribute to safety mechanisms. We propose \textbf{G}lobal \textbf{O}ptimization for \textbf{S}afety \textbf{V}ector Extraction (GOSV), a framework that identifies safety-critical attention heads through global optimization over all heads simultaneously. We employ two complementary activation repatching strategies: Harmful Patching and Zero Ablation. These strategies identify two spatially distinct sets of safety vectors with consistently low overlap, termed Malicious Injection Vectors and Safety Suppression Vectors, demonstrating that aligned LLMs maintain separate functional pathways for safety purposes. Through systematic analyses, we find that complete safety breakdown occurs when approximately 30\% of total heads are repatched across all models. Building on these insights, we develop a novel inference-time white-box jailbreak method that exploits the identified safety vectors through activation repatching. Our attack substantially outperforms existing white-box attacks across all test models, providing strong evidence for the effectiveness of the proposed GOSV framework on LLM safety interpretability.
Muse: Towards Reproducible Long-Form Song Generation with Fine-Grained Style Control
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Recent commercial systems such as Suno demonstrate strong capabilities in long-form song generation, while academic research remains largely non-reproducible due to the lack of publicly available training data, hindering fair comparison and progress. To this end, we release a fully open-source system for long-form song generation with fine-grained style conditioning, including a licensed synthetic dataset, training and evaluation pipelines, and Muse, an easy-to-deploy song generation model. The dataset consists of 116k fully licensed synthetic songs with automatically generated lyrics and style descriptions paired with audio synthesized by SunoV5. We train Muse via single-stage supervised finetuning of a Qwen-based language model extended with discrete audio tokens using MuCodec, without task-specific losses, auxiliary objectives, or additional architectural components. Our evaluations find that although Muse is trained with a modest data scale and model size, it achieves competitive performance on phoneme error rate, text--music style similarity, and audio aesthetic quality, while enabling controllable segment-level generation across different musical structures. All data, model weights, and training and evaluation pipelines will be publicly released, paving the way for continued progress in controllable long-form song generation research. The project repository is available at https://github.com/yuhui1038/Muse.
The Eminence in Shadow: Exploiting Feature Boundary Ambiguity for Robust Backdoor Attacks
Dec 17, 2025Abstract:Deep neural networks (DNNs) underpin critical applications yet remain vulnerable to backdoor attacks, typically reliant on heuristic brute-force methods. Despite significant empirical advancements in backdoor research, the lack of rigorous theoretical analysis limits understanding of underlying mechanisms, constraining attack predictability and adaptability. Therefore, we provide a theoretical analysis targeting backdoor attacks, focusing on how sparse decision boundaries enable disproportionate model manipulation. Based on this finding, we derive a closed-form, ambiguous boundary region, wherein negligible relabeled samples induce substantial misclassification. Influence function analysis further quantifies significant parameter shifts caused by these margin samples, with minimal impact on clean accuracy, formally grounding why such low poison rates suffice for efficacious attacks. Leveraging these insights, we propose Eminence, an explainable and robust black-box backdoor framework with provable theoretical guarantees and inherent stealth properties. Eminence optimizes a universal, visually subtle trigger that strategically exploits vulnerable decision boundaries and effectively achieves robust misclassification with exceptionally low poison rates (< 0.1%, compared to SOTA methods typically requiring > 1%). Comprehensive experiments validate our theoretical discussions and demonstrate the effectiveness of Eminence, confirming an exponential relationship between margin poisoning and adversarial boundary manipulation. Eminence maintains > 90% attack success rate, exhibits negligible clean-accuracy loss, and demonstrates high transferability across diverse models, datasets and scenarios.
MaskAttn-SDXL: Controllable Region-Level Text-To-Image Generation
Sep 18, 2025Abstract:Text-to-image diffusion models achieve impressive realism but often suffer from compositional failures on prompts with multiple objects, attributes, and spatial relations, resulting in cross-token interference where entities entangle, attributes mix across objects, and spatial cues are violated. To address these failures, we propose MaskAttn-SDXL,a region-level gating mechanism applied to the cross-attention logits of Stable Diffusion XL(SDXL)'s UNet. MaskAttn-SDXL learns a binary mask per layer, injecting it into each cross-attention logit map before softmax to sparsify token-to-latent interactions so that only semantically relevant connections remain active. The method requires no positional encodings, auxiliary tokens, or external region masks, and preserves the original inference path with negligible overhead. In practice, our model improves spatial compliance and attribute binding in multi-object prompts while preserving overall image quality and diversity. These findings demonstrate that logit-level maksed cross-attention is an data-efficient primitve for enforcing compositional control, and our method thus serves as a practical extension for spatial control in text-to-image generation.
SeqAffordSplat: Scene-level Sequential Affordance Reasoning on 3D Gaussian Splatting
Jul 31, 2025Abstract:3D affordance reasoning, the task of associating human instructions with the functional regions of 3D objects, is a critical capability for embodied agents. Current methods based on 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) are fundamentally limited to single-object, single-step interactions, a paradigm that falls short of addressing the long-horizon, multi-object tasks required for complex real-world applications. To bridge this gap, we introduce the novel task of Sequential 3D Gaussian Affordance Reasoning and establish SeqAffordSplat, a large-scale benchmark featuring 1800+ scenes to support research on long-horizon affordance understanding in complex 3DGS environments. We then propose SeqSplatNet, an end-to-end framework that directly maps an instruction to a sequence of 3D affordance masks. SeqSplatNet employs a large language model that autoregressively generates text interleaved with special segmentation tokens, guiding a conditional decoder to produce the corresponding 3D mask. To handle complex scene geometry, we introduce a pre-training strategy, Conditional Geometric Reconstruction, where the model learns to reconstruct complete affordance region masks from known geometric observations, thereby building a robust geometric prior. Furthermore, to resolve semantic ambiguities, we design a feature injection mechanism that lifts rich semantic features from 2D Vision Foundation Models (VFM) and fuses them into the 3D decoder at multiple scales. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method sets a new state-of-the-art on our challenging benchmark, effectively advancing affordance reasoning from single-step interactions to complex, sequential tasks at the scene level.
Kimi K2: Open Agentic Intelligence
Jul 28, 2025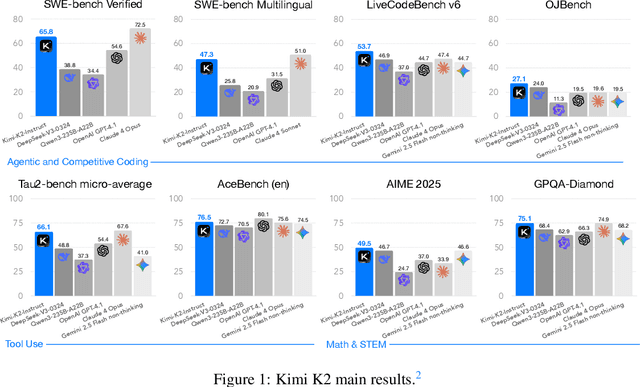
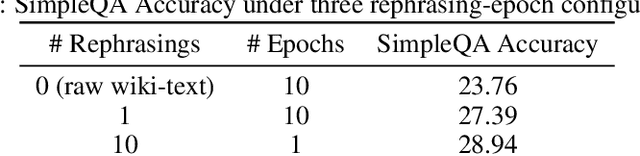
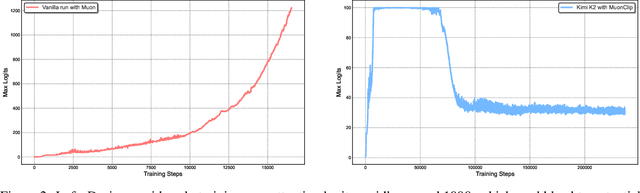
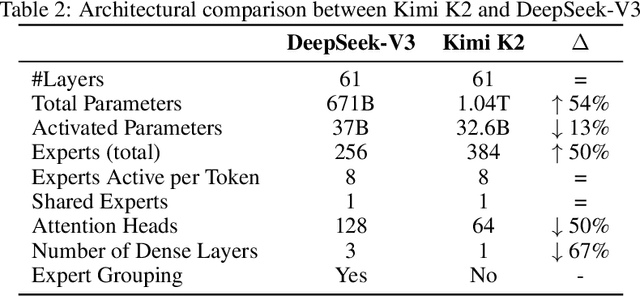
Abstract:We introduce Kimi K2, a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) large language model with 32 billion activated parameters and 1 trillion total parameters. We propose the MuonClip optimizer, which improves upon Muon with a novel QK-clip technique to address training instability while enjoying the advanced token efficiency of Muon. Based on MuonClip, K2 was pre-trained on 15.5 trillion tokens with zero loss spike. During post-training, K2 undergoes a multi-stage post-training process, highlighted by a large-scale agentic data synthesis pipeline and a joint reinforcement learning (RL) stage, where the model improves its capabilities through interactions with real and synthetic environments. Kimi K2 achieves state-of-the-art performance among open-source non-thinking models, with strengths in agentic capabilities. Notably, K2 obtains 66.1 on Tau2-Bench, 76.5 on ACEBench (En), 65.8 on SWE-Bench Verified, and 47.3 on SWE-Bench Multilingual -- surpassing most open and closed-sourced baselines in non-thinking settings. It also exhibits strong capabilities in coding, mathematics, and reasoning tasks, with a score of 53.7 on LiveCodeBench v6, 49.5 on AIME 2025, 75.1 on GPQA-Diamond, and 27.1 on OJBench, all without extended thinking. These results position Kimi K2 as one of the most capable open-source large language models to date, particularly in software engineering and agentic tasks. We release our base and post-trained model checkpoints to facilitate future research and applications of agentic intelligence.
The Singapore Consensus on Global AI Safety Research Priorities
Jun 25, 2025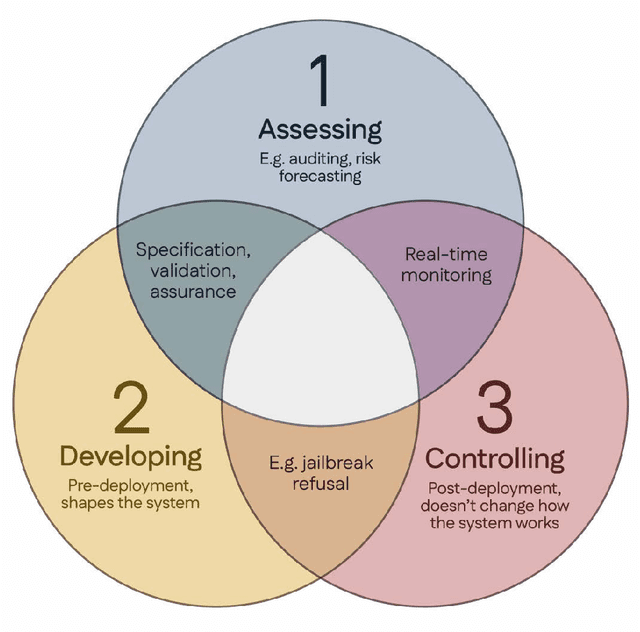
Abstract:Rapidly improving AI capabilities and autonomy hold significant promise of transformation, but are also driving vigorous debate on how to ensure that AI is safe, i.e., trustworthy, reliable, and secure. Building a trusted ecosystem is therefore essential -- it helps people embrace AI with confidence and gives maximal space for innovation while avoiding backlash. The "2025 Singapore Conference on AI (SCAI): International Scientific Exchange on AI Safety" aimed to support research in this space by bringing together AI scientists across geographies to identify and synthesise research priorities in AI safety. This resulting report builds on the International AI Safety Report chaired by Yoshua Bengio and backed by 33 governments. By adopting a defence-in-depth model, this report organises AI safety research domains into three types: challenges with creating trustworthy AI systems (Development), challenges with evaluating their risks (Assessment), and challenges with monitoring and intervening after deployment (Control).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge