Licheng Jiao
STVG-R1: Incentivizing Instance-Level Reasoning and Grounding in Videos via Reinforcement Learning
Feb 12, 2026Abstract:In vision-language models (VLMs), misalignment between textual descriptions and visual coordinates often induces hallucinations. This issue becomes particularly severe in dense prediction tasks such as spatial-temporal video grounding (STVG). Prior approaches typically focus on enhancing visual-textual alignment or attaching auxiliary decoders. However, these strategies inevitably introduce additional trainable modules, leading to significant annotation costs and computational overhead. In this work, we propose a novel visual prompting paradigm that avoids the difficult problem of aligning coordinates across modalities. Specifically, we reformulate per-frame coordinate prediction as a compact instance-level identification problem by assigning each object a unique, temporally consistent ID. These IDs are embedded into the video as visual prompts, providing explicit and interpretable inputs to the VLMs. Furthermore, we introduce STVG-R1, the first reinforcement learning framework for STVG, which employs a task-driven reward to jointly optimize temporal accuracy, spatial consistency, and structural format regularization. Extensive experiments on six benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach. STVG-R1 surpasses the baseline Qwen2.5-VL-7B by a remarkable margin of 20.9% on m_IoU on the HCSTVG-v2 benchmark, establishing a new state of the art (SOTA). Surprisingly, STVG-R1 also exhibits strong zero-shot generalization to multi-object referring video object segmentation tasks, achieving a SOTA 47.3% J&F on MeViS.
Task-free Adaptive Meta Black-box Optimization
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Handcrafted optimizers become prohibitively inefficient for complex black-box optimization (BBO) tasks. MetaBBO addresses this challenge by meta-learning to automatically configure optimizers for low-level BBO tasks, thereby eliminating heuristic dependencies. However, existing methods typically require extensive handcrafted training tasks to learn meta-strategies that generalize to target tasks, which poses a critical limitation for realistic applications with unknown task distributions. To overcome the issue, we propose the Adaptive meta Black-box Optimization Model (ABOM), which performs online parameter adaptation using solely optimization data from the target task, obviating the need for predefined task distributions. Unlike conventional metaBBO frameworks that decouple meta-training and optimization phases, ABOM introduces a closed-loop adaptive parameter learning mechanism, where parameterized evolutionary operators continuously self-update by leveraging generated populations during optimization. This paradigm shift enables zero-shot optimization: ABOM achieves competitive performance on synthetic BBO benchmarks and realistic unmanned aerial vehicle path planning problems without any handcrafted training tasks. Visualization studies reveal that parameterized evolutionary operators exhibit statistically significant search patterns, including natural selection and genetic recombination.
CLNet: Cross-View Correspondence Makes a Stronger Geo-Localizationer
Dec 16, 2025Abstract:Image retrieval-based cross-view geo-localization (IRCVGL) aims to match images captured from significantly different viewpoints, such as satellite and street-level images. Existing methods predominantly rely on learning robust global representations or implicit feature alignment, which often fail to model explicit spatial correspondences crucial for accurate localization. In this work, we propose a novel correspondence-aware feature refinement framework, termed CLNet, that explicitly bridges the semantic and geometric gaps between different views. CLNet decomposes the view alignment process into three learnable and complementary modules: a Neural Correspondence Map (NCM) that spatially aligns cross-view features via latent correspondence fields; a Nonlinear Embedding Converter (NEC) that remaps features across perspectives using an MLP-based transformation; and a Global Feature Recalibration (GFR) module that reweights informative feature channels guided by learned spatial cues. The proposed CLNet can jointly capture both high-level semantics and fine-grained alignments. Extensive experiments on four public benchmarks, CVUSA, CVACT, VIGOR, and University-1652, demonstrate that our proposed CLNet achieves state-of-the-art performance while offering better interpretability and generalizability.
DI3CL: Contrastive Learning With Dynamic Instances and Contour Consistency for SAR Land-Cover Classification Foundation Model
Nov 12, 2025Abstract:Although significant advances have been achieved in SAR land-cover classification, recent methods remain predominantly focused on supervised learning, which relies heavily on extensive labeled datasets. This dependency not only limits scalability and generalization but also restricts adaptability to diverse application scenarios. In this paper, a general-purpose foundation model for SAR land-cover classification is developed, serving as a robust cornerstone to accelerate the development and deployment of various downstream models. Specifically, a Dynamic Instance and Contour Consistency Contrastive Learning (DI3CL) pre-training framework is presented, which incorporates a Dynamic Instance (DI) module and a Contour Consistency (CC) module. DI module enhances global contextual awareness by enforcing local consistency across different views of the same region. CC module leverages shallow feature maps to guide the model to focus on the geometric contours of SAR land-cover objects, thereby improving structural discrimination. Additionally, to enhance robustness and generalization during pre-training, a large-scale and diverse dataset named SARSense, comprising 460,532 SAR images, is constructed to enable the model to capture comprehensive and representative features. To evaluate the generalization capability of our foundation model, we conducted extensive experiments across a variety of SAR land-cover classification tasks, including SAR land-cover mapping, water body detection, and road extraction. The results consistently demonstrate that the proposed DI3CL outperforms existing methods. Our code and pre-trained weights are publicly available at: https://github.com/SARpre-train/DI3CL.
SoccerNet 2025 Challenges Results
Aug 26, 2025Abstract:The SoccerNet 2025 Challenges mark the fifth annual edition of the SoccerNet open benchmarking effort, dedicated to advancing computer vision research in football video understanding. This year's challenges span four vision-based tasks: (1) Team Ball Action Spotting, focused on detecting ball-related actions in football broadcasts and assigning actions to teams; (2) Monocular Depth Estimation, targeting the recovery of scene geometry from single-camera broadcast clips through relative depth estimation for each pixel; (3) Multi-View Foul Recognition, requiring the analysis of multiple synchronized camera views to classify fouls and their severity; and (4) Game State Reconstruction, aimed at localizing and identifying all players from a broadcast video to reconstruct the game state on a 2D top-view of the field. Across all tasks, participants were provided with large-scale annotated datasets, unified evaluation protocols, and strong baselines as starting points. This report presents the results of each challenge, highlights the top-performing solutions, and provides insights into the progress made by the community. The SoccerNet Challenges continue to serve as a driving force for reproducible, open research at the intersection of computer vision, artificial intelligence, and sports. Detailed information about the tasks, challenges, and leaderboards can be found at https://www.soccer-net.org, with baselines and development kits available at https://github.com/SoccerNet.
Self-similarity Analysis in Deep Neural Networks
Jul 23, 2025Abstract:Current research has found that some deep neural networks exhibit strong hierarchical self-similarity in feature representation or parameter distribution. However, aside from preliminary studies on how the power-law distribution of weights across different training stages affects model performance,there has been no quantitative analysis on how the self-similarity of hidden space geometry influences model weight optimization, nor is there a clear understanding of the dynamic behavior of internal neurons. Therefore, this paper proposes a complex network modeling method based on the output features of hidden-layer neurons to investigate the self-similarity of feature networks constructed at different hidden layers, and analyzes how adjusting the degree of self-similarity in feature networks can enhance the classification performance of deep neural networks. Validated on three types of networks MLP architectures, convolutional networks, and attention architectures this study reveals that the degree of self-similarity exhibited by feature networks varies across different model architectures. Furthermore, embedding constraints on the self-similarity of feature networks during the training process can improve the performance of self-similar deep neural networks (MLP architectures and attention architectures) by up to 6 percentage points.
Meta knowledge assisted Evolutionary Neural Architecture Search
Apr 30, 2025Abstract:Evolutionary computation (EC)-based neural architecture search (NAS) has achieved remarkable performance in the automatic design of neural architectures. However, the high computational cost associated with evaluating searched architectures poses a challenge for these methods, and a fixed form of learning rate (LR) schedule means greater information loss on diverse searched architectures. This paper introduces an efficient EC-based NAS method to solve these problems via an innovative meta-learning framework. Specifically, a meta-learning-rate (Meta-LR) scheme is used through pretraining to obtain a suitable LR schedule, which guides the training process with lower information loss when evaluating each individual. An adaptive surrogate model is designed through an adaptive threshold to select the potential architectures in a few epochs and then evaluate the potential architectures with complete epochs. Additionally, a periodic mutation operator is proposed to increase the diversity of the population, which enhances the generalizability and robustness. Experiments on CIFAR-10, CIFAR-100, and ImageNet1K datasets demonstrate that the proposed method achieves high performance comparable to that of many state-of-the-art peer methods, with lower computational cost and greater robustness.
Lightweight Adapter Learning for More Generalized Remote Sensing Change Detection
Apr 28, 2025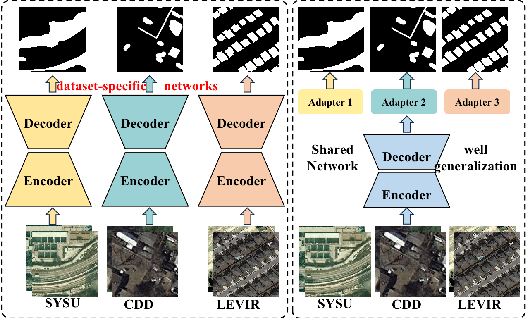
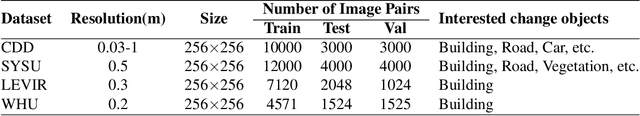
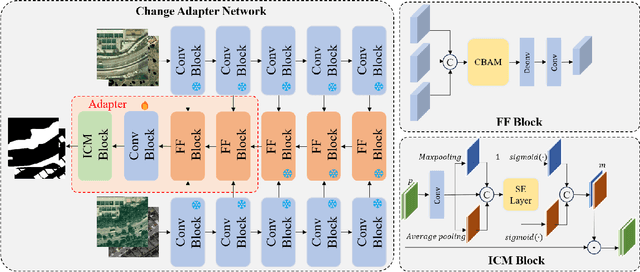
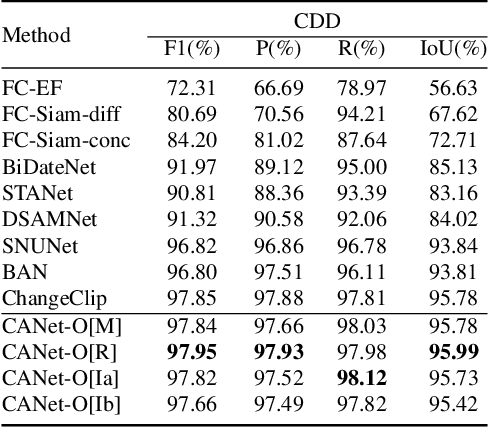
Abstract:Deep learning methods have shown promising performances in remote sensing image change detection (CD). However, existing methods usually train a dataset-specific deep network for each dataset. Due to the significant differences in the data distribution and labeling between various datasets, the trained dataset-specific deep network has poor generalization performances on other datasets. To solve this problem, this paper proposes a change adapter network (CANet) for a more universal and generalized CD. CANet contains dataset-shared and dataset-specific learning modules. The former explores the discriminative features of images, and the latter designs a lightweight adapter model, to deal with the characteristics of different datasets in data distribution and labeling. The lightweight adapter can quickly generalize the deep network for new CD tasks with a small computation cost. Specifically, this paper proposes an interesting change region mask (ICM) in the adapter, which can adaptively focus on interested change objects and decrease the influence of labeling differences in various datasets. Moreover, CANet adopts a unique batch normalization layer for each dataset to deal with data distribution differences. Compared with existing deep learning methods, CANet can achieve satisfactory CD performances on various datasets simultaneously. Experimental results on several public datasets have verified the effectiveness and advantages of the proposed CANet on CD. CANet has a stronger generalization ability, smaller training costs (merely updating 4.1%-7.7% parameters), and better performances under limited training datasets than other deep learning methods, which also can be flexibly inserted with existing deep models.
ACMamba: Fast Unsupervised Anomaly Detection via An Asymmetrical Consensus State Space Model
Apr 16, 2025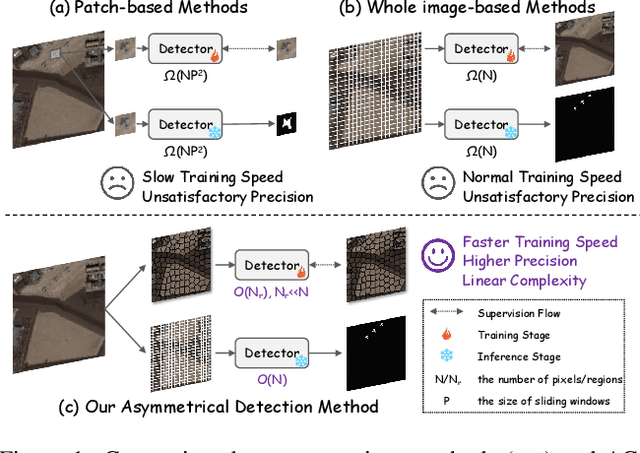
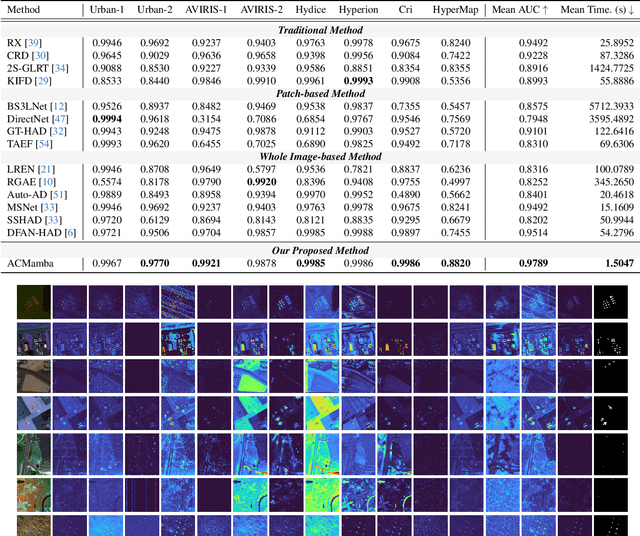
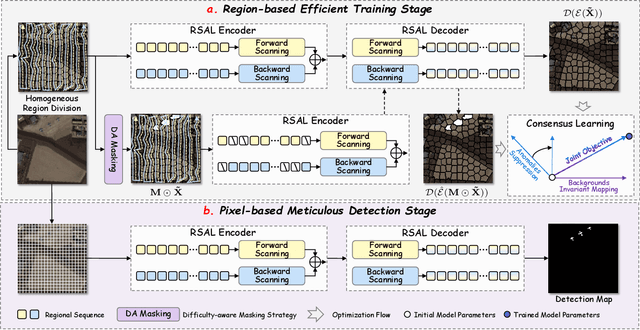
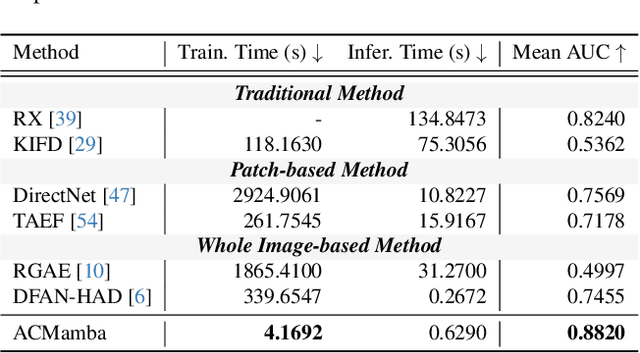
Abstract:Unsupervised anomaly detection in hyperspectral images (HSI), aiming to detect unknown targets from backgrounds, is challenging for earth surface monitoring. However, current studies are hindered by steep computational costs due to the high-dimensional property of HSI and dense sampling-based training paradigm, constraining their rapid deployment. Our key observation is that, during training, not all samples within the same homogeneous area are indispensable, whereas ingenious sampling can provide a powerful substitute for reducing costs. Motivated by this, we propose an Asymmetrical Consensus State Space Model (ACMamba) to significantly reduce computational costs without compromising accuracy. Specifically, we design an asymmetrical anomaly detection paradigm that utilizes region-level instances as an efficient alternative to dense pixel-level samples. In this paradigm, a low-cost Mamba-based module is introduced to discover global contextual attributes of regions that are essential for HSI reconstruction. Additionally, we develop a consensus learning strategy from the optimization perspective to simultaneously facilitate background reconstruction and anomaly compression, further alleviating the negative impact of anomaly reconstruction. Theoretical analysis and extensive experiments across eight benchmarks verify the superiority of ACMamba, demonstrating a faster speed and stronger performance over the state-of-the-art.
PVUW 2025 Challenge Report: Advances in Pixel-level Understanding of Complex Videos in the Wild
Apr 15, 2025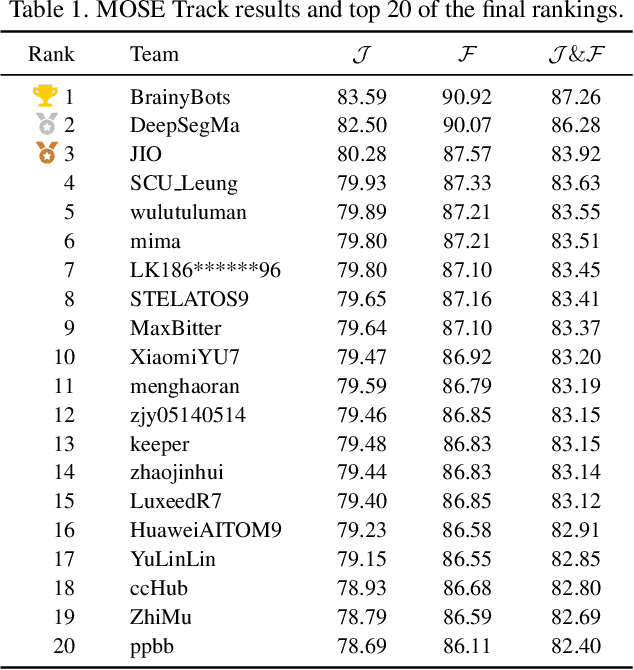
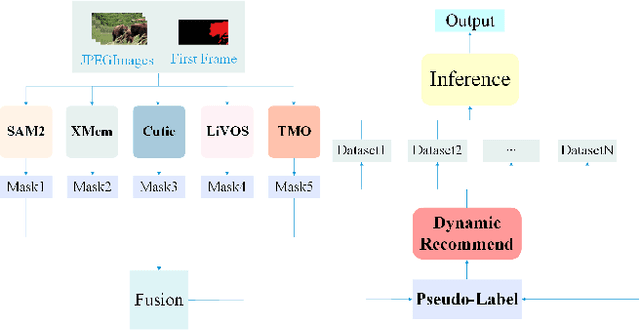
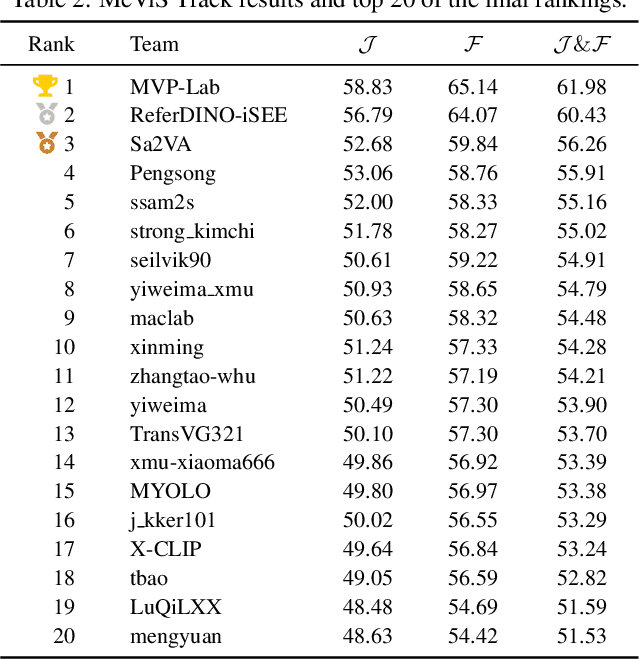
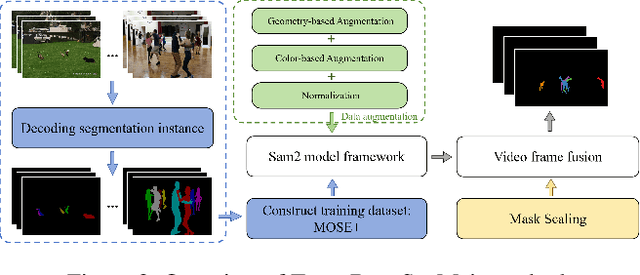
Abstract:This report provides a comprehensive overview of the 4th Pixel-level Video Understanding in the Wild (PVUW) Challenge, held in conjunction with CVPR 2025. It summarizes the challenge outcomes, participating methodologies, and future research directions. The challenge features two tracks: MOSE, which focuses on complex scene video object segmentation, and MeViS, which targets motion-guided, language-based video segmentation. Both tracks introduce new, more challenging datasets designed to better reflect real-world scenarios. Through detailed evaluation and analysis, the challenge offers valuable insights into the current state-of-the-art and emerging trends in complex video segmentation. More information can be found on the workshop website: https://pvuw.github.io/.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge