Qi Zang
Orthogonal Projection Subspace to Aggregate Online Prior-knowledge for Continual Test-time Adaptation
Jun 23, 2025



Abstract:Continual Test Time Adaptation (CTTA) is a task that requires a source pre-trained model to continually adapt to new scenarios with changing target distributions. Existing CTTA methods primarily focus on mitigating the challenges of catastrophic forgetting and error accumulation. Though there have been emerging methods based on forgetting adaptation with parameter-efficient fine-tuning, they still struggle to balance competitive performance and efficient model adaptation, particularly in complex tasks like semantic segmentation. In this paper, to tackle the above issues, we propose a novel pipeline, Orthogonal Projection Subspace to aggregate online Prior-knowledge, dubbed OoPk. Specifically, we first project a tuning subspace orthogonally which allows the model to adapt to new domains while preserving the knowledge integrity of the pre-trained source model to alleviate catastrophic forgetting. Then, we elaborate an online prior-knowledge aggregation strategy that employs an aggressive yet efficient image masking strategy to mimic potential target dynamism, enhancing the student model's domain adaptability. This further gradually ameliorates the teacher model's knowledge, ensuring high-quality pseudo labels and reducing error accumulation. We demonstrate our method with extensive experiments that surpass previous CTTA methods and achieve competitive performances across various continual TTA benchmarks in semantic segmentation tasks.
Generalization-aware Remote Sensing Change Detection via Domain-agnostic Learning
Apr 01, 2025Abstract:Change detection has essential significance for the region's development, in which pseudo-changes between bitemporal images induced by imaging environmental factors are key challenges. Existing transformation-based methods regard pseudo-changes as a kind of style shift and alleviate it by transforming bitemporal images into the same style using generative adversarial networks (GANs). However, their efforts are limited by two drawbacks: 1) Transformed images suffer from distortion that reduces feature discrimination. 2) Alignment hampers the model from learning domain-agnostic representations that degrades performance on scenes with domain shifts from the training data. Therefore, oriented from pseudo-changes caused by style differences, we present a generalizable domain-agnostic difference learning network (DonaNet). For the drawback 1), we argue for local-level statistics as style proxies to assist against domain shifts. For the drawback 2), DonaNet learns domain-agnostic representations by removing domain-specific style of encoded features and highlighting the class characteristics of objects. In the removal, we propose a domain difference removal module to reduce feature variance while preserving discriminative properties and propose its enhanced version to provide possibilities for eliminating more style by decorrelating the correlation between features. In the highlighting, we propose a cross-temporal generalization learning strategy to imitate latent domain shifts, thus enabling the model to extract feature representations more robust to shifts actively. Extensive experiments conducted on three public datasets demonstrate that DonaNet outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods with a smaller model size and is more robust to domain shift.
ChangeDiff: A Multi-Temporal Change Detection Data Generator with Flexible Text Prompts via Diffusion Model
Dec 20, 2024



Abstract:Data-driven deep learning models have enabled tremendous progress in change detection (CD) with the support of pixel-level annotations. However, collecting diverse data and manually annotating them is costly, laborious, and knowledge-intensive. Existing generative methods for CD data synthesis show competitive potential in addressing this issue but still face the following limitations: 1) difficulty in flexibly controlling change events, 2) dependence on additional data to train the data generators, 3) focus on specific change detection tasks. To this end, this paper focuses on the semantic CD (SCD) task and develops a multi-temporal SCD data generator ChangeDiff by exploring powerful diffusion models. ChangeDiff innovatively generates change data in two steps: first, it uses text prompts and a text-to-layout (T2L) model to create continuous layouts, and then it employs layout-to-image (L2I) to convert these layouts into images. Specifically, we propose multi-class distribution-guided text prompts (MCDG-TP), allowing for layouts to be generated flexibly through controllable classes and their corresponding ratios. Subsequently, to generalize the T2L model to the proposed MCDG-TP, a class distribution refinement loss is further designed as training supervision. %For the former, a multi-classdistribution-guided text prompt (MCDG-TP) is proposed to complement via controllable classes and ratios. To generalize the text-to-image diffusion model to the proposed MCDG-TP, a class distribution refinement loss is designed as training supervision. For the latter, MCDG-TP in three modes is proposed to synthesize new layout masks from various texts. Our generated data shows significant progress in temporal continuity, spatial diversity, and quality realism, empowering change detectors with accuracy and transferability. The code is available at https://github.com/DZhaoXd/ChangeDiff
Stable Neighbor Denoising for Source-free Domain Adaptive Segmentation
Jun 10, 2024
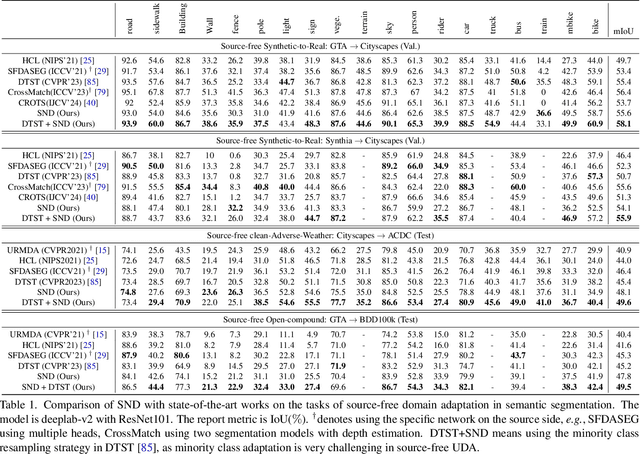
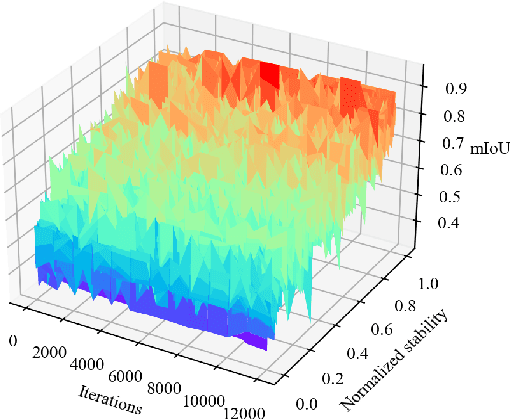
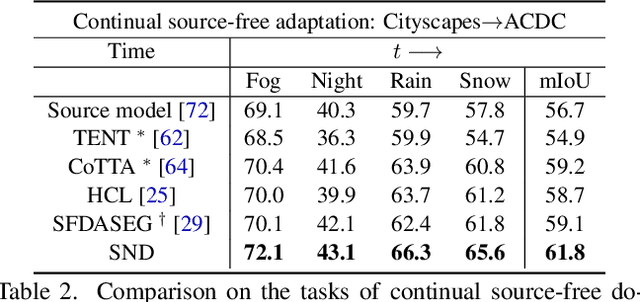
Abstract:We study source-free unsupervised domain adaptation (SFUDA) for semantic segmentation, which aims to adapt a source-trained model to the target domain without accessing the source data. Many works have been proposed to address this challenging problem, among which uncertainty-based self-training is a predominant approach. However, without comprehensive denoising mechanisms, they still largely fall into biased estimates when dealing with different domains and confirmation bias. In this paper, we observe that pseudo-label noise is mainly contained in unstable samples in which the predictions of most pixels undergo significant variations during self-training. Inspired by this, we propose a novel mechanism to denoise unstable samples with stable ones. Specifically, we introduce the Stable Neighbor Denoising (SND) approach, which effectively discovers highly correlated stable and unstable samples by nearest neighbor retrieval and guides the reliable optimization of unstable samples by bi-level learning. Moreover, we compensate for the stable set by object-level object paste, which can further eliminate the bias caused by less learned classes. Our SND enjoys two advantages. First, SND does not require a specific segmentor structure, endowing its universality. Second, SND simultaneously addresses the issues of class, domain, and confirmation biases during adaptation, ensuring its effectiveness. Extensive experiments show that SND consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods in various SFUDA semantic segmentation settings. In addition, SND can be easily integrated with other approaches, obtaining further improvements.
* 2024 Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition
Semantic Connectivity-Driven Pseudo-labeling for Cross-domain Segmentation
Dec 11, 2023



Abstract:Presently, self-training stands as a prevailing approach in cross-domain semantic segmentation, enhancing model efficacy by training with pixels assigned with reliable pseudo-labels. However, we find two critical limitations in this paradigm. (1) The majority of reliable pixels exhibit a speckle-shaped pattern and are primarily located in the central semantic region. This presents challenges for the model in accurately learning semantics. (2) Category noise in speckle pixels is difficult to locate and correct, leading to error accumulation in self-training. To address these limitations, we propose a novel approach called Semantic Connectivity-driven pseudo-labeling (SeCo). This approach formulates pseudo-labels at the connectivity level and thus can facilitate learning structured and low-noise semantics. Specifically, SeCo comprises two key components: Pixel Semantic Aggregation (PSA) and Semantic Connectivity Correction (SCC). Initially, PSA divides semantics into 'stuff' and 'things' categories and aggregates speckled pseudo-labels into semantic connectivity through efficient interaction with the Segment Anything Model (SAM). This enables us not only to obtain accurate boundaries but also simplifies noise localization. Subsequently, SCC introduces a simple connectivity classification task, which enables locating and correcting connectivity noise with the guidance of loss distribution. Extensive experiments demonstrate that SeCo can be flexibly applied to various cross-domain semantic segmentation tasks, including traditional unsupervised, source-free, and black-box domain adaptation, significantly improving the performance of existing state-of-the-art methods. The code is available at https://github.com/DZhaoXd/SeCo.
The Outcome of the 2022 Landslide4Sense Competition: Advanced Landslide Detection from Multi-Source Satellite Imagery
Sep 12, 2022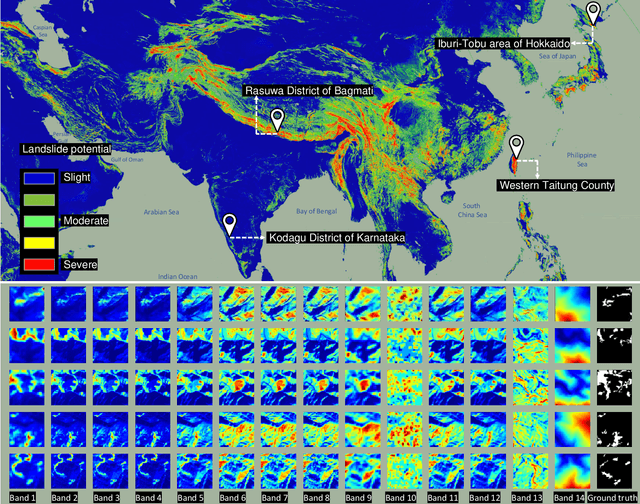
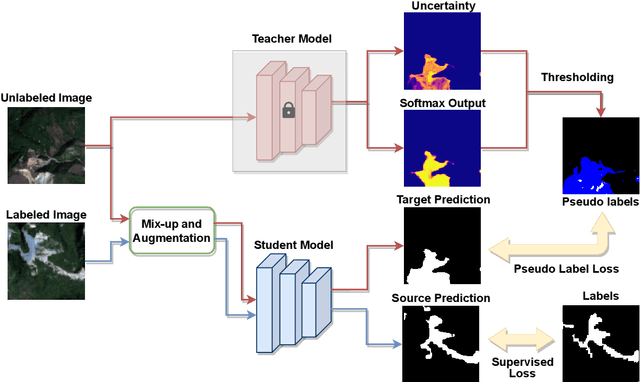
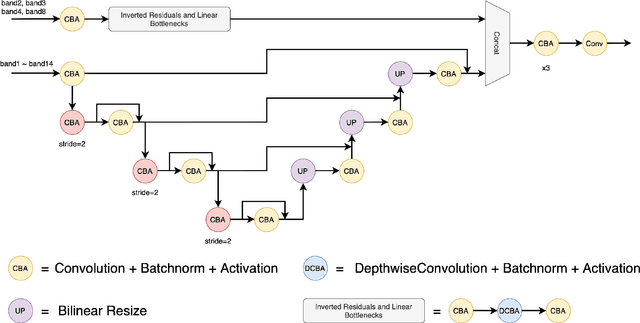
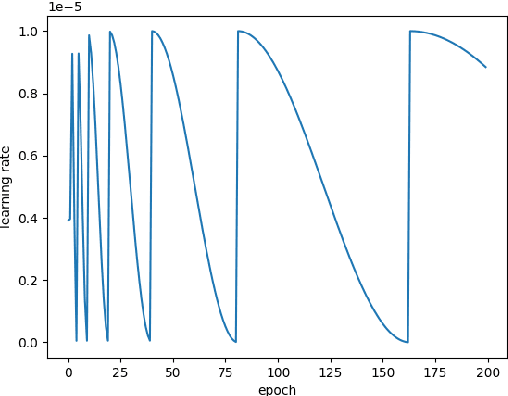
Abstract:The scientific outcomes of the 2022 Landslide4Sense (L4S) competition organized by the Institute of Advanced Research in Artificial Intelligence (IARAI) are presented here. The objective of the competition is to automatically detect landslides based on large-scale multiple sources of satellite imagery collected globally. The 2022 L4S aims to foster interdisciplinary research on recent developments in deep learning (DL) models for the semantic segmentation task using satellite imagery. In the past few years, DL-based models have achieved performance that meets expectations on image interpretation, due to the development of convolutional neural networks (CNNs). The main objective of this article is to present the details and the best-performing algorithms featured in this competition. The winning solutions are elaborated with state-of-the-art models like the Swin Transformer, SegFormer, and U-Net. Advanced machine learning techniques and strategies such as hard example mining, self-training, and mix-up data augmentation are also considered. Moreover, we describe the L4S benchmark data set in order to facilitate further comparisons, and report the results of the accuracy assessment online. The data is accessible on \textit{Future Development Leaderboard} for future evaluation at \url{https://www.iarai.ac.at/landslide4sense/challenge/}, and researchers are invited to submit more prediction results, evaluate the accuracy of their methods, compare them with those of other users, and, ideally, improve the landslide detection results reported in this article.
More Separable and Easier to Segment: A Cluster Alignment Method for Cross-Domain Semantic Segmentation
May 07, 2021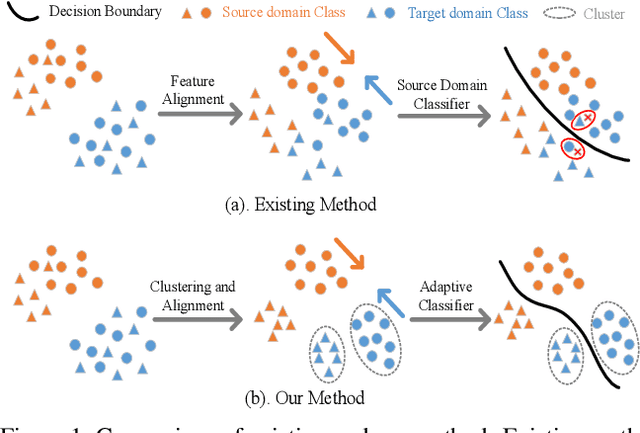



Abstract:Feature alignment between domains is one of the mainstream methods for Unsupervised Domain Adaptation (UDA) semantic segmentation. Existing feature alignment methods for semantic segmentation learn domain-invariant features by adversarial training to reduce domain discrepancy, but they have two limits: 1) associations among pixels are not maintained, 2) the classifier trained on the source domain couldn't adapted well to the target. In this paper, we propose a new UDA semantic segmentation approach based on domain closeness assumption to alleviate the above problems. Specifically, a prototype clustering strategy is applied to cluster pixels with the same semantic, which will better maintain associations among target domain pixels during the feature alignment. After clustering, to make the classifier more adaptive, a normalized cut loss based on the affinity graph of the target domain is utilized, which will make the decision boundary target-specific. Sufficient experiments conducted on GTA5 $\rightarrow$ Cityscapes and SYNTHIA $\rightarrow$ Cityscapes proved the effectiveness of our method, which illustrated that our results achieved the new state-of-the-art.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge