Yi Li
Victor
CoSA: Compressed Sensing-Based Adaptation of Large Language Models
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT) has emerged as a practical paradigm for adapting large language models (LLMs) without updating all parameters. Most existing approaches, such as LoRA and PiSSA, rely on low-rank decompositions of weight updates. However, the low-rank assumption may restrict expressivity, particularly in task-specific adaptation scenarios where singular values are distributed relatively uniformly. To address this limitation, we propose CoSA (Compressed Sensing-Based Adaptation), a new PEFT method extended from compressed sensing theory. Instead of constraining weight updates to a low-rank subspace, CoSA expresses them through fixed random projection matrices and a compact learnable core. We provide a formal theoretical analysis of CoSA as a synthesis process, proving that weight updates can be compactly encoded into a low-dimensional space and mapped back through random projections. Extensive experimental results show that CoSA provides a principled perspective for efficient and expressive multi-scale model adaptation. Specifically, we evaluate CoSA on 10 diverse tasks, including natural language understanding and generation, employing 5 models of different scales from RoBERTa, Llama, and Qwen families. Across these settings, CoSA consistently matches or outperforms state-of-the-art PEFT methods.
Accelerating Scientific Research with Gemini: Case Studies and Common Techniques
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) have opened new avenues for accelerating scientific research. While models are increasingly capable of assisting with routine tasks, their ability to contribute to novel, expert-level mathematical discovery is less understood. We present a collection of case studies demonstrating how researchers have successfully collaborated with advanced AI models, specifically Google's Gemini-based models (in particular Gemini Deep Think and its advanced variants), to solve open problems, refute conjectures, and generate new proofs across diverse areas in theoretical computer science, as well as other areas such as economics, optimization, and physics. Based on these experiences, we extract common techniques for effective human-AI collaboration in theoretical research, such as iterative refinement, problem decomposition, and cross-disciplinary knowledge transfer. While the majority of our results stem from this interactive, conversational methodology, we also highlight specific instances that push beyond standard chat interfaces. These include deploying the model as a rigorous adversarial reviewer to detect subtle flaws in existing proofs, and embedding it within a "neuro-symbolic" loop that autonomously writes and executes code to verify complex derivations. Together, these examples highlight the potential of AI not just as a tool for automation, but as a versatile, genuine partner in the creative process of scientific discovery.
Leveraging Data to Say No: Memory Augmented Plug-and-Play Selective Prediction
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Selective prediction aims to endow predictors with a reject option, to avoid low confidence predictions. However, existing literature has primarily focused on closed-set tasks, such as visual question answering with predefined options or fixed-category classification. This paper considers selective prediction for visual language foundation models, addressing a taxonomy of tasks ranging from closed to open set and from finite to unbounded vocabularies, as in image captioning. We seek training-free approaches of low-complexity, applicable to any foundation model and consider methods based on external vision-language model embeddings, like CLIP. This is denoted as Plug-and-Play Selective Prediction (PaPSP). We identify two key challenges: (1) instability of the visual-language representations, leading to high variance in image-text embeddings, and (2) poor calibration of similarity scores. To address these issues, we propose a memory augmented PaPSP (MA-PaPSP) model, which augments PaPSP with a retrieval dataset of image-text pairs. This is leveraged to reduce embedding variance by averaging retrieved nearest-neighbor pairs and is complemented by the use of contrastive normalization to improve score calibration. Through extensive experiments on multiple datasets, we show that MA-PaPSP outperforms PaPSP and other selective prediction baselines for selective captioning, image-text matching, and fine-grained classification. Code is publicly available at https://github.com/kingston-aditya/MA-PaPSP.
Youtu-VL: Unleashing Visual Potential via Unified Vision-Language Supervision
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Despite the significant advancements represented by Vision-Language Models (VLMs), current architectures often exhibit limitations in retaining fine-grained visual information, leading to coarse-grained multimodal comprehension. We attribute this deficiency to a suboptimal training paradigm inherent in prevailing VLMs, which exhibits a text-dominant optimization bias by conceptualizing visual signals merely as passive conditional inputs rather than supervisory targets. To mitigate this, we introduce Youtu-VL, a framework leveraging the Vision-Language Unified Autoregressive Supervision (VLUAS) paradigm, which fundamentally shifts the optimization objective from ``vision-as-input'' to ``vision-as-target.'' By integrating visual tokens directly into the prediction stream, Youtu-VL applies unified autoregressive supervision to both visual details and linguistic content. Furthermore, we extend this paradigm to encompass vision-centric tasks, enabling a standard VLM to perform vision-centric tasks without task-specific additions. Extensive empirical evaluations demonstrate that Youtu-VL achieves competitive performance on both general multimodal tasks and vision-centric tasks, establishing a robust foundation for the development of comprehensive generalist visual agents.
LLM Review: Enhancing Creative Writing via Blind Peer Review Feedback
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) often struggle with creative generation, and multi-agent frameworks that improve reasoning through interaction can paradoxically hinder creativity by inducing content homogenization. We introduce LLM Review, a peer-review-inspired framework implementing Blind Peer Review: agents exchange targeted feedback while revising independently, preserving divergent creative trajectories. To enable rigorous evaluation, we propose SciFi-100, a science fiction writing dataset with a unified framework combining LLM-as-a-judge scoring, human annotation, and rule-based novelty metrics. Experiments demonstrate that LLM Review consistently outperforms multi-agent baselines, and smaller models with our framework can surpass larger single-agent models, suggesting interaction structure may substitute for model scale.
MAGMA: A Multi-Graph based Agentic Memory Architecture for AI Agents
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Memory-Augmented Generation (MAG) extends Large Language Models with external memory to support long-context reasoning, but existing approaches largely rely on semantic similarity over monolithic memory stores, entangling temporal, causal, and entity information. This design limits interpretability and alignment between query intent and retrieved evidence, leading to suboptimal reasoning accuracy. In this paper, we propose MAGMA, a multi-graph agentic memory architecture that represents each memory item across orthogonal semantic, temporal, causal, and entity graphs. MAGMA formulates retrieval as policy-guided traversal over these relational views, enabling query-adaptive selection and structured context construction. By decoupling memory representation from retrieval logic, MAGMA provides transparent reasoning paths and fine-grained control over retrieval. Experiments on LoCoMo and LongMemEval demonstrate that MAGMA consistently outperforms state-of-the-art agentic memory systems in long-horizon reasoning tasks.
Grading Scale Impact on LLM-as-a-Judge: Human-LLM Alignment Is Highest on 0-5 Grading Scale
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly used as automated evaluators, yet prior works demonstrate that these LLM judges often lack consistency in scoring when the prompt is altered. However, the effect of the grading scale itself remains underexplored. We study the LLM-as-a-judge problem by comparing two kinds of raters: humans and LLMs. We collect ratings from both groups on three scales and across six benchmarks that include objective, open-ended subjective, and mixed tasks. Using intraclass correlation coefficients (ICC) to measure absolute agreement, we find that LLM judgments are not perfectly consistent across scales on subjective benchmarks, and that the choice of scale substantially shifts human-LLM agreement, even when within-group panel reliability is high. Aggregated over tasks, the grading scale of 0-5 yields the strongest human-LLM alignment. We further demonstrate that pooled reliability can mask benchmark heterogeneity and reveal systematic subgroup differences in alignment across gender groups, strengthening the importance of scale design and sub-level diagnostics as essential components of LLM-as-a-judge protocols.
AmPLe: Supporting Vision-Language Models via Adaptive-Debiased Ensemble Multi-Prompt Learning
Dec 20, 2025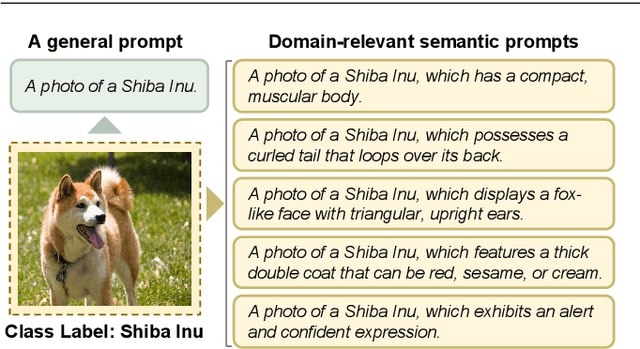

Abstract:Multi-prompt learning methods have emerged as an effective approach for facilitating the rapid adaptation of vision-language models to downstream tasks with limited resources. Existing multi-prompt learning methods primarily focus on utilizing various meticulously designed prompts within a single foundation vision-language model to achieve superior performance. However, the overlooked model-prompt matching bias hinders the development of multi-prompt learning, i.e., the same prompt can convey different semantics across distinct vision-language models, such as CLIP-ViT-B/16 and CLIP-ViT-B/32, resulting in inconsistent predictions of identical prompt. To mitigate the impact of this bias on downstream tasks, we explore an ensemble learning approach to sufficiently aggregate the benefits of diverse predictions. Additionally, we further disclose the presence of sample-prompt matching bias, which originates from the prompt-irrelevant semantics encapsulated in the input samples. Thus, directly utilizing all information from the input samples for generating weights of ensemble learning can lead to suboptimal performance. In response, we extract prompt-relevant semantics from input samples by leveraging the guidance of the information theory-based analysis, adaptively calculating debiased ensemble weights. Overall, we propose Adaptive-Debiased Ensemble MultiPrompt Learning, abbreviated as AmPLe, to mitigate the two types of bias simultaneously. Extensive experiments on three representative tasks, i.e., generalization to novel classes, new target datasets, and unseen domain shifts, show that AmPLe can widely outperform existing methods. Theoretical validation from a causal perspective further supports the effectiveness of AmPLe.
Robust and Efficient Communication in Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning
Nov 14, 2025Abstract:Multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) has made significant strides in enabling coordinated behaviors among autonomous agents. However, most existing approaches assume that communication is instantaneous, reliable, and has unlimited bandwidth; these conditions are rarely met in real-world deployments. This survey systematically reviews recent advances in robust and efficient communication strategies for MARL under realistic constraints, including message perturbations, transmission delays, and limited bandwidth. Furthermore, because the challenges of low-latency reliability, bandwidth-intensive data sharing, and communication-privacy trade-offs are central to practical MARL systems, we focus on three applications involving cooperative autonomous driving, distributed simultaneous localization and mapping, and federated learning. Finally, we identify key open challenges and future research directions, advocating a unified approach that co-designs communication, learning, and robustness to bridge the gap between theoretical MARL models and practical implementations.
GPR: Towards a Generative Pre-trained One-Model Paradigm for Large-Scale Advertising Recommendation
Nov 13, 2025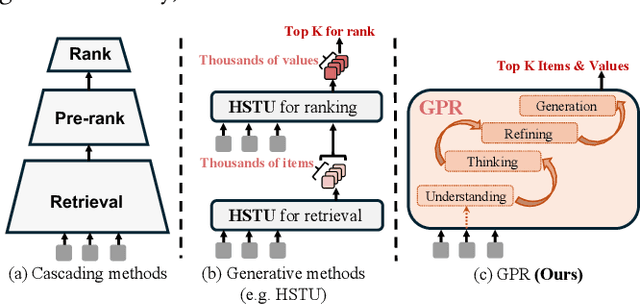
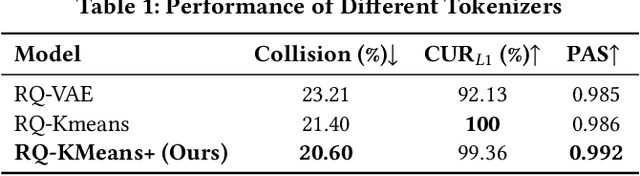
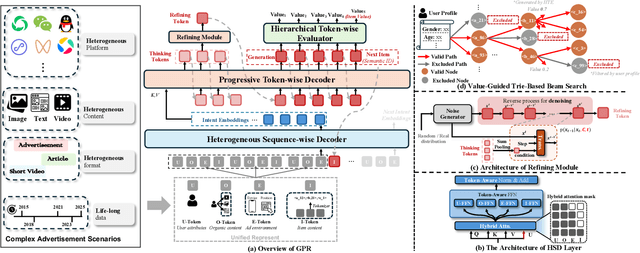
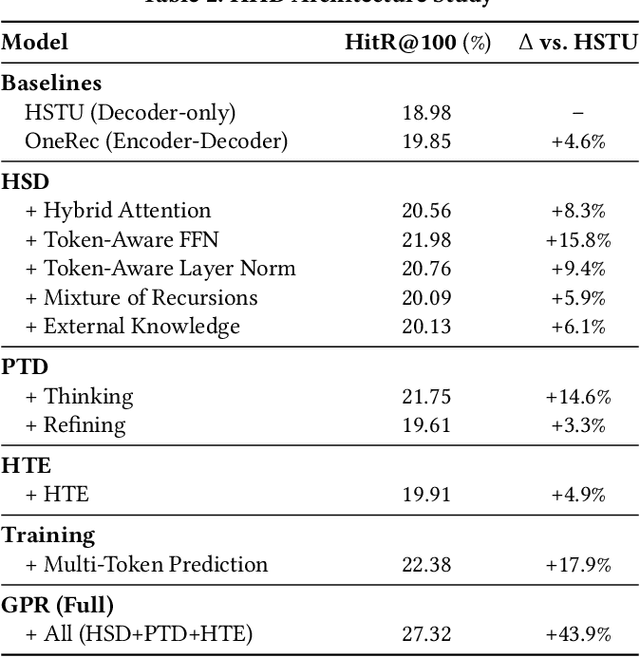
Abstract:As an intelligent infrastructure connecting users with commercial content, advertising recommendation systems play a central role in information flow and value creation within the digital economy. However, existing multi-stage advertising recommendation systems suffer from objective misalignment and error propagation, making it difficult to achieve global optimality, while unified generative recommendation models still struggle to meet the demands of practical industrial applications. To address these issues, we propose GPR (Generative Pre-trained Recommender), the first one-model framework that redefines advertising recommendation as an end-to-end generative task, replacing the traditional cascading paradigm with a unified generative approach. To realize GPR, we introduce three key innovations spanning unified representation, network architecture, and training strategy. First, we design a unified input schema and tokenization method tailored to advertising scenarios, mapping both ads and organic content into a shared multi-level semantic ID space, thereby enhancing semantic alignment and modeling consistency across heterogeneous data. Second, we develop the Heterogeneous Hierarchical Decoder (HHD), a dual-decoder architecture that decouples user intent modeling from ad generation, achieving a balance between training efficiency and inference flexibility while maintaining strong modeling capacity. Finally, we propose a multi-stage joint training strategy that integrates Multi-Token Prediction (MTP), Value-Aware Fine-Tuning and the Hierarchy Enhanced Policy Optimization (HEPO) algorithm, forming a complete generative recommendation pipeline that unifies interest modeling, value alignment, and policy optimization. GPR has been fully deployed in the Tencent Weixin Channels advertising system, delivering significant improvements in key business metrics including GMV and CTCVR.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge