Zhiyuan Zhang
EquiForm: Noise-Robust SE(3)-Equivariant Policy Learning from 3D Point Clouds
Jan 24, 2026Abstract:Visual imitation learning with 3D point clouds has advanced robotic manipulation by providing geometry-aware, appearance-invariant observations. However, point cloud-based policies remain highly sensitive to sensor noise, pose perturbations, and occlusion-induced artifacts, which distort geometric structure and break the equivariance assumptions required for robust generalization. Existing equivariant approaches primarily encode symmetry constraints into neural architectures, but do not explicitly correct noise-induced geometric deviations or enforce equivariant consistency in learned representations. We introduce EquiForm, a noise-robust SE(3)-equivariant policy learning framework for point cloud-based manipulation. EquiForm formalizes how noise-induced geometric distortions lead to equivariance deviations in observation-to-action mappings, and introduces a geometric denoising module to restore consistent 3D structure under noisy or incomplete observations. In addition, we propose a contrastive equivariant alignment objective that enforces representation consistency under both rigid transformations and noise perturbations. Built upon these components, EquiForm forms a flexible policy learning pipeline that integrates noise-robust geometric reasoning with modern generative models. We evaluate EquiForm on 16 simulated tasks and 4 real-world manipulation tasks across diverse objects and scene layouts. Compared to state-of-the-art point cloud imitation learning methods, EquiForm achieves an average improvement of 17.2% in simulation and 28.1% in real-world experiments, demonstrating strong noise robustness and spatial generalization.
EmbryoDiff: A Conditional Diffusion Framework with Multi-Focal Feature Fusion for Fine-Grained Embryo Developmental Stage Recognition
Nov 14, 2025Abstract:Identification of fine-grained embryo developmental stages during In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) is crucial for assessing embryo viability. Although recent deep learning methods have achieved promising accuracy, existing discriminative models fail to utilize the distributional prior of embryonic development to improve accuracy. Moreover, their reliance on single-focal information leads to incomplete embryonic representations, making them susceptible to feature ambiguity under cell occlusions. To address these limitations, we propose EmbryoDiff, a two-stage diffusion-based framework that formulates the task as a conditional sequence denoising process. Specifically, we first train and freeze a frame-level encoder to extract robust multi-focal features. In the second stage, we introduce a Multi-Focal Feature Fusion Strategy that aggregates information across focal planes to construct a 3D-aware morphological representation, effectively alleviating ambiguities arising from cell occlusions. Building on this fused representation, we derive complementary semantic and boundary cues and design a Hybrid Semantic-Boundary Condition Block to inject them into the diffusion-based denoising process, enabling accurate embryonic stage classification. Extensive experiments on two benchmark datasets show that our method achieves state-of-the-art results. Notably, with only a single denoising step, our model obtains the best average test performance, reaching 82.8% and 81.3% accuracy on the two datasets, respectively.
Private-RAG: Answering Multiple Queries with LLMs while Keeping Your Data Private
Nov 10, 2025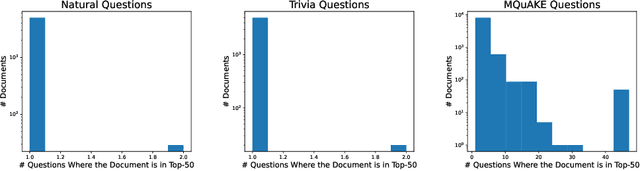
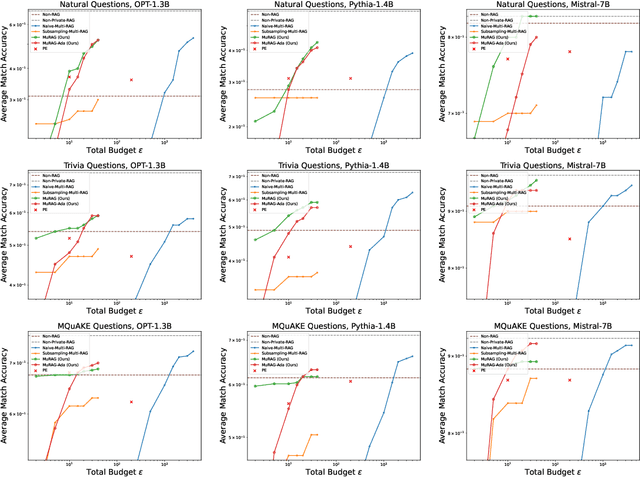
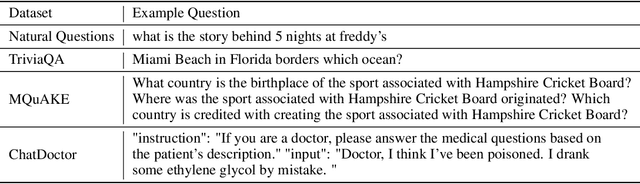
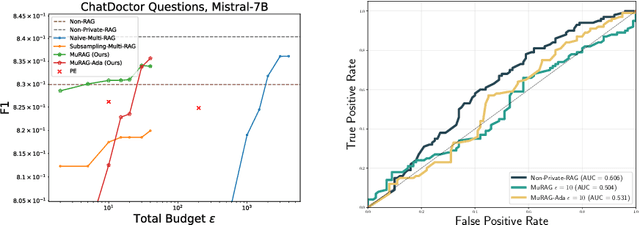
Abstract:Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) enhances large language models (LLMs) by retrieving documents from an external corpus at inference time. When this corpus contains sensitive information, however, unprotected RAG systems are at risk of leaking private information. Prior work has introduced differential privacy (DP) guarantees for RAG, but only in single-query settings, which fall short of realistic usage. In this paper, we study the more practical multi-query setting and propose two DP-RAG algorithms. The first, MURAG, leverages an individual privacy filter so that the accumulated privacy loss only depends on how frequently each document is retrieved rather than the total number of queries. The second, MURAG-ADA, further improves utility by privately releasing query-specific thresholds, enabling more precise selection of relevant documents. Our experiments across multiple LLMs and datasets demonstrate that the proposed methods scale to hundreds of queries within a practical DP budget ($\varepsilon\approx10$), while preserving meaningful utility.
Super LiDAR Reflectance for Robotic Perception
Aug 14, 2025Abstract:Conventionally, human intuition often defines vision as a modality of passive optical sensing, while active optical sensing is typically regarded as measuring rather than the default modality of vision. However, the situation now changes: sensor technologies and data-driven paradigms empower active optical sensing to redefine the boundaries of vision, ushering in a new era of active vision. Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR) sensors capture reflectance from object surfaces, which remains invariant under varying illumination conditions, showcasing significant potential in robotic perception tasks such as detection, recognition, segmentation, and Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM). These applications often rely on dense sensing capabilities, typically achieved by high-resolution, expensive LiDAR sensors. A key challenge with low-cost LiDARs lies in the sparsity of scan data, which limits their broader application. To address this limitation, this work introduces an innovative framework for generating dense LiDAR reflectance images from sparse data, leveraging the unique attributes of non-repeating scanning LiDAR (NRS-LiDAR). We tackle critical challenges, including reflectance calibration and the transition from static to dynamic scene domains, facilitating the reconstruction of dense reflectance images in real-world settings. The key contributions of this work include a comprehensive dataset for LiDAR reflectance image densification, a densification network tailored for NRS-LiDAR, and diverse applications such as loop closure and traffic lane detection using the generated dense reflectance images.
LSFDNet: A Single-Stage Fusion and Detection Network for Ships Using SWIR and LWIR
Jul 28, 2025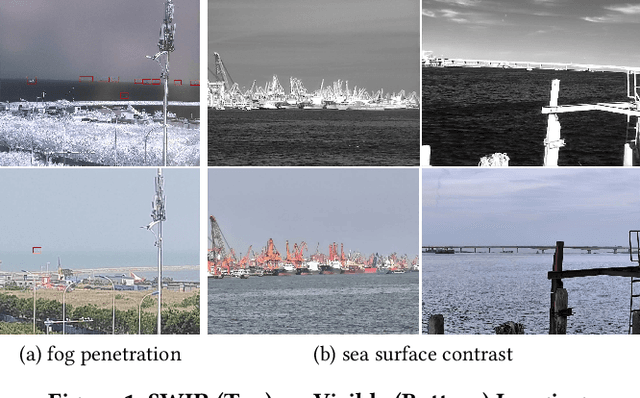
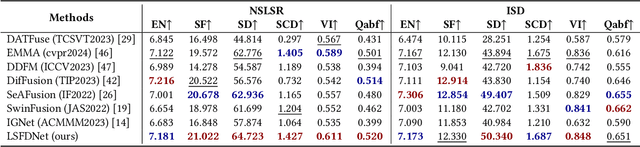

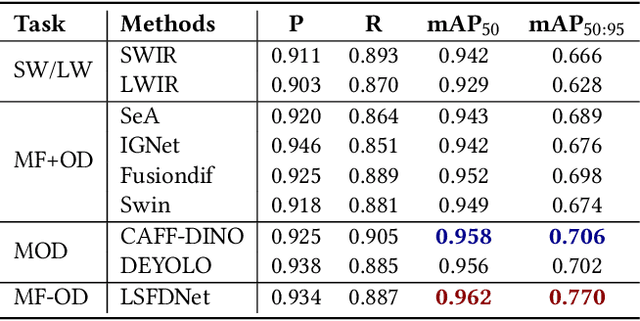
Abstract:Traditional ship detection methods primarily rely on single-modal approaches, such as visible or infrared images, which limit their application in complex scenarios involving varying lighting conditions and heavy fog. To address this issue, we explore the advantages of short-wave infrared (SWIR) and long-wave infrared (LWIR) in ship detection and propose a novel single-stage image fusion detection algorithm called LSFDNet. This algorithm leverages feature interaction between the image fusion and object detection subtask networks, achieving remarkable detection performance and generating visually impressive fused images. To further improve the saliency of objects in the fused images and improve the performance of the downstream detection task, we introduce the Multi-Level Cross-Fusion (MLCF) module. This module combines object-sensitive fused features from the detection task and aggregates features across multiple modalities, scales, and tasks to obtain more semantically rich fused features. Moreover, we utilize the position prior from the detection task in the Object Enhancement (OE) loss function, further increasing the retention of object semantics in the fused images. The detection task also utilizes preliminary fused features from the fusion task to complement SWIR and LWIR features, thereby enhancing detection performance. Additionally, we have established a Nearshore Ship Long-Short Wave Registration (NSLSR) dataset to train effective SWIR and LWIR image fusion and detection networks, bridging a gap in this field. We validated the superiority of our proposed single-stage fusion detection algorithm on two datasets. The source code and dataset are available at https://github.com/Yanyin-Guo/LSFDNet
High-Fidelity Differential-information Driven Binary Vision Transformer
Jul 03, 2025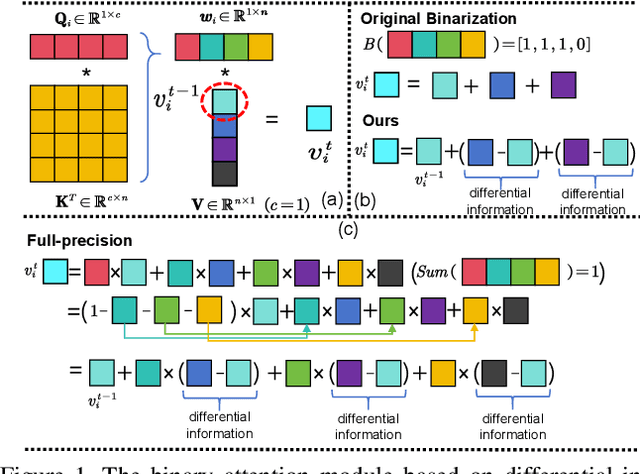
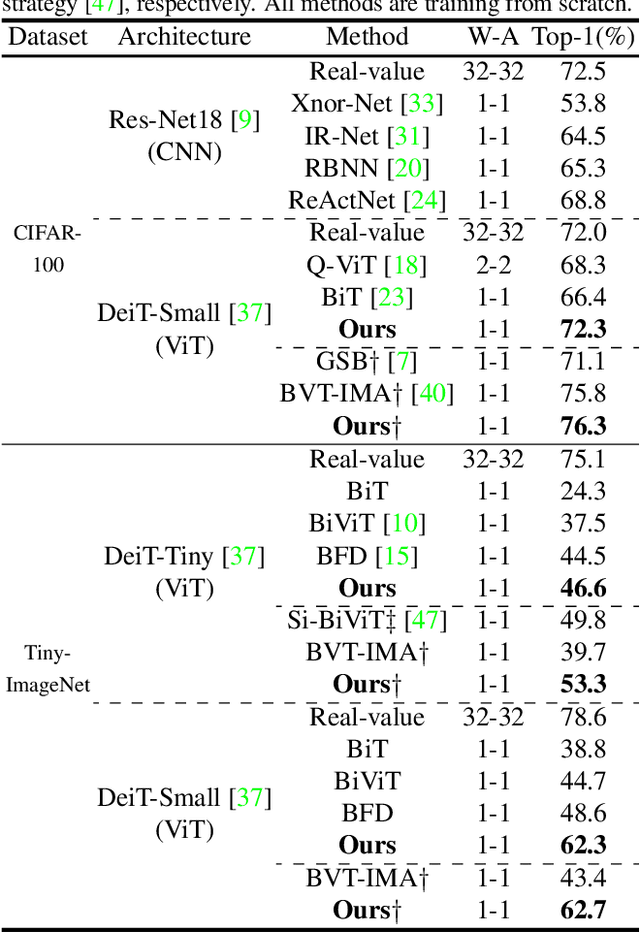
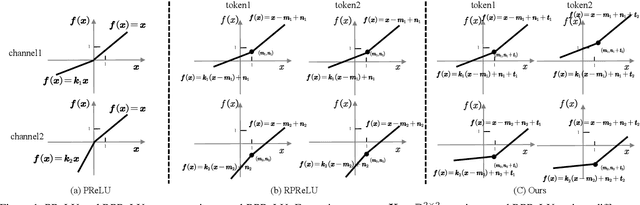
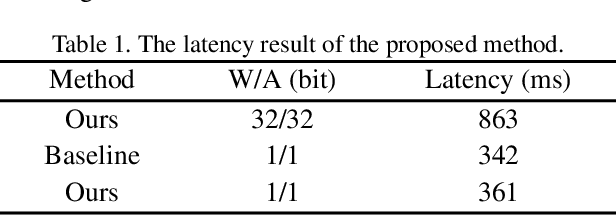
Abstract:The binarization of vision transformers (ViTs) offers a promising approach to addressing the trade-off between high computational/storage demands and the constraints of edge-device deployment. However, existing binary ViT methods often suffer from severe performance degradation or rely heavily on full-precision modules. To address these issues, we propose DIDB-ViT, a novel binary ViT that is highly informative while maintaining the original ViT architecture and computational efficiency. Specifically, we design an informative attention module incorporating differential information to mitigate information loss caused by binarization and enhance high-frequency retention. To preserve the fidelity of the similarity calculations between binary Q and K tensors, we apply frequency decomposition using the discrete Haar wavelet and integrate similarities across different frequencies. Additionally, we introduce an improved RPReLU activation function to restructure the activation distribution, expanding the model's representational capacity. Experimental results demonstrate that our DIDB-ViT significantly outperforms state-of-the-art network quantization methods in multiple ViT architectures, achieving superior image classification and segmentation performance.
Time-Lapse Video-Based Embryo Grading via Complementary Spatial-Temporal Pattern Mining
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:Artificial intelligence has recently shown promise in automated embryo selection for In-Vitro Fertilization (IVF). However, current approaches either address partial embryo evaluation lacking holistic quality assessment or target clinical outcomes inevitably confounded by extra-embryonic factors, both limiting clinical utility. To bridge this gap, we propose a new task called Video-Based Embryo Grading - the first paradigm that directly utilizes full-length time-lapse monitoring (TLM) videos to predict embryologists' overall quality assessments. To support this task, we curate a real-world clinical dataset comprising over 2,500 TLM videos, each annotated with a grading label indicating the overall quality of embryos. Grounded in clinical decision-making principles, we propose a Complementary Spatial-Temporal Pattern Mining (CoSTeM) framework that conceptually replicates embryologists' evaluation process. The CoSTeM comprises two branches: (1) a morphological branch using a Mixture of Cross-Attentive Experts layer and a Temporal Selection Block to select discriminative local structural features, and (2) a morphokinetic branch employing a Temporal Transformer to model global developmental trajectories, synergistically integrating static and dynamic determinants for grading embryos. Extensive experimental results demonstrate the superiority of our design. This work provides a valuable methodological framework for AI-assisted embryo selection. The dataset and source code will be publicly available upon acceptance.
Canonical Policy: Learning Canonical 3D Representation for Equivariant Policy
May 24, 2025



Abstract:Visual Imitation learning has achieved remarkable progress in robotic manipulation, yet generalization to unseen objects, scene layouts, and camera viewpoints remains a key challenge. Recent advances address this by using 3D point clouds, which provide geometry-aware, appearance-invariant representations, and by incorporating equivariance into policy architectures to exploit spatial symmetries. However, existing equivariant approaches often lack interpretability and rigor due to unstructured integration of equivariant components. We introduce canonical policy, a principled framework for 3D equivariant imitation learning that unifies 3D point cloud observations under a canonical representation. We first establish a theory of 3D canonical representations, enabling equivariant observation-to-action mappings by grouping both in-distribution and out-of-distribution point clouds to a canonical representation. We then propose a flexible policy learning pipeline that leverages geometric symmetries from canonical representation and the expressiveness of modern generative models. We validate canonical policy on 12 diverse simulated tasks and 4 real-world manipulation tasks across 16 configurations, involving variations in object color, shape, camera viewpoint, and robot platform. Compared to state-of-the-art imitation learning policies, canonical policy achieves an average improvement of 18.0% in simulation and 37.6% in real-world experiments, demonstrating superior generalization capability and sample efficiency. For more details, please refer to the project website: https://zhangzhiyuanzhang.github.io/cp-website/.
ManiFeel: Benchmarking and Understanding Visuotactile Manipulation Policy Learning
May 24, 2025Abstract:Supervised visuomotor policies have shown strong performance in robotic manipulation but often struggle in tasks with limited visual input, such as operations in confined spaces, dimly lit environments, or scenarios where perceiving the object's properties and state is critical for task success. In such cases, tactile feedback becomes essential for manipulation. While the rapid progress of supervised visuomotor policies has benefited greatly from high-quality, reproducible simulation benchmarks in visual imitation, the visuotactile domain still lacks a similarly comprehensive and reliable benchmark for large-scale and rigorous evaluation. To address this, we introduce ManiFeel, a reproducible and scalable simulation benchmark for studying supervised visuotactile manipulation policies across a diverse set of tasks and scenarios. ManiFeel presents a comprehensive benchmark suite spanning a diverse set of manipulation tasks, evaluating various policies, input modalities, and tactile representation methods. Through extensive experiments, our analysis reveals key factors that influence supervised visuotactile policy learning, identifies the types of tasks where tactile sensing is most beneficial, and highlights promising directions for future research in visuotactile policy learning. ManiFeel aims to establish a reproducible benchmark for supervised visuotactile policy learning, supporting progress in visuotactile manipulation and perception. To facilitate future research and ensure reproducibility, we will release our codebase, datasets, training logs, and pretrained checkpoints. Please visit the project website for more details: https://zhengtongxu.github.io/manifeel-website/
ExoGait-MS: Learning Periodic Dynamics with Multi-Scale Graph Network for Exoskeleton Gait Recognition
May 23, 2025
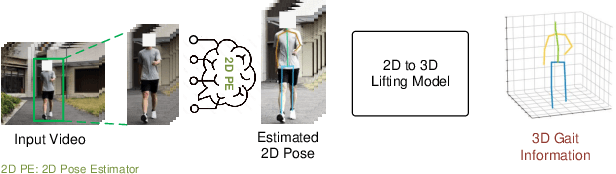


Abstract:Current exoskeleton control methods often face challenges in delivering personalized treatment. Standardized walking gaits can lead to patient discomfort or even injury. Therefore, personalized gait is essential for the effectiveness of exoskeleton robots, as it directly impacts their adaptability, comfort, and rehabilitation outcomes for individual users. To enable personalized treatment in exoskeleton-assisted therapy and related applications, accurate recognition of personal gait is crucial for implementing tailored gait control. The key challenge in gait recognition lies in effectively capturing individual differences in subtle gait features caused by joint synergy, such as step frequency and step length. To tackle this issue, we propose a novel approach, which uses Multi-Scale Global Dense Graph Convolutional Networks (GCN) in the spatial domain to identify latent joint synergy patterns. Moreover, we propose a Gait Non-linear Periodic Dynamics Learning module to effectively capture the periodic characteristics of gait in the temporal domain. To support our individual gait recognition task, we have constructed a comprehensive gait dataset that ensures both completeness and reliability. Our experimental results demonstrate that our method achieves an impressive accuracy of 94.34% on this dataset, surpassing the current state-of-the-art (SOTA) by 3.77%. This advancement underscores the potential of our approach to enhance personalized gait control in exoskeleton-assisted therapy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge