Tian Gao
Resting Neurons, Active Insights: Improving Input Sparsification for Large Language Models
Dec 14, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) achieve state-of-the-art performance across a wide range of applications, but their massive scale poses significant challenges for both efficiency and interpretability. Structural pruning, which reduces model size by removing redundant computational units such as neurons, has been widely explored as a solution, and this study devotes to input sparsification, an increasingly popular technique that improves efficiency by selectively activating only a subset of entry values for each input. However, existing approaches focus primarily on computational savings, often overlooking the representational consequences of sparsification and leaving a noticeable performance gap compared to full models. In this work, we first reinterpret input sparsification as a form of dynamic structural pruning. Motivated by the spontaneous baseline firing rates observed in biological neurons, we introduce a small set of trainable spontaneous neurons that act as compensatory units to stabilize activations in sparsified LLMs. Experiments demonstrate that these auxiliary neurons substantially reduce the sparsification-induced performance gap while generalizing effectively across tasks.
AlphaCast: A Human Wisdom-LLM Intelligence Co-Reasoning Framework for Interactive Time Series Forecasting
Nov 12, 2025Abstract:Time series forecasting plays a critical role in high-stakes domains such as energy, healthcare, and climate. Although recent advances have improved accuracy, most approaches still treat forecasting as a static one-time mapping task, lacking the interaction, reasoning, and adaptability of human experts. This gap limits their usefulness in complex real-world environments. To address this, we propose AlphaCast, a human wisdom-large language model (LLM) intelligence co-reasoning framework that redefines forecasting as an interactive process. The key idea is to enable step-by-step collaboration between human wisdom and LLM intelligence to jointly prepare, generate, and verify forecasts. The framework consists of two stages: (1) automated prediction preparation, where AlphaCast builds a multi-source cognitive foundation comprising a feature set that captures key statistics and time patterns, a domain knowledge base distilled from corpora and historical series, a contextual repository that stores rich information for each time window, and a case base that retrieves optimal strategies via pattern clustering and matching; and (2) generative reasoning and reflective optimization, where AlphaCast integrates statistical temporal features, prior knowledge, contextual information, and forecasting strategies, triggering a meta-reasoning loop for continuous self-correction and strategy refinement. Extensive experiments on short- and long-term datasets show that AlphaCast consistently outperforms state-of-the-art baselines in predictive accuracy. Code is available at this repository: https://github.com/SkyeGT/AlphaCast_Official .
High-Fidelity Differential-information Driven Binary Vision Transformer
Jul 03, 2025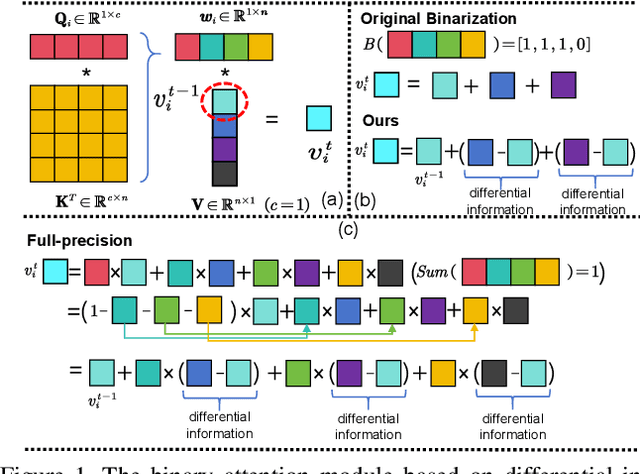
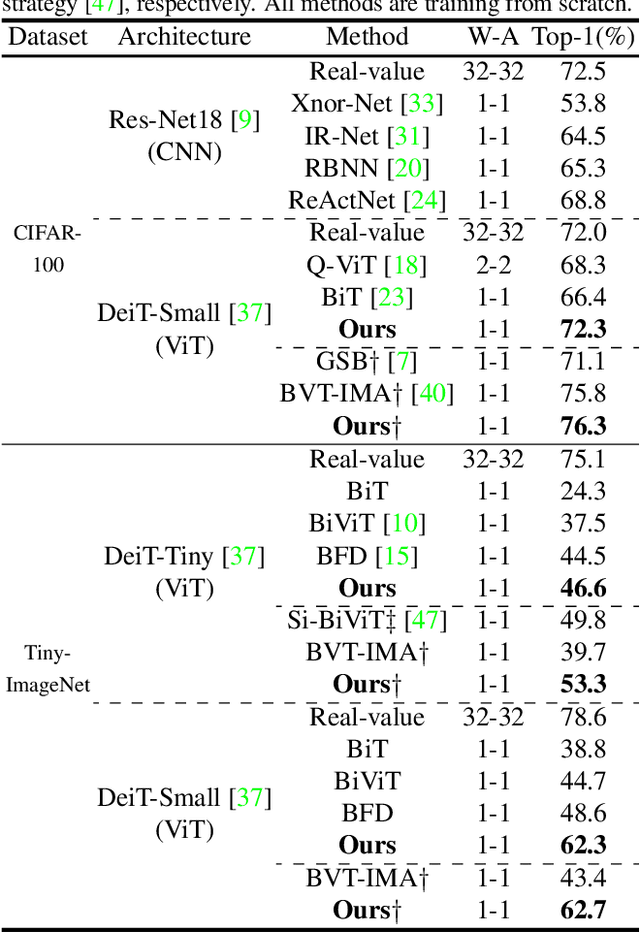
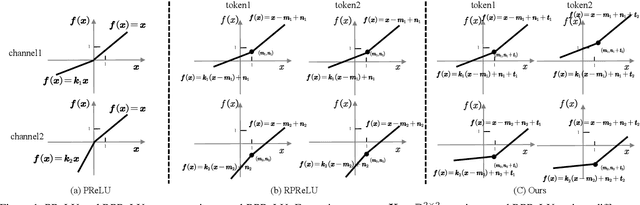
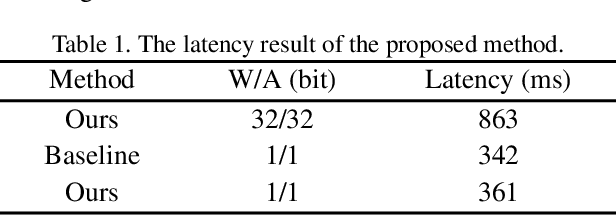
Abstract:The binarization of vision transformers (ViTs) offers a promising approach to addressing the trade-off between high computational/storage demands and the constraints of edge-device deployment. However, existing binary ViT methods often suffer from severe performance degradation or rely heavily on full-precision modules. To address these issues, we propose DIDB-ViT, a novel binary ViT that is highly informative while maintaining the original ViT architecture and computational efficiency. Specifically, we design an informative attention module incorporating differential information to mitigate information loss caused by binarization and enhance high-frequency retention. To preserve the fidelity of the similarity calculations between binary Q and K tensors, we apply frequency decomposition using the discrete Haar wavelet and integrate similarities across different frequencies. Additionally, we introduce an improved RPReLU activation function to restructure the activation distribution, expanding the model's representational capacity. Experimental results demonstrate that our DIDB-ViT significantly outperforms state-of-the-art network quantization methods in multiple ViT architectures, achieving superior image classification and segmentation performance.
Q-function Decomposition with Intervention Semantics with Factored Action Spaces
Apr 30, 2025Abstract:Many practical reinforcement learning environments have a discrete factored action space that induces a large combinatorial set of actions, thereby posing significant challenges. Existing approaches leverage the regular structure of the action space and resort to a linear decomposition of Q-functions, which avoids enumerating all combinations of factored actions. In this paper, we consider Q-functions defined over a lower dimensional projected subspace of the original action space, and study the condition for the unbiasedness of decomposed Q-functions using causal effect estimation from the no unobserved confounder setting in causal statistics. This leads to a general scheme which we call action decomposed reinforcement learning that uses the projected Q-functions to approximate the Q-function in standard model-free reinforcement learning algorithms. The proposed approach is shown to improve sample complexity in a model-based reinforcement learning setting. We demonstrate improvements in sample efficiency compared to state-of-the-art baselines in online continuous control environments and a real-world offline sepsis treatment environment.
Other Vehicle Trajectories Are Also Needed: A Driving World Model Unifies Ego-Other Vehicle Trajectories in Video Latant Space
Mar 12, 2025Abstract:Advanced end-to-end autonomous driving systems predict other vehicles' motions and plan ego vehicle's trajectory. The world model that can foresee the outcome of the trajectory has been used to evaluate the end-to-end autonomous driving system. However, existing world models predominantly emphasize the trajectory of the ego vehicle and leave other vehicles uncontrollable. This limitation hinders their ability to realistically simulate the interaction between the ego vehicle and the driving scenario. In addition, it remains a challenge to match multiple trajectories with each vehicle in the video to control the video generation. To address above issues, a driving \textbf{W}orld \textbf{M}odel named EOT-WM is proposed in this paper, unifying \textbf{E}go-\textbf{O}ther vehicle \textbf{T}rajectories in videos. Specifically, we first project ego and other vehicle trajectories in the BEV space into the image coordinate to match each trajectory with its corresponding vehicle in the video. Then, trajectory videos are encoded by the Spatial-Temporal Variational Auto Encoder to align with driving video latents spatially and temporally in the unified visual space. A trajectory-injected diffusion Transformer is further designed to denoise the noisy video latents for video generation with the guidance of ego-other vehicle trajectories. In addition, we propose a metric based on control latent similarity to evaluate the controllability of trajectories. Extensive experiments are conducted on the nuScenes dataset, and the proposed model outperforms the state-of-the-art method by 30\% in FID and 55\% in FVD. The model can also predict unseen driving scenes with self-produced trajectories.
BHViT: Binarized Hybrid Vision Transformer
Mar 05, 2025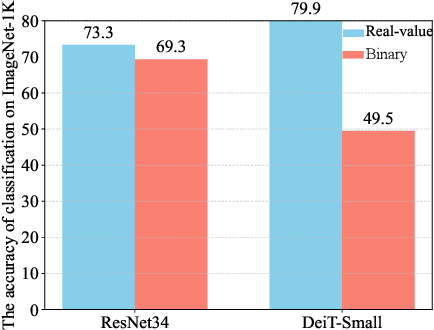
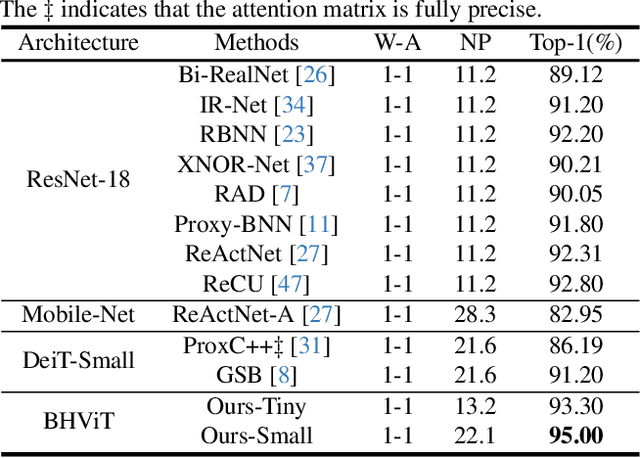
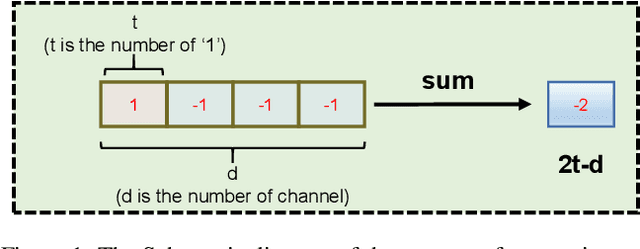
Abstract:Model binarization has made significant progress in enabling real-time and energy-efficient computation for convolutional neural networks (CNN), offering a potential solution to the deployment challenges faced by Vision Transformers (ViTs) on edge devices. However, due to the structural differences between CNN and Transformer architectures, simply applying binary CNN strategies to the ViT models will lead to a significant performance drop. To tackle this challenge, we propose BHViT, a binarization-friendly hybrid ViT architecture and its full binarization model with the guidance of three important observations. Initially, BHViT utilizes the local information interaction and hierarchical feature aggregation technique from coarse to fine levels to address redundant computations stemming from excessive tokens. Then, a novel module based on shift operations is proposed to enhance the performance of the binary Multilayer Perceptron (MLP) module without significantly increasing computational overhead. In addition, an innovative attention matrix binarization method based on quantization decomposition is proposed to evaluate the token's importance in the binarized attention matrix. Finally, we propose a regularization loss to address the inadequate optimization caused by the incompatibility between the weight oscillation in the binary layers and the Adam Optimizer. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that our proposed algorithm achieves SOTA performance among binary ViT methods.
Few-shot Policy (de)composition in Conversational Question Answering
Jan 20, 2025



Abstract:The task of policy compliance detection (PCD) is to determine if a scenario is in compliance with respect to a set of written policies. In a conversational setting, the results of PCD can indicate if clarifying questions must be asked to determine compliance status. Existing approaches usually claim to have reasoning capabilities that are latent or require a large amount of annotated data. In this work, we propose logical decomposition for policy compliance (LDPC): a neuro-symbolic framework to detect policy compliance using large language models (LLMs) in a few-shot setting. By selecting only a few exemplars alongside recently developed prompting techniques, we demonstrate that our approach soundly reasons about policy compliance conversations by extracting sub-questions to be answered, assigning truth values from contextual information, and explicitly producing a set of logic statements from the given policies. The formulation of explicit logic graphs can in turn help answer PCDrelated questions with increased transparency and explainability. We apply this approach to the popular PCD and conversational machine reading benchmark, ShARC, and show competitive performance with no task-specific finetuning. We also leverage the inherently interpretable architecture of LDPC to understand where errors occur, revealing ambiguities in the ShARC dataset and highlighting the challenges involved with reasoning for conversational question answering.
Policy Agnostic RL: Offline RL and Online RL Fine-Tuning of Any Class and Backbone
Dec 09, 2024Abstract:Recent advances in learning decision-making policies can largely be attributed to training expressive policy models, largely via imitation learning. While imitation learning discards non-expert data, reinforcement learning (RL) can still learn from suboptimal data. However, instantiating RL training of a new policy class often presents a different challenge: most deep RL machinery is co-developed with assumptions on the policy class and backbone, resulting in poor performance when the policy class changes. For instance, SAC utilizes a low-variance reparameterization policy gradient for Gaussian policies, but this is unstable for diffusion policies and intractable for autoregressive categorical policies. To address this issue, we develop an offline RL and online fine-tuning approach called policy-agnostic RL (PA-RL) that can effectively train multiple policy classes, with varying architectures and sizes. We build off the basic idea that a universal supervised learning loss can replace the policy improvement step in RL, as long as it is applied on "optimized" actions. To obtain these optimized actions, we first sample multiple actions from a base policy, and run global optimization (i.e., re-ranking multiple action samples using the Q-function) and local optimization (i.e., running gradient steps on an action sample) to maximize the critic on these candidates. PA-RL enables fine-tuning diffusion and transformer policies with either autoregressive tokens or continuous action outputs, at different sizes, entirely via actor-critic RL. Moreover, PA-RL improves the performance and sample-efficiency by up to 2 times compared to existing offline RL and online fine-tuning methods. We show the first result that successfully fine-tunes OpenVLA, a 7B generalist robot policy, autonomously with Cal-QL, an online RL fine-tuning algorithm, improving from 40% to 70% in the real world in 40 minutes.
DCF-DS: Deep Cascade Fusion of Diarization and Separation for Speech Recognition under Realistic Single-Channel Conditions
Nov 11, 2024



Abstract:We propose a single-channel Deep Cascade Fusion of Diarization and Separation (DCF-DS) framework for back-end speech recognition, combining neural speaker diarization (NSD) and speech separation (SS). First, we sequentially integrate the NSD and SS modules within a joint training framework, enabling the separation module to leverage speaker time boundaries from the diarization module effectively. Then, to complement DCF-DS training, we introduce a window-level decoding scheme that allows the DCF-DS framework to handle the sparse data convergence instability (SDCI) problem. We also explore using an NSD system trained on real datasets to provide more accurate speaker boundaries during decoding. Additionally, we incorporate an optional multi-input multi-output speech enhancement module (MIMO-SE) within the DCF-DS framework, which offers further performance gains. Finally, we enhance diarization results by re-clustering DCF-DS outputs, improving ASR accuracy. By incorporating the DCF-DS method, we achieved first place in the realistic single-channel track of the CHiME-8 NOTSOFAR-1 challenge. We also perform the evaluation on the open LibriCSS dataset, achieving a new state-of-the-art performance on single-channel speech recognition.
Identifying Sub-networks in Neural Networks via Functionally Similar Representations
Oct 21, 2024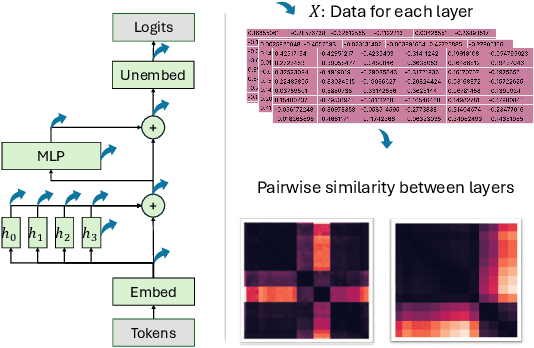
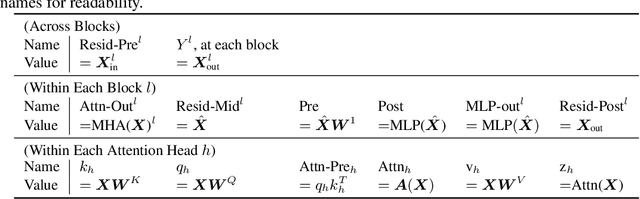
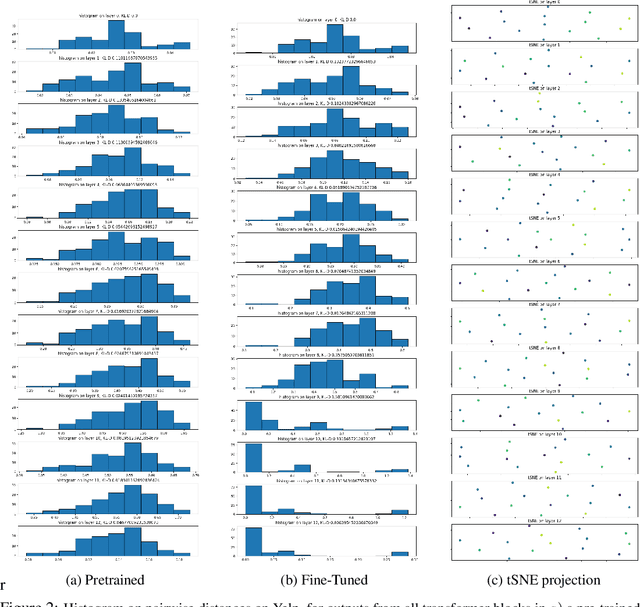

Abstract:Mechanistic interpretability aims to provide human-understandable insights into the inner workings of neural network models by examining their internals. Existing approaches typically require significant manual effort and prior knowledge, with strategies tailored to specific tasks. In this work, we take a step toward automating the understanding of the network by investigating the existence of distinct sub-networks. Specifically, we explore a novel automated and task-agnostic approach based on the notion of functionally similar representations within neural networks, reducing the need for human intervention. Our method identifies similar and dissimilar layers in the network, revealing potential sub-components. We achieve this by proposing, for the first time to our knowledge, the use of Gromov-Wasserstein distance, which overcomes challenges posed by varying distributions and dimensionalities across intermediate representations, issues that complicate direct layer-to-layer comparisons. Through experiments on algebraic and language tasks, we observe the emergence of sub-groups within neural network layers corresponding to functional abstractions. Additionally, we find that different training strategies influence the positioning of these sub-groups. Our approach offers meaningful insights into the behavior of neural networks with minimal human and computational cost.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge