Rosario Uceda-Sosa
Domain specific ontologies from Linked Open Data (LOD)
May 28, 2025Abstract:Logical and probabilistic reasoning tasks that require a deeper knowledge of semantics are increasingly relying on general purpose ontologies such as Wikidata and DBpedia. However, tasks such as entity disambiguation and linking may benefit from domain specific knowledge graphs, which make it more efficient to consume the knowledge and easier to extend with proprietary content. We discuss our experience bootstrapping one such ontology for IT with a domain-agnostic pipeline, and extending it using domain-specific glossaries.
Cross-Examiner: Evaluating Consistency of Large Language Model-Generated Explanations
Mar 11, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are often asked to explain their outputs to enhance accuracy and transparency. However, evidence suggests that these explanations can misrepresent the models' true reasoning processes. One effective way to identify inaccuracies or omissions in these explanations is through consistency checking, which typically involves asking follow-up questions. This paper introduces, cross-examiner, a new method for generating follow-up questions based on a model's explanation of an initial question. Our method combines symbolic information extraction with language model-driven question generation, resulting in better follow-up questions than those produced by LLMs alone. Additionally, this approach is more flexible than other methods and can generate a wider variety of follow-up questions.
Few-shot Policy (de)composition in Conversational Question Answering
Jan 20, 2025



Abstract:The task of policy compliance detection (PCD) is to determine if a scenario is in compliance with respect to a set of written policies. In a conversational setting, the results of PCD can indicate if clarifying questions must be asked to determine compliance status. Existing approaches usually claim to have reasoning capabilities that are latent or require a large amount of annotated data. In this work, we propose logical decomposition for policy compliance (LDPC): a neuro-symbolic framework to detect policy compliance using large language models (LLMs) in a few-shot setting. By selecting only a few exemplars alongside recently developed prompting techniques, we demonstrate that our approach soundly reasons about policy compliance conversations by extracting sub-questions to be answered, assigning truth values from contextual information, and explicitly producing a set of logic statements from the given policies. The formulation of explicit logic graphs can in turn help answer PCDrelated questions with increased transparency and explainability. We apply this approach to the popular PCD and conversational machine reading benchmark, ShARC, and show competitive performance with no task-specific finetuning. We also leverage the inherently interpretable architecture of LDPC to understand where errors occur, revealing ambiguities in the ShARC dataset and highlighting the challenges involved with reasoning for conversational question answering.
Reasoning about concepts with LLMs: Inconsistencies abound
May 30, 2024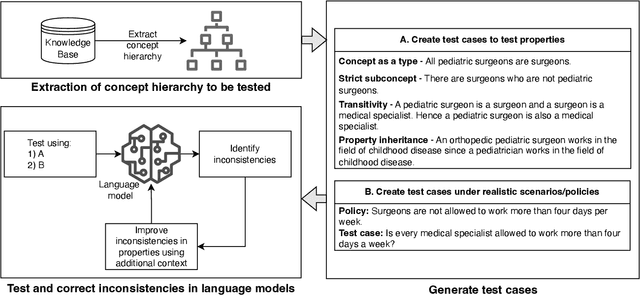
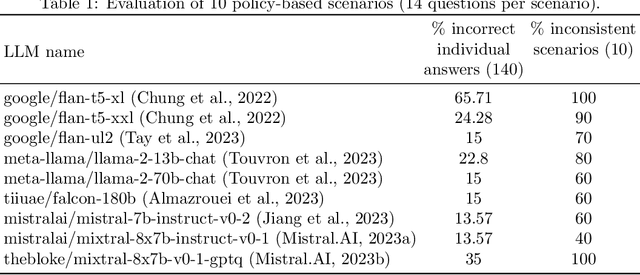
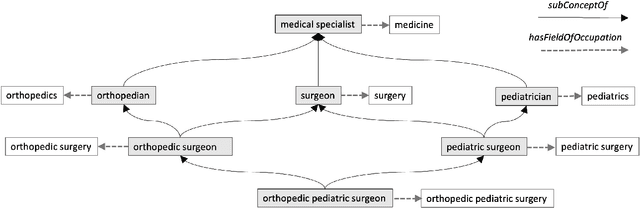
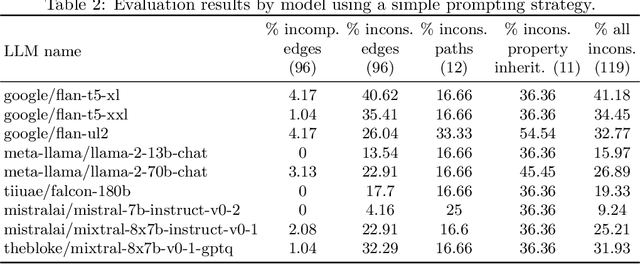
Abstract:The ability to summarize and organize knowledge into abstract concepts is key to learning and reasoning. Many industrial applications rely on the consistent and systematic use of concepts, especially when dealing with decision-critical knowledge. However, we demonstrate that, when methodically questioned, large language models (LLMs) often display and demonstrate significant inconsistencies in their knowledge. Computationally, the basic aspects of the conceptualization of a given domain can be represented as Is-A hierarchies in a knowledge graph (KG) or ontology, together with a few properties or axioms that enable straightforward reasoning. We show that even simple ontologies can be used to reveal conceptual inconsistencies across several LLMs. We also propose strategies that domain experts can use to evaluate and improve the coverage of key domain concepts in LLMs of various sizes. In particular, we have been able to significantly enhance the performance of LLMs of various sizes with openly available weights using simple knowledge-graph (KG) based prompting strategies.
Learning Symbolic Rules over Abstract Meaning Representations for Textual Reinforcement Learning
Jul 05, 2023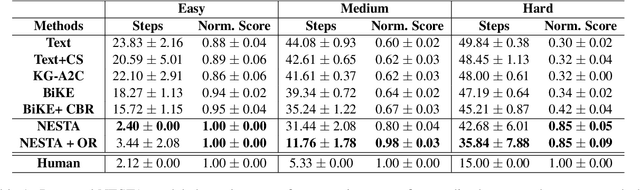
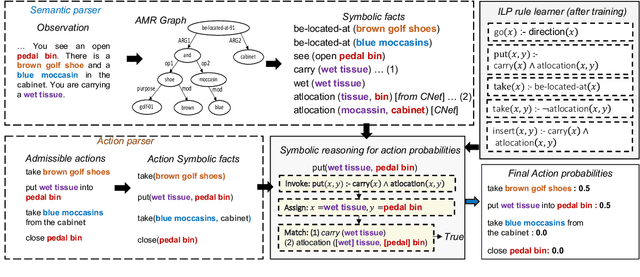
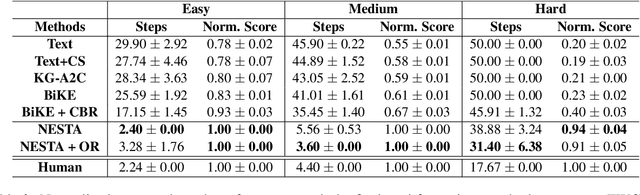
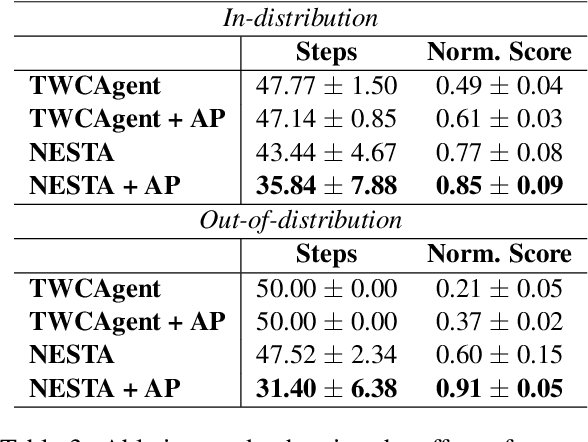
Abstract:Text-based reinforcement learning agents have predominantly been neural network-based models with embeddings-based representation, learning uninterpretable policies that often do not generalize well to unseen games. On the other hand, neuro-symbolic methods, specifically those that leverage an intermediate formal representation, are gaining significant attention in language understanding tasks. This is because of their advantages ranging from inherent interpretability, the lesser requirement of training data, and being generalizable in scenarios with unseen data. Therefore, in this paper, we propose a modular, NEuro-Symbolic Textual Agent (NESTA) that combines a generic semantic parser with a rule induction system to learn abstract interpretable rules as policies. Our experiments on established text-based game benchmarks show that the proposed NESTA method outperforms deep reinforcement learning-based techniques by achieving better generalization to unseen test games and learning from fewer training interactions.
A Benchmark for Generalizable and Interpretable Temporal Question Answering over Knowledge Bases
Jan 15, 2022
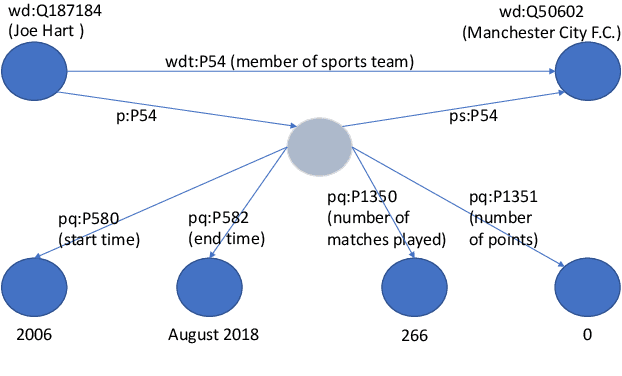


Abstract:Knowledge Base Question Answering (KBQA) tasks that involve complex reasoning are emerging as an important research direction. However, most existing KBQA datasets focus primarily on generic multi-hop reasoning over explicit facts, largely ignoring other reasoning types such as temporal, spatial, and taxonomic reasoning. In this paper, we present a benchmark dataset for temporal reasoning, TempQA-WD, to encourage research in extending the present approaches to target a more challenging set of complex reasoning tasks. Specifically, our benchmark is a temporal question answering dataset with the following advantages: (a) it is based on Wikidata, which is the most frequently curated, openly available knowledge base, (b) it includes intermediate sparql queries to facilitate the evaluation of semantic parsing based approaches for KBQA, and (c) it generalizes to multiple knowledge bases: Freebase and Wikidata. The TempQA-WD dataset is available at https://github.com/IBM/tempqa-wd.
SYGMA: System for Generalizable Modular Question Answering OverKnowledge Bases
Sep 28, 2021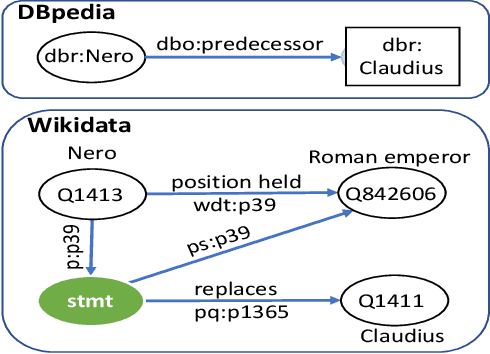
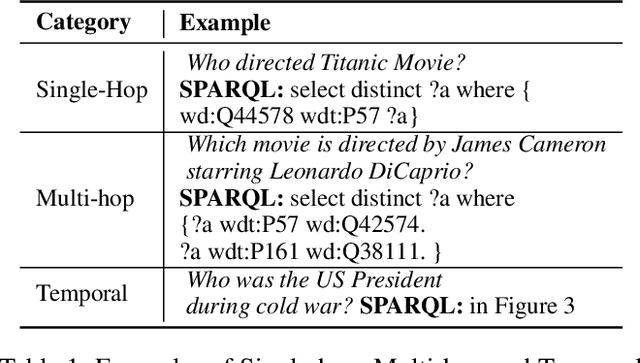
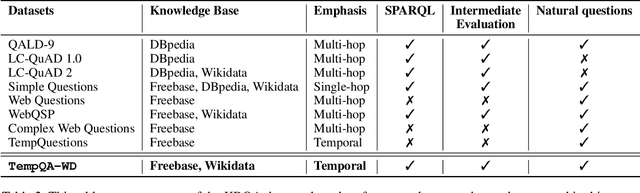
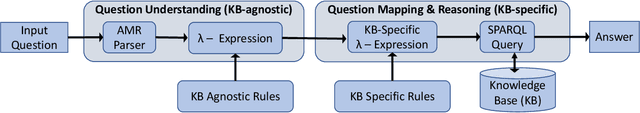
Abstract:Knowledge Base Question Answering (KBQA) tasks that in-volve complex reasoning are emerging as an important re-search direction. However, most KBQA systems struggle withgeneralizability, particularly on two dimensions: (a) acrossmultiple reasoning types where both datasets and systems haveprimarily focused on multi-hop reasoning, and (b) across mul-tiple knowledge bases, where KBQA approaches are specif-ically tuned to a single knowledge base. In this paper, wepresent SYGMA, a modular approach facilitating general-izability across multiple knowledge bases and multiple rea-soning types. Specifically, SYGMA contains three high levelmodules: 1) KB-agnostic question understanding module thatis common across KBs 2) Rules to support additional reason-ing types and 3) KB-specific question mapping and answeringmodule to address the KB-specific aspects of the answer ex-traction. We demonstrate effectiveness of our system by evalu-ating on datasets belonging to two distinct knowledge bases,DBpedia and Wikidata. In addition, to demonstrate extensi-bility to additional reasoning types we evaluate on multi-hopreasoning datasets and a new Temporal KBQA benchmarkdataset on Wikidata, namedTempQA-WD1, introduced in thispaper. We show that our generalizable approach has bettercompetetive performance on multiple datasets on DBpediaand Wikidata that requires both multi-hop and temporal rea-soning
The TechQA Dataset
Nov 08, 2019

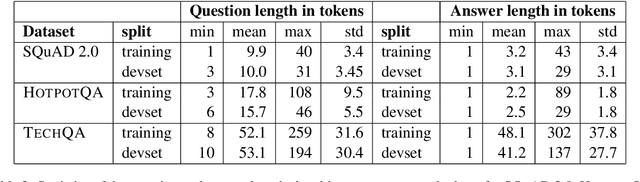
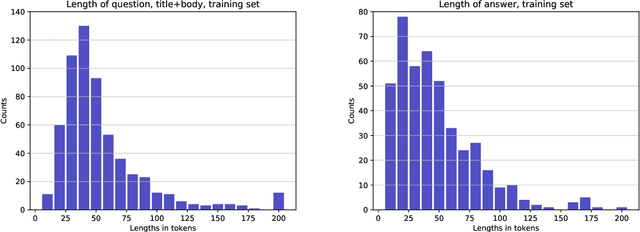
Abstract:We introduce TechQA, a domain-adaptation question answering dataset for the technical support domain. The TechQA corpus highlights two real-world issues from the automated customer support domain. First, it contains actual questions posed by users on a technical forum, rather than questions generated specifically for a competition or a task. Second, it has a real-world size -- 600 training, 310 dev, and 490 evaluation question/answer pairs -- thus reflecting the cost of creating large labeled datasets with actual data. Consequently, TechQA is meant to stimulate research in domain adaptation rather than being a resource to build QA systems from scratch. The dataset was obtained by crawling the IBM Developer and IBM DeveloperWorks forums for questions with accepted answers that appear in a published IBM Technote---a technical document that addresses a specific technical issue. We also release a collection of the 801,998 publicly available Technotes as of April 4, 2019 as a companion resource that might be used for pretraining, to learn representations of the IT domain language.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge