Miao Liu
The Llama 4 Herd: Architecture, Training, Evaluation, and Deployment Notes
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:This document consolidates publicly reported technical details about Metas Llama 4 model family. It summarizes (i) released variants (Scout and Maverick) and the broader herd context including the previewed Behemoth teacher model, (ii) architectural characteristics beyond a high-level MoE description covering routed/shared-expert structure, early-fusion multimodality, and long-context design elements reported for Scout (iRoPE and length generalization strategies), (iii) training disclosures spanning pre-training, mid-training for long-context extension, and post-training methodology (lightweight SFT, online RL, and lightweight DPO) as described in release materials, (iv) developer-reported benchmark results for both base and instruction-tuned checkpoints, and (v) practical deployment constraints observed across major serving environments, including provider-specific context limits and quantization packaging. The manuscript also summarizes licensing obligations relevant to redistribution and derivative naming, and reviews publicly described safeguards and evaluation practices. The goal is to provide a compact technical reference for researchers and practitioners who need precise, source-backed facts about Llama 4.
The Effectiveness of Approximate Regularized Replay for Efficient Supervised Fine-Tuning of Large Language Models
Dec 26, 2025Abstract:Although parameter-efficient fine-tuning methods, such as LoRA, only modify a small subset of parameters, they can have a significant impact on the model. Our instruction-tuning experiments show that LoRA-based supervised fine-tuning can catastrophically degrade model capabilities, even when trained on very small datasets for relatively few steps. With that said, we demonstrate that while the most straightforward approach (that is likely the most used in practice) fails spectacularly, small tweaks to the training procedure with very little overhead can virtually eliminate the problem. Particularly, in this paper we consider a regularized approximate replay approach which penalizes KL divergence with respect to the initial model and interleaves in data for next token prediction from a different, yet similar, open access corpus to what was used in pre-training. When applied to Qwen instruction-tuned models, we find that this recipe preserves general knowledge in the model without hindering plasticity to new tasks by adding a modest amount of computational overhead.
In the Eye of MLLM: Benchmarking Egocentric Video Intent Understanding with Gaze-Guided Prompting
Sep 09, 2025Abstract:The emergence of advanced multimodal large language models (MLLMs) has significantly enhanced AI assistants' ability to process complex information across modalities. Recently, egocentric videos, by directly capturing user focus, actions, and context in an unified coordinate, offer an exciting opportunity to enable proactive and personalized AI user experiences with MLLMs. However, existing benchmarks overlook the crucial role of gaze as an indicator of user intent. To address this gap, we introduce EgoGazeVQA, an egocentric gaze-guided video question answering benchmark that leverages gaze information to improve the understanding of longer daily-life videos. EgoGazeVQA consists of gaze-based QA pairs generated by MLLMs and refined by human annotators. Our experiments reveal that existing MLLMs struggle to accurately interpret user intentions. In contrast, our gaze-guided intent prompting methods significantly enhance performance by integrating spatial, temporal, and intent-related cues. We further conduct experiments on gaze-related fine-tuning and analyze how gaze estimation accuracy impacts prompting effectiveness. These results underscore the value of gaze for more personalized and effective AI assistants in egocentric settings.
Q-function Decomposition with Intervention Semantics with Factored Action Spaces
Apr 30, 2025Abstract:Many practical reinforcement learning environments have a discrete factored action space that induces a large combinatorial set of actions, thereby posing significant challenges. Existing approaches leverage the regular structure of the action space and resort to a linear decomposition of Q-functions, which avoids enumerating all combinations of factored actions. In this paper, we consider Q-functions defined over a lower dimensional projected subspace of the original action space, and study the condition for the unbiasedness of decomposed Q-functions using causal effect estimation from the no unobserved confounder setting in causal statistics. This leads to a general scheme which we call action decomposed reinforcement learning that uses the projected Q-functions to approximate the Q-function in standard model-free reinforcement learning algorithms. The proposed approach is shown to improve sample complexity in a model-based reinforcement learning setting. We demonstrate improvements in sample efficiency compared to state-of-the-art baselines in online continuous control environments and a real-world offline sepsis treatment environment.
Learning Predictive Visuomotor Coordination
Mar 30, 2025Abstract:Understanding and predicting human visuomotor coordination is crucial for applications in robotics, human-computer interaction, and assistive technologies. This work introduces a forecasting-based task for visuomotor modeling, where the goal is to predict head pose, gaze, and upper-body motion from egocentric visual and kinematic observations. We propose a \textit{Visuomotor Coordination Representation} (VCR) that learns structured temporal dependencies across these multimodal signals. We extend a diffusion-based motion modeling framework that integrates egocentric vision and kinematic sequences, enabling temporally coherent and accurate visuomotor predictions. Our approach is evaluated on the large-scale EgoExo4D dataset, demonstrating strong generalization across diverse real-world activities. Our results highlight the importance of multimodal integration in understanding visuomotor coordination, contributing to research in visuomotor learning and human behavior modeling.
A Generalist Hanabi Agent
Mar 17, 2025Abstract:Traditional multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) systems can develop cooperative strategies through repeated interactions. However, these systems are unable to perform well on any other setting than the one they have been trained on, and struggle to successfully cooperate with unfamiliar collaborators. This is particularly visible in the Hanabi benchmark, a popular 2-to-5 player cooperative card-game which requires complex reasoning and precise assistance to other agents. Current MARL agents for Hanabi can only learn one specific game-setting (e.g., 2-player games), and play with the same algorithmic agents. This is in stark contrast to humans, who can quickly adjust their strategies to work with unfamiliar partners or situations. In this paper, we introduce Recurrent Replay Relevance Distributed DQN (R3D2), a generalist agent for Hanabi, designed to overcome these limitations. We reformulate the task using text, as language has been shown to improve transfer. We then propose a distributed MARL algorithm that copes with the resulting dynamic observation- and action-space. In doing so, our agent is the first that can play all game settings concurrently, and extend strategies learned from one setting to other ones. As a consequence, our agent also demonstrates the ability to collaborate with different algorithmic agents -- agents that are themselves unable to do so. The implementation code is available at: $\href{https://github.com/chandar-lab/R3D2-A-Generalist-Hanabi-Agent}{R3D2-A-Generalist-Hanabi-Agent}$
ST-Think: How Multimodal Large Language Models Reason About 4D Worlds from Ego-Centric Videos
Mar 16, 2025Abstract:Humans excel at spatio-temporal reasoning, effortlessly interpreting dynamic visual events from an egocentric viewpoint. However, whether multimodal large language models (MLLMs) can similarly comprehend the 4D world remains uncertain. This paper explores multimodal spatio-temporal reasoning from an egocentric perspective, aiming to equip MLLMs with human-like reasoning capabilities. To support this objective, we introduce Ego-ST Bench, a novel benchmark containing over 5,000 question-answer pairs across four categories, systematically evaluating spatial, temporal, and integrated spatio-temporal reasoning. Additionally, we propose the ST-R1 Video model, a video-based reasoning model that incorporates reverse thinking into its reinforcement learning process, significantly enhancing performance. We combine long-chain-of-thought (long-CoT) supervised fine-tuning with Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) reinforcement learning, achieving notable improvements with limited high-quality data. Ego-ST Bench and ST-R1 provide valuable insights and resources for advancing video-based spatio-temporal reasoning research.
X-LeBench: A Benchmark for Extremely Long Egocentric Video Understanding
Jan 12, 2025Abstract:Long-form egocentric video understanding provides rich contextual information and unique insights into long-term human behaviors, holding significant potential for applications in embodied intelligence, long-term activity analysis, and personalized assistive technologies. However, existing benchmark datasets primarily focus on single, short-duration videos or moderately long videos up to dozens of minutes, leaving a substantial gap in evaluating extensive, ultra-long egocentric video recordings. To address this, we introduce X-LeBench, a novel benchmark dataset specifically crafted for evaluating tasks on extremely long egocentric video recordings. Leveraging the advanced text processing capabilities of large language models (LLMs), X-LeBench develops a life-logging simulation pipeline that produces realistic, coherent daily plans aligned with real-world video data. This approach enables the flexible integration of synthetic daily plans with real-world footage from Ego4D-a massive-scale egocentric video dataset covers a wide range of daily life scenarios-resulting in 432 simulated video life logs that mirror realistic daily activities in contextually rich scenarios. The video life-log durations span from 23 minutes to 16.4 hours. The evaluation of several baseline systems and multimodal large language models (MLLMs) reveals their poor performance across the board, highlighting the inherent challenges of long-form egocentric video understanding and underscoring the need for more advanced models.
Building a Mind Palace: Structuring Environment-Grounded Semantic Graphs for Effective Long Video Analysis with LLMs
Jan 08, 2025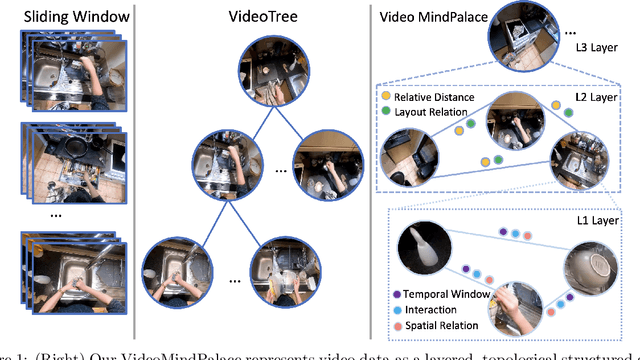
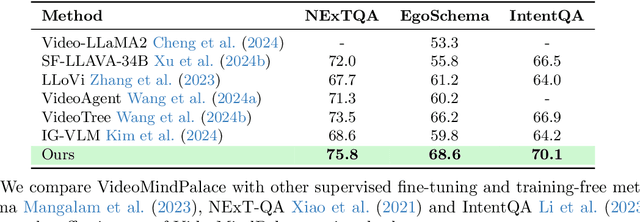
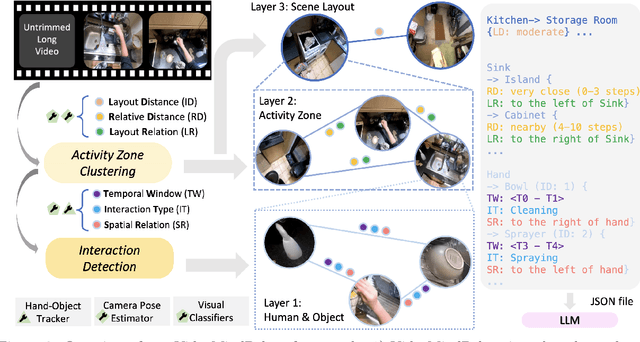
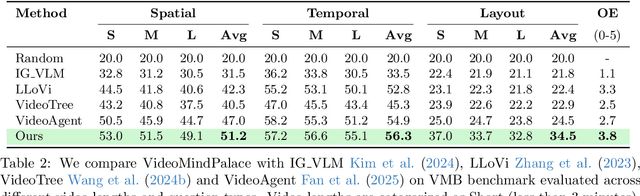
Abstract:Long-form video understanding with Large Vision Language Models is challenged by the need to analyze temporally dispersed yet spatially concentrated key moments within limited context windows. In this work, we introduce VideoMindPalace, a new framework inspired by the "Mind Palace", which organizes critical video moments into a topologically structured semantic graph. VideoMindPalace organizes key information through (i) hand-object tracking and interaction, (ii) clustered activity zones representing specific areas of recurring activities, and (iii) environment layout mapping, allowing natural language parsing by LLMs to provide grounded insights on spatio-temporal and 3D context. In addition, we propose the Video MindPalace Benchmark (VMB), to assess human-like reasoning, including spatial localization, temporal reasoning, and layout-aware sequential understanding. Evaluated on VMB and established video QA datasets, including EgoSchema, NExT-QA, IntentQA, and the Active Memories Benchmark, VideoMindPalace demonstrates notable gains in spatio-temporal coherence and human-aligned reasoning, advancing long-form video analysis capabilities in VLMs.
Can Large Language Models Adapt to Other Agents In-Context?
Dec 27, 2024Abstract:As the research community aims to build better AI assistants that are more dynamic and personalized to the diversity of humans that they interact with, there is increased interest in evaluating the theory of mind capabilities of large language models (LLMs). Indeed, several recent studies suggest that LLM theory of mind capabilities are quite impressive, approximating human-level performance. Our paper aims to rebuke this narrative and argues instead that past studies were not directly measuring agent performance, potentially leading to findings that are illusory in nature as a result. We draw a strong distinction between what we call literal theory of mind i.e. measuring the agent's ability to predict the behavior of others and functional theory of mind i.e. adapting to agents in-context based on a rational response to predictions of their behavior. We find that top performing open source LLMs may display strong capabilities in literal theory of mind, depending on how they are prompted, but seem to struggle with functional theory of mind -- even when partner policies are exceedingly simple. Our work serves to highlight the double sided nature of inductive bias in LLMs when adapting to new situations. While this bias can lead to strong performance over limited horizons, it often hinders convergence to optimal long-term behavior.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge