Sangmin Lee
Data Intelligence Laboratory, LG AI Research
MuCo: Multi-turn Contrastive Learning for Multimodal Embedding Model
Feb 06, 2026Abstract:Universal Multimodal embedding models built on Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have traditionally employed contrastive learning, which aligns representations of query-target pairs across different modalities. Yet, despite its empirical success, they are primarily built on a "single-turn" formulation where each query-target pair is treated as an independent data point. This paradigm leads to computational inefficiency when scaling, as it requires a separate forward pass for each pair and overlooks potential contextual relationships between multiple queries that can relate to the same context. In this work, we introduce Multi-Turn Contrastive Learning (MuCo), a dialogue-inspired framework that revisits this process. MuCo leverages the conversational nature of MLLMs to process multiple, related query-target pairs associated with a single image within a single forward pass. This allows us to extract a set of multiple query and target embeddings simultaneously, conditioned on a shared context representation, amplifying the effective batch size and overall training efficiency. Experiments exhibit MuCo with a newly curated 5M multimodal multi-turn dataset (M3T), which yields state-of-the-art retrieval performance on MMEB and M-BEIR benchmarks, while markedly enhancing both training efficiency and representation coherence across modalities. Code and M3T are available at https://github.com/naver-ai/muco
UniverSR: Unified and Versatile Audio Super-Resolution via Vocoder-Free Flow Matching
Oct 01, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we present a vocoder-free framework for audio super-resolution that employs a flow matching generative model to capture the conditional distribution of complex-valued spectral coefficients. Unlike conventional two-stage diffusion-based approaches that predict a mel-spectrogram and then rely on a pre-trained neural vocoder to synthesize waveforms, our method directly reconstructs waveforms via the inverse Short-Time Fourier Transform (iSTFT), thereby eliminating the dependence on a separate vocoder. This design not only simplifies end-to-end optimization but also overcomes a critical bottleneck of two-stage pipelines, where the final audio quality is fundamentally constrained by vocoder performance. Experiments show that our model consistently produces high-fidelity 48 kHz audio across diverse upsampling factors, achieving state-of-the-art performance on both speech and general audio datasets.
SAGE-LD: Towards Scalable and Generalizable End-to-End Language Diarization via Simulated Data Augmentation
Oct 01, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we present a neural spoken language diarization model that supports an unconstrained span of languages within a single framework. Our approach integrates a learnable query-based architecture grounded in multilingual awareness, with large-scale pretraining on simulated code-switching data. By jointly leveraging these two components, our method overcomes the limitations of conventional approaches in data scarcity and architecture optimization, and generalizes effectively to real-world multilingual settings across diverse environments. Experimental results demonstrate that our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance on several language diarization benchmarks, with a relative performance improvement of 23% to 52% over previous methods. We believe that this work not only advances research in language diarization but also establishes a foundational framework for code-switching speech technologies.
UniCoM: A Universal Code-Switching Speech Generator
Aug 21, 2025Abstract:Code-switching (CS), the alternation between two or more languages within a single speaker's utterances, is common in real-world conversations and poses significant challenges for multilingual speech technology. However, systems capable of handling this phenomenon remain underexplored, primarily due to the scarcity of suitable datasets. To resolve this issue, we propose Universal Code-Mixer (UniCoM), a novel pipeline for generating high-quality, natural CS samples without altering sentence semantics. Our approach utilizes an algorithm we call Substituting WORDs with Synonyms (SWORDS), which generates CS speech by replacing selected words with their translations while considering their parts of speech. Using UniCoM, we construct Code-Switching FLEURS (CS-FLEURS), a multilingual CS corpus designed for automatic speech recognition (ASR) and speech-to-text translation (S2TT). Experimental results show that CS-FLEURS achieves high intelligibility and naturalness, performing comparably to existing datasets on both objective and subjective metrics. We expect our approach to advance CS speech technology and enable more inclusive multilingual systems.
MemoryTalker: Personalized Speech-Driven 3D Facial Animation via Audio-Guided Stylization
Jul 28, 2025Abstract:Speech-driven 3D facial animation aims to synthesize realistic facial motion sequences from given audio, matching the speaker's speaking style. However, previous works often require priors such as class labels of a speaker or additional 3D facial meshes at inference, which makes them fail to reflect the speaking style and limits their practical use. To address these issues, we propose MemoryTalker which enables realistic and accurate 3D facial motion synthesis by reflecting speaking style only with audio input to maximize usability in applications. Our framework consists of two training stages: 1-stage is storing and retrieving general motion (i.e., Memorizing), and 2-stage is to perform the personalized facial motion synthesis (i.e., Animating) with the motion memory stylized by the audio-driven speaking style feature. In this second stage, our model learns about which facial motion types should be emphasized for a particular piece of audio. As a result, our MemoryTalker can generate a reliable personalized facial animation without additional prior information. With quantitative and qualitative evaluations, as well as user study, we show the effectiveness of our model and its performance enhancement for personalized facial animation over state-of-the-art methods.
Thunder-Tok: Minimizing Tokens per Word in Tokenizing Korean Texts for Generative Language Models
Jun 18, 2025Abstract:This paper introduces Thunder-Tok, a new Korean tokenizer designed to reduce token fertility without compromising model performance. Our approach uses a rule-based pre-tokenization method that aligns with the linguistic structure of the Korean language. We also create a seed vocabulary containing tokens that resemble linguistic units and employ a branching entropy-based selection algorithm. These techniques increase the average token length, thus lowering fertility while preserving linguistic information. Experimental results indicate that Thunder-Tok reduces fertility by approximately 10% (i.e., reduces the number of tokens by 10%, improving the inference speed by 10%) compared to BPE without compromising performance across various downstream tasks. These findings demonstrate that our linguistically informed approach is effective and practical for designing efficient tokenizers for language models.
Incorporating Flexible Image Conditioning into Text-to-Video Diffusion Models without Training
May 27, 2025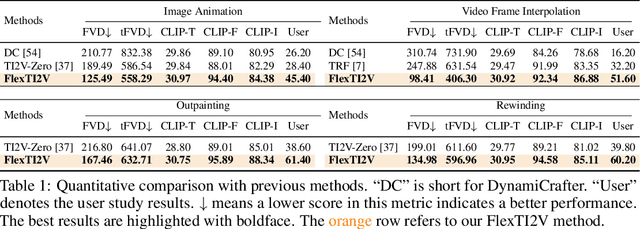
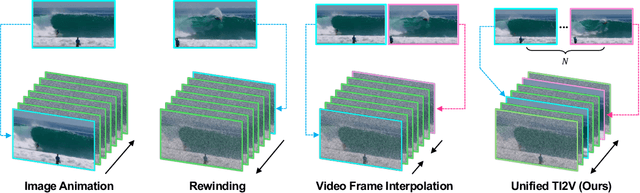
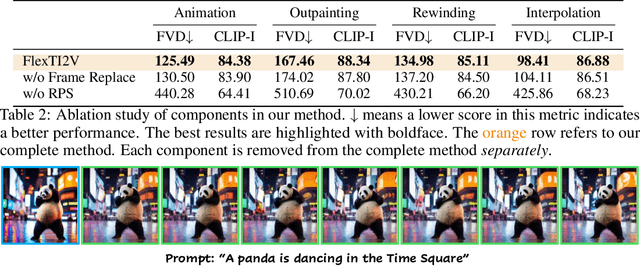
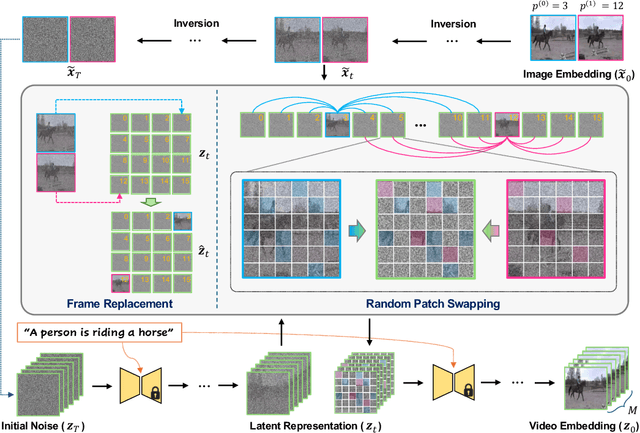
Abstract:Text-image-to-video (TI2V) generation is a critical problem for controllable video generation using both semantic and visual conditions. Most existing methods typically add visual conditions to text-to-video (T2V) foundation models by finetuning, which is costly in resources and only limited to a few predefined conditioning settings. To tackle this issue, we introduce a unified formulation for TI2V generation with flexible visual conditioning. Furthermore, we propose an innovative training-free approach, dubbed FlexTI2V, that can condition T2V foundation models on an arbitrary amount of images at arbitrary positions. Specifically, we firstly invert the condition images to noisy representation in a latent space. Then, in the denoising process of T2V models, our method uses a novel random patch swapping strategy to incorporate visual features into video representations through local image patches. To balance creativity and fidelity, we use a dynamic control mechanism to adjust the strength of visual conditioning to each video frame. Extensive experiments validate that our method surpasses previous training-free image conditioning methods by a notable margin. We also show more insights of our method by detailed ablation study and analysis.
NTIRE 2025 Challenge on Efficient Burst HDR and Restoration: Datasets, Methods, and Results
May 17, 2025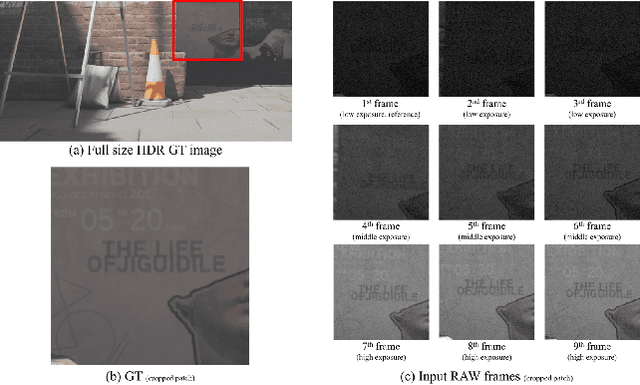
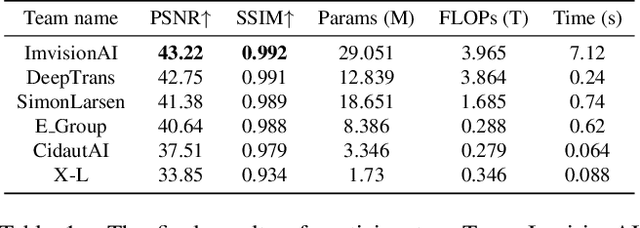

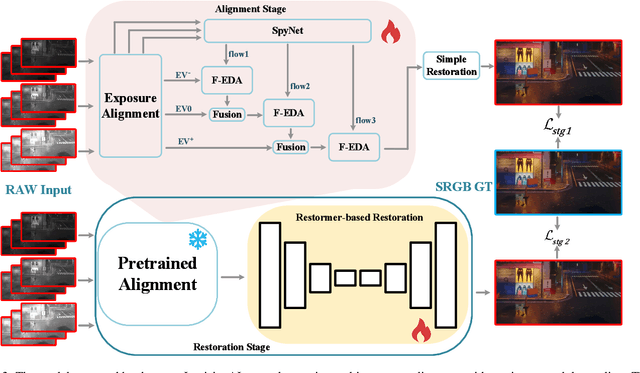
Abstract:This paper reviews the NTIRE 2025 Efficient Burst HDR and Restoration Challenge, which aims to advance efficient multi-frame high dynamic range (HDR) and restoration techniques. The challenge is based on a novel RAW multi-frame fusion dataset, comprising nine noisy and misaligned RAW frames with various exposure levels per scene. Participants were tasked with developing solutions capable of effectively fusing these frames while adhering to strict efficiency constraints: fewer than 30 million model parameters and a computational budget under 4.0 trillion FLOPs. A total of 217 participants registered, with six teams finally submitting valid solutions. The top-performing approach achieved a PSNR of 43.22 dB, showcasing the potential of novel methods in this domain. This paper provides a comprehensive overview of the challenge, compares the proposed solutions, and serves as a valuable reference for researchers and practitioners in efficient burst HDR and restoration.
SocialGesture: Delving into Multi-person Gesture Understanding
Apr 03, 2025Abstract:Previous research in human gesture recognition has largely overlooked multi-person interactions, which are crucial for understanding the social context of naturally occurring gestures. This limitation in existing datasets presents a significant challenge in aligning human gestures with other modalities like language and speech. To address this issue, we introduce SocialGesture, the first large-scale dataset specifically designed for multi-person gesture analysis. SocialGesture features a diverse range of natural scenarios and supports multiple gesture analysis tasks, including video-based recognition and temporal localization, providing a valuable resource for advancing the study of gesture during complex social interactions. Furthermore, we propose a novel visual question answering (VQA) task to benchmark vision language models'(VLMs) performance on social gesture understanding. Our findings highlight several limitations of current gesture recognition models, offering insights into future directions for improvement in this field. SocialGesture is available at huggingface.co/datasets/IrohXu/SocialGesture.
Question-Aware Gaussian Experts for Audio-Visual Question Answering
Mar 07, 2025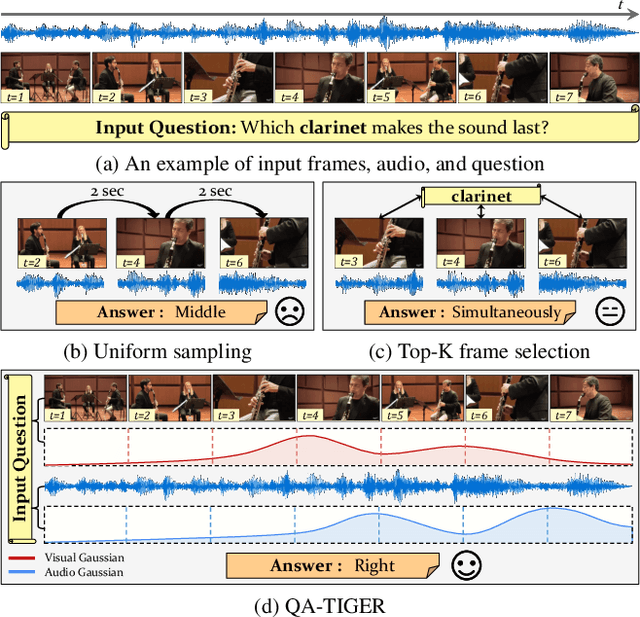
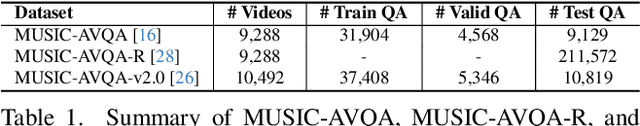
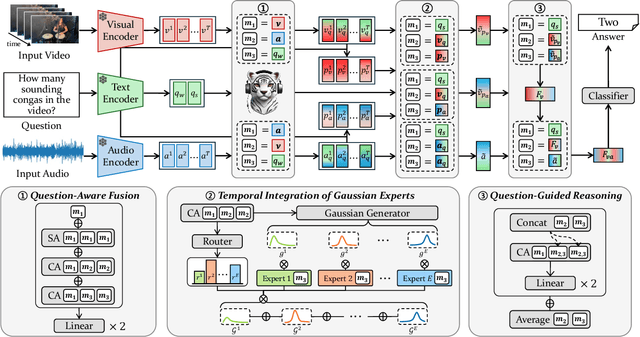
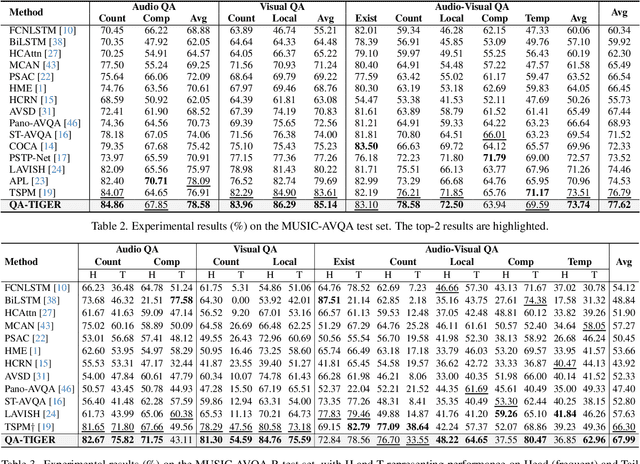
Abstract:Audio-Visual Question Answering (AVQA) requires not only question-based multimodal reasoning but also precise temporal grounding to capture subtle dynamics for accurate prediction. However, existing methods mainly use question information implicitly, limiting focus on question-specific details. Furthermore, most studies rely on uniform frame sampling, which can miss key question-relevant frames. Although recent Top-K frame selection methods aim to address this, their discrete nature still overlooks fine-grained temporal details. This paper proposes QA-TIGER, a novel framework that explicitly incorporates question information and models continuous temporal dynamics. Our key idea is to use Gaussian-based modeling to adaptively focus on both consecutive and non-consecutive frames based on the question, while explicitly injecting question information and applying progressive refinement. We leverage a Mixture of Experts (MoE) to flexibly implement multiple Gaussian models, activating temporal experts specifically tailored to the question. Extensive experiments on multiple AVQA benchmarks show that QA-TIGER consistently achieves state-of-the-art performance. Code is available at https://aim-skku.github.io/QA-TIGER/
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge