Fiona Ryan
Improving Personalized Search with Regularized Low-Rank Parameter Updates
Jun 11, 2025Abstract:Personalized vision-language retrieval seeks to recognize new concepts (e.g. "my dog Fido") from only a few examples. This task is challenging because it requires not only learning a new concept from a few images, but also integrating the personal and general knowledge together to recognize the concept in different contexts. In this paper, we show how to effectively adapt the internal representation of a vision-language dual encoder model for personalized vision-language retrieval. We find that regularized low-rank adaption of a small set of parameters in the language encoder's final layer serves as a highly effective alternative to textual inversion for recognizing the personal concept while preserving general knowledge. Additionally, we explore strategies for combining parameters of multiple learned personal concepts, finding that parameter addition is effective. To evaluate how well general knowledge is preserved in a finetuned representation, we introduce a metric that measures image retrieval accuracy based on captions generated by a vision language model (VLM). Our approach achieves state-of-the-art accuracy on two benchmarks for personalized image retrieval with natural language queries - DeepFashion2 and ConCon-Chi - outperforming the prior art by 4%-22% on personal retrievals.
SocialGesture: Delving into Multi-person Gesture Understanding
Apr 03, 2025Abstract:Previous research in human gesture recognition has largely overlooked multi-person interactions, which are crucial for understanding the social context of naturally occurring gestures. This limitation in existing datasets presents a significant challenge in aligning human gestures with other modalities like language and speech. To address this issue, we introduce SocialGesture, the first large-scale dataset specifically designed for multi-person gesture analysis. SocialGesture features a diverse range of natural scenarios and supports multiple gesture analysis tasks, including video-based recognition and temporal localization, providing a valuable resource for advancing the study of gesture during complex social interactions. Furthermore, we propose a novel visual question answering (VQA) task to benchmark vision language models'(VLMs) performance on social gesture understanding. Our findings highlight several limitations of current gesture recognition models, offering insights into future directions for improvement in this field. SocialGesture is available at huggingface.co/datasets/IrohXu/SocialGesture.
Gaze-LLE: Gaze Target Estimation via Large-Scale Learned Encoders
Dec 12, 2024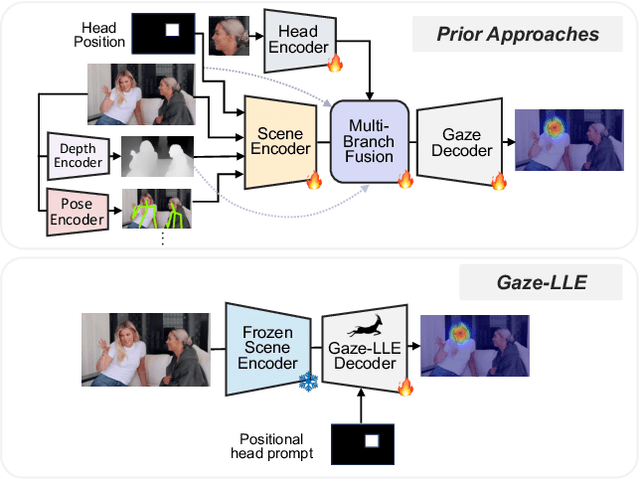
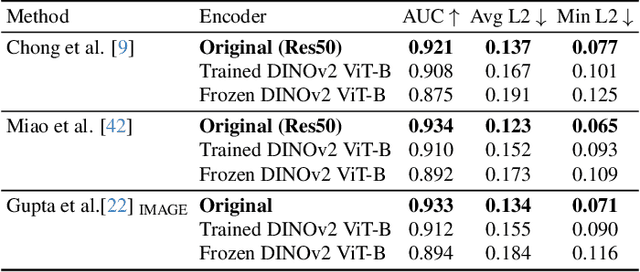
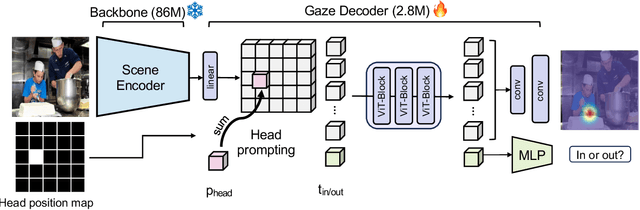
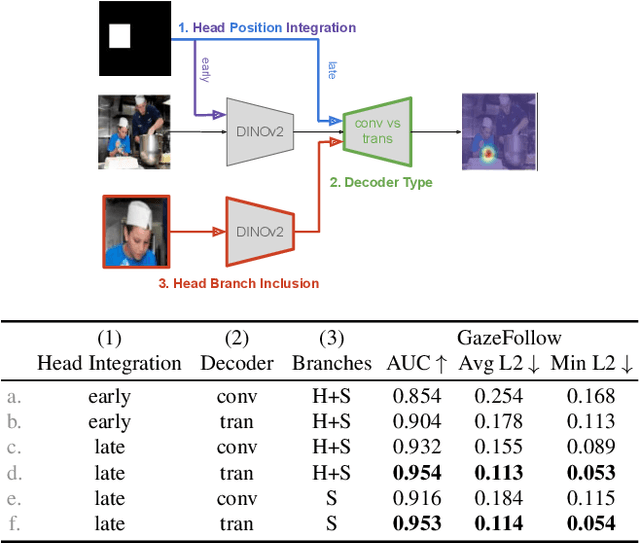
Abstract:We address the problem of gaze target estimation, which aims to predict where a person is looking in a scene. Predicting a person's gaze target requires reasoning both about the person's appearance and the contents of the scene. Prior works have developed increasingly complex, hand-crafted pipelines for gaze target estimation that carefully fuse features from separate scene encoders, head encoders, and auxiliary models for signals like depth and pose. Motivated by the success of general-purpose feature extractors on a variety of visual tasks, we propose Gaze-LLE, a novel transformer framework that streamlines gaze target estimation by leveraging features from a frozen DINOv2 encoder. We extract a single feature representation for the scene, and apply a person-specific positional prompt to decode gaze with a lightweight module. We demonstrate state-of-the-art performance across several gaze benchmarks and provide extensive analysis to validate our design choices. Our code is available at: http://github.com/fkryan/gazelle .
Modeling Multimodal Social Interactions: New Challenges and Baselines with Densely Aligned Representations
Mar 04, 2024


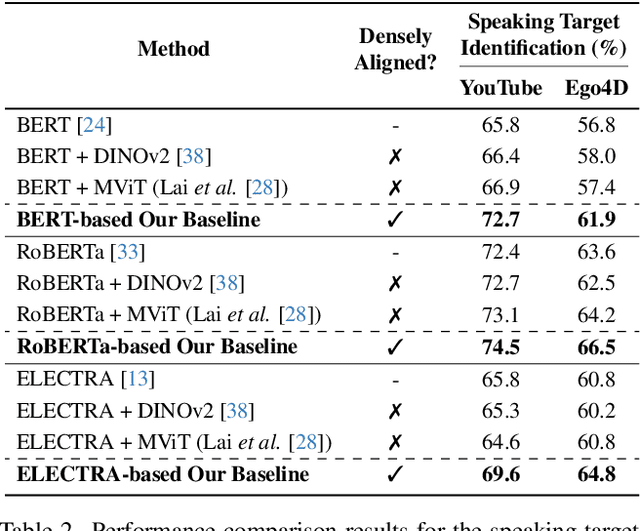
Abstract:Understanding social interactions involving both verbal and non-verbal cues is essential to effectively interpret social situations. However, most prior works on multimodal social cues focus predominantly on single-person behaviors or rely on holistic visual representations that are not densely aligned to utterances in multi-party environments. They are limited in modeling the intricate dynamics of multi-party interactions. In this paper, we introduce three new challenging tasks to model the fine-grained dynamics between multiple people: speaking target identification, pronoun coreference resolution, and mentioned player prediction. We contribute extensive data annotations to curate these new challenges in social deduction game settings. Furthermore, we propose a novel multimodal baseline that leverages densely aligned language-visual representations by synchronizing visual features with their corresponding utterances. This facilitates concurrently capturing verbal and non-verbal cues pertinent to social reasoning. Experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach with densely aligned multimodal representations in modeling social interactions. We will release our benchmarks and source code to facilitate further research.
Ego-Exo4D: Understanding Skilled Human Activity from First- and Third-Person Perspectives
Nov 30, 2023



Abstract:We present Ego-Exo4D, a diverse, large-scale multimodal multiview video dataset and benchmark challenge. Ego-Exo4D centers around simultaneously-captured egocentric and exocentric video of skilled human activities (e.g., sports, music, dance, bike repair). More than 800 participants from 13 cities worldwide performed these activities in 131 different natural scene contexts, yielding long-form captures from 1 to 42 minutes each and 1,422 hours of video combined. The multimodal nature of the dataset is unprecedented: the video is accompanied by multichannel audio, eye gaze, 3D point clouds, camera poses, IMU, and multiple paired language descriptions -- including a novel "expert commentary" done by coaches and teachers and tailored to the skilled-activity domain. To push the frontier of first-person video understanding of skilled human activity, we also present a suite of benchmark tasks and their annotations, including fine-grained activity understanding, proficiency estimation, cross-view translation, and 3D hand/body pose. All resources will be open sourced to fuel new research in the community.
Listen to Look into the Future: Audio-Visual Egocentric Gaze Anticipation
May 06, 2023
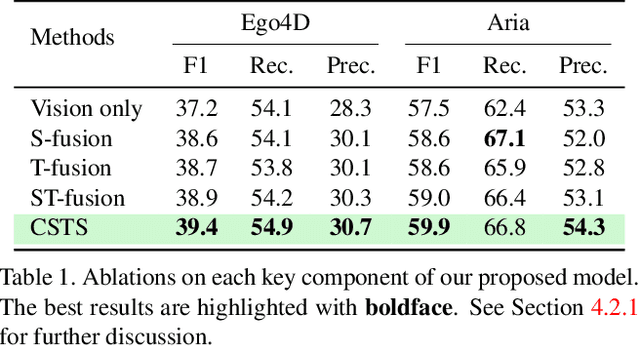

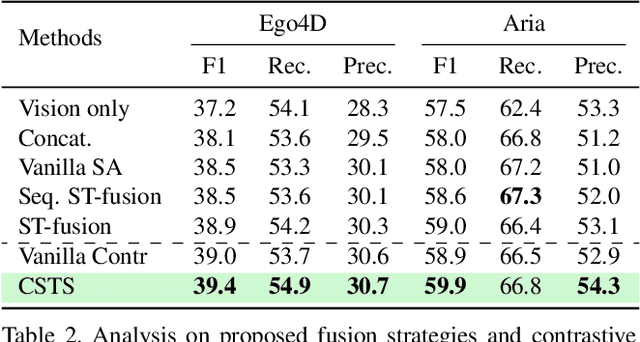
Abstract:Egocentric gaze anticipation serves as a key building block for the emerging capability of Augmented Reality. Notably, gaze behavior is driven by both visual cues and audio signals during daily activities. Motivated by this observation, we introduce the first model that leverages both the video and audio modalities for egocentric gaze anticipation. Specifically, we propose a Contrastive Spatial-Temporal Separable (CSTS) fusion approach that adopts two modules to separately capture audio-visual correlations in spatial and temporal dimensions, and applies a contrastive loss on the re-weighted audio-visual features from fusion modules for representation learning. We conduct extensive ablation studies and thorough analysis using two egocentric video datasets: Ego4D and Aria, to validate our model design. We also demonstrate improvements over prior state-of-the-art methods. Moreover, we provide visualizations to show the gaze anticipation results and provide additional insights into audio-visual representation learning.
Egocentric Auditory Attention Localization in Conversations
Mar 28, 2023


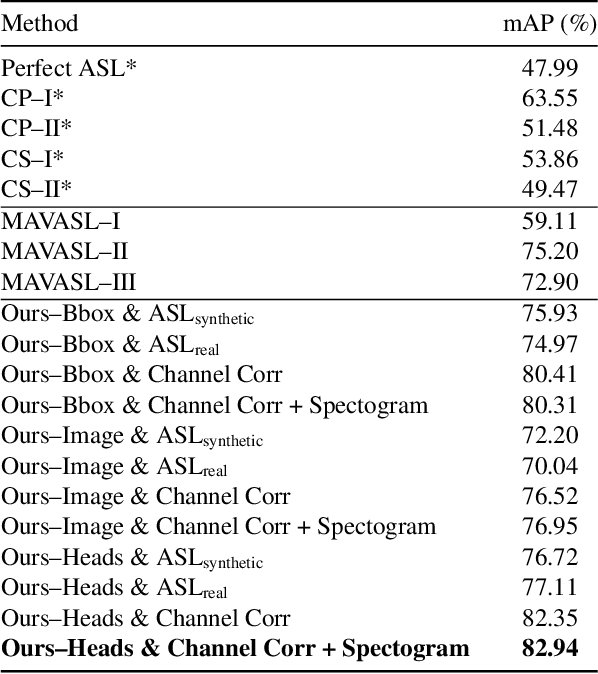
Abstract:In a noisy conversation environment such as a dinner party, people often exhibit selective auditory attention, or the ability to focus on a particular speaker while tuning out others. Recognizing who somebody is listening to in a conversation is essential for developing technologies that can understand social behavior and devices that can augment human hearing by amplifying particular sound sources. The computer vision and audio research communities have made great strides towards recognizing sound sources and speakers in scenes. In this work, we take a step further by focusing on the problem of localizing auditory attention targets in egocentric video, or detecting who in a camera wearer's field of view they are listening to. To tackle the new and challenging Selective Auditory Attention Localization problem, we propose an end-to-end deep learning approach that uses egocentric video and multichannel audio to predict the heatmap of the camera wearer's auditory attention. Our approach leverages spatiotemporal audiovisual features and holistic reasoning about the scene to make predictions, and outperforms a set of baselines on a challenging multi-speaker conversation dataset. Project page: https://fkryan.github.io/saal
Werewolf Among Us: A Multimodal Dataset for Modeling Persuasion Behaviors in Social Deduction Games
Dec 16, 2022
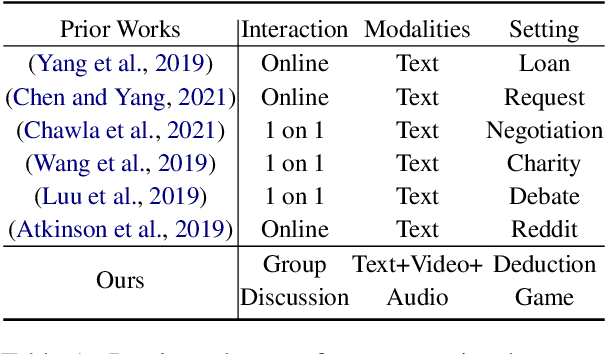


Abstract:Persuasion modeling is a key building block for conversational agents. Existing works in this direction are limited to analyzing textual dialogue corpus. We argue that visual signals also play an important role in understanding human persuasive behaviors. In this paper, we introduce the first multimodal dataset for modeling persuasion behaviors. Our dataset includes 199 dialogue transcriptions and videos captured in a multi-player social deduction game setting, 26,647 utterance level annotations of persuasion strategy, and game level annotations of deduction game outcomes. We provide extensive experiments to show how dialogue context and visual signals benefit persuasion strategy prediction. We also explore the generalization ability of language models for persuasion modeling and the role of persuasion strategies in predicting social deduction game outcomes. Our dataset, code, and models can be found at https://persuasion-deductiongame.socialai-data.org.
In the Eye of Transformer: Global-Local Correlation for Egocentric Gaze Estimation
Aug 10, 2022
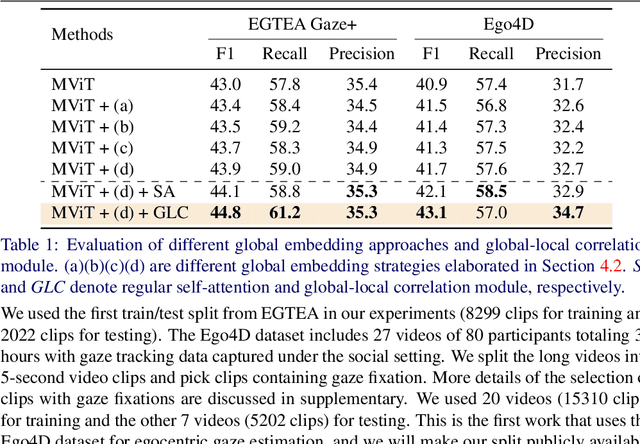
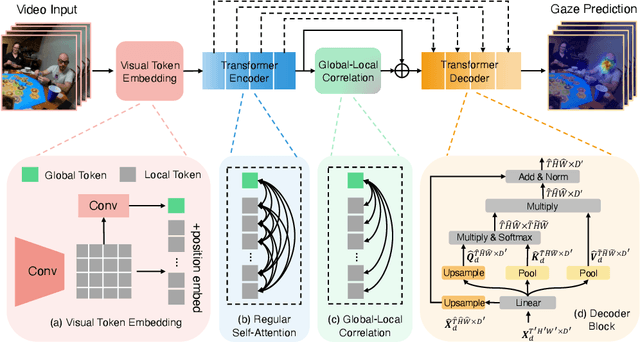
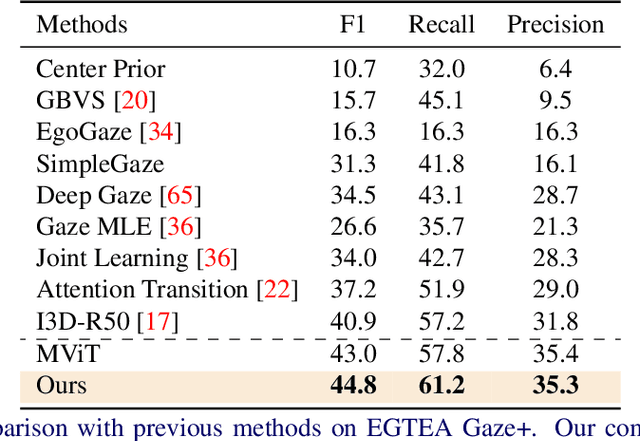
Abstract:In this paper, we present the first transformer-based model to address the challenging problem of egocentric gaze estimation. We observe that the connection between the global scene context and local visual information is vital for localizing the gaze fixation from egocentric video frames. To this end, we design the transformer encoder to embed the global context as one additional visual token and further propose a novel Global-Local Correlation (GLC) module to explicitly model the correlation of the global token and each local token. We validate our model on two egocentric video datasets - EGTEA Gaze+ and Ego4D. Our detailed ablation studies demonstrate the benefits of our method. In addition, our approach exceeds previous state-of-the-arts by a large margin. We also provide additional visualizations to support our claim that global-local correlation serves a key representation for predicting gaze fixation from egocentric videos. More details can be found in our website (https://bolinlai.github.io/GLC-EgoGazeEst).
Robust and Efficient Medical Imaging with Self-Supervision
May 19, 2022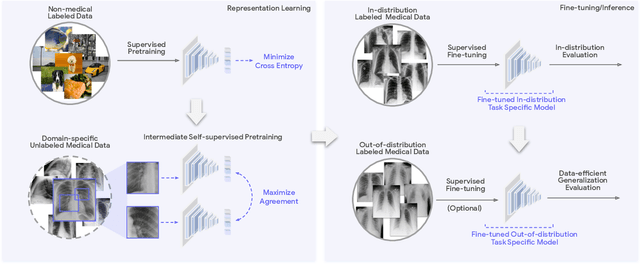
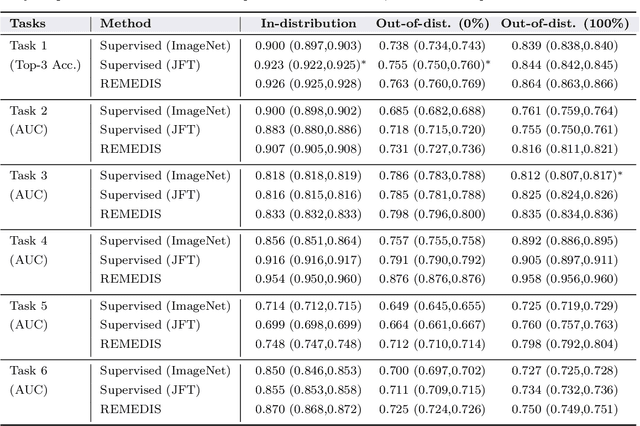
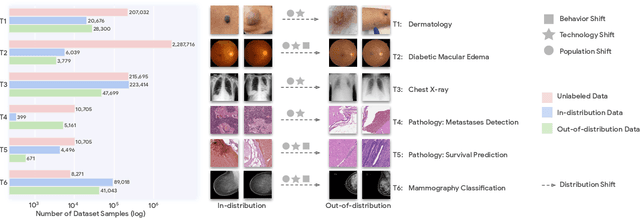
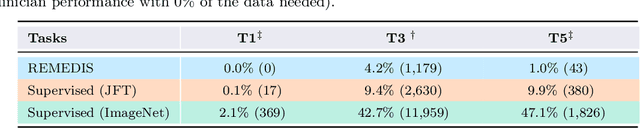
Abstract:Recent progress in Medical Artificial Intelligence (AI) has delivered systems that can reach clinical expert level performance. However, such systems tend to demonstrate sub-optimal "out-of-distribution" performance when evaluated in clinical settings different from the training environment. A common mitigation strategy is to develop separate systems for each clinical setting using site-specific data [1]. However, this quickly becomes impractical as medical data is time-consuming to acquire and expensive to annotate [2]. Thus, the problem of "data-efficient generalization" presents an ongoing difficulty for Medical AI development. Although progress in representation learning shows promise, their benefits have not been rigorously studied, specifically for out-of-distribution settings. To meet these challenges, we present REMEDIS, a unified representation learning strategy to improve robustness and data-efficiency of medical imaging AI. REMEDIS uses a generic combination of large-scale supervised transfer learning with self-supervised learning and requires little task-specific customization. We study a diverse range of medical imaging tasks and simulate three realistic application scenarios using retrospective data. REMEDIS exhibits significantly improved in-distribution performance with up to 11.5% relative improvement in diagnostic accuracy over a strong supervised baseline. More importantly, our strategy leads to strong data-efficient generalization of medical imaging AI, matching strong supervised baselines using between 1% to 33% of retraining data across tasks. These results suggest that REMEDIS can significantly accelerate the life-cycle of medical imaging AI development thereby presenting an important step forward for medical imaging AI to deliver broad impact.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge