Kris Kitani
MHR: Momentum Human Rig
Nov 19, 2025Abstract:We present MHR, a parametric human body model that combines the decoupled skeleton/shape paradigm of ATLAS with a flexible, modern rig and pose corrective system inspired by the Momentum library. Our model enables expressive, anatomically plausible human animation, supporting non-linear pose correctives, and is designed for robust integration in AR/VR and graphics pipelines.
BFM-Zero: A Promptable Behavioral Foundation Model for Humanoid Control Using Unsupervised Reinforcement Learning
Nov 06, 2025Abstract:Building Behavioral Foundation Models (BFMs) for humanoid robots has the potential to unify diverse control tasks under a single, promptable generalist policy. However, existing approaches are either exclusively deployed on simulated humanoid characters, or specialized to specific tasks such as tracking. We propose BFM-Zero, a framework that learns an effective shared latent representation that embeds motions, goals, and rewards into a common space, enabling a single policy to be prompted for multiple downstream tasks without retraining. This well-structured latent space in BFM-Zero enables versatile and robust whole-body skills on a Unitree G1 humanoid in the real world, via diverse inference methods, including zero-shot motion tracking, goal reaching, and reward optimization, and few-shot optimization-based adaptation. Unlike prior on-policy reinforcement learning (RL) frameworks, BFM-Zero builds upon recent advancements in unsupervised RL and Forward-Backward (FB) models, which offer an objective-centric, explainable, and smooth latent representation of whole-body motions. We further extend BFM-Zero with critical reward shaping, domain randomization, and history-dependent asymmetric learning to bridge the sim-to-real gap. Those key design choices are quantitatively ablated in simulation. A first-of-its-kind model, BFM-Zero establishes a step toward scalable, promptable behavioral foundation models for whole-body humanoid control.
S2GO: Streaming Sparse Gaussian Occupancy Prediction
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:Despite the demonstrated efficiency and performance of sparse query-based representations for perception, state-of-the-art 3D occupancy prediction methods still rely on voxel-based or dense Gaussian-based 3D representations. However, dense representations are slow, and they lack flexibility in capturing the temporal dynamics of driving scenes. Distinct from prior work, we instead summarize the scene into a compact set of 3D queries which are propagated through time in an online, streaming fashion. These queries are then decoded into semantic Gaussians at each timestep. We couple our framework with a denoising rendering objective to guide the queries and their constituent Gaussians in effectively capturing scene geometry. Owing to its efficient, query-based representation, S2GO achieves state-of-the-art performance on the nuScenes and KITTI occupancy benchmarks, outperforming prior art (e.g., GaussianWorld) by 1.5 IoU with 5.9x faster inference.
CacheFlow: Fast Human Motion Prediction by Cached Normalizing Flow
May 19, 2025Abstract:Many density estimation techniques for 3D human motion prediction require a significant amount of inference time, often exceeding the duration of the predicted time horizon. To address the need for faster density estimation for 3D human motion prediction, we introduce a novel flow-based method for human motion prediction called CacheFlow. Unlike previous conditional generative models that suffer from time efficiency, CacheFlow takes advantage of an unconditional flow-based generative model that transforms a Gaussian mixture into the density of future motions. The results of the computation of the flow-based generative model can be precomputed and cached. Then, for conditional prediction, we seek a mapping from historical trajectories to samples in the Gaussian mixture. This mapping can be done by a much more lightweight model, thus saving significant computation overhead compared to a typical conditional flow model. In such a two-stage fashion and by caching results from the slow flow model computation, we build our CacheFlow without loss of prediction accuracy and model expressiveness. This inference process is completed in approximately one millisecond, making it 4 times faster than previous VAE methods and 30 times faster than previous diffusion-based methods on standard benchmarks such as Human3.6M and AMASS datasets. Furthermore, our method demonstrates improved density estimation accuracy and comparable prediction accuracy to a SOTA method on Human3.6M. Our code and models will be publicly available.
Emergent Active Perception and Dexterity of Simulated Humanoids from Visual Reinforcement Learning
May 18, 2025Abstract:Human behavior is fundamentally shaped by visual perception -- our ability to interact with the world depends on actively gathering relevant information and adapting our movements accordingly. Behaviors like searching for objects, reaching, and hand-eye coordination naturally emerge from the structure of our sensory system. Inspired by these principles, we introduce Perceptive Dexterous Control (PDC), a framework for vision-driven dexterous whole-body control with simulated humanoids. PDC operates solely on egocentric vision for task specification, enabling object search, target placement, and skill selection through visual cues, without relying on privileged state information (e.g., 3D object positions and geometries). This perception-as-interface paradigm enables learning a single policy to perform multiple household tasks, including reaching, grasping, placing, and articulated object manipulation. We also show that training from scratch with reinforcement learning can produce emergent behaviors such as active search. These results demonstrate how vision-driven control and complex tasks induce human-like behaviors and can serve as the key ingredients in closing the perception-action loop for animation, robotics, and embodied AI.
ZeroGrasp: Zero-Shot Shape Reconstruction Enabled Robotic Grasping
Apr 15, 2025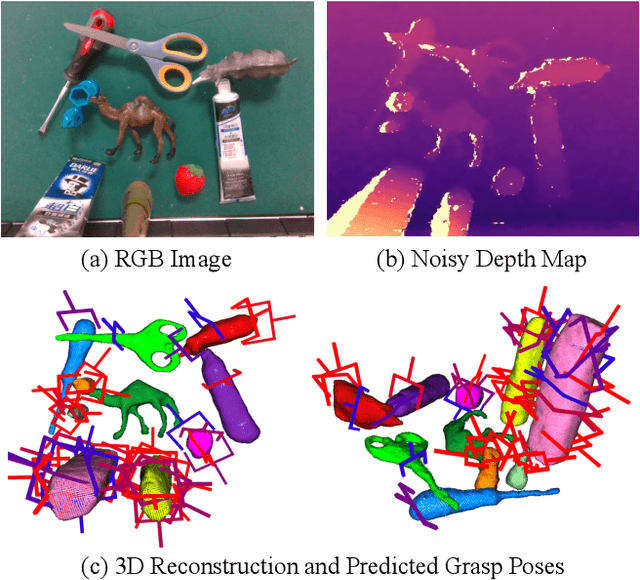
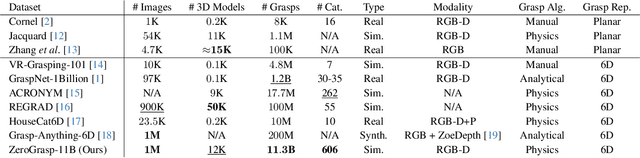
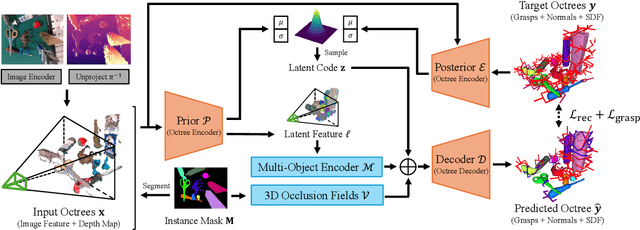
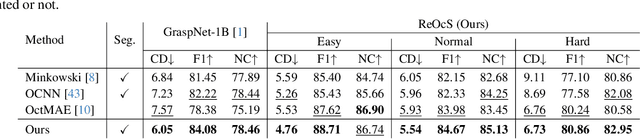
Abstract:Robotic grasping is a cornerstone capability of embodied systems. Many methods directly output grasps from partial information without modeling the geometry of the scene, leading to suboptimal motion and even collisions. To address these issues, we introduce ZeroGrasp, a novel framework that simultaneously performs 3D reconstruction and grasp pose prediction in near real-time. A key insight of our method is that occlusion reasoning and modeling the spatial relationships between objects is beneficial for both accurate reconstruction and grasping. We couple our method with a novel large-scale synthetic dataset, which comprises 1M photo-realistic images, high-resolution 3D reconstructions and 11.3B physically-valid grasp pose annotations for 12K objects from the Objaverse-LVIS dataset. We evaluate ZeroGrasp on the GraspNet-1B benchmark as well as through real-world robot experiments. ZeroGrasp achieves state-of-the-art performance and generalizes to novel real-world objects by leveraging synthetic data.
HOIGPT: Learning Long Sequence Hand-Object Interaction with Language Models
Mar 24, 2025



Abstract:We introduce HOIGPT, a token-based generative method that unifies 3D hand-object interactions (HOI) perception and generation, offering the first comprehensive solution for captioning and generating high-quality 3D HOI sequences from a diverse range of conditional signals (\eg text, objects, partial sequences). At its core, HOIGPT utilizes a large language model to predict the bidrectional transformation between HOI sequences and natural language descriptions. Given text inputs, HOIGPT generates a sequence of hand and object meshes; given (partial) HOI sequences, HOIGPT generates text descriptions and completes the sequences. To facilitate HOI understanding with a large language model, this paper introduces two key innovations: (1) a novel physically grounded HOI tokenizer, the hand-object decomposed VQ-VAE, for discretizing HOI sequences, and (2) a motion-aware language model trained to process and generate both text and HOI tokens. Extensive experiments demonstrate that HOIGPT sets new state-of-the-art performance on both text generation (+2.01% R Precision) and HOI generation (-2.56 FID) across multiple tasks and benchmarks.
ASAP: Aligning Simulation and Real-World Physics for Learning Agile Humanoid Whole-Body Skills
Feb 03, 2025Abstract:Humanoid robots hold the potential for unparalleled versatility in performing human-like, whole-body skills. However, achieving agile and coordinated whole-body motions remains a significant challenge due to the dynamics mismatch between simulation and the real world. Existing approaches, such as system identification (SysID) and domain randomization (DR) methods, often rely on labor-intensive parameter tuning or result in overly conservative policies that sacrifice agility. In this paper, we present ASAP (Aligning Simulation and Real-World Physics), a two-stage framework designed to tackle the dynamics mismatch and enable agile humanoid whole-body skills. In the first stage, we pre-train motion tracking policies in simulation using retargeted human motion data. In the second stage, we deploy the policies in the real world and collect real-world data to train a delta (residual) action model that compensates for the dynamics mismatch. Then, ASAP fine-tunes pre-trained policies with the delta action model integrated into the simulator to align effectively with real-world dynamics. We evaluate ASAP across three transfer scenarios: IsaacGym to IsaacSim, IsaacGym to Genesis, and IsaacGym to the real-world Unitree G1 humanoid robot. Our approach significantly improves agility and whole-body coordination across various dynamic motions, reducing tracking error compared to SysID, DR, and delta dynamics learning baselines. ASAP enables highly agile motions that were previously difficult to achieve, demonstrating the potential of delta action learning in bridging simulation and real-world dynamics. These results suggest a promising sim-to-real direction for developing more expressive and agile humanoids.
Harmony4D: A Video Dataset for In-The-Wild Close Human Interactions
Oct 27, 2024



Abstract:Understanding how humans interact with each other is key to building realistic multi-human virtual reality systems. This area remains relatively unexplored due to the lack of large-scale datasets. Recent datasets focusing on this issue mainly consist of activities captured entirely in controlled indoor environments with choreographed actions, significantly affecting their diversity. To address this, we introduce Harmony4D, a multi-view video dataset for human-human interaction featuring in-the-wild activities such as wrestling, dancing, MMA, and more. We use a flexible multi-view capture system to record these dynamic activities and provide annotations for human detection, tracking, 2D/3D pose estimation, and mesh recovery for closely interacting subjects. We propose a novel markerless algorithm to track 3D human poses in severe occlusion and close interaction to obtain our annotations with minimal manual intervention. Harmony4D consists of 1.66 million images and 3.32 million human instances from more than 20 synchronized cameras with 208 video sequences spanning diverse environments and 24 unique subjects. We rigorously evaluate existing state-of-the-art methods for mesh recovery and highlight their significant limitations in modeling close interaction scenarios. Additionally, we fine-tune a pre-trained HMR2.0 model on Harmony4D and demonstrate an improved performance of 54.8% PVE in scenes with severe occlusion and contact. Code and data are available at https://jyuntins.github.io/harmony4d/.
Human Action Anticipation: A Survey
Oct 17, 2024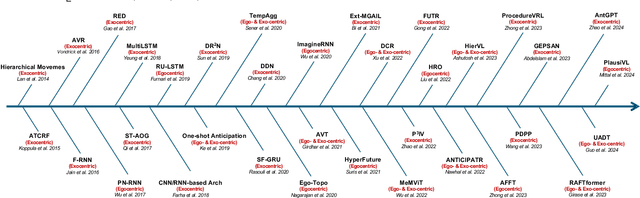
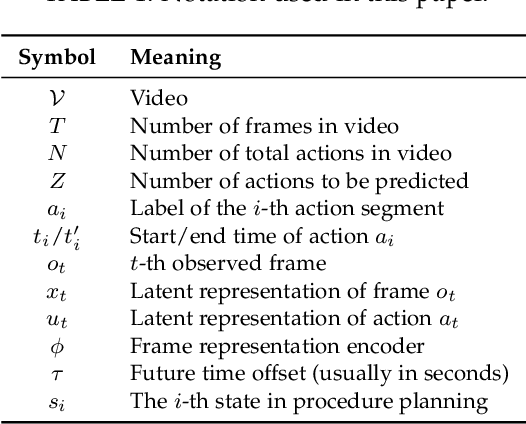
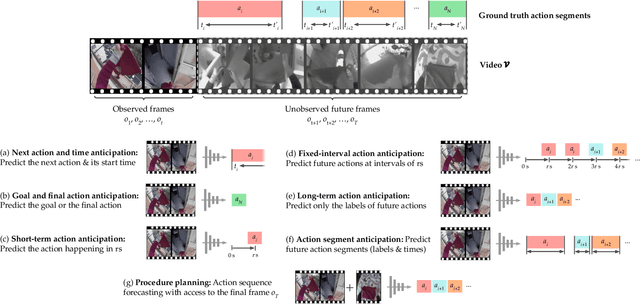
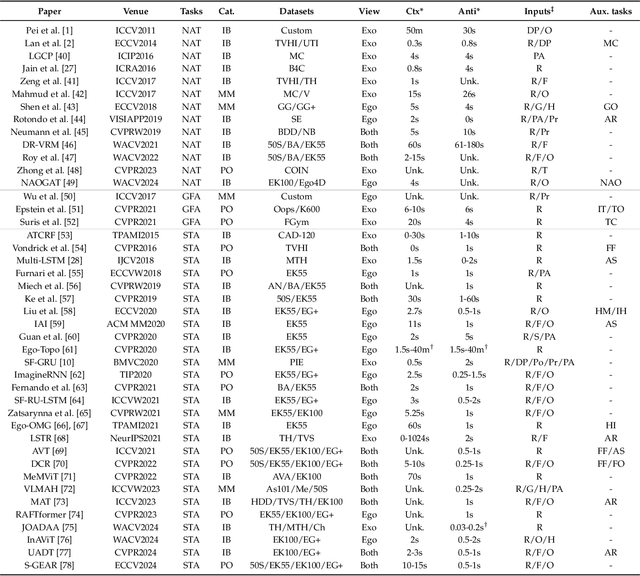
Abstract:Predicting future human behavior is an increasingly popular topic in computer vision, driven by the interest in applications such as autonomous vehicles, digital assistants and human-robot interactions. The literature on behavior prediction spans various tasks, including action anticipation, activity forecasting, intent prediction, goal prediction, and so on. Our survey aims to tie together this fragmented literature, covering recent technical innovations as well as the development of new large-scale datasets for model training and evaluation. We also summarize the widely-used metrics for different tasks and provide a comprehensive performance comparison of existing approaches on eleven action anticipation datasets. This survey serves as not only a reference for contemporary methodologies in action anticipation, but also a guideline for future research direction of this evolving landscape.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge