Gedas Bertasius
TimeBlind: A Spatio-Temporal Compositionality Benchmark for Video LLMs
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Fine-grained spatio-temporal understanding is essential for video reasoning and embodied AI. Yet, while Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) master static semantics, their grasp of temporal dynamics remains brittle. We present TimeBlind, a diagnostic benchmark for compositional spatio-temporal understanding. Inspired by cognitive science, TimeBlind categorizes fine-grained temporal understanding into three levels: recognizing atomic events, characterizing event properties, and reasoning about event interdependencies. Unlike benchmarks that conflate recognition with temporal reasoning, TimeBlind leverages a minimal-pairs paradigm: video pairs share identical static visual content but differ solely in temporal structure, utilizing complementary questions to neutralize language priors. Evaluating over 20 state-of-the-art MLLMs (e.g., GPT-5, Gemini 3 Pro) on 600 curated instances (2400 video-question pairs), reveals that the Instance Accuracy (correctly distinguishing both videos in a pair) of the best performing MLLM is only 48.2%, far below the human performance (98.2%). These results demonstrate that even frontier models rely heavily on static visual shortcuts rather than genuine temporal logic, positioning TimeBlind as a vital diagnostic tool for next-generation video understanding. Dataset and code are available at https://baiqi-li.github.io/timeblind_project/ .
DocSLM: A Small Vision-Language Model for Long Multimodal Document Understanding
Nov 17, 2025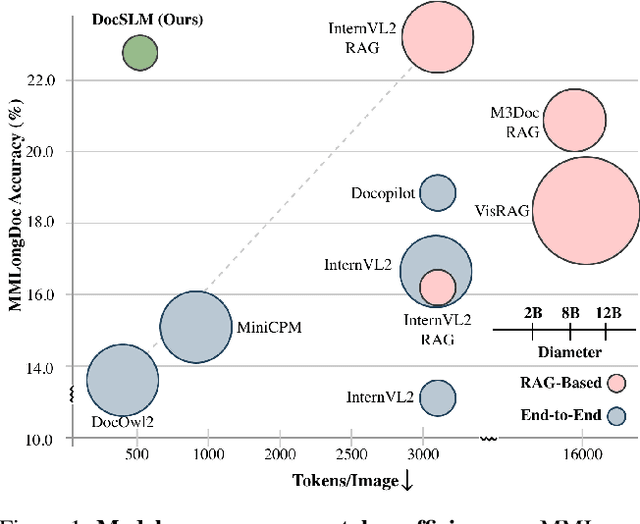

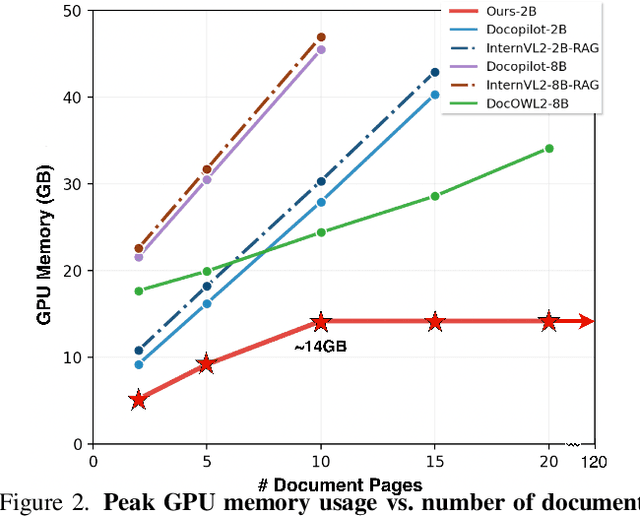
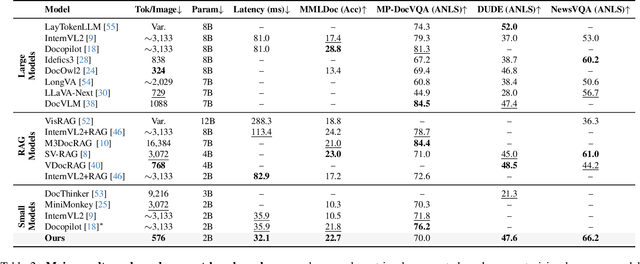
Abstract:Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) have demonstrated strong multimodal reasoning capabilities on long and complex documents. However, their high memory footprint makes them impractical for deployment on resource-constrained edge devices. We present DocSLM, an efficient Small Vision-Language Model designed for long-document understanding under constrained memory resources. DocSLM incorporates a Hierarchical Multimodal Compressor that jointly encodes visual, textual, and layout information from each page into a fixed-length sequence, greatly reducing memory consumption while preserving both local and global semantics. To enable scalable processing over arbitrarily long inputs, we introduce a Streaming Abstention mechanism that operates on document segments sequentially and filters low-confidence responses using an entropy-based uncertainty calibrator. Across multiple long multimodal document benchmarks, DocSLM matches or surpasses state-of-the-art methods while using 82\% fewer visual tokens, 75\% fewer parameters, and 71\% lower latency, delivering reliable multimodal document understanding on lightweight edge devices. Code is available in the supplementary material.
Video-RTS: Rethinking Reinforcement Learning and Test-Time Scaling for Efficient and Enhanced Video Reasoning
Jul 09, 2025Abstract:Despite advances in reinforcement learning (RL)-based video reasoning with large language models (LLMs), data collection and finetuning remain significant challenges. These methods often rely on large-scale supervised fine-tuning (SFT) with extensive video data and long Chain-of-Thought (CoT) annotations, making them costly and hard to scale. To address this, we present Video-RTS, a new approach to improve video reasoning capability with drastically improved data efficiency by combining data-efficient RL with a video-adaptive test-time scaling (TTS) strategy. Based on observations about the data scaling of RL samples, we skip the resource-intensive SFT step and employ efficient pure-RL training with output-based rewards, requiring no additional annotations or extensive fine-tuning. Furthermore, to utilize computational resources more efficiently, we introduce a sparse-to-dense video TTS strategy that improves inference by iteratively adding frames based on output consistency. We validate our approach on multiple video reasoning benchmarks, showing that Video-RTS surpasses existing video reasoning models by an average of 2.4% in accuracy using only 3.6% training samples. For example, Video-RTS achieves a 4.2% improvement on Video-Holmes, a recent and challenging video reasoning benchmark, and a 2.6% improvement on MMVU. Notably, our pure RL training and adaptive video TTS offer complementary strengths, enabling Video-RTS's strong reasoning performance.
ExAct: A Video-Language Benchmark for Expert Action Analysis
Jun 06, 2025Abstract:We present ExAct, a new video-language benchmark for expert-level understanding of skilled physical human activities. Our new benchmark contains 3521 expert-curated video question-answer pairs spanning 11 physical activities in 6 domains: Sports, Bike Repair, Cooking, Health, Music, and Dance. ExAct requires the correct answer to be selected from five carefully designed candidate options, thus necessitating a nuanced, fine-grained, expert-level understanding of physical human skills. Evaluating the recent state-of-the-art VLMs on ExAct reveals a substantial performance gap relative to human expert performance. Specifically, the best-performing GPT-4o model achieves only 44.70% accuracy, well below the 82.02% attained by trained human specialists/experts. We believe that ExAct will be beneficial for developing and evaluating VLMs capable of precise understanding of human skills in various physical and procedural domains. Dataset and code are available at https://texaser.github.io/exact_project_page/
SiLVR: A Simple Language-based Video Reasoning Framework
May 30, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in test-time optimization have led to remarkable reasoning capabilities in Large Language Models (LLMs), enabling them to solve highly complex problems in math and coding. However, the reasoning capabilities of multimodal LLMs (MLLMs) still significantly lag, especially for complex video-language tasks. To address this issue, we present SiLVR, a Simple Language-based Video Reasoning framework that decomposes complex video understanding into two stages. In the first stage, SiLVR transforms raw video into language-based representations using multisensory inputs, such as short clip captions and audio/speech subtitles. In the second stage, language descriptions are fed into a powerful reasoning LLM to solve complex video-language understanding tasks. To handle long-context multisensory inputs, we use an adaptive token reduction scheme, which dynamically determines the temporal granularity with which to sample the tokens. Our simple, modular, and training-free video reasoning framework achieves the best-reported results on Video-MME (long), Video-MMMU (comprehension), Video-MMLU, CGBench, and EgoLife. Furthermore, our empirical study focused on video reasoning capabilities shows that, despite not being explicitly trained on video, strong reasoning LLMs can effectively aggregate multisensory input information from video, speech, and audio for complex temporal, causal, long-context, and knowledge acquisition reasoning tasks in video. Code is available at https://github.com/CeeZh/SILVR.
BASKET: A Large-Scale Video Dataset for Fine-Grained Skill Estimation
Mar 26, 2025Abstract:We present BASKET, a large-scale basketball video dataset for fine-grained skill estimation. BASKET contains 4,477 hours of video capturing 32,232 basketball players from all over the world. Compared to prior skill estimation datasets, our dataset includes a massive number of skilled participants with unprecedented diversity in terms of gender, age, skill level, geographical location, etc. BASKET includes 20 fine-grained basketball skills, challenging modern video recognition models to capture the intricate nuances of player skill through in-depth video analysis. Given a long highlight video (8-10 minutes) of a particular player, the model needs to predict the skill level (e.g., excellent, good, average, fair, poor) for each of the 20 basketball skills. Our empirical analysis reveals that the current state-of-the-art video models struggle with this task, significantly lagging behind the human baseline. We believe that BASKET could be a useful resource for developing new video models with advanced long-range, fine-grained recognition capabilities. In addition, we hope that our dataset will be useful for domain-specific applications such as fair basketball scouting, personalized player development, and many others. Dataset and code are available at https://github.com/yulupan00/BASKET.
Zero-Shot Audio-Visual Editing via Cross-Modal Delta Denoising
Mar 26, 2025
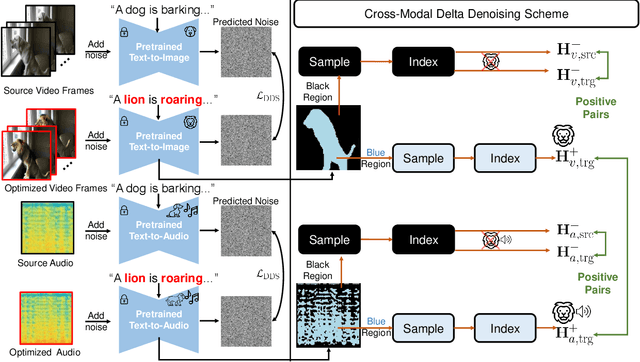
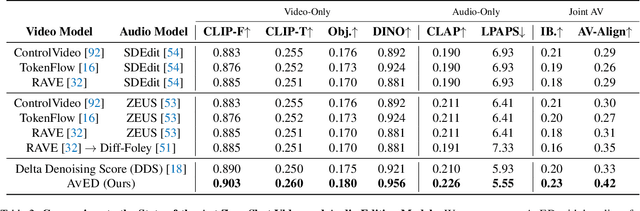
Abstract:In this paper, we introduce zero-shot audio-video editing, a novel task that requires transforming original audio-visual content to align with a specified textual prompt without additional model training. To evaluate this task, we curate a benchmark dataset, AvED-Bench, designed explicitly for zero-shot audio-video editing. AvED-Bench includes 110 videos, each with a 10-second duration, spanning 11 categories from VGGSound. It offers diverse prompts and scenarios that require precise alignment between auditory and visual elements, enabling robust evaluation. We identify limitations in existing zero-shot audio and video editing methods, particularly in synchronization and coherence between modalities, which often result in inconsistent outcomes. To address these challenges, we propose AvED, a zero-shot cross-modal delta denoising framework that leverages audio-video interactions to achieve synchronized and coherent edits. AvED demonstrates superior results on both AvED-Bench and the recent OAVE dataset to validate its generalization capabilities. Results are available at https://genjib.github.io/project_page/AVED/index.html
ReBot: Scaling Robot Learning with Real-to-Sim-to-Real Robotic Video Synthesis
Mar 15, 2025Abstract:Vision-language-action (VLA) models present a promising paradigm by training policies directly on real robot datasets like Open X-Embodiment. However, the high cost of real-world data collection hinders further data scaling, thereby restricting the generalizability of VLAs. In this paper, we introduce ReBot, a novel real-to-sim-to-real approach for scaling real robot datasets and adapting VLA models to target domains, which is the last-mile deployment challenge in robot manipulation. Specifically, ReBot replays real-world robot trajectories in simulation to diversify manipulated objects (real-to-sim), and integrates the simulated movements with inpainted real-world background to synthesize physically realistic and temporally consistent robot videos (sim-to-real). Our approach has several advantages: 1) it enjoys the benefit of real data to minimize the sim-to-real gap; 2) it leverages the scalability of simulation; and 3) it can generalize a pretrained VLA to a target domain with fully automated data pipelines. Extensive experiments in both simulation and real-world environments show that ReBot significantly enhances the performance and robustness of VLAs. For example, in SimplerEnv with the WidowX robot, ReBot improved the in-domain performance of Octo by 7.2% and OpenVLA by 21.8%, and out-of-domain generalization by 19.9% and 9.4%, respectively. For real-world evaluation with a Franka robot, ReBot increased the success rates of Octo by 17% and OpenVLA by 20%. More information can be found at: https://yuffish.github.io/rebot/
BIMBA: Selective-Scan Compression for Long-Range Video Question Answering
Mar 13, 2025Abstract:Video Question Answering (VQA) in long videos poses the key challenge of extracting relevant information and modeling long-range dependencies from many redundant frames. The self-attention mechanism provides a general solution for sequence modeling, but it has a prohibitive cost when applied to a massive number of spatiotemporal tokens in long videos. Most prior methods rely on compression strategies to lower the computational cost, such as reducing the input length via sparse frame sampling or compressing the output sequence passed to the large language model (LLM) via space-time pooling. However, these naive approaches over-represent redundant information and often miss salient events or fast-occurring space-time patterns. In this work, we introduce BIMBA, an efficient state-space model to handle long-form videos. Our model leverages the selective scan algorithm to learn to effectively select critical information from high-dimensional video and transform it into a reduced token sequence for efficient LLM processing. Extensive experiments demonstrate that BIMBA achieves state-of-the-art accuracy on multiple long-form VQA benchmarks, including PerceptionTest, NExT-QA, EgoSchema, VNBench, LongVideoBench, and Video-MME. Code, and models are publicly available at https://sites.google.com/view/bimba-mllm.
BOSS: Benchmark for Observation Space Shift in Long-Horizon Task
Feb 21, 2025Abstract:Robotics has long sought to develop visual-servoing robots capable of completing previously unseen long-horizon tasks. Hierarchical approaches offer a pathway for achieving this goal by executing skill combinations arranged by a task planner, with each visuomotor skill pre-trained using a specific imitation learning (IL) algorithm. However, even in simple long-horizon tasks like skill chaining, hierarchical approaches often struggle due to a problem we identify as Observation Space Shift (OSS), where the sequential execution of preceding skills causes shifts in the observation space, disrupting the performance of subsequent individually trained skill policies. To validate OSS and evaluate its impact on long-horizon tasks, we introduce BOSS (a Benchmark for Observation Space Shift). BOSS comprises three distinct challenges: "Single Predicate Shift", "Accumulated Predicate Shift", and "Skill Chaining", each designed to assess a different aspect of OSS's negative effect. We evaluated several recent popular IL algorithms on BOSS, including three Behavioral Cloning methods and the Visual Language Action model OpenVLA. Even on the simplest challenge, we observed average performance drops of 67%, 35%, 34%, and 54%, respectively, when comparing skill performance with and without OSS. Additionally, we investigate a potential solution to OSS that scales up the training data for each skill with a larger and more visually diverse set of demonstrations, with our results showing it is not sufficient to resolve OSS. The project page is: https://boss-benchmark.github.io/
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge