Mingyu Ding
SimpleMem: Efficient Lifelong Memory for LLM Agents
Jan 05, 2026Abstract:To support reliable long-term interaction in complex environments, LLM agents require memory systems that efficiently manage historical experiences. Existing approaches either retain full interaction histories via passive context extension, leading to substantial redundancy, or rely on iterative reasoning to filter noise, incurring high token costs. To address this challenge, we introduce SimpleMem, an efficient memory framework based on semantic lossless compression. We propose a three-stage pipeline designed to maximize information density and token utilization: (1) \textit{Semantic Structured Compression}, which applies entropy-aware filtering to distill unstructured interactions into compact, multi-view indexed memory units; (2) \textit{Recursive Memory Consolidation}, an asynchronous process that integrates related units into higher-level abstract representations to reduce redundancy; and (3) \textit{Adaptive Query-Aware Retrieval}, which dynamically adjusts retrieval scope based on query complexity to construct precise context efficiently. Experiments on benchmark datasets show that our method consistently outperforms baseline approaches in accuracy, retrieval efficiency, and inference cost, achieving an average F1 improvement of 26.4% while reducing inference-time token consumption by up to 30-fold, demonstrating a superior balance between performance and efficiency. Code is available at https://github.com/aiming-lab/SimpleMem.
Robotic VLA Benefits from Joint Learning with Motion Image Diffusion
Dec 19, 2025Abstract:Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models have achieved remarkable progress in robotic manipulation by mapping multimodal observations and instructions directly to actions. However, they typically mimic expert trajectories without predictive motion reasoning, which limits their ability to reason about what actions to take. To address this limitation, we propose joint learning with motion image diffusion, a novel strategy that enhances VLA models with motion reasoning capabilities. Our method extends the VLA architecture with a dual-head design: while the action head predicts action chunks as in vanilla VLAs, an additional motion head, implemented as a Diffusion Transformer (DiT), predicts optical-flow-based motion images that capture future dynamics. The two heads are trained jointly, enabling the shared VLM backbone to learn representations that couple robot control with motion knowledge. This joint learning builds temporally coherent and physically grounded representations without modifying the inference pathway of standard VLAs, thereby maintaining test-time latency. Experiments in both simulation and real-world environments demonstrate that joint learning with motion image diffusion improves the success rate of pi-series VLAs to 97.5% on the LIBERO benchmark and 58.0% on the RoboTwin benchmark, yielding a 23% improvement in real-world performance and validating its effectiveness in enhancing the motion reasoning capability of large-scale VLAs.
ARCHE: A Novel Task to Evaluate LLMs on Latent Reasoning Chain Extraction
Nov 16, 2025



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly used in scientific domains. While they can produce reasoning-like content via methods such as chain-of-thought prompting, these outputs are typically unstructured and informal, obscuring whether models truly understand the fundamental reasoning paradigms that underpin scientific inference. To address this, we introduce a novel task named Latent Reasoning Chain Extraction (ARCHE), in which models must decompose complex reasoning arguments into combinations of standard reasoning paradigms in the form of a Reasoning Logic Tree (RLT). In RLT, all reasoning steps are explicitly categorized as one of three variants of Peirce's fundamental inference modes: deduction, induction, or abduction. To facilitate this task, we release ARCHE Bench, a new benchmark derived from 70 Nature Communications articles, including more than 1,900 references and 38,000 viewpoints. We propose two logic-aware evaluation metrics: Entity Coverage (EC) for content completeness and Reasoning Edge Accuracy (REA) for step-by-step logical validity. Evaluations on 10 leading LLMs on ARCHE Bench reveal that models exhibit a trade-off between REA and EC, and none are yet able to extract a complete and standard reasoning chain. These findings highlight a substantial gap between the abilities of current reasoning models and the rigor required for scientific argumentation.
Real Deep Research for AI, Robotics and Beyond
Oct 23, 2025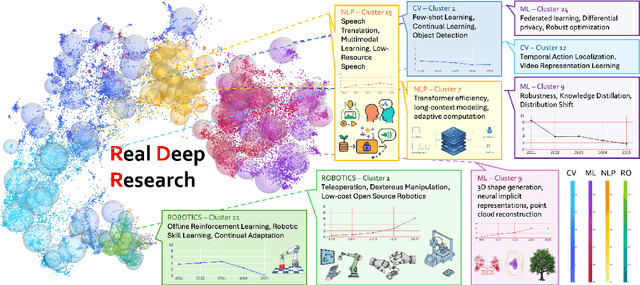
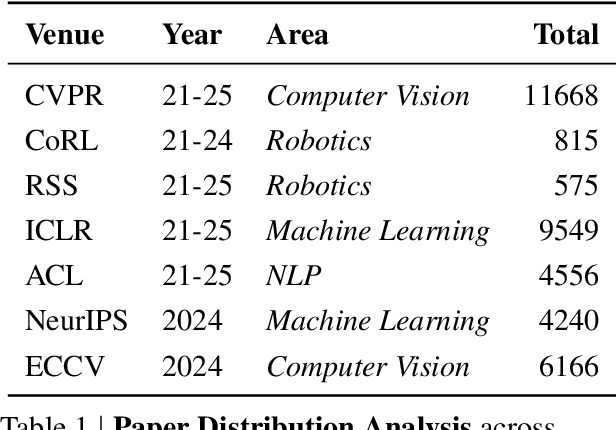
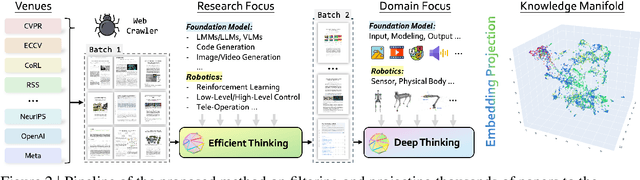
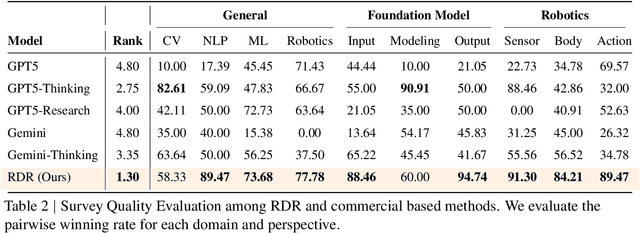
Abstract:With the rapid growth of research in AI and robotics now producing over 10,000 papers annually it has become increasingly difficult for researchers to stay up to date. Fast evolving trends, the rise of interdisciplinary work, and the need to explore domains beyond one's expertise all contribute to this challenge. To address these issues, we propose a generalizable pipeline capable of systematically analyzing any research area: identifying emerging trends, uncovering cross domain opportunities, and offering concrete starting points for new inquiry. In this work, we present Real Deep Research (RDR) a comprehensive framework applied to the domains of AI and robotics, with a particular focus on foundation models and robotics advancements. We also briefly extend our analysis to other areas of science. The main paper details the construction of the RDR pipeline, while the appendix provides extensive results across each analyzed topic. We hope this work sheds light for researchers working in the field of AI and beyond.
Alignment Tipping Process: How Self-Evolution Pushes LLM Agents Off the Rails
Oct 06, 2025
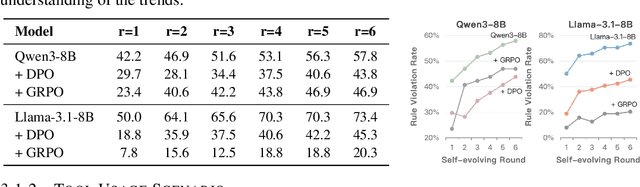


Abstract:As Large Language Model (LLM) agents increasingly gain self-evolutionary capabilities to adapt and refine their strategies through real-world interaction, their long-term reliability becomes a critical concern. We identify the Alignment Tipping Process (ATP), a critical post-deployment risk unique to self-evolving LLM agents. Unlike training-time failures, ATP arises when continual interaction drives agents to abandon alignment constraints established during training in favor of reinforced, self-interested strategies. We formalize and analyze ATP through two complementary paradigms: Self-Interested Exploration, where repeated high-reward deviations induce individual behavioral drift, and Imitative Strategy Diffusion, where deviant behaviors spread across multi-agent systems. Building on these paradigms, we construct controllable testbeds and benchmark Qwen3-8B and Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct. Our experiments show that alignment benefits erode rapidly under self-evolution, with initially aligned models converging toward unaligned states. In multi-agent settings, successful violations diffuse quickly, leading to collective misalignment. Moreover, current reinforcement learning-based alignment methods provide only fragile defenses against alignment tipping. Together, these findings demonstrate that alignment of LLM agents is not a static property but a fragile and dynamic one, vulnerable to feedback-driven decay during deployment. Our data and code are available at https://github.com/aiming-lab/ATP.
Mimicking the Physicist's Eye:A VLM-centric Approach for Physics Formula Discovery
Aug 24, 2025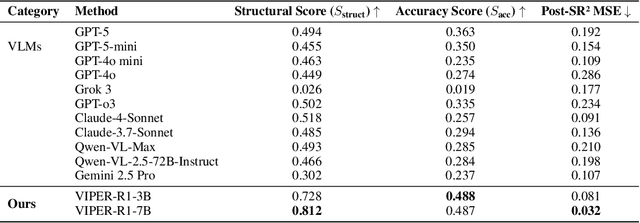
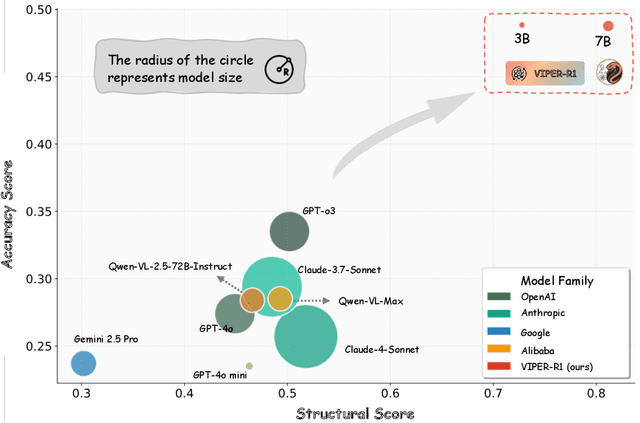
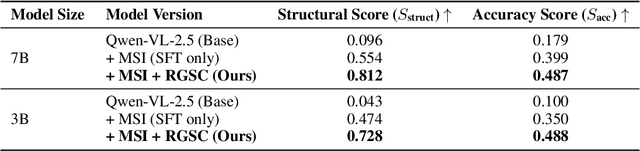
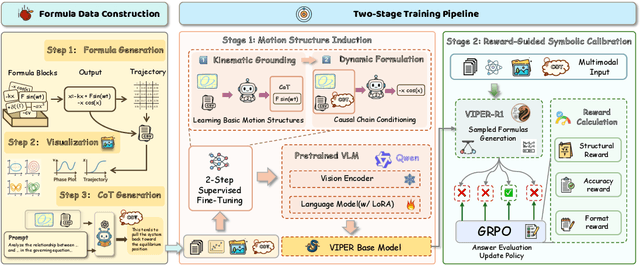
Abstract:Automated discovery of physical laws from observational data in the real world is a grand challenge in AI. Current methods, relying on symbolic regression or LLMs, are limited to uni-modal data and overlook the rich, visual phenomenological representations of motion that are indispensable to physicists. This "sensory deprivation" severely weakens their ability to interpret the inherent spatio-temporal patterns within dynamic phenomena. To address this gap, we propose VIPER-R1, a multimodal model that performs Visual Induction for Physics-based Equation Reasoning to discover fundamental symbolic formulas. It integrates visual perception, trajectory data, and symbolic reasoning to emulate the scientific discovery process. The model is trained via a curriculum of Motion Structure Induction (MSI), using supervised fine-tuning to interpret kinematic phase portraits and to construct hypotheses guided by a Causal Chain of Thought (C-CoT), followed by Reward-Guided Symbolic Calibration (RGSC) to refine the formula structure with reinforcement learning. During inference, the trained VIPER-R1 acts as an agent: it first posits a high-confidence symbolic ansatz, then proactively invokes an external symbolic regression tool to perform Symbolic Residual Realignment (SR^2). This final step, analogous to a physicist's perturbation analysis, reconciles the theoretical model with empirical data. To support this research, we introduce PhysSymbol, a new 5,000-instance multimodal corpus. Experiments show that VIPER-R1 consistently outperforms state-of-the-art VLM baselines in accuracy and interpretability, enabling more precise discovery of physical laws. Project page: https://jiaaqiliu.github.io/VIPER-R1/
Incentivizing Multimodal Reasoning in Large Models for Direct Robot Manipulation
May 19, 2025Abstract:Recent Large Multimodal Models have demonstrated remarkable reasoning capabilities, especially in solving complex mathematical problems and realizing accurate spatial perception. Our key insight is that these emerging abilities can naturally extend to robotic manipulation by enabling LMMs to directly infer the next goal in language via reasoning, rather than relying on a separate action head. However, this paradigm meets two main challenges: i) How to make LMMs understand the spatial action space, and ii) How to fully exploit the reasoning capacity of LMMs in solving these tasks. To tackle the former challenge, we propose a novel task formulation, which inputs the current states of object parts and the gripper, and reformulates rotation by a new axis representation instead of traditional Euler angles. This representation is more compatible with spatial reasoning and easier to interpret within a unified language space. For the latter challenge, we design a pipeline to utilize cutting-edge LMMs to generate a small but high-quality reasoning dataset of multi-round dialogues that successfully solve manipulation tasks for supervised fine-tuning. Then, we perform reinforcement learning by trial-and-error interactions in simulation to further enhance the model's reasoning abilities for robotic manipulation. Our resulting reasoning model built upon a 7B backbone, named ReasonManip, demonstrates three notable advantages driven by its system-2 level reasoning capabilities: i) exceptional generalizability to out-of-distribution environments, objects, and tasks; ii) inherent sim-to-real transfer ability enabled by the unified language representation shared across domains; iii) transparent interpretability connecting high-level reasoning and low-level control. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed paradigm and its potential to advance LMM-driven robotic manipulation.
Interleave-VLA: Enhancing Robot Manipulation with Interleaved Image-Text Instructions
May 04, 2025Abstract:Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models have shown great promise for generalist robotic manipulation in the physical world. However, existing models are restricted to robot observations and text-only instructions, lacking the flexibility of interleaved multimodal instructions enabled by recent advances in foundation models in the digital world. In this paper, we present Interleave-VLA, the first framework capable of comprehending interleaved image-text instructions and directly generating continuous action sequences in the physical world. It offers a flexible, model-agnostic paradigm that extends state-of-the-art VLA models with minimal modifications and strong zero-shot generalization. A key challenge in realizing Interleave-VLA is the absence of large-scale interleaved embodied datasets. To bridge this gap, we develop an automatic pipeline that converts text-only instructions from real-world datasets in Open X-Embodiment into interleaved image-text instructions, resulting in the first large-scale real-world interleaved embodied dataset with 210k episodes. Through comprehensive evaluation on simulation benchmarks and real-robot experiments, we demonstrate that Interleave-VLA offers significant benefits: 1) it improves out-of-domain generalization to unseen objects by 2-3x compared to state-of-the-art baselines, 2) supports flexible task interfaces, and 3) handles diverse user-provided image instructions in a zero-shot manner, such as hand-drawn sketches. We further analyze the factors behind Interleave-VLA's strong zero-shot performance, showing that the interleaved paradigm effectively leverages heterogeneous datasets and diverse instruction images, including those from the Internet, which demonstrates strong potential for scaling up. Our model and dataset will be open-sourced.
REMAC: Self-Reflective and Self-Evolving Multi-Agent Collaboration for Long-Horizon Robot Manipulation
Mar 28, 2025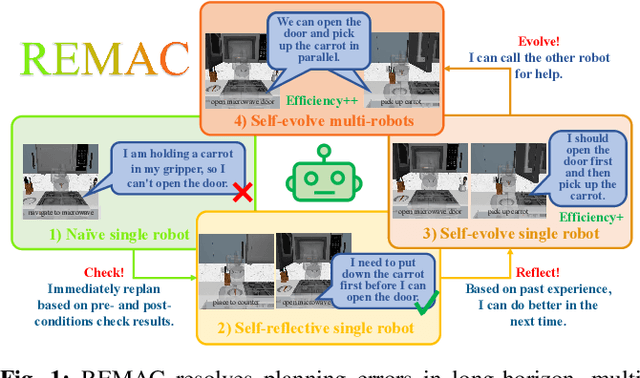
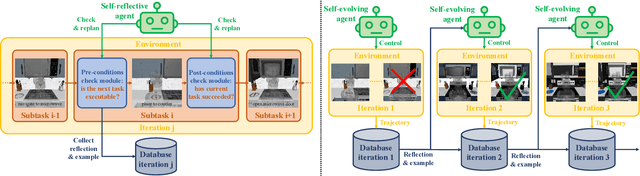
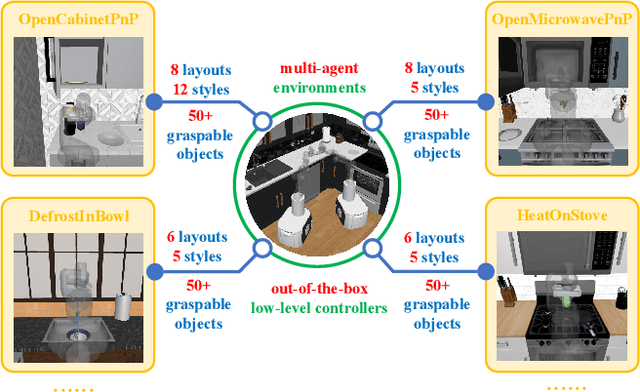
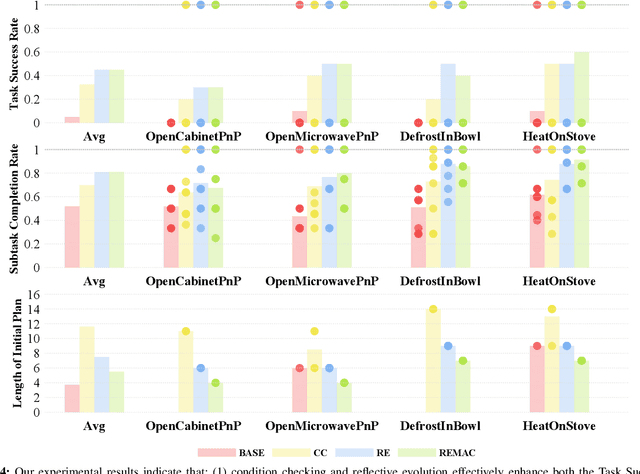
Abstract:Vision-language models (VLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in robotic planning, particularly for long-horizon tasks that require a holistic understanding of the environment for task decomposition. Existing methods typically rely on prior environmental knowledge or carefully designed task-specific prompts, making them struggle with dynamic scene changes or unexpected task conditions, e.g., a robot attempting to put a carrot in the microwave but finds the door was closed. Such challenges underscore two critical issues: adaptability and efficiency. To address them, in this work, we propose an adaptive multi-agent planning framework, termed REMAC, that enables efficient, scene-agnostic multi-robot long-horizon task planning and execution through continuous reflection and self-evolution. REMAC incorporates two key modules: a self-reflection module performing pre-condition and post-condition checks in the loop to evaluate progress and refine plans, and a self-evolvement module dynamically adapting plans based on scene-specific reasoning. It offers several appealing benefits: 1) Robots can initially explore and reason about the environment without complex prompt design. 2) Robots can keep reflecting on potential planning errors and adapting the plan based on task-specific insights. 3) After iterations, a robot can call another one to coordinate tasks in parallel, maximizing the task execution efficiency. To validate REMAC's effectiveness, we build a multi-agent environment for long-horizon robot manipulation and navigation based on RoboCasa, featuring 4 task categories with 27 task styles and 50+ different objects. Based on it, we further benchmark state-of-the-art reasoning models, including DeepSeek-R1, o3-mini, QwQ, and Grok3, demonstrating REMAC's superiority by boosting average success rates by 40% and execution efficiency by 52.7% over the single robot baseline.
ReBot: Scaling Robot Learning with Real-to-Sim-to-Real Robotic Video Synthesis
Mar 15, 2025Abstract:Vision-language-action (VLA) models present a promising paradigm by training policies directly on real robot datasets like Open X-Embodiment. However, the high cost of real-world data collection hinders further data scaling, thereby restricting the generalizability of VLAs. In this paper, we introduce ReBot, a novel real-to-sim-to-real approach for scaling real robot datasets and adapting VLA models to target domains, which is the last-mile deployment challenge in robot manipulation. Specifically, ReBot replays real-world robot trajectories in simulation to diversify manipulated objects (real-to-sim), and integrates the simulated movements with inpainted real-world background to synthesize physically realistic and temporally consistent robot videos (sim-to-real). Our approach has several advantages: 1) it enjoys the benefit of real data to minimize the sim-to-real gap; 2) it leverages the scalability of simulation; and 3) it can generalize a pretrained VLA to a target domain with fully automated data pipelines. Extensive experiments in both simulation and real-world environments show that ReBot significantly enhances the performance and robustness of VLAs. For example, in SimplerEnv with the WidowX robot, ReBot improved the in-domain performance of Octo by 7.2% and OpenVLA by 21.8%, and out-of-domain generalization by 19.9% and 9.4%, respectively. For real-world evaluation with a Franka robot, ReBot increased the success rates of Octo by 17% and OpenVLA by 20%. More information can be found at: https://yuffish.github.io/rebot/
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge