Yunchao Yao
Web2Grasp: Learning Functional Grasps from Web Images of Hand-Object Interactions
May 07, 2025Abstract:Functional grasp is essential for enabling dexterous multi-finger robot hands to manipulate objects effectively. However, most prior work either focuses on power grasping, which simply involves holding an object still, or relies on costly teleoperated robot demonstrations to teach robots how to grasp each object functionally. Instead, we propose extracting human grasp information from web images since they depict natural and functional object interactions, thereby bypassing the need for curated demonstrations. We reconstruct human hand-object interaction (HOI) 3D meshes from RGB images, retarget the human hand to multi-finger robot hands, and align the noisy object mesh with its accurate 3D shape. We show that these relatively low-quality HOI data from inexpensive web sources can effectively train a functional grasping model. To further expand the grasp dataset for seen and unseen objects, we use the initially-trained grasping policy with web data in the IsaacGym simulator to generate physically feasible grasps while preserving functionality. We train the grasping model on 10 object categories and evaluate it on 9 unseen objects, including challenging items such as syringes, pens, spray bottles, and tongs, which are underrepresented in existing datasets. The model trained on the web HOI dataset, achieving a 75.8% success rate on seen objects and 61.8% across all objects in simulation, with a 6.7% improvement in success rate and a 1.8x increase in functionality ratings over baselines. Simulator-augmented data further boosts performance from 61.8% to 83.4%. The sim-to-real transfer to the LEAP Hand achieves a 85% success rate. Project website is at: https://webgrasp.github.io/.
REMAC: Self-Reflective and Self-Evolving Multi-Agent Collaboration for Long-Horizon Robot Manipulation
Mar 28, 2025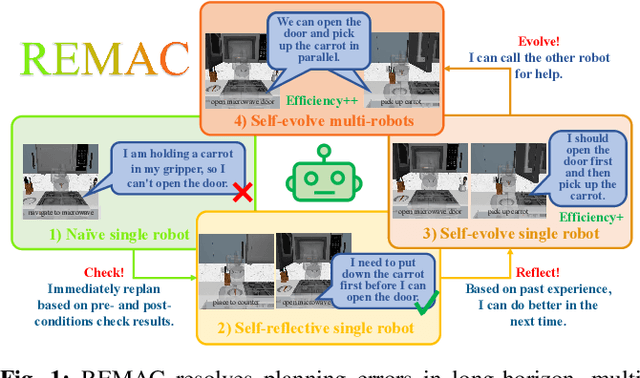
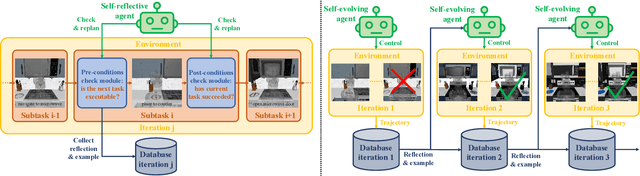
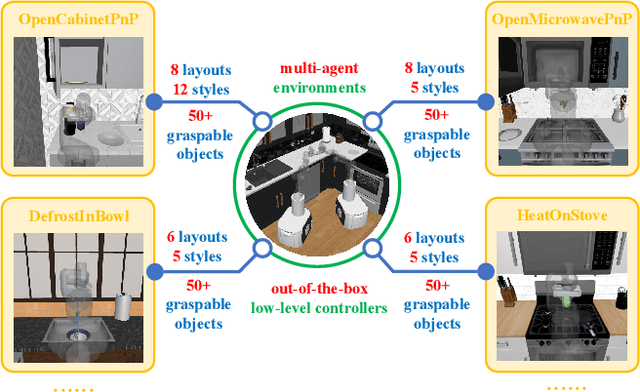
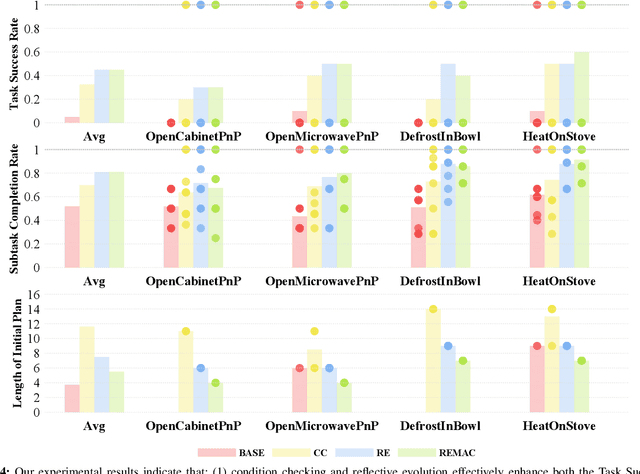
Abstract:Vision-language models (VLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in robotic planning, particularly for long-horizon tasks that require a holistic understanding of the environment for task decomposition. Existing methods typically rely on prior environmental knowledge or carefully designed task-specific prompts, making them struggle with dynamic scene changes or unexpected task conditions, e.g., a robot attempting to put a carrot in the microwave but finds the door was closed. Such challenges underscore two critical issues: adaptability and efficiency. To address them, in this work, we propose an adaptive multi-agent planning framework, termed REMAC, that enables efficient, scene-agnostic multi-robot long-horizon task planning and execution through continuous reflection and self-evolution. REMAC incorporates two key modules: a self-reflection module performing pre-condition and post-condition checks in the loop to evaluate progress and refine plans, and a self-evolvement module dynamically adapting plans based on scene-specific reasoning. It offers several appealing benefits: 1) Robots can initially explore and reason about the environment without complex prompt design. 2) Robots can keep reflecting on potential planning errors and adapting the plan based on task-specific insights. 3) After iterations, a robot can call another one to coordinate tasks in parallel, maximizing the task execution efficiency. To validate REMAC's effectiveness, we build a multi-agent environment for long-horizon robot manipulation and navigation based on RoboCasa, featuring 4 task categories with 27 task styles and 50+ different objects. Based on it, we further benchmark state-of-the-art reasoning models, including DeepSeek-R1, o3-mini, QwQ, and Grok3, demonstrating REMAC's superiority by boosting average success rates by 40% and execution efficiency by 52.7% over the single robot baseline.
When Should We Prefer State-to-Visual DAgger Over Visual Reinforcement Learning?
Dec 18, 2024



Abstract:Learning policies from high-dimensional visual inputs, such as pixels and point clouds, is crucial in various applications. Visual reinforcement learning is a promising approach that directly trains policies from visual observations, although it faces challenges in sample efficiency and computational costs. This study conducts an empirical comparison of State-to-Visual DAgger, a two-stage framework that initially trains a state policy before adopting online imitation to learn a visual policy, and Visual RL across a diverse set of tasks. We evaluate both methods across 16 tasks from three benchmarks, focusing on their asymptotic performance, sample efficiency, and computational costs. Surprisingly, our findings reveal that State-to-Visual DAgger does not universally outperform Visual RL but shows significant advantages in challenging tasks, offering more consistent performance. In contrast, its benefits in sample efficiency are less pronounced, although it often reduces the overall wall-clock time required for training. Based on our findings, we provide recommendations for practitioners and hope that our results contribute valuable perspectives for future research in visual policy learning.
Soft Robotic Dynamic In-Hand Pen Spinning
Nov 19, 2024



Abstract:Dynamic in-hand manipulation remains a challenging task for soft robotic systems that have demonstrated advantages in safe compliant interactions but struggle with high-speed dynamic tasks. In this work, we present SWIFT, a system for learning dynamic tasks using a soft and compliant robotic hand. Unlike previous works that rely on simulation, quasi-static actions and precise object models, the proposed system learns to spin a pen through trial-and-error using only real-world data without requiring explicit prior knowledge of the pen's physical attributes. With self-labeled trials sampled from the real world, the system discovers the set of pen grasping and spinning primitive parameters that enables a soft hand to spin a pen robustly and reliably. After 130 sampled actions per object, SWIFT achieves 100% success rate across three pens with different weights and weight distributions, demonstrating the system's generalizability and robustness to changes in object properties. The results highlight the potential for soft robotic end-effectors to perform dynamic tasks including rapid in-hand manipulation. We also demonstrate that SWIFT generalizes to spinning items with different shapes and weights such as a brush and a screwdriver which we spin with 10/10 and 5/10 success rates respectively. Videos, data, and code are available at https://soft-spin.github.io.
Automating Robot Failure Recovery Using Vision-Language Models With Optimized Prompts
Sep 06, 2024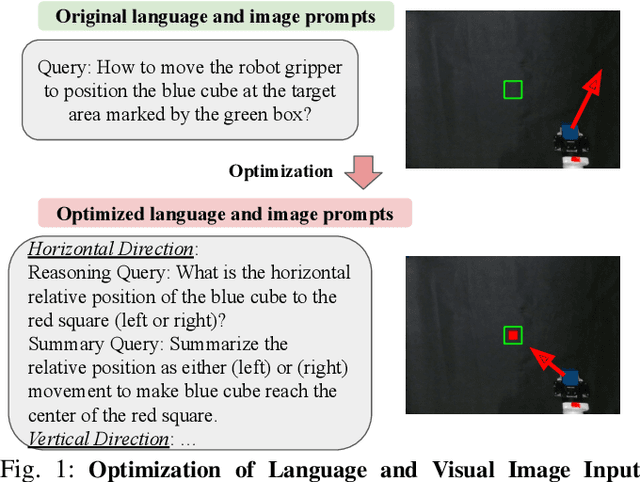
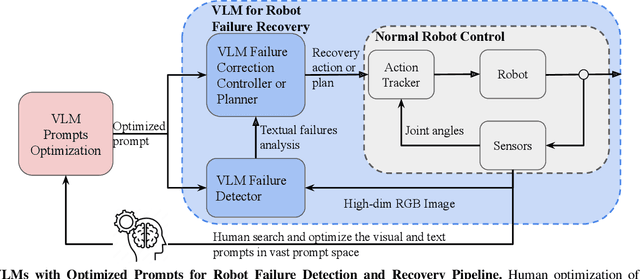
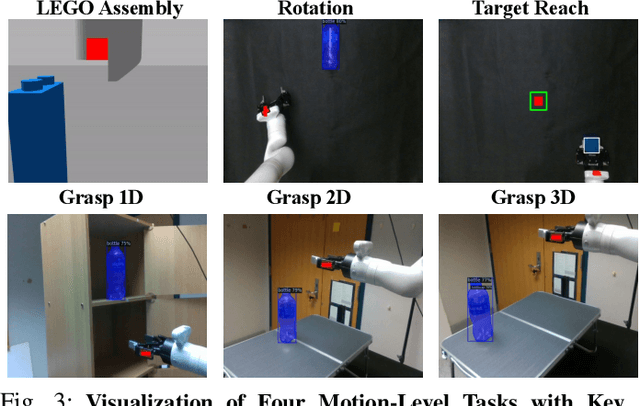
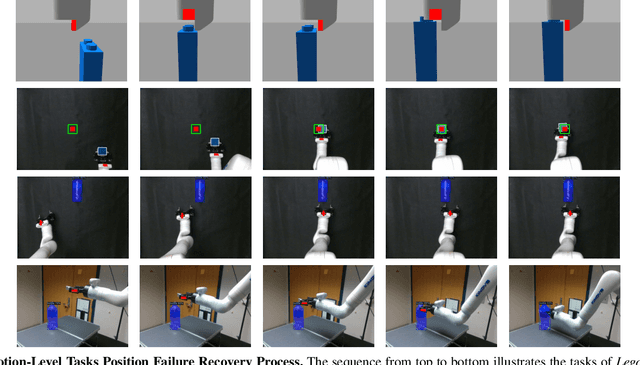
Abstract:Current robot autonomy struggles to operate beyond the assumed Operational Design Domain (ODD), the specific set of conditions and environments in which the system is designed to function, while the real-world is rife with uncertainties that may lead to failures. Automating recovery remains a significant challenge. Traditional methods often rely on human intervention to manually address failures or require exhaustive enumeration of failure cases and the design of specific recovery policies for each scenario, both of which are labor-intensive. Foundational Vision-Language Models (VLMs), which demonstrate remarkable common-sense generalization and reasoning capabilities, have broader, potentially unbounded ODDs. However, limitations in spatial reasoning continue to be a common challenge for many VLMs when applied to robot control and motion-level error recovery. In this paper, we investigate how optimizing visual and text prompts can enhance the spatial reasoning of VLMs, enabling them to function effectively as black-box controllers for both motion-level position correction and task-level recovery from unknown failures. Specifically, the optimizations include identifying key visual elements in visual prompts, highlighting these elements in text prompts for querying, and decomposing the reasoning process for failure detection and control generation. In experiments, prompt optimizations significantly outperform pre-trained Vision-Language-Action Models in correcting motion-level position errors and improve accuracy by 65.78% compared to VLMs with unoptimized prompts. Additionally, for task-level failures, optimized prompts enhanced the success rate by 5.8%, 5.8%, and 7.5% in VLMs' abilities to detect failures, analyze issues, and generate recovery plans, respectively, across a wide range of unknown errors in Lego assembly.
MD-Splatting: Learning Metric Deformation from 4D Gaussians in Highly Deformable Scenes
Nov 30, 2023



Abstract:Accurate 3D tracking in highly deformable scenes with occlusions and shadows can facilitate new applications in robotics, augmented reality, and generative AI. However, tracking under these conditions is extremely challenging due to the ambiguity that arises with large deformations, shadows, and occlusions. We introduce MD-Splatting, an approach for simultaneous 3D tracking and novel view synthesis, using video captures of a dynamic scene from various camera poses. MD-Splatting builds on recent advances in Gaussian splatting, a method that learns the properties of a large number of Gaussians for state-of-the-art and fast novel view synthesis. MD-Splatting learns a deformation function to project a set of Gaussians with non-metric, thus canonical, properties into metric space. The deformation function uses a neural-voxel encoding and a multilayer perceptron (MLP) to infer Gaussian position, rotation, and a shadow scalar. We enforce physics-inspired regularization terms based on local rigidity, conservation of momentum, and isometry, which leads to trajectories with smaller trajectory errors. MD-Splatting achieves high-quality 3D tracking on highly deformable scenes with shadows and occlusions. Compared to state-of-the-art, we improve 3D tracking by an average of 23.9 %, while simultaneously achieving high-quality novel view synthesis. With sufficient texture such as in scene 6, MD-Splatting achieves a median tracking error of 3.39 mm on a cloth of 1 x 1 meters in size. Project website: https://md-splatting.github.io/.
Occlusion-Aware 2D and 3D Centerline Detection for Urban Driving via Automatic Label Generation
Nov 03, 2023

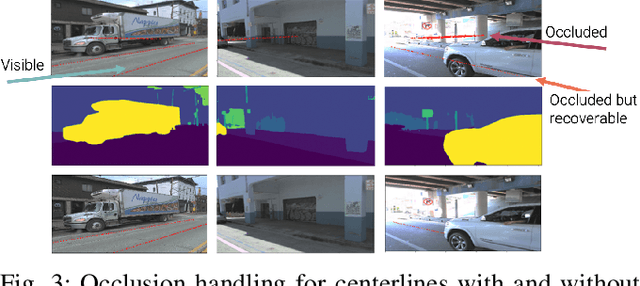
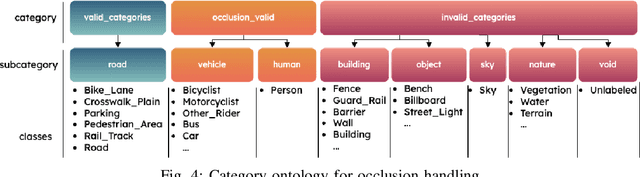
Abstract:This research work seeks to explore and identify strategies that can determine road topology information in 2D and 3D under highly dynamic urban driving scenarios. To facilitate this exploration, we introduce a substantial dataset comprising nearly one million automatically labeled data frames. A key contribution of our research lies in developing an automatic label-generation process and an occlusion handling strategy. This strategy is designed to model a wide range of occlusion scenarios, from mild disruptions to severe blockages. Furthermore, we present a comprehensive ablation study wherein multiple centerline detection methods are developed and evaluated. This analysis not only benchmarks the performance of various approaches but also provides valuable insights into the interpretability of these methods. Finally, we demonstrate the practicality of our methods and assess their adaptability across different sensor configurations, highlighting their versatility and relevance in real-world scenarios. Our dataset and experimental models are publicly available.
On the Efficacy of 3D Point Cloud Reinforcement Learning
Jun 11, 2023



Abstract:Recent studies on visual reinforcement learning (visual RL) have explored the use of 3D visual representations. However, none of these work has systematically compared the efficacy of 3D representations with 2D representations across different tasks, nor have they analyzed 3D representations from the perspective of agent-object / object-object relationship reasoning. In this work, we seek answers to the question of when and how do 3D neural networks that learn features in the 3D-native space provide a beneficial inductive bias for visual RL. We specifically focus on 3D point clouds, one of the most common forms of 3D representations. We systematically investigate design choices for 3D point cloud RL, leading to the development of a robust algorithm for various robotic manipulation and control tasks. Furthermore, through comparisons between 2D image vs 3D point cloud RL methods on both minimalist synthetic tasks and complex robotic manipulation tasks, we find that 3D point cloud RL can significantly outperform the 2D counterpart when agent-object / object-object relationship encoding is a key factor.
ManiSkill2: A Unified Benchmark for Generalizable Manipulation Skills
Feb 09, 2023Abstract:Generalizable manipulation skills, which can be composed to tackle long-horizon and complex daily chores, are one of the cornerstones of Embodied AI. However, existing benchmarks, mostly composed of a suite of simulatable environments, are insufficient to push cutting-edge research works because they lack object-level topological and geometric variations, are not based on fully dynamic simulation, or are short of native support for multiple types of manipulation tasks. To this end, we present ManiSkill2, the next generation of the SAPIEN ManiSkill benchmark, to address critical pain points often encountered by researchers when using benchmarks for generalizable manipulation skills. ManiSkill2 includes 20 manipulation task families with 2000+ object models and 4M+ demonstration frames, which cover stationary/mobile-base, single/dual-arm, and rigid/soft-body manipulation tasks with 2D/3D-input data simulated by fully dynamic engines. It defines a unified interface and evaluation protocol to support a wide range of algorithms (e.g., classic sense-plan-act, RL, IL), visual observations (point cloud, RGBD), and controllers (e.g., action type and parameterization). Moreover, it empowers fast visual input learning algorithms so that a CNN-based policy can collect samples at about 2000 FPS with 1 GPU and 16 processes on a regular workstation. It implements a render server infrastructure to allow sharing rendering resources across all environments, thereby significantly reducing memory usage. We open-source all codes of our benchmark (simulator, environments, and baselines) and host an online challenge open to interdisciplinary researchers.
CLiNet: Joint Detection of Road Network Centerlines in 2D and 3D
Feb 04, 2023Abstract:This work introduces a new approach for joint detection of centerlines based on image data by localizing the features jointly in 2D and 3D. In contrast to existing work that focuses on detection of visual cues, we explore feature extraction methods that are directly amenable to the urban driving task. To develop and evaluate our approach, a large urban driving dataset dubbed AV Breadcrumbs is automatically labeled by leveraging vector map representations and projective geometry to annotate over 900,000 images. Our results demonstrate potential for dynamic scene modeling across various urban driving scenarios. Our model achieves an F1 score of 0.684 and an average normalized depth error of 2.083. The code and data annotations are publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge