Shi Qiu
AdaptOVCD: Training-Free Open-Vocabulary Remote Sensing Change Detection via Adaptive Information Fusion
Feb 06, 2026Abstract:Remote sensing change detection plays a pivotal role in domains such as environmental monitoring, urban planning, and disaster assessment. However, existing methods typically rely on predefined categories and large-scale pixel-level annotations, which limit their generalization and applicability in open-world scenarios. To address these limitations, this paper proposes AdaptOVCD, a training-free Open-Vocabulary Change Detection (OVCD) architecture based on dual-dimensional multi-level information fusion. The framework integrates multi-level information fusion across data, feature, and decision levels vertically while incorporating targeted adaptive designs horizontally, achieving deep synergy among heterogeneous pre-trained models to effectively mitigate error propagation. Specifically, (1) at the data level, Adaptive Radiometric Alignment (ARA) fuses radiometric statistics with original texture features and synergizes with SAM-HQ to achieve radiometrically consistent segmentation; (2) at the feature level, Adaptive Change Thresholding (ACT) combines global difference distributions with edge structure priors and leverages DINOv3 to achieve robust change detection; (3) at the decision level, Adaptive Confidence Filtering (ACF) integrates semantic confidence with spatial constraints and collaborates with DGTRS-CLIP to achieve high-confidence semantic identification. Comprehensive evaluations across nine scenarios demonstrate that AdaptOVCD detects arbitrary category changes in a zero-shot manner, significantly outperforming existing training-free methods. Meanwhile, it achieves 84.89\% of the fully-supervised performance upper bound in cross-dataset evaluations and exhibits superior generalization capabilities. The code is available at https://github.com/Dmygithub/AdaptOVCD.
EgoHandICL: Egocentric 3D Hand Reconstruction with In-Context Learning
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Robust 3D hand reconstruction in egocentric vision is challenging due to depth ambiguity, self-occlusion, and complex hand-object interactions. Prior methods mitigate these issues by scaling training data or adding auxiliary cues, but they often struggle in unseen contexts. We present EgoHandICL, the first in-context learning (ICL) framework for 3D hand reconstruction that improves semantic alignment, visual consistency, and robustness under challenging egocentric conditions. EgoHandICL introduces complementary exemplar retrieval guided by vision-language models (VLMs), an ICL-tailored tokenizer for multimodal context, and a masked autoencoder (MAE)-based architecture trained with hand-guided geometric and perceptual objectives. Experiments on ARCTIC and EgoExo4D show consistent gains over state-of-the-art methods. We also demonstrate real-world generalization and improve EgoVLM hand-object interaction reasoning by using reconstructed hands as visual prompts. Code and data: https://github.com/Nicous20/EgoHandICL
How and Why LLMs Generalize: A Fine-Grained Analysis of LLM Reasoning from Cognitive Behaviors to Low-Level Patterns
Dec 30, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) display strikingly different generalization behaviors: supervised fine-tuning (SFT) often narrows capability, whereas reinforcement-learning (RL) tuning tends to preserve it. The reasons behind this divergence remain unclear, as prior studies have largely relied on coarse accuracy metrics. We address this gap by introducing a novel benchmark that decomposes reasoning into atomic core skills such as calculation, fact retrieval, simulation, enumeration, and diagnostic, providing a concrete framework for addressing the fundamental question of what constitutes reasoning in LLMs. By isolating and measuring these core skills, the benchmark offers a more granular view of how specific cognitive abilities emerge, transfer, and sometimes collapse during post-training. Combined with analyses of low-level statistical patterns such as distributional divergence and parameter statistics, it enables a fine-grained study of how generalization evolves under SFT and RL across mathematical, scientific reasoning, and non-reasoning tasks. Our meta-probing framework tracks model behavior at different training stages and reveals that RL-tuned models maintain more stable behavioral profiles and resist collapse in reasoning skills, whereas SFT models exhibit sharper drift and overfit to surface patterns. This work provides new insights into the nature of reasoning in LLMs and points toward principles for designing training strategies that foster broad, robust generalization.
Trade-offs in Image Generation: How Do Different Dimensions Interact?
Jul 29, 2025Abstract:Model performance in text-to-image (T2I) and image-to-image (I2I) generation often depends on multiple aspects, including quality, alignment, diversity, and robustness. However, models' complex trade-offs among these dimensions have rarely been explored due to (1) the lack of datasets that allow fine-grained quantification of these trade-offs, and (2) the use of a single metric for multiple dimensions. To bridge this gap, we introduce TRIG-Bench (Trade-offs in Image Generation), which spans 10 dimensions (Realism, Originality, Aesthetics, Content, Relation, Style, Knowledge, Ambiguity, Toxicity, and Bias), contains 40,200 samples, and covers 132 pairwise dimensional subsets. Furthermore, we develop TRIGScore, a VLM-as-judge metric that automatically adapts to various dimensions. Based on TRIG-Bench and TRIGScore, we evaluate 14 models across T2I and I2I tasks. In addition, we propose the Relation Recognition System to generate the Dimension Trade-off Map (DTM) that visualizes the trade-offs among model-specific capabilities. Our experiments demonstrate that DTM consistently provides a comprehensive understanding of the trade-offs between dimensions for each type of generative model. Notably, we show that the model's dimension-specific weaknesses can be mitigated through fine-tuning on DTM to enhance overall performance. Code is available at: https://github.com/fesvhtr/TRIG
NoiseSDF2NoiseSDF: Learning Clean Neural Fields from Noisy Supervision
Jul 18, 2025Abstract:Reconstructing accurate implicit surface representations from point clouds remains a challenging task, particularly when data is captured using low-quality scanning devices. These point clouds often contain substantial noise, leading to inaccurate surface reconstructions. Inspired by the Noise2Noise paradigm for 2D images, we introduce NoiseSDF2NoiseSDF, a novel method designed to extend this concept to 3D neural fields. Our approach enables learning clean neural SDFs directly from noisy point clouds through noisy supervision by minimizing the MSE loss between noisy SDF representations, allowing the network to implicitly denoise and refine surface estimations. We evaluate the effectiveness of NoiseSDF2NoiseSDF on benchmarks, including the ShapeNet, ABC, Famous, and Real datasets. Experimental results demonstrate that our framework significantly improves surface reconstruction quality from noisy inputs.
ClipGS: Clippable Gaussian Splatting for Interactive Cinematic Visualization of Volumetric Medical Data
Jul 09, 2025Abstract:The visualization of volumetric medical data is crucial for enhancing diagnostic accuracy and improving surgical planning and education. Cinematic rendering techniques significantly enrich this process by providing high-quality visualizations that convey intricate anatomical details, thereby facilitating better understanding and decision-making in medical contexts. However, the high computing cost and low rendering speed limit the requirement of interactive visualization in practical applications. In this paper, we introduce ClipGS, an innovative Gaussian splatting framework with the clipping plane supported, for interactive cinematic visualization of volumetric medical data. To address the challenges posed by dynamic interactions, we propose a learnable truncation scheme that automatically adjusts the visibility of Gaussian primitives in response to the clipping plane. Besides, we also design an adaptive adjustment model to dynamically adjust the deformation of Gaussians and refine the rendering performance. We validate our method on five volumetric medical data (including CT and anatomical slice data), and reach an average 36.635 PSNR rendering quality with 156 FPS and 16.1 MB model size, outperforming state-of-the-art methods in rendering quality and efficiency.
From EduVisBench to EduVisAgent: A Benchmark and Multi-Agent Framework for Pedagogical Visualization
May 22, 2025

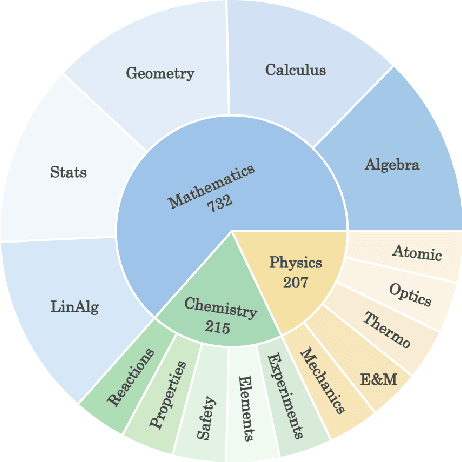

Abstract:While foundation models (FMs), such as diffusion models and large vision-language models (LVLMs), have been widely applied in educational contexts, their ability to generate pedagogically effective visual explanations remains limited. Most existing approaches focus primarily on textual reasoning, overlooking the critical role of structured and interpretable visualizations in supporting conceptual understanding. To better assess the visual reasoning capabilities of FMs in educational settings, we introduce EduVisBench, a multi-domain, multi-level benchmark. EduVisBench features diverse STEM problem sets requiring visually grounded solutions, along with a fine-grained evaluation rubric informed by pedagogical theory. Our empirical analysis reveals that existing models frequently struggle with the inherent challenge of decomposing complex reasoning and translating it into visual representations aligned with human cognitive processes. To address these limitations, we propose EduVisAgent, a multi-agent collaborative framework that coordinates specialized agents for instructional planning, reasoning decomposition, metacognitive prompting, and visualization design. Experimental results show that EduVisAgent substantially outperforms all baselines, achieving a 40.2% improvement and delivering more educationally aligned visualizations. EduVisBench and EduVisAgent are available at https://github.com/aiming-lab/EduVisBench and https://github.com/aiming-lab/EduVisAgent.
PHYBench: Holistic Evaluation of Physical Perception and Reasoning in Large Language Models
Apr 22, 2025



Abstract:We introduce PHYBench, a novel, high-quality benchmark designed for evaluating reasoning capabilities of large language models (LLMs) in physical contexts. PHYBench consists of 500 meticulously curated physics problems based on real-world physical scenarios, designed to assess the ability of models to understand and reason about realistic physical processes. Covering mechanics, electromagnetism, thermodynamics, optics, modern physics, and advanced physics, the benchmark spans difficulty levels from high school exercises to undergraduate problems and Physics Olympiad challenges. Additionally, we propose the Expression Edit Distance (EED) Score, a novel evaluation metric based on the edit distance between mathematical expressions, which effectively captures differences in model reasoning processes and results beyond traditional binary scoring methods. We evaluate various LLMs on PHYBench and compare their performance with human experts. Our results reveal that even state-of-the-art reasoning models significantly lag behind human experts, highlighting their limitations and the need for improvement in complex physical reasoning scenarios. Our benchmark results and dataset are publicly available at https://phybench-official.github.io/phybench-demo/.
Rethinking End-to-End 2D to 3D Scene Segmentation in Gaussian Splatting
Mar 18, 2025Abstract:Lifting multi-view 2D instance segmentation to a radiance field has proven to be effective to enhance 3D understanding. Existing methods rely on direct matching for end-to-end lifting, yielding inferior results; or employ a two-stage solution constrained by complex pre- or post-processing. In this work, we design a new end-to-end object-aware lifting approach, named Unified-Lift that provides accurate 3D segmentation based on the 3D Gaussian representation. To start, we augment each Gaussian point with an additional Gaussian-level feature learned using a contrastive loss to encode instance information. Importantly, we introduce a learnable object-level codebook to account for individual objects in the scene for an explicit object-level understanding and associate the encoded object-level features with the Gaussian-level point features for segmentation predictions. While promising, achieving effective codebook learning is non-trivial and a naive solution leads to degraded performance. Therefore, we formulate the association learning module and the noisy label filtering module for effective and robust codebook learning. We conduct experiments on three benchmarks: LERF-Masked, Replica, and Messy Rooms datasets. Both qualitative and quantitative results manifest that our Unified-Lift clearly outperforms existing methods in terms of segmentation quality and time efficiency. The code is publicly available at \href{https://github.com/Runsong123/Unified-Lift}{https://github.com/Runsong123/Unified-Lift}.
KDSelector: A Knowledge-Enhanced and Data-Efficient Model Selector Learning Framework for Time Series Anomaly Detection
Mar 16, 2025



Abstract:Model selection has been raised as an essential problem in the area of time series anomaly detection (TSAD), because there is no single best TSAD model for the highly heterogeneous time series in real-world applications. However, despite the success of existing model selection solutions that train a classification model (especially neural network, NN) using historical data as a selector to predict the correct TSAD model for each series, the NN-based selector learning methods used by existing solutions do not make full use of the knowledge in the historical data and require iterating over all training samples, which limits the accuracy and training speed of the selector. To address these limitations, we propose KDSelector, a novel knowledge-enhanced and data-efficient framework for learning the NN-based TSAD model selector, of which three key components are specifically designed to integrate available knowledge into the selector and dynamically prune less important and redundant samples during the learning. We develop a TSAD model selection system with KDSelector as the internal, to demonstrate how users improve the accuracy and training speed of their selectors by using KDSelector as a plug-and-play module. Our demonstration video is hosted at https://youtu.be/2uqupDWvTF0.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge