Junchi Yan
LongR: Unleashing Long-Context Reasoning via Reinforcement Learning with Dense Utility Rewards
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Reinforcement Learning has emerged as a key driver for LLM reasoning. This capability is equally pivotal in long-context scenarios--such as long-dialogue understanding and structured data analysis, where the challenge extends beyond consuming tokens to performing rigorous deduction. While existing efforts focus on data synthesis or architectural changes, recent work points out that relying solely on sparse, outcome-only rewards yields limited gains, as such coarse signals are often insufficient to effectively guide the complex long-context reasoning. To address this, we propose LongR, a unified framework that enhances long-context performance by integrating a dynamic "Think-and-Read" mechanism, which interleaves reasoning with document consultation, with a contextual density reward based on relative information gain to quantify the utility of the relevant documents. Empirically, LongR achieves a 9% gain on LongBench v2 and consistent improvements on RULER and InfiniteBench, demonstrating robust efficiency in navigating extensive contexts. Furthermore, LongR consistently enhances performance across diverse RL algorithms (e.g., DAPO, GSPO). Finally, we conduct in-depth analyses to investigate the impact of reasoning chain length on efficiency and the model's robustness against distractors.
Euphonium: Steering Video Flow Matching via Process Reward Gradient Guided Stochastic Dynamics
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:While online Reinforcement Learning has emerged as a crucial technique for aligning flow matching models with human preferences, current approaches are hindered by inefficient exploration during training rollouts. Relying on undirected stochasticity and sparse outcome rewards, these methods struggle to discover high-reward samples, resulting in data-inefficient and slow optimization. To address these limitations, we propose Euphonium, a novel framework that steers generation via process reward gradient guided dynamics. Our key insight is to formulate the sampling process as a theoretically principled Stochastic Differential Equation that explicitly incorporates the gradient of a Process Reward Model into the flow drift. This design enables dense, step-by-step steering toward high-reward regions, advancing beyond the unguided exploration in prior works, and theoretically encompasses existing sampling methods (e.g., Flow-GRPO, DanceGRPO) as special cases. We further derive a distillation objective that internalizes the guidance signal into the flow network, eliminating inference-time dependency on the reward model. We instantiate this framework with a Dual-Reward Group Relative Policy Optimization algorithm, combining latent process rewards for efficient credit assignment with pixel-level outcome rewards for final visual fidelity. Experiments on text-to-video generation show that Euphonium achieves better alignment compared to existing methods while accelerating training convergence by 1.66x.
JTok: On Token Embedding as another Axis of Scaling Law via Joint Token Self-modulation
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:LLMs have traditionally scaled along dense dimensions, where performance is coupled with near-linear increases in computational cost. While MoE decouples capacity from compute, it introduces large memory overhead and hardware efficiency challenges. To overcome these, we propose token-indexed parameters as a novel, orthogonal scaling axis that decouple model capacity from FLOPs. Specifically, we introduce Joint-Token (JTok) and Mixture of Joint-Token (JTok-M), which augment Transformer layers with modulation vectors retrieved from auxiliary embedding tables. These vectors modulate the backbone via lightweight, element-wise operations, incurring negligible FLOPs overhead. Extensive experiments on both dense and MoE backbones, spanning from 650M (190M + 460M embedding) to 61B (17B + 44B embedding) total parameters, demonstrate that our approach consistently reduces validation loss and significantly improves downstream task performance (e.g., +4.1 on MMLU, +8.3 on ARC, +8.9 on CEval). Rigorous isoFLOPs analysis further confirms that JTok-M fundamentally shifts the quality-compute Pareto frontier, achieving comparable model quality with 35% less compute relative to vanilla MoE architectures, and we validate that token-indexed parameters exhibit a predictable power-law scaling behavior. Moreover, our efficient implementation ensures that the overhead introduced by JTok and JTok-M remains marginal.
Learning to Decode Against Compositional Hallucination in Video Multimodal Large Language Models
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Current research on video hallucination mitigation primarily focuses on isolated error types, leaving compositional hallucinations, arising from incorrect reasoning over multiple interacting spatial and temporal factors largely underexplored. We introduce OmniVCHall, a benchmark designed to systematically evaluate both isolated and compositional hallucinations in video multimodal large language models (VLLMs). OmniVCHall spans diverse video domains, introduces a novel camera-based hallucination type, and defines a fine-grained taxonomy, together with adversarial answer options (e.g., "All are correct" and "None of the above") to prevent shortcut reasoning. The evaluations of 39 representative VLLMs reveal that even advanced models (e.g., Qwen3-VL and GPT-5) exhibit substantial performance degradation. We propose TriCD, a contrastive decoding framework with a triple-pathway calibration mechanism. An adaptive perturbation controller dynamically selects distracting operations to construct negative video variants, while a saliency-guided enhancement module adaptively reinforces grounded token-wise visual evidences. These components are optimized via reinforcement learning to encourage precise decision-making under compositional hallucination settings. Experimental results show that TriCD consistently improves performance across two representative backbones, achieving an average accuracy improvement of over 10%. The data and code can be find at https://github.com/BMRETURN/OmniVCHall.
RulePlanner: All-in-One Reinforcement Learner for Unifying Design Rules in 3D Floorplanning
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Floorplanning determines the coordinate and shape of each module in Integrated Circuits. With the scaling of technology nodes, in floorplanning stage especially 3D scenarios with multiple stacked layers, it has become increasingly challenging to adhere to complex hardware design rules. Current methods are only capable of handling specific and limited design rules, while violations of other rules require manual and meticulous adjustment. This leads to labor-intensive and time-consuming post-processing for expert engineers. In this paper, we propose an all-in-one deep reinforcement learning-based approach to tackle these challenges, and design novel representations for real-world IC design rules that have not been addressed by previous approaches. Specifically, the processing of various hardware design rules is unified into a single framework with three key components: 1) novel matrix representations to model the design rules, 2) constraints on the action space to filter out invalid actions that cause rule violations, and 3) quantitative analysis of constraint satisfaction as reward signals. Experiments on public benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness and validity of our approach. Furthermore, transferability is well demonstrated on unseen circuits. Our framework is extensible to accommodate new design rules, thus providing flexibility to address emerging challenges in future chip design. Code will be available at: https://github.com/Thinklab-SJTU/EDA-AI
INFA-Guard: Mitigating Malicious Propagation via Infection-Aware Safeguarding in LLM-Based Multi-Agent Systems
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:The rapid advancement of Large Language Model (LLM)-based Multi-Agent Systems (MAS) has introduced significant security vulnerabilities, where malicious influence can propagate virally through inter-agent communication. Conventional safeguards often rely on a binary paradigm that strictly distinguishes between benign and attack agents, failing to account for infected agents i.e., benign entities converted by attack agents. In this paper, we propose Infection-Aware Guard, INFA-Guard, a novel defense framework that explicitly identifies and addresses infected agents as a distinct threat category. By leveraging infection-aware detection and topological constraints, INFA-Guard accurately localizes attack sources and infected ranges. During remediation, INFA-Guard replaces attackers and rehabilitates infected ones, avoiding malicious propagation while preserving topological integrity. Extensive experiments demonstrate that INFA-Guard achieves state-of-the-art performance, reducing the Attack Success Rate (ASR) by an average of 33%, while exhibiting cross-model robustness, superior topological generalization, and high cost-effectiveness.
Milestones over Outcome: Unlocking Geometric Reasoning with Sub-Goal Verifiable Reward
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) struggle with complex geometric reasoning, largely because "black box" outcome-based supervision fails to distinguish between lucky guesses and rigorous deduction. To address this, we introduce a paradigm shift towards subgoal-level evaluation and learning. We first construct GeoGoal, a benchmark synthesized via a rigorous formal verification data engine, which converts abstract proofs into verifiable numeric subgoals. This structure reveals a critical divergence between reasoning quality and outcome accuracy. Leveraging this, we propose the Sub-Goal Verifiable Reward (SGVR) framework, which replaces sparse signals with dense rewards based on the Skeleton Rate. Experiments demonstrate that SGVR not only enhances geometric performance (+9.7%) but also exhibits strong generalization, transferring gains to general math (+8.0%) and other general reasoning tasks (+2.8%), demonstrating broad applicability across diverse domains.
GeoBench: Rethinking Multimodal Geometric Problem-Solving via Hierarchical Evaluation
Dec 30, 2025Abstract:Geometric problem solving constitutes a critical branch of mathematical reasoning, requiring precise analysis of shapes and spatial relationships. Current evaluations of geometric reasoning in vision-language models (VLMs) face limitations, including the risk of test data contamination from textbook-based benchmarks, overemphasis on final answers over reasoning processes, and insufficient diagnostic granularity. To address these issues, we present GeoBench, a hierarchical benchmark featuring four reasoning levels in geometric problem-solving: Visual Perception, Goal-Oriented Planning, Rigorous Theorem Application, and Self-Reflective Backtracking. Through six formally verified tasks generated via TrustGeoGen, we systematically assess capabilities ranging from attribute extraction to logical error correction. Experiments reveal that while reasoning models like OpenAI-o3 outperform general MLLMs, performance declines significantly with increasing task complexity. Key findings demonstrate that sub-goal decomposition and irrelevant premise filtering critically influence final problem-solving accuracy, whereas Chain-of-Thought prompting unexpectedly degrades performance in some tasks. These findings establish GeoBench as a comprehensive benchmark while offering actionable guidelines for developing geometric problem-solving systems.
LoPA: Scaling dLLM Inference via Lookahead Parallel Decoding
Dec 22, 2025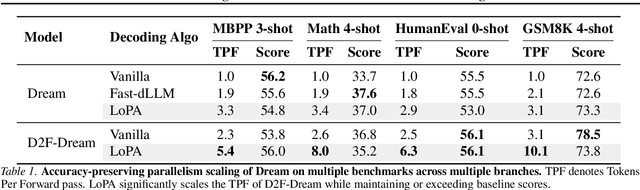
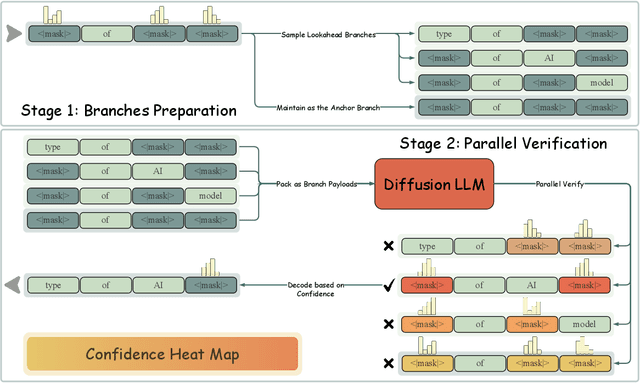
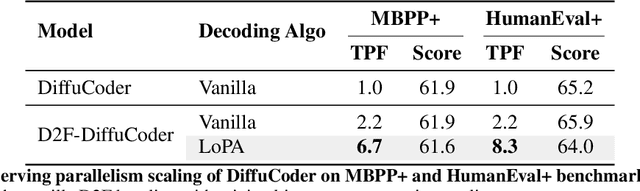
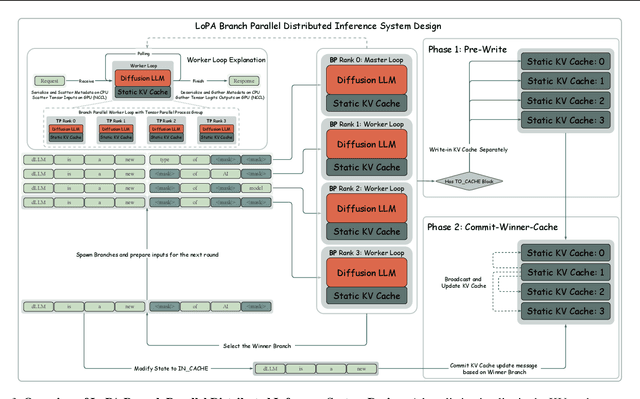
Abstract:Diffusion Large Language Models (dLLMs) have demonstrated significant potential for high-speed inference. However, current confidence-driven decoding strategies are constrained by limited parallelism, typically achieving only 1--3 tokens per forward pass (TPF). In this work, we identify that the degree of parallelism during dLLM inference is highly sensitive to the Token Filling Order (TFO). Then, we introduce Lookahead PArallel Decoding LoPA, a training-free, plug-and-play algorithm, to identify a superior TFO and hence accelerate inference. LoPA concurrently explores distinct candidate TFOs via parallel branches, and selects the one with the highest potential for future parallelism based on branch confidence. We apply LoPA to the state-of-the-art D2F model and observe a substantial enhancement in decoding efficiency. Notably, LoPA increases the TPF of D2F-Dream to 10.1 on the GSM8K while maintaining performance superior to the Dream baseline. Furthermore, to facilitate this unprecedented degree of parallelism, we develop a specialized multi-device inference system featuring Branch Parallelism (BP), which achieves a single-sample throughput of 1073.9 tokens per second under multi-GPU deployment. The code is available at https://github.com/zhijie-group/LoPA.
Reasoning Palette: Modulating Reasoning via Latent Contextualization for Controllable Exploration for (V)LMs
Dec 19, 2025



Abstract:Exploration capacity shapes both inference-time performance and reinforcement learning (RL) training for large (vision-) language models, as stochastic sampling often yields redundant reasoning paths with little high-level diversity. This paper proposes Reasoning Palette, a novel latent-modulation framework that endows the model with a stochastic latent variable for strategic contextualization, guiding its internal planning prior to token generation. This latent context is inferred from the mean-pooled embedding of a question-answer pair via a variational autoencoder (VAE), where each sampled latent potentially encodes a distinct reasoning context. During inference, a sampled latent is decoded into learnable token prefixes and prepended to the input prompt, modulating the model's internal reasoning trajectory. In this way, the model performs internal sampling over reasoning strategies prior to output generation, which shapes the style and structure of the entire response sequence. A brief supervised fine-tuning (SFT) warm-up phase allows the model to adapt to this latent conditioning. Within RL optimization, Reasoning Palette facilitates structured exploration by enabling on-demand injection for diverse reasoning modes, significantly enhancing exploration efficiency and sustained learning capability. Experiments across multiple reasoning benchmarks demonstrate that our method enables interpretable and controllable control over the (vision-) language model's strategic behavior, thereby achieving consistent performance gains over standard RL methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge