Taiji Suzuki
Transformers as Measure-Theoretic Associative Memory: A Statistical Perspective and Minimax Optimality
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Transformers excel through content-addressable retrieval and the ability to exploit contexts of, in principle, unbounded length. We recast associative memory at the level of probability measures, treating a context as a distribution over tokens and viewing attention as an integral operator on measures. Concretely, for mixture contexts $ν= I^{-1} \sum_{i=1}^I μ^{(i^*)}$ and a query $x_{\mathrm{q}}(i^*)$, the task decomposes into (i) recall of the relevant component $μ^{(i^*)}$ and (ii) prediction from $(μ_{i^*},x_\mathrm{q})$. We study learned softmax attention (not a frozen kernel) trained by empirical risk minimization and show that a shallow measure-theoretic Transformer composed with an MLP learns the recall-and-predict map under a spectral assumption on the input densities. We further establish a matching minimax lower bound with the same rate exponent (up to multiplicative constants), proving sharpness of the convergence order. The framework offers a principled recipe for designing and analyzing Transformers that recall from arbitrarily long, distributional contexts with provable generalization guarantees.
A Relative-Budget Theory for Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards in Large Language Model Reasoning
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL) is a dominant paradigm for improving the reasoning abilities of large language models, yet its effectiveness varies across tasks and compute budgets. We propose a \emph{relative-budget} theory explaining this variation through a single quantity called relative budget $ξ:= H/\mathbb{E}[T]$, where $H$ is the generation horizon (token budget) and $T$ denotes the number of tokens until the first correct solution under a base policy. We show that $ξ$ determines sample efficiency by controlling reward variance and the likelihood of informative trajectories. Our analysis reveals three regimes: in the \emph{deficient} regime ($ξ\to 0$), informative trajectories are rare and the sample complexity explodes; in the \emph{balanced} regime ($ξ=Θ(1)$), informative trajectories occur with non-negligible probability and RL is maximally sample-efficient; and in the \emph{ample} regime ($ξ\to \infty$), learning remains stable but marginal gains per iteration diminish. We further provide finite-sample guarantees for online RL that characterize learning progress across these regimes. Specifically, in a case study under idealized distributional assumptions, we show that the relative budget grows linearly over iterations. Our empirical results confirm these predictions in realistic settings, identifying a budget $ξ\in [1.5, 2.0]$ that maximizes learning efficiency and coincides with peak reasoning performance.
Inference-Aware Meta-Alignment of LLMs via Non-Linear GRPO
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Aligning large language models (LLMs) to diverse human preferences is fundamentally challenging since criteria can often conflict with each other. Inference-time alignment methods have recently gained popularity as they allow LLMs to be aligned to multiple criteria via different alignment algorithms at inference time. However, inference-time alignment is computationally expensive since it often requires multiple forward passes of the base model. In this work, we propose inference-aware meta-alignment (IAMA), a novel approach that enables LLMs to be aligned to multiple criteria with limited computational budget at inference time. IAMA trains a base model such that it can be effectively aligned to multiple tasks via different inference-time alignment algorithms. To solve the non-linear optimization problems involved in IAMA, we propose non-linear GRPO, which provably converges to the optimal solution in the space of probability measures.
Zero-Flow Encoders
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Flow-based methods have achieved significant success in various generative modeling tasks, capturing nuanced details within complex data distributions. However, few existing works have exploited this unique capability to resolve fine-grained structural details beyond generation tasks. This paper presents a flow-inspired framework for representation learning. First, we demonstrate that a rectified flow trained using independent coupling is zero everywhere at $t=0.5$ if and only if the source and target distributions are identical. We term this property the \emph{zero-flow criterion}. Second, we show that this criterion can certify conditional independence, thereby extracting \emph{sufficient information} from the data. Third, we translate this criterion into a tractable, simulation-free loss function that enables learning amortized Markov blankets in graphical models and latent representations in self-supervised learning tasks. Experiments on both simulated and real-world datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach. The code reproducing our experiments can be found at: https://github.com/probabilityFLOW/zfe.
From Shortcut to Induction Head: How Data Diversity Shapes Algorithm Selection in Transformers
Dec 21, 2025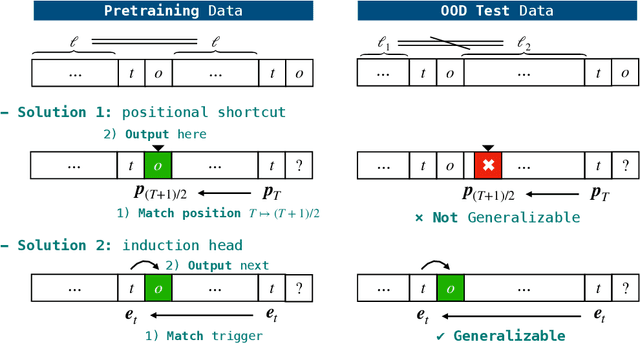
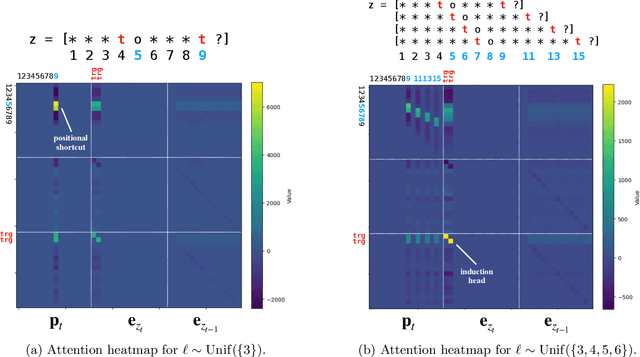
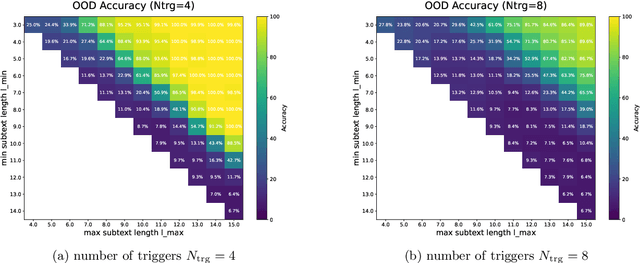
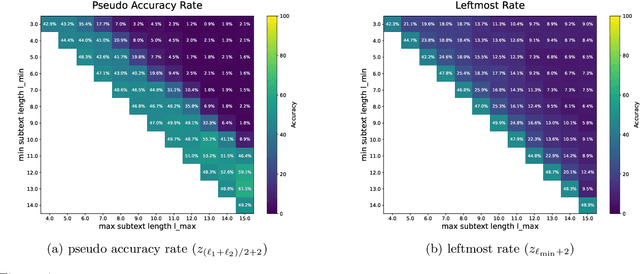
Abstract:Transformers can implement both generalizable algorithms (e.g., induction heads) and simple positional shortcuts (e.g., memorizing fixed output positions). In this work, we study how the choice of pretraining data distribution steers a shallow transformer toward one behavior or the other. Focusing on a minimal trigger-output prediction task -- copying the token immediately following a special trigger upon its second occurrence -- we present a rigorous analysis of gradient-based training of a single-layer transformer. In both the infinite and finite sample regimes, we prove a transition in the learned mechanism: if input sequences exhibit sufficient diversity, measured by a low ``max-sum'' ratio of trigger-to-trigger distances, the trained model implements an induction head and generalizes to unseen contexts; by contrast, when this ratio is large, the model resorts to a positional shortcut and fails to generalize out-of-distribution (OOD). We also reveal a trade-off between the pretraining context length and OOD generalization, and derive the optimal pretraining distribution that minimizes computational cost per sample. Finally, we validate our theoretical predictions with controlled synthetic experiments, demonstrating that broadening context distributions robustly induces induction heads and enables OOD generalization. Our results shed light on the algorithmic biases of pretrained transformers and offer conceptual guidelines for data-driven control of their learned behaviors.
Sliding Window Recurrences for Sequence Models
Dec 15, 2025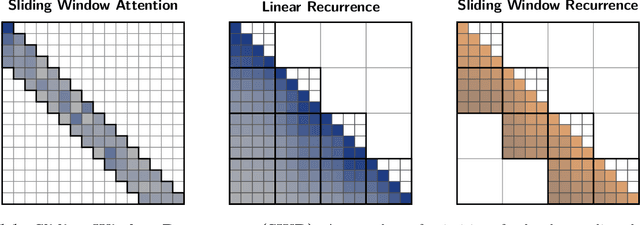
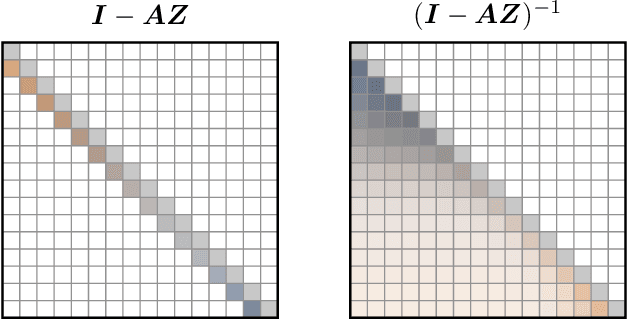
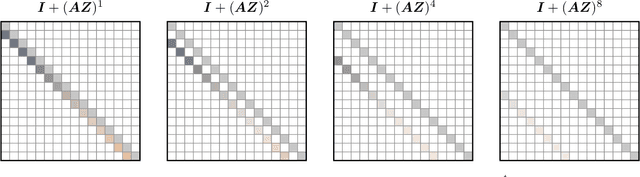
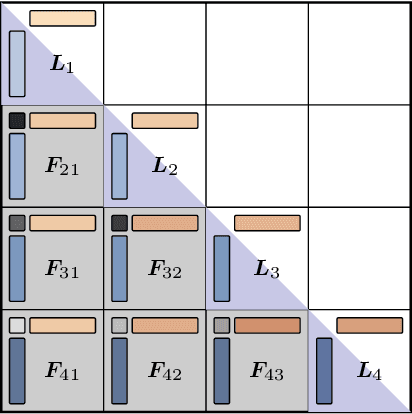
Abstract:Multi-hybrid architectures are poised to take over language modeling due to better quality and performance. We introduce a hierarchical decomposition framework for linear recurrences that allows us to develop algorithms aligned with GPU memory hierarchies, yielding Sliding Window Recurrences. We focus specifically on truncating recurrences to hardware-aligned windows which are naturally jagged, limiting costly inter-warp communication. Using SWR, we develop Phalanx layers that serve as drop-in replacements for windowed attention or linear recurrences. In 1B parameter multi-hybrid models, Phalanx achieves over 10-40% speedup across 4K to 32K context length over optimized Transformers while matching perplexity.
Towards a Unified Analysis of Neural Networks in Nonparametric Instrumental Variable Regression: Optimization and Generalization
Nov 18, 2025Abstract:We establish the first global convergence result of neural networks for two stage least squares (2SLS) approach in nonparametric instrumental variable regression (NPIV). This is achieved by adopting a lifted perspective through mean-field Langevin dynamics (MFLD), unlike standard MFLD, however, our setting of 2SLS entails a \emph{bilevel} optimization problem in the space of probability measures. To address this challenge, we leverage the penalty gradient approach recently developed for bilevel optimization which formulates bilevel optimization as a Lagrangian problem. This leads to a novel fully first-order algorithm, termed \texttt{F$^2$BMLD}. Apart from the convergence bound, we further provide a generalization bound, revealing an inherent trade-off in the choice of the Lagrange multiplier between optimization and statistical guarantees. Finally, we empirically validate the effectiveness of the proposed method on an offline reinforcement learning benchmark.
Consistency Is Not Always Correct: Towards Understanding the Role of Exploration in Post-Training Reasoning
Nov 10, 2025Abstract:Foundation models exhibit broad knowledge but limited task-specific reasoning, motivating post-training strategies such as RLVR and inference scaling with outcome or process reward models (ORM/PRM). While recent work highlights the role of exploration and entropy stability in improving pass@K, empirical evidence points to a paradox: RLVR and ORM/PRM typically reinforce existing tree-like reasoning paths rather than expanding the reasoning scope, raising the question of why exploration helps at all if no new patterns emerge. To reconcile this paradox, we adopt the perspective of Kim et al. (2025), viewing easy (e.g., simplifying a fraction) versus hard (e.g., discovering a symmetry) reasoning steps as low- versus high-probability Markov transitions, and formalize post-training dynamics through Multi-task Tree-structured Markov Chains (TMC). In this tractable model, pretraining corresponds to tree expansion, while post-training corresponds to chain-of-thought reweighting. We show that several phenomena recently observed in empirical studies arise naturally in this setting: (1) RLVR induces a squeezing effect, reducing reasoning entropy and forgetting some correct paths; (2) population rewards of ORM/PRM encourage consistency rather than accuracy, thereby favoring common patterns; and (3) certain rare, high-uncertainty reasoning paths by the base model are responsible for solving hard problem instances. Together, these explain why exploration -- even when confined to the base model's reasoning scope -- remains essential: it preserves access to rare but crucial reasoning traces needed for difficult cases, which are squeezed out by RLVR or unfavored by inference scaling. Building on this, we further show that exploration strategies such as rejecting easy instances and KL regularization help preserve rare reasoning traces. Empirical simulations corroborate our theoretical results.
Provable Benefit of Curriculum in Transformer Tree-Reasoning Post-Training
Nov 10, 2025Abstract:Recent curriculum techniques in the post-training stage of LLMs have been widely observed to outperform non-curriculum approaches in enhancing reasoning performance, yet a principled understanding of why and to what extent they work remains elusive. To address this gap, we develop a theoretical framework grounded in the intuition that progressively learning through manageable steps is more efficient than directly tackling a hard reasoning task, provided each stage stays within the model's effective competence. Under mild complexity conditions linking consecutive curriculum stages, we show that curriculum post-training avoids the exponential complexity bottleneck. To substantiate this result, drawing insights from the Chain-of-Thoughts (CoTs) solving mathematical problems such as Countdown and parity, we model CoT generation as a states-conditioned autoregressive reasoning tree, define a uniform-branching base model to capture pretrained behavior, and formalize curriculum stages as either depth-increasing (longer reasoning chains) or hint-decreasing (shorter prefixes) subtasks. Our analysis shows that, under outcome-only reward signals, reinforcement learning finetuning achieves high accuracy with polynomial sample complexity, whereas direct learning suffers from an exponential bottleneck. We further establish analogous guarantees for test-time scaling, where curriculum-aware querying reduces both reward oracle calls and sampling cost from exponential to polynomial order.
Generalization Bound of Gradient Flow through Training Trajectory and Data-dependent Kernel
Jun 12, 2025Abstract:Gradient-based optimization methods have shown remarkable empirical success, yet their theoretical generalization properties remain only partially understood. In this paper, we establish a generalization bound for gradient flow that aligns with the classical Rademacher complexity bounds for kernel methods-specifically those based on the RKHS norm and kernel trace-through a data-dependent kernel called the loss path kernel (LPK). Unlike static kernels such as NTK, the LPK captures the entire training trajectory, adapting to both data and optimization dynamics, leading to tighter and more informative generalization guarantees. Moreover, the bound highlights how the norm of the training loss gradients along the optimization trajectory influences the final generalization performance. The key technical ingredients in our proof combine stability analysis of gradient flow with uniform convergence via Rademacher complexity. Our bound recovers existing kernel regression bounds for overparameterized neural networks and shows the feature learning capability of neural networks compared to kernel methods. Numerical experiments on real-world datasets validate that our bounds correlate well with the true generalization gap.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge