Zhiqiang Xu
Path-Guided Flow Matching for Dataset Distillation
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Dataset distillation compresses large datasets into compact synthetic sets with comparable performance in training models. Despite recent progress on diffusion-based distillation, this type of method typically depends on heuristic guidance or prototype assignment, which comes with time-consuming sampling and trajectory instability and thus hurts downstream generalization especially under strong control or low IPC. We propose \emph{Path-Guided Flow Matching (PGFM)}, the first flow matching-based framework for generative distillation, which enables fast deterministic synthesis by solving an ODE in a few steps. PGFM conducts flow matching in the latent space of a frozen VAE to learn class-conditional transport from Gaussian noise to data distribution. Particularly, we develop a continuous path-to-prototype guidance algorithm for ODE-consistent path control, which allows trajectories to reliably land on assigned prototypes while preserving diversity and efficiency. Extensive experiments across high-resolution benchmarks demonstrate that PGFM matches or surpasses prior diffusion-based distillation approaches with fewer steps of sampling while delivering competitive performance with remarkably improved efficiency, e.g., 7.6$\times$ more efficient than the diffusion-based counterparts with 78\% mode coverage.
Sharpness-aware Federated Graph Learning
Dec 18, 2025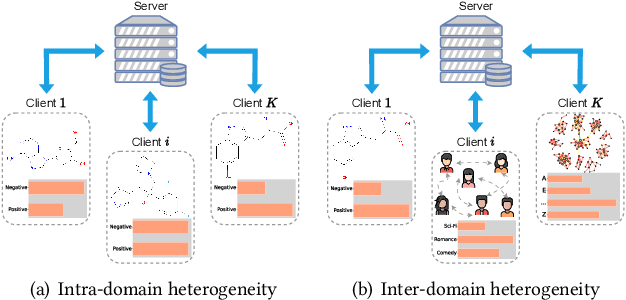
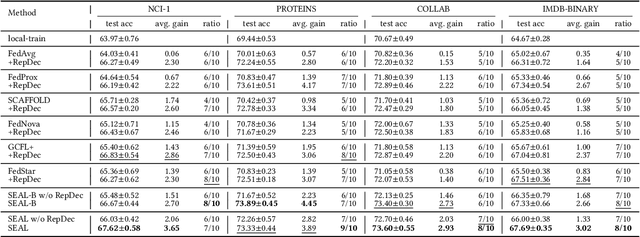
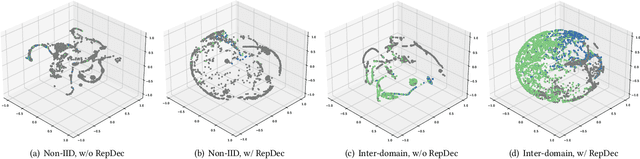
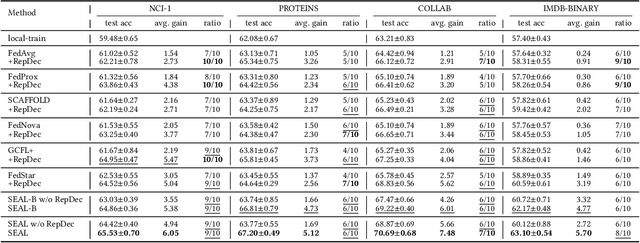
Abstract:One of many impediments to applying graph neural networks (GNNs) to large-scale real-world graph data is the challenge of centralized training, which requires aggregating data from different organizations, raising privacy concerns. Federated graph learning (FGL) addresses this by enabling collaborative GNN model training without sharing private data. However, a core challenge in FGL systems is the variation in local training data distributions among clients, known as the data heterogeneity problem. Most existing solutions suffer from two problems: (1) The typical optimizer based on empirical risk minimization tends to cause local models to fall into sharp valleys and weakens their generalization to out-of-distribution graph data. (2) The prevalent dimensional collapse in the learned representations of local graph data has an adverse impact on the classification capacity of the GNN model. To this end, we formulate a novel optimization objective that is aware of the sharpness (i.e., the curvature of the loss surface) of local GNN models. By minimizing the loss function and its sharpness simultaneously, we seek out model parameters in a flat region with uniformly low loss values, thus improving the generalization over heterogeneous data. By introducing a regularizer based on the correlation matrix of local representations, we relax the correlations of representations generated by individual local graph samples, so as to alleviate the dimensional collapse of the learned model. The proposed \textbf{S}harpness-aware f\textbf{E}derated gr\textbf{A}ph \textbf{L}earning (SEAL) algorithm can enhance the classification accuracy and generalization ability of local GNN models in federated graph learning. Experimental studies on several graph classification benchmarks show that SEAL consistently outperforms SOTA FGL baselines and provides gains for more participants.
User-Feedback-Driven Continual Adaptation for Vision-and-Language Navigation
Dec 11, 2025Abstract:Vision-and-Language Navigation (VLN) requires agents to navigate complex environments by following natural-language instructions. General Scene Adaptation for VLN (GSA-VLN) shifts the focus from zero-shot generalization to continual, environment-specific adaptation, narrowing the gap between static benchmarks and real-world deployment. However, current GSA-VLN frameworks exclude user feedback, relying solely on unsupervised adaptation from repeated environmental exposure. In practice, user feedback offers natural and valuable supervision that can significantly enhance adaptation quality. We introduce a user-feedback-driven adaptation framework that extends GSA-VLN by systematically integrating human interactions into continual learning. Our approach converts user feedback-navigation instructions and corrective signals-into high-quality, environment-aligned training data, enabling efficient and realistic adaptation. A memory-bank warm-start mechanism further reuses previously acquired environmental knowledge, mitigating cold-start degradation and ensuring stable redeployment. Experiments on the GSA-R2R benchmark show that our method consistently surpasses strong baselines such as GR-DUET, improving navigation success and path efficiency. The memory-bank warm start stabilizes early navigation and reduces performance drops after updates. Results under both continual and hybrid adaptation settings confirm the robustness and generality of our framework, demonstrating sustained improvement across diverse deployment conditions.
KGOT: Unified Knowledge Graph and Optimal Transport Pseudo-Labeling for Molecule-Protein Interaction Prediction
Dec 10, 2025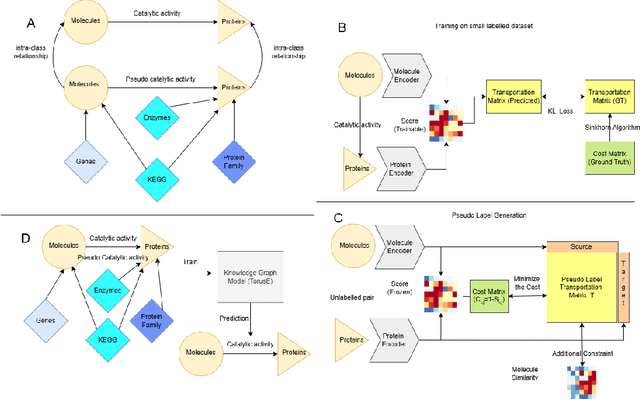
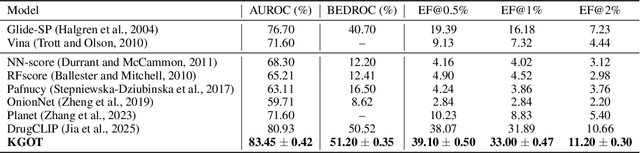
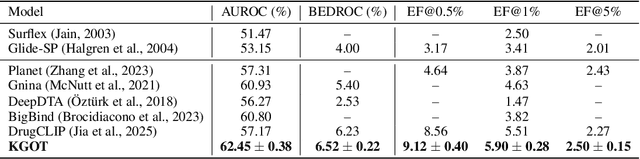
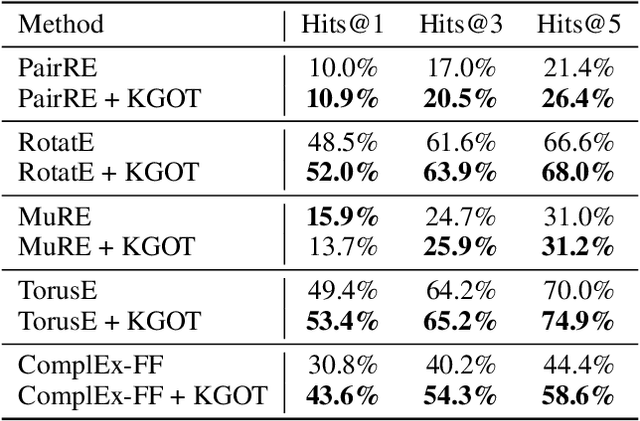
Abstract:Predicting molecule-protein interactions (MPIs) is a fundamental task in computational biology, with crucial applications in drug discovery and molecular function annotation. However, existing MPI models face two major challenges. First, the scarcity of labeled molecule-protein pairs significantly limits model performance, as available datasets capture only a small fraction of biological relevant interactions. Second, most methods rely solely on molecular and protein features, ignoring broader biological context such as genes, metabolic pathways, and functional annotations that could provide essential complementary information. To address these limitations, our framework first aggregates diverse biological datasets, including molecular, protein, genes and pathway-level interactions, and then develop an optimal transport-based approach to generate high-quality pseudo-labels for unlabeled molecule-protein pairs, leveraging the underlying distribution of known interactions to guide label assignment. By treating pseudo-labeling as a mechanism for bridging disparate biological modalities, our approach enables the effective use of heterogeneous data to enhance MPI prediction. We evaluate our framework on multiple MPI datasets including virtual screening tasks and protein retrieval tasks, demonstrating substantial improvements over state-of-the-art methods in prediction accuracies and zero shot ability across unseen interactions. Beyond MPI prediction, our approach provides a new paradigm for leveraging diverse biological data sources to tackle problems traditionally constrained by single- or bi-modal learning, paving the way for future advances in computational biology and drug discovery.
GeoDM: Geometry-aware Distribution Matching for Dataset Distillation
Dec 10, 2025Abstract:Dataset distillation aims to synthesize a compact subset of the original data, enabling models trained on it to achieve performance comparable to those trained on the original large dataset. Existing distribution-matching methods are confined to Euclidean spaces, making them only capture linear structures and overlook the intrinsic geometry of real data, e.g., curvature. However, high-dimensional data often lie on low-dimensional manifolds, suggesting that dataset distillation should have the distilled data manifold aligned with the original data manifold. In this work, we propose a geometry-aware distribution-matching framework, called \textbf{GeoDM}, which operates in the Cartesian product of Euclidean, hyperbolic, and spherical manifolds, with flat, hierarchical, and cyclical structures all captured by a unified representation. To adapt to the underlying data geometry, we introduce learnable curvature and weight parameters for three kinds of geometries. At the same time, we design an optimal transport loss to enhance the distribution fidelity. Our theoretical analysis shows that the geometry-aware distribution matching in a product space yields a smaller generalization error bound than the Euclidean counterparts. Extensive experiments conducted on standard benchmarks demonstrate that our algorithm outperforms state-of-the-art data distillation methods and remains effective across various distribution-matching strategies for the single geometries.
Local-Curvature-Aware Knowledge Graph Embedding: An Extended Ricci Flow Approach
Dec 10, 2025Abstract:Knowledge graph embedding (KGE) relies on the geometry of the embedding space to encode semantic and structural relations. Existing methods place all entities on one homogeneous manifold, Euclidean, spherical, hyperbolic, or their product/multi-curvature variants, to model linear, symmetric, or hierarchical patterns. Yet a predefined, homogeneous manifold cannot accommodate the sharply varying curvature that real-world graphs exhibit across local regions. Since this geometry is imposed a priori, any mismatch with the knowledge graph's local curvatures will distort distances between entities and hurt the expressiveness of the resulting KGE. To rectify this, we propose RicciKGE to have the KGE loss gradient coupled with local curvatures in an extended Ricci flow such that entity embeddings co-evolve dynamically with the underlying manifold geometry towards mutual adaptation. Theoretically, when the coupling coefficient is bounded and properly selected, we rigorously prove that i) all the edge-wise curvatures decay exponentially, meaning that the manifold is driven toward the Euclidean flatness; and ii) the KGE distances strictly converge to a global optimum, which indicates that geometric flattening and embedding optimization are promoting each other. Experimental improvements on link prediction and node classification benchmarks demonstrate RicciKGE's effectiveness in adapting to heterogeneous knowledge graph structures.
Finite Samples for Shallow Neural Networks
Mar 17, 2025Abstract:This paper investigates the ability of finite samples to identify two-layer irreducible shallow networks with various nonlinear activation functions, including rectified linear units (ReLU) and analytic functions such as the logistic sigmoid and hyperbolic tangent. An ``irreducible" network is one whose function cannot be represented by another network with fewer neurons. For ReLU activation functions, we first establish necessary and sufficient conditions for determining the irreducibility of a network. Subsequently, we prove a negative result: finite samples are insufficient for definitive identification of any irreducible ReLU shallow network. Nevertheless, we demonstrate that for a given irreducible network, one can construct a finite set of sampling points that can distinguish it from other network with the same neuron count. Conversely, for logistic sigmoid and hyperbolic tangent activation functions, we provide a positive result. We construct finite samples that enable the recovery of two-layer irreducible shallow analytic networks. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to investigate the exact identification of two-layer irreducible networks using finite sample function values. Our findings provide insights into the comparative performance of networks with different activation functions under limited sampling conditions.
MagicDistillation: Weak-to-Strong Video Distillation for Large-Scale Portrait Few-Step Synthesis
Mar 17, 2025



Abstract:Fine-tuning open-source large-scale VDMs for the portrait video synthesis task can result in significant improvements across multiple dimensions, such as visual quality and natural facial motion dynamics. Despite their advancements, how to achieve step distillation and reduce the substantial computational overhead of large-scale VDMs remains unexplored. To fill this gap, this paper proposes Weak-to-Strong Video Distillation (W2SVD) to mitigate both the issue of insufficient training memory and the problem of training collapse observed in vanilla DMD during the training process. Specifically, we first leverage LoRA to fine-tune the fake diffusion transformer (DiT) to address the out-of-memory issue. Then, we employ the W2S distribution matching to adjust the real DiT's parameter, subtly shifting it toward the fake DiT's parameter. This adjustment is achieved by utilizing the weak weight of the low-rank branch, effectively alleviate the conundrum where the video synthesized by the few-step generator deviates from the real data distribution, leading to inaccuracies in the KL divergence approximation. Additionally, we minimize the distance between the fake data distribution and the ground truth distribution to further enhance the visual quality of the synthesized videos. As experimentally demonstrated on HunyuanVideo, W2SVD surpasses the standard Euler, LCM, DMD and even the 28-step standard sampling in FID/FVD and VBench in 1/4-step video synthesis. The project page is in https://w2svd.github.io/W2SVD/.
Pastiche Novel Generation Creating: Fan Fiction You Love in Your Favorite Author's Style
Feb 21, 2025Abstract:Great novels create immersive worlds with rich character arcs, well-structured plots, and nuanced writing styles. However, current novel generation methods often rely on brief, simplistic story outlines and generate details using plain, generic language. To bridge this gap, we introduce the task of Pastiche Novel Generation, which requires the generated novels to imitate the distinctive features of the original work, including understanding character profiles, predicting plausible plot developments, and writing concrete details using vivid, expressive language. To achieve this, we propose WriterAgent, a novel generation system designed to master the core aspects of literary pastiche. WriterAgent is trained through a curriculum learning paradigm, progressing from low-level stylistic mastery to high-level narrative coherence. Its key tasks include language style learning, character modeling, plot planning, and stylish writing, ensuring comprehensive narrative control. To support this, WriterAgent leverages the WriterLoRA framework, an extension of LoRA with hierarchical and cumulative task-specific modules, each specializing in a different narrative aspect. We evaluate WriterAgent on multilingual classics like Harry Potter and Dream of the Red Chamber, demonstrating its superiority over baselines in capturing the target author's settings, character dynamics, and writing style to produce coherent, faithful narratives.
FedMHO: Heterogeneous One-Shot Federated Learning Towards Resource-Constrained Edge Devices
Feb 12, 2025



Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) is increasingly adopted in edge computing scenarios, where a large number of heterogeneous clients operate under constrained or sufficient resources. The iterative training process in conventional FL introduces significant computation and communication overhead, which is unfriendly for resource-constrained edge devices. One-shot FL has emerged as a promising approach to mitigate communication overhead, and model-heterogeneous FL solves the problem of diverse computing resources across clients. However, existing methods face challenges in effectively managing model-heterogeneous one-shot FL, often leading to unsatisfactory global model performance or reliance on auxiliary datasets. To address these challenges, we propose a novel FL framework named FedMHO, which leverages deep classification models on resource-sufficient clients and lightweight generative models on resource-constrained devices. On the server side, FedMHO involves a two-stage process that includes data generation and knowledge fusion. Furthermore, we introduce FedMHO-MD and FedMHO-SD to mitigate the knowledge-forgetting problem during the knowledge fusion stage, and an unsupervised data optimization solution to improve the quality of synthetic samples. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our methods, as they outperform state-of-the-art baselines in various experimental setups.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge