Michael Lingelbach
MagicDistillation: Weak-to-Strong Video Distillation for Large-Scale Portrait Few-Step Synthesis
Mar 17, 2025



Abstract:Fine-tuning open-source large-scale VDMs for the portrait video synthesis task can result in significant improvements across multiple dimensions, such as visual quality and natural facial motion dynamics. Despite their advancements, how to achieve step distillation and reduce the substantial computational overhead of large-scale VDMs remains unexplored. To fill this gap, this paper proposes Weak-to-Strong Video Distillation (W2SVD) to mitigate both the issue of insufficient training memory and the problem of training collapse observed in vanilla DMD during the training process. Specifically, we first leverage LoRA to fine-tune the fake diffusion transformer (DiT) to address the out-of-memory issue. Then, we employ the W2S distribution matching to adjust the real DiT's parameter, subtly shifting it toward the fake DiT's parameter. This adjustment is achieved by utilizing the weak weight of the low-rank branch, effectively alleviate the conundrum where the video synthesized by the few-step generator deviates from the real data distribution, leading to inaccuracies in the KL divergence approximation. Additionally, we minimize the distance between the fake data distribution and the ground truth distribution to further enhance the visual quality of the synthesized videos. As experimentally demonstrated on HunyuanVideo, W2SVD surpasses the standard Euler, LCM, DMD and even the 28-step standard sampling in FID/FVD and VBench in 1/4-step video synthesis. The project page is in https://w2svd.github.io/W2SVD/.
MagicInfinite: Generating Infinite Talking Videos with Your Words and Voice
Mar 07, 2025Abstract:We present MagicInfinite, a novel diffusion Transformer (DiT) framework that overcomes traditional portrait animation limitations, delivering high-fidelity results across diverse character types-realistic humans, full-body figures, and stylized anime characters. It supports varied facial poses, including back-facing views, and animates single or multiple characters with input masks for precise speaker designation in multi-character scenes. Our approach tackles key challenges with three innovations: (1) 3D full-attention mechanisms with a sliding window denoising strategy, enabling infinite video generation with temporal coherence and visual quality across diverse character styles; (2) a two-stage curriculum learning scheme, integrating audio for lip sync, text for expressive dynamics, and reference images for identity preservation, enabling flexible multi-modal control over long sequences; and (3) region-specific masks with adaptive loss functions to balance global textual control and local audio guidance, supporting speaker-specific animations. Efficiency is enhanced via our innovative unified step and cfg distillation techniques, achieving a 20x inference speed boost over the basemodel: generating a 10 second 540x540p video in 10 seconds or 720x720p in 30 seconds on 8 H100 GPUs, without quality loss. Evaluations on our new benchmark demonstrate MagicInfinite's superiority in audio-lip synchronization, identity preservation, and motion naturalness across diverse scenarios. It is publicly available at https://www.hedra.com/, with examples at https://magicinfinite.github.io/.
Magic 1-For-1: Generating One Minute Video Clips within One Minute
Feb 11, 2025Abstract:In this technical report, we present Magic 1-For-1 (Magic141), an efficient video generation model with optimized memory consumption and inference latency. The key idea is simple: factorize the text-to-video generation task into two separate easier tasks for diffusion step distillation, namely text-to-image generation and image-to-video generation. We verify that with the same optimization algorithm, the image-to-video task is indeed easier to converge over the text-to-video task. We also explore a bag of optimization tricks to reduce the computational cost of training the image-to-video (I2V) models from three aspects: 1) model convergence speedup by using a multi-modal prior condition injection; 2) inference latency speed up by applying an adversarial step distillation, and 3) inference memory cost optimization with parameter sparsification. With those techniques, we are able to generate 5-second video clips within 3 seconds. By applying a test time sliding window, we are able to generate a minute-long video within one minute with significantly improved visual quality and motion dynamics, spending less than 1 second for generating 1 second video clips on average. We conduct a series of preliminary explorations to find out the optimal tradeoff between computational cost and video quality during diffusion step distillation and hope this could be a good foundation model for open-source explorations. The code and the model weights are available at https://github.com/DA-Group-PKU/Magic-1-For-1.
Real-time One-Step Diffusion-based Expressive Portrait Videos Generation
Dec 18, 2024



Abstract:Latent diffusion models have made great strides in generating expressive portrait videos with accurate lip-sync and natural motion from a single reference image and audio input. However, these models are far from real-time, often requiring many sampling steps that take minutes to generate even one second of video-significantly limiting practical use. We introduce OSA-LCM (One-Step Avatar Latent Consistency Model), paving the way for real-time diffusion-based avatars. Our method achieves comparable video quality to existing methods but requires only one sampling step, making it more than 10x faster. To accomplish this, we propose a novel avatar discriminator design that guides lip-audio consistency and motion expressiveness to enhance video quality in limited sampling steps. Additionally, we employ a second-stage training architecture using an editing fine-tuned method (EFT), transforming video generation into an editing task during training to effectively address the temporal gap challenge in single-step generation. Experiments demonstrate that OSA-LCM outperforms existing open-source portrait video generation models while operating more efficiently with a single sampling step.
Phased Consistency Model
May 28, 2024Abstract:The consistency model (CM) has recently made significant progress in accelerating the generation of diffusion models. However, its application to high-resolution, text-conditioned image generation in the latent space (a.k.a., LCM) remains unsatisfactory. In this paper, we identify three key flaws in the current design of LCM. We investigate the reasons behind these limitations and propose the Phased Consistency Model (PCM), which generalizes the design space and addresses all identified limitations. Our evaluations demonstrate that PCM significantly outperforms LCM across 1--16 step generation settings. While PCM is specifically designed for multi-step refinement, it achieves even superior or comparable 1-step generation results to previously state-of-the-art specifically designed 1-step methods. Furthermore, we show that PCM's methodology is versatile and applicable to video generation, enabling us to train the state-of-the-art few-step text-to-video generator. More details are available at https://g-u-n.github.io/projects/pcm/.
BEHAVIOR-1K: A Human-Centered, Embodied AI Benchmark with 1,000 Everyday Activities and Realistic Simulation
Mar 14, 2024



Abstract:We present BEHAVIOR-1K, a comprehensive simulation benchmark for human-centered robotics. BEHAVIOR-1K includes two components, guided and motivated by the results of an extensive survey on "what do you want robots to do for you?". The first is the definition of 1,000 everyday activities, grounded in 50 scenes (houses, gardens, restaurants, offices, etc.) with more than 9,000 objects annotated with rich physical and semantic properties. The second is OMNIGIBSON, a novel simulation environment that supports these activities via realistic physics simulation and rendering of rigid bodies, deformable bodies, and liquids. Our experiments indicate that the activities in BEHAVIOR-1K are long-horizon and dependent on complex manipulation skills, both of which remain a challenge for even state-of-the-art robot learning solutions. To calibrate the simulation-to-reality gap of BEHAVIOR-1K, we provide an initial study on transferring solutions learned with a mobile manipulator in a simulated apartment to its real-world counterpart. We hope that BEHAVIOR-1K's human-grounded nature, diversity, and realism make it valuable for embodied AI and robot learning research. Project website: https://behavior.stanford.edu.
Task-Driven Graph Attention for Hierarchical Relational Object Navigation
Jun 23, 2023Abstract:Embodied AI agents in large scenes often need to navigate to find objects. In this work, we study a naturally emerging variant of the object navigation task, hierarchical relational object navigation (HRON), where the goal is to find objects specified by logical predicates organized in a hierarchical structure - objects related to furniture and then to rooms - such as finding an apple on top of a table in the kitchen. Solving such a task requires an efficient representation to reason about object relations and correlate the relations in the environment and in the task goal. HRON in large scenes (e.g. homes) is particularly challenging due to its partial observability and long horizon, which invites solutions that can compactly store the past information while effectively exploring the scene. We demonstrate experimentally that scene graphs are the best-suited representation compared to conventional representations such as images or 2D maps. We propose a solution that uses scene graphs as part of its input and integrates graph neural networks as its backbone, with an integrated task-driven attention mechanism, and demonstrate its better scalability and learning efficiency than state-of-the-art baselines.
Modeling Dynamic Environments with Scene Graph Memory
Jun 12, 2023Abstract:Embodied AI agents that search for objects in large environments such as households often need to make efficient decisions by predicting object locations based on partial information. We pose this as a new type of link prediction problem: link prediction on partially observable dynamic graphs. Our graph is a representation of a scene in which rooms and objects are nodes, and their relationships are encoded in the edges; only parts of the changing graph are known to the agent at each timestep. This partial observability poses a challenge to existing link prediction approaches, which we address. We propose a novel state representation -- Scene Graph Memory (SGM) -- with captures the agent's accumulated set of observations, as well as a neural net architecture called a Node Edge Predictor (NEP) that extracts information from the SGM to search efficiently. We evaluate our method in the Dynamic House Simulator, a new benchmark that creates diverse dynamic graphs following the semantic patterns typically seen at homes, and show that NEP can be trained to predict the locations of objects in a variety of environments with diverse object movement dynamics, outperforming baselines both in terms of new scene adaptability and overall accuracy. The codebase and more can be found at https://www.scenegraphmemory.com.
iGibson 2.0: Object-Centric Simulation for Robot Learning of Everyday Household Tasks
Aug 10, 2021



Abstract:Recent research in embodied AI has been boosted by the use of simulation environments to develop and train robot learning approaches. However, the use of simulation has skewed the attention to tasks that only require what robotics simulators can simulate: motion and physical contact. We present iGibson 2.0, an open-source simulation environment that supports the simulation of a more diverse set of household tasks through three key innovations. First, iGibson 2.0 supports object states, including temperature, wetness level, cleanliness level, and toggled and sliced states, necessary to cover a wider range of tasks. Second, iGibson 2.0 implements a set of predicate logic functions that map the simulator states to logic states like Cooked or Soaked. Additionally, given a logic state, iGibson 2.0 can sample valid physical states that satisfy it. This functionality can generate potentially infinite instances of tasks with minimal effort from the users. The sampling mechanism allows our scenes to be more densely populated with small objects in semantically meaningful locations. Third, iGibson 2.0 includes a virtual reality (VR) interface to immerse humans in its scenes to collect demonstrations. As a result, we can collect demonstrations from humans on these new types of tasks, and use them for imitation learning. We evaluate the new capabilities of iGibson 2.0 to enable robot learning of novel tasks, in the hope of demonstrating the potential of this new simulator to support new research in embodied AI. iGibson 2.0 and its new dataset will be publicly available at http://svl.stanford.edu/igibson/.
BEHAVIOR: Benchmark for Everyday Household Activities in Virtual, Interactive, and Ecological Environments
Aug 06, 2021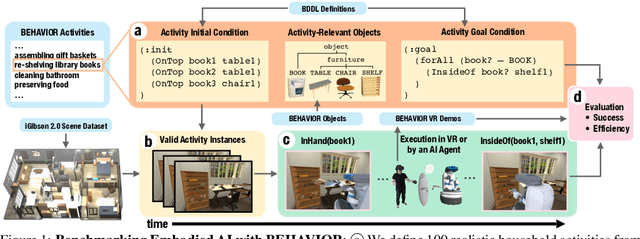
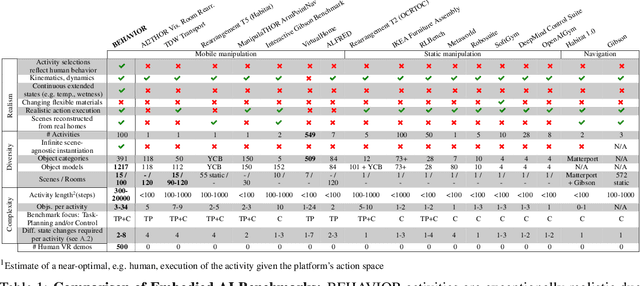

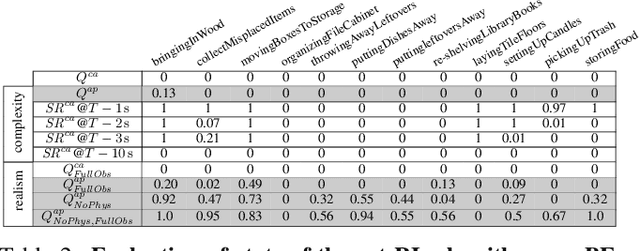
Abstract:We introduce BEHAVIOR, a benchmark for embodied AI with 100 activities in simulation, spanning a range of everyday household chores such as cleaning, maintenance, and food preparation. These activities are designed to be realistic, diverse, and complex, aiming to reproduce the challenges that agents must face in the real world. Building such a benchmark poses three fundamental difficulties for each activity: definition (it can differ by time, place, or person), instantiation in a simulator, and evaluation. BEHAVIOR addresses these with three innovations. First, we propose an object-centric, predicate logic-based description language for expressing an activity's initial and goal conditions, enabling generation of diverse instances for any activity. Second, we identify the simulator-agnostic features required by an underlying environment to support BEHAVIOR, and demonstrate its realization in one such simulator. Third, we introduce a set of metrics to measure task progress and efficiency, absolute and relative to human demonstrators. We include 500 human demonstrations in virtual reality (VR) to serve as the human ground truth. Our experiments demonstrate that even state of the art embodied AI solutions struggle with the level of realism, diversity, and complexity imposed by the activities in our benchmark. We make BEHAVIOR publicly available at behavior.stanford.edu to facilitate and calibrate the development of new embodied AI solutions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge