Peng Gao
University of Massachusetts Amherst
How Do Optical Flow and Textual Prompts Collaborate to Assist in Audio-Visual Semantic Segmentation?
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:Audio-visual semantic segmentation (AVSS) represents an extension of the audio-visual segmentation (AVS) task, necessitating a semantic understanding of audio-visual scenes beyond merely identifying sound-emitting objects at the visual pixel level. Contrary to a previous methodology, by decomposing the AVSS task into two discrete subtasks by initially providing a prompted segmentation mask to facilitate subsequent semantic analysis, our approach innovates on this foundational strategy. We introduce a novel collaborative framework, \textit{S}tepping \textit{S}tone \textit{P}lus (SSP), which integrates optical flow and textual prompts to assist the segmentation process. In scenarios where sound sources frequently coexist with moving objects, our pre-mask technique leverages optical flow to capture motion dynamics, providing essential temporal context for precise segmentation. To address the challenge posed by stationary sound-emitting objects, such as alarm clocks, SSP incorporates two specific textual prompts: one identifies the category of the sound-emitting object, and the other provides a broader description of the scene. Additionally, we implement a visual-textual alignment module (VTA) to facilitate cross-modal integration, delivering more coherent and contextually relevant semantic interpretations. Our training regimen involves a post-mask technique aimed at compelling the model to learn the diagram of the optical flow. Experimental results demonstrate that SSP outperforms existing AVS methods, delivering efficient and precise segmentation results.
A Dual-Branch Local-Global Framework for Cross-Resolution Land Cover Mapping
Dec 23, 2025Abstract:Cross-resolution land cover mapping aims to produce high-resolution semantic predictions from coarse or low-resolution supervision, yet the severe resolution mismatch makes effective learning highly challenging. Existing weakly supervised approaches often struggle to align fine-grained spatial structures with coarse labels, leading to noisy supervision and degraded mapping accuracy. To tackle this problem, we propose DDTM, a dual-branch weakly supervised framework that explicitly decouples local semantic refinement from global contextual reasoning. Specifically, DDTM introduces a diffusion-based branch to progressively refine fine-scale local semantics under coarse supervision, while a transformer-based branch enforces long-range contextual consistency across large spatial extents. In addition, we design a pseudo-label confidence evaluation module to mitigate noise induced by cross-resolution inconsistencies and to selectively exploit reliable supervisory signals. Extensive experiments demonstrate that DDTM establishes a new state-of-the-art on the Chesapeake Bay benchmark, achieving 66.52\% mIoU and substantially outperforming prior weakly supervised methods. The code is available at https://github.com/gpgpgp123/DDTM.
Distribution Matching Distillation Meets Reinforcement Learning
Nov 19, 2025Abstract:Distribution Matching Distillation (DMD) distills a pre-trained multi-step diffusion model to a few-step one to improve inference efficiency. However, the performance of the latter is often capped by the former. To circumvent this dilemma, we propose DMDR, a novel framework that combines Reinforcement Learning (RL) techniques into the distillation process. We show that for the RL of the few-step generator, the DMD loss itself is a more effective regularization compared to the traditional ones. In turn, RL can help to guide the mode coverage process in DMD more effectively. These allow us to unlock the capacity of the few-step generator by conducting distillation and RL simultaneously. Meanwhile, we design the dynamic distribution guidance and dynamic renoise sampling training strategies to improve the initial distillation process. The experiments demonstrate that DMDR can achieve leading visual quality, prompt coherence among few-step methods, and even exhibit performance that exceeds the multi-step teacher.
Remember Me: Bridging the Long-Range Gap in LVLMs with Three-Step Inference-Only Decay Resilience Strategies
Nov 13, 2025Abstract:Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) have achieved impressive performance across a wide range of multimodal tasks. However, they still face critical challenges in modeling long-range dependencies under the usage of Rotary Positional Encoding (ROPE). Although it can facilitate precise modeling of token positions, it induces progressive attention decay as token distance increases, especially with progressive attention decay over distant token pairs, which severely impairs the model's ability to remember global context. To alleviate this issue, we propose inference-only Three-step Decay Resilience Strategies (T-DRS), comprising (1) Semantic-Driven DRS (SD-DRS), amplifying semantically meaningful but distant signals via content-aware residuals, (2) Distance-aware Control DRS (DC-DRS), which can purify attention by smoothly modulating weights based on positional distances, suppressing noise while preserving locality, and (3) re-Reinforce Distant DRS (reRD-DRS), consolidating the remaining informative remote dependencies to maintain global coherence. Together, the T-DRS recover suppressed long-range token pairs without harming local inductive biases. Extensive experiments on Vision Question Answering (VQA) benchmarks demonstrate that T-DRS can consistently improve performance in a training-free manner. The code can be accessed in https://github.com/labixiaoq-qq/Remember-me
Spatial Preference Rewarding for MLLMs Spatial Understanding
Oct 16, 2025Abstract:Multimodal large language models~(MLLMs) have demonstrated promising spatial understanding capabilities, such as referencing and grounding object descriptions. Despite their successes, MLLMs still fall short in fine-grained spatial perception abilities, such as generating detailed region descriptions or accurately localizing objects. Additionally, they often fail to respond to the user's requirements for desired fine-grained spatial understanding. This issue might arise because existing approaches primarily focus on tuning MLLMs to model pre-annotated instruction data to inject spatial knowledge, without direct supervision of MLLMs' actual responses. We address this issue by SPR, a Spatial Preference Rewarding~(SPR) approach that enhances MLLMs' spatial capabilities by rewarding MLLMs' detailed responses with precise object localization over vague or inaccurate responses. With randomly selected image regions and region descriptions from MLLMs, SPR introduces semantic and localization scores to comprehensively evaluate the text quality and localization quality in MLLM-generated descriptions. We also refine the MLLM descriptions with better localization accuracy and pair the best-scored refinement with the initial descriptions of the lowest score for direct preference optimization, thereby enhancing fine-grained alignment with visual input. Extensive experiments over standard referring and grounding benchmarks show that SPR improves MLLM spatial understanding capabilities effectively with minimal overhead in training. Data and code will be released at https://github.com/hanqiu-hq/SPR
ACPO: Adaptive Curriculum Policy Optimization for Aligning Vision-Language Models in Complex Reasoning
Oct 01, 2025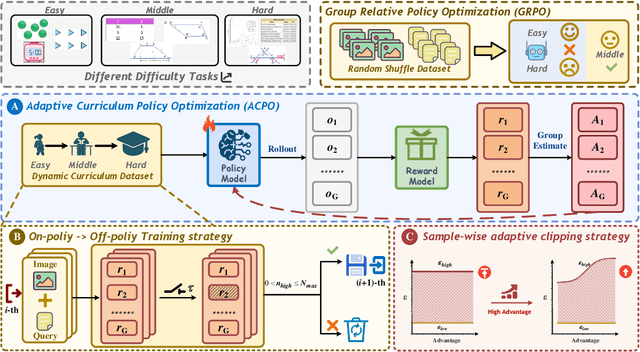
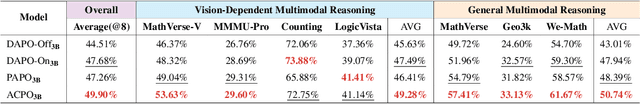
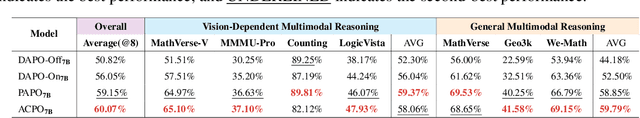
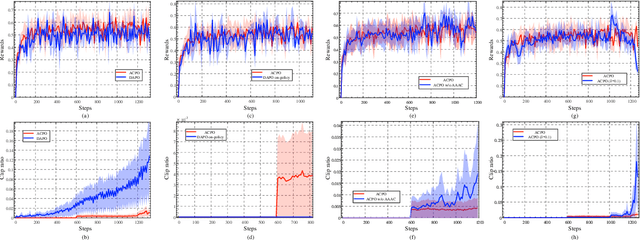
Abstract:Aligning large-scale vision-language models (VLMs) for complex reasoning via reinforcement learning is often hampered by the limitations of existing policy optimization algorithms, such as static training schedules and the rigid, uniform clipping mechanism in Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO). In this work, we introduce Adaptive Curriculum Policy Optimization (ACPO), a novel framework that addresses these challenges through a dual-component adaptive learning strategy. First, ACPO employs a dynamic curriculum that orchestrates a principled transition from a stable, near on-policy exploration phase to an efficient, off-policy exploitation phase by progressively increasing sample reuse. Second, we propose an Advantage-Aware Adaptive Clipping (AAAC) mechanism that replaces the fixed clipping hyperparameter with dynamic, sample-wise bounds modulated by the normalized advantage of each token. This allows for more granular and robust policy updates, enabling larger gradients for high-potential samples while safeguarding against destructive ones. We conduct extensive experiments on a suite of challenging multimodal reasoning benchmarks, including MathVista, LogicVista, and MMMU-Pro. Results demonstrate that ACPO consistently outperforms strong baselines such as DAPO and PAPO, achieving state-of-the-art performance, accelerated convergence, and superior training stability.
Lumina-mGPT 2.0: Stand-Alone AutoRegressive Image Modeling
Jul 23, 2025



Abstract:We present Lumina-mGPT 2.0, a stand-alone, decoder-only autoregressive model that revisits and revitalizes the autoregressive paradigm for high-quality image generation and beyond. Unlike existing approaches that rely on pretrained components or hybrid architectures, Lumina-mGPT 2.0 is trained entirely from scratch, enabling unrestricted architectural design and licensing freedom. It achieves generation quality on par with state-of-the-art diffusion models such as DALL-E 3 and SANA, while preserving the inherent flexibility and compositionality of autoregressive modeling. Our unified tokenization scheme allows the model to seamlessly handle a wide spectrum of tasks-including subject-driven generation, image editing, controllable synthesis, and dense prediction-within a single generative framework. To further boost usability, we incorporate efficient decoding strategies like inference-time scaling and speculative Jacobi sampling to improve quality and speed, respectively. Extensive evaluations on standard text-to-image benchmarks (e.g., GenEval, DPG) demonstrate that Lumina-mGPT 2.0 not only matches but in some cases surpasses diffusion-based models. Moreover, we confirm its multi-task capabilities on the Graph200K benchmark, with the native Lumina-mGPT 2.0 performing exceptionally well. These results position Lumina-mGPT 2.0 as a strong, flexible foundation model for unified multimodal generation. We have released our training details, code, and models at https://github.com/Alpha-VLLM/Lumina-mGPT-2.0.
Resurrect Mask AutoRegressive Modeling for Efficient and Scalable Image Generation
Jul 17, 2025
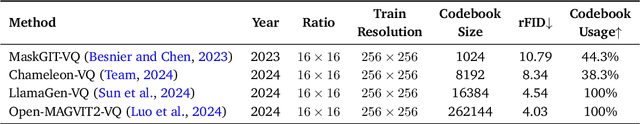
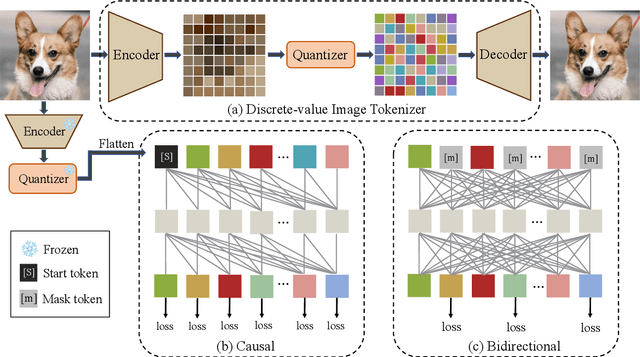
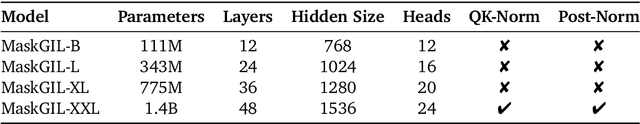
Abstract:AutoRegressive (AR) models have made notable progress in image generation, with Masked AutoRegressive (MAR) models gaining attention for their efficient parallel decoding. However, MAR models have traditionally underperformed when compared to standard AR models. This study refines the MAR architecture to improve image generation quality. We begin by evaluating various image tokenizers to identify the most effective one. Subsequently, we introduce an improved Bidirectional LLaMA architecture by replacing causal attention with bidirectional attention and incorporating 2D RoPE, which together form our advanced model, MaskGIL. Scaled from 111M to 1.4B parameters, MaskGIL achieves a FID score of 3.71, matching state-of-the-art AR models in the ImageNet 256x256 benchmark, while requiring only 8 inference steps compared to the 256 steps of AR models. Furthermore, we develop a text-driven MaskGIL model with 775M parameters for generating images from text at various resolutions. Beyond image generation, MaskGIL extends to accelerate AR-based generation and enable real-time speech-to-image conversion. Our codes and models are available at https://github.com/synbol/MaskGIL.
Non-Overlap-Aware Egocentric Pose Estimation for Collaborative Perception in Connected Autonomy
Jun 17, 2025Abstract:Egocentric pose estimation is a fundamental capability for multi-robot collaborative perception in connected autonomy, such as connected autonomous vehicles. During multi-robot operations, a robot needs to know the relative pose between itself and its teammates with respect to its own coordinates. However, different robots usually observe completely different views that contains similar objects, which leads to wrong pose estimation. In addition, it is unrealistic to allow robots to share their raw observations to detect overlap due to the limited communication bandwidth constraint. In this paper, we introduce a novel method for Non-Overlap-Aware Egocentric Pose Estimation (NOPE), which performs egocentric pose estimation in a multi-robot team while identifying the non-overlap views and satifying the communication bandwidth constraint. NOPE is built upon an unified hierarchical learning framework that integrates two levels of robot learning: (1) high-level deep graph matching for correspondence identification, which allows to identify if two views are overlapping or not, (2) low-level position-aware cross-attention graph learning for egocentric pose estimation. To evaluate NOPE, we conduct extensive experiments in both high-fidelity simulation and real-world scenarios. Experimental results have demonstrated that NOPE enables the novel capability for non-overlapping-aware egocentric pose estimation and achieves state-of-art performance compared with the existing methods. Our project page at https://hongh0.github.io/NOPE/.
MiniMax-M1: Scaling Test-Time Compute Efficiently with Lightning Attention
Jun 16, 2025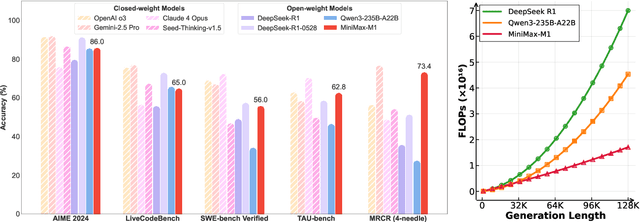
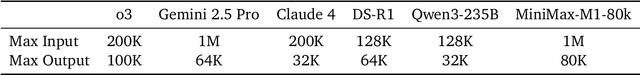
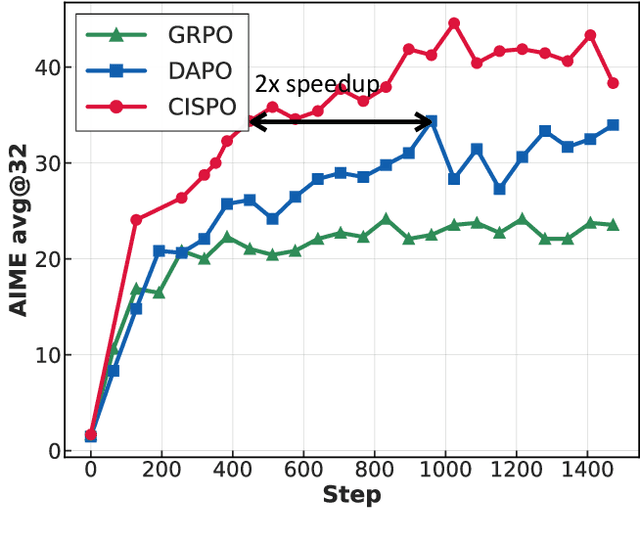
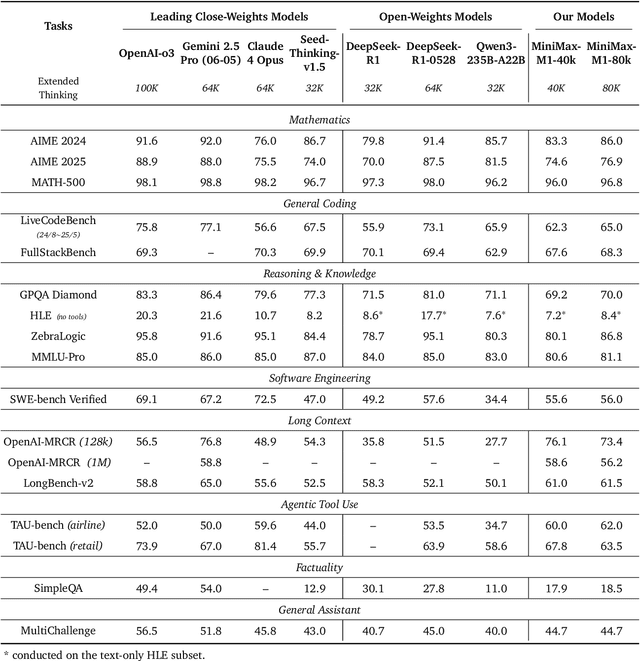
Abstract:We introduce MiniMax-M1, the world's first open-weight, large-scale hybrid-attention reasoning model. MiniMax-M1 is powered by a hybrid Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architecture combined with a lightning attention mechanism. The model is developed based on our previous MiniMax-Text-01 model, which contains a total of 456 billion parameters with 45.9 billion parameters activated per token. The M1 model natively supports a context length of 1 million tokens, 8x the context size of DeepSeek R1. Furthermore, the lightning attention mechanism in MiniMax-M1 enables efficient scaling of test-time compute. These properties make M1 particularly suitable for complex tasks that require processing long inputs and thinking extensively. MiniMax-M1 is trained using large-scale reinforcement learning (RL) on diverse problems including sandbox-based, real-world software engineering environments. In addition to M1's inherent efficiency advantage for RL training, we propose CISPO, a novel RL algorithm to further enhance RL efficiency. CISPO clips importance sampling weights rather than token updates, outperforming other competitive RL variants. Combining hybrid-attention and CISPO enables MiniMax-M1's full RL training on 512 H800 GPUs to complete in only three weeks, with a rental cost of just $534,700. We release two versions of MiniMax-M1 models with 40K and 80K thinking budgets respectively, where the 40K model represents an intermediate phase of the 80K training. Experiments on standard benchmarks show that our models are comparable or superior to strong open-weight models such as the original DeepSeek-R1 and Qwen3-235B, with particular strengths in complex software engineering, tool utilization, and long-context tasks. We publicly release MiniMax-M1 at https://github.com/MiniMax-AI/MiniMax-M1.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge