Chao Dong
Harnessing Diffusion-Yielded Score Priors for Image Restoration
Jul 28, 2025Abstract:Deep image restoration models aim to learn a mapping from degraded image space to natural image space. However, they face several critical challenges: removing degradation, generating realistic details, and ensuring pixel-level consistency. Over time, three major classes of methods have emerged, including MSE-based, GAN-based, and diffusion-based methods. However, they fail to achieve a good balance between restoration quality, fidelity, and speed. We propose a novel method, HYPIR, to address these challenges. Our solution pipeline is straightforward: it involves initializing the image restoration model with a pre-trained diffusion model and then fine-tuning it with adversarial training. This approach does not rely on diffusion loss, iterative sampling, or additional adapters. We theoretically demonstrate that initializing adversarial training from a pre-trained diffusion model positions the initial restoration model very close to the natural image distribution. Consequently, this initialization improves numerical stability, avoids mode collapse, and substantially accelerates the convergence of adversarial training. Moreover, HYPIR inherits the capabilities of diffusion models with rich user control, enabling text-guided restoration and adjustable texture richness. Requiring only a single forward pass, it achieves faster convergence and inference speed than diffusion-based methods. Extensive experiments show that HYPIR outperforms previous state-of-the-art methods, achieving efficient and high-quality image restoration.
SimpleGVR: A Simple Baseline for Latent-Cascaded Video Super-Resolution
Jun 24, 2025Abstract:Latent diffusion models have emerged as a leading paradigm for efficient video generation. However, as user expectations shift toward higher-resolution outputs, relying solely on latent computation becomes inadequate. A promising approach involves decoupling the process into two stages: semantic content generation and detail synthesis. The former employs a computationally intensive base model at lower resolutions, while the latter leverages a lightweight cascaded video super-resolution (VSR) model to achieve high-resolution output. In this work, we focus on studying key design principles for latter cascaded VSR models, which are underexplored currently. First, we propose two degradation strategies to generate training pairs that better mimic the output characteristics of the base model, ensuring alignment between the VSR model and its upstream generator. Second, we provide critical insights into VSR model behavior through systematic analysis of (1) timestep sampling strategies, (2) noise augmentation effects on low-resolution (LR) inputs. These findings directly inform our architectural and training innovations. Finally, we introduce interleaving temporal unit and sparse local attention to achieve efficient training and inference, drastically reducing computational overhead. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of our framework over existing methods, with ablation studies confirming the efficacy of each design choice. Our work establishes a simple yet effective baseline for cascaded video super-resolution generation, offering practical insights to guide future advancements in efficient cascaded synthesis systems.
Joint Computation Offloading and Resource Allocation for Uncertain Maritime MEC via Cooperation of UAVs and Vessels
Jun 18, 2025



Abstract:The computation demands from the maritime Internet of Things (MIoT) increase rapidly in recent years, and the unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and vessels based multi-access edge computing (MEC) can fulfill these MIoT requirements. However, the uncertain maritime tasks present significant challenges of inefficient computation offloading and resource allocation. In this paper, we focus on the maritime computation offloading and resource allocation through the cooperation of UAVs and vessels, with consideration of uncertain tasks. Specifically, we propose a cooperative MEC framework for computation offloading and resource allocation, including MIoT devices, UAVs and vessels. Then, we formulate the optimization problem to minimize the total execution time. As for the uncertain MIoT tasks, we leverage Lyapunov optimization to tackle the unpredictable task arrivals and varying computational resource availability. By converting the long-term constraints into short-term constraints, we obtain a set of small-scale optimization problems. Further, considering the heterogeneity of actions and resources of UAVs and vessels, we reformulate the small-scale optimization problem into a Markov game (MG). Moreover, a heterogeneous-agent soft actor-critic is proposed to sequentially update various neural networks and effectively solve the MG problem. Finally, simulations are conducted to verify the effectiveness in addressing computational offloading and resource allocation.
DualX-VSR: Dual Axial Spatial$\times$Temporal Transformer for Real-World Video Super-Resolution without Motion Compensation
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:Transformer-based models like ViViT and TimeSformer have advanced video understanding by effectively modeling spatiotemporal dependencies. Recent video generation models, such as Sora and Vidu, further highlight the power of transformers in long-range feature extraction and holistic spatiotemporal modeling. However, directly applying these models to real-world video super-resolution (VSR) is challenging, as VSR demands pixel-level precision, which can be compromised by tokenization and sequential attention mechanisms. While recent transformer-based VSR models attempt to address these issues using smaller patches and local attention, they still face limitations such as restricted receptive fields and dependence on optical flow-based alignment, which can introduce inaccuracies in real-world settings. To overcome these issues, we propose Dual Axial Spatial$\times$Temporal Transformer for Real-World Video Super-Resolution (DualX-VSR), which introduces a novel dual axial spatial$\times$temporal attention mechanism that integrates spatial and temporal information along orthogonal directions. DualX-VSR eliminates the need for motion compensation, offering a simplified structure that provides a cohesive representation of spatiotemporal information. As a result, DualX-VSR achieves high fidelity and superior performance in real-world VSR task.
Semantics-Aware Human Motion Generation from Audio Instructions
May 29, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in interactive technologies have highlighted the prominence of audio signals for semantic encoding. This paper explores a new task, where audio signals are used as conditioning inputs to generate motions that align with the semantics of the audio. Unlike text-based interactions, audio provides a more natural and intuitive communication method. However, existing methods typically focus on matching motions with music or speech rhythms, which often results in a weak connection between the semantics of the audio and generated motions. We propose an end-to-end framework using a masked generative transformer, enhanced by a memory-retrieval attention module to handle sparse and lengthy audio inputs. Additionally, we enrich existing datasets by converting descriptions into conversational style and generating corresponding audio with varied speaker identities. Experiments demonstrate the effectiveness and efficiency of the proposed framework, demonstrating that audio instructions can convey semantics similar to text while providing more practical and user-friendly interactions.
SpikeVideoFormer: An Efficient Spike-Driven Video Transformer with Hamming Attention and $\mathcal{O}(T)$ Complexity
May 15, 2025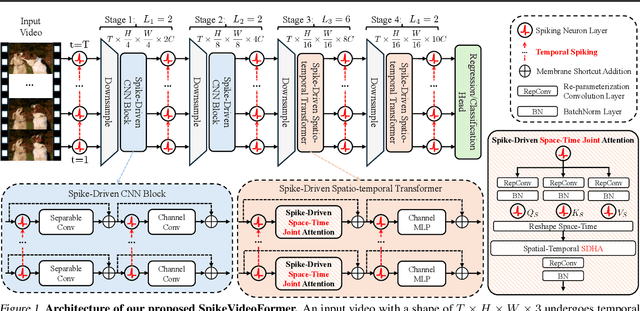
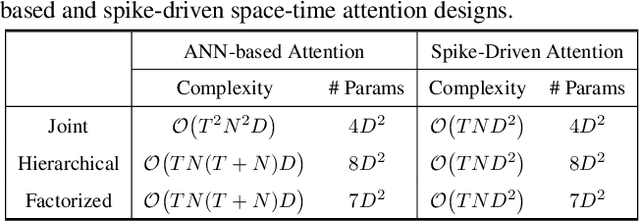
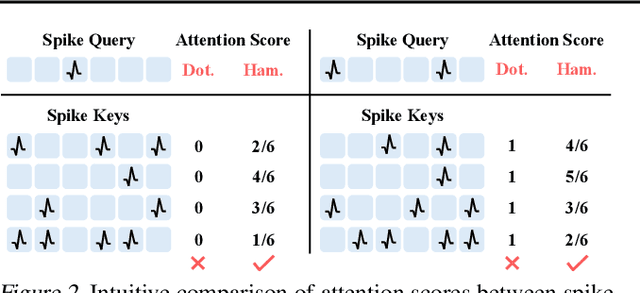
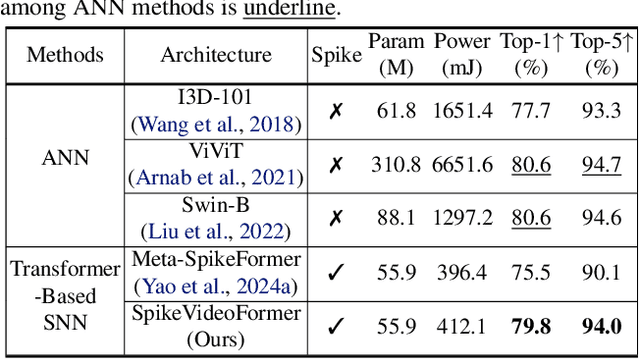
Abstract:Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs) have shown competitive performance to Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs) in various vision tasks, while offering superior energy efficiency. However, existing SNN-based Transformers primarily focus on single-image tasks, emphasizing spatial features while not effectively leveraging SNNs' efficiency in video-based vision tasks. In this paper, we introduce SpikeVideoFormer, an efficient spike-driven video Transformer, featuring linear temporal complexity $\mathcal{O}(T)$. Specifically, we design a spike-driven Hamming attention (SDHA) which provides a theoretically guided adaptation from traditional real-valued attention to spike-driven attention. Building on SDHA, we further analyze various spike-driven space-time attention designs and identify an optimal scheme that delivers appealing performance for video tasks, while maintaining only linear temporal complexity. The generalization ability and efficiency of our model are demonstrated across diverse downstream video tasks, including classification, human pose tracking, and semantic segmentation. Empirical results show our method achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance compared to existing SNN approaches, with over 15\% improvement on the latter two tasks. Additionally, it matches the performance of recent ANN-based methods while offering significant efficiency gains, achieving $\times 16$, $\times 10$ and $\times 5$ improvements on the three tasks. https://github.com/JimmyZou/SpikeVideoFormer
Lumina-OmniLV: A Unified Multimodal Framework for General Low-Level Vision
Apr 08, 2025Abstract:We present Lunima-OmniLV (abbreviated as OmniLV), a universal multimodal multi-task framework for low-level vision that addresses over 100 sub-tasks across four major categories: image restoration, image enhancement, weak-semantic dense prediction, and stylization. OmniLV leverages both textual and visual prompts to offer flexible and user-friendly interactions. Built on Diffusion Transformer (DiT)-based generative priors, our framework supports arbitrary resolutions -- achieving optimal performance at 1K resolution -- while preserving fine-grained details and high fidelity. Through extensive experiments, we demonstrate that separately encoding text and visual instructions, combined with co-training using shallow feature control, is essential to mitigate task ambiguity and enhance multi-task generalization. Our findings also reveal that integrating high-level generative tasks into low-level vision models can compromise detail-sensitive restoration. These insights pave the way for more robust and generalizable low-level vision systems.
TurboFill: Adapting Few-step Text-to-image Model for Fast Image Inpainting
Apr 01, 2025Abstract:This paper introduces TurboFill, a fast image inpainting model that enhances a few-step text-to-image diffusion model with an inpainting adapter for high-quality and efficient inpainting. While standard diffusion models generate high-quality results, they incur high computational costs. We overcome this by training an inpainting adapter on a few-step distilled text-to-image model, DMD2, using a novel 3-step adversarial training scheme to ensure realistic, structurally consistent, and visually harmonious inpainted regions. To evaluate TurboFill, we propose two benchmarks: DilationBench, which tests performance across mask sizes, and HumanBench, based on human feedback for complex prompts. Experiments show that TurboFill outperforms both multi-step BrushNet and few-step inpainting methods, setting a new benchmark for high-performance inpainting tasks. Our project page: https://liangbinxie.github.io/projects/TurboFill/
UniCon: Unidirectional Information Flow for Effective Control of Large-Scale Diffusion Models
Mar 21, 2025Abstract:We introduce UniCon, a novel architecture designed to enhance control and efficiency in training adapters for large-scale diffusion models. Unlike existing methods that rely on bidirectional interaction between the diffusion model and control adapter, UniCon implements a unidirectional flow from the diffusion network to the adapter, allowing the adapter alone to generate the final output. UniCon reduces computational demands by eliminating the need for the diffusion model to compute and store gradients during adapter training. Our results indicate that UniCon reduces GPU memory usage by one-third and increases training speed by 2.3 times, while maintaining the same adapter parameter size. Additionally, without requiring extra computational resources, UniCon enables the training of adapters with double the parameter volume of existing ControlNets. In a series of image conditional generation tasks, UniCon has demonstrated precise responsiveness to control inputs and exceptional generation capabilities.
Joint ADS-B in B5G for Hierarchical UAV Networks: Performance Analysis and MEC Based Optimization
Mar 18, 2025Abstract:Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) play significant roles in multiple fields, which brings great challenges for the airspace safety. In order to achieve efficient surveillance and break the limitation of application scenarios caused by single communication, we propose the collaborative surveillance model for hierarchical UAVs based on the cooperation of automatic dependent surveillance-broadcast (ADS-B) and 5G. Specifically, UAVs are hierarchical deployed, with the low-altitude central UAV equipped with the 5G module, and the high-altitude central UAV with ADS-B, which helps automatically broadcast the flight information to surrounding aircraft and ground stations. Firstly, we build the framework, derive the analytic expression, and analyze the channel performance of both air-to-ground (A2G) and air-to-air (A2A). Then, since the redundancy or information loss during transmission aggravates the monitoring performance, the mobile edge computing (MEC) based on-board processing algorithm is proposed. Finally, the performances of the proposed model and algorithm are verified through both simulations and experiments. In detail, the redundant data filtered out by the proposed algorithm accounts for 53.48%, and the supplementary data accounts for 16.42% of the optimized data. This work designs a UAV monitoring framework and proposes an algorithm to enhance the observability of trajectory surveillance, which helps improve the airspace safety and enhance the air traffic flow management.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge