Yongkui Yang
A Brain-inspired Embodied Intelligence for Fluid and Fast Reflexive Robotics Control
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:Recent advances in embodied intelligence have leveraged massive scaling of data and model parameters to master natural-language command following and multi-task control. In contrast, biological systems demonstrate an innate ability to acquire skills rapidly from sparse experience. Crucially, current robotic policies struggle to replicate the dynamic stability, reflexive responsiveness, and temporal memory inherent in biological motion. Here we present Neuromorphic Vision-Language-Action (NeuroVLA), a framework that mimics the structural organization of the bio-nervous system between the cortex, cerebellum, and spinal cord. We adopt a system-level bio-inspired design: a high-level model plans goals, an adaptive cerebellum module stabilizes motion using high-frequency sensors feedback, and a bio-inspired spinal layer executes lightning-fast actions generation. NeuroVLA represents the first deployment of a neuromorphic VLA on physical robotics, achieving state-of-the-art performance. We observe the emergence of biological motor characteristics without additional data or special guidance: it stops the shaking in robotic arms, saves significant energy(only 0.4w on Neuromorphic Processor), shows temporal memory ability and triggers safety reflexes in less than 20 milliseconds.
RT-Focuser: A Real-Time Lightweight Model for Edge-side Image Deblurring
Dec 26, 2025Abstract:Motion blur caused by camera or object movement severely degrades image quality and poses challenges for real-time applications such as autonomous driving, UAV perception, and medical imaging. In this paper, a lightweight U-shaped network tailored for real-time deblurring is presented and named RT-Focuser. To balance speed and accuracy, we design three key components: Lightweight Deblurring Block (LD) for edge-aware feature extraction, Multi-Level Integrated Aggregation module (MLIA) for encoder integration, and Cross-source Fusion Block (X-Fuse) for progressive decoder refinement. Trained on a single blurred input, RT-Focuser achieves 30.67 dB PSNR with only 5.85M parameters and 15.76 GMACs. It runs 6ms per frame on GPU and mobile, exceeds 140 FPS on both, showing strong potential for deployment on the edge. The official code and usage are available on: https://github.com/ReaganWu/RT-Focuser.
SpikeVideoFormer: An Efficient Spike-Driven Video Transformer with Hamming Attention and $\mathcal{O}(T)$ Complexity
May 15, 2025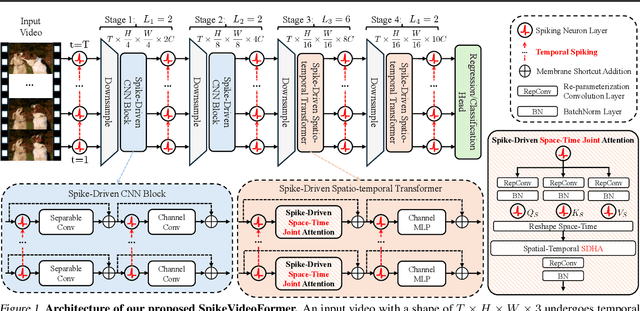
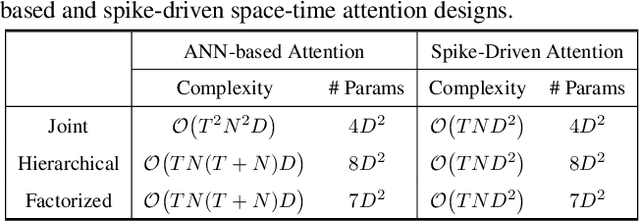
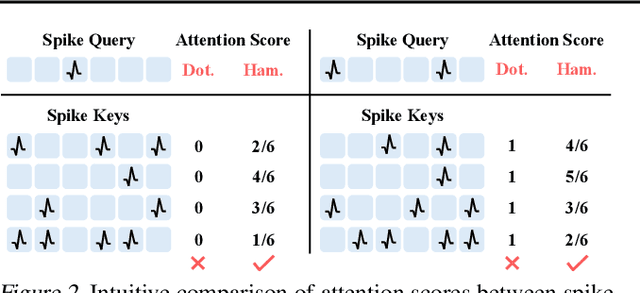
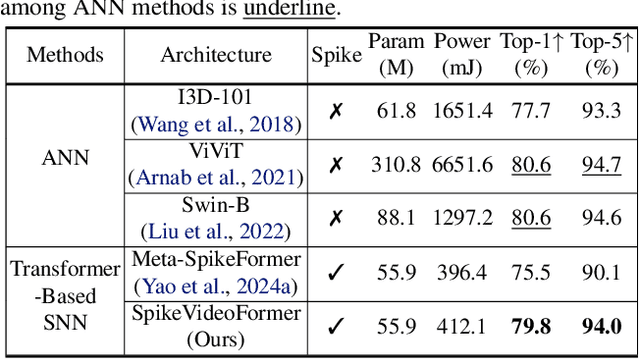
Abstract:Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs) have shown competitive performance to Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs) in various vision tasks, while offering superior energy efficiency. However, existing SNN-based Transformers primarily focus on single-image tasks, emphasizing spatial features while not effectively leveraging SNNs' efficiency in video-based vision tasks. In this paper, we introduce SpikeVideoFormer, an efficient spike-driven video Transformer, featuring linear temporal complexity $\mathcal{O}(T)$. Specifically, we design a spike-driven Hamming attention (SDHA) which provides a theoretically guided adaptation from traditional real-valued attention to spike-driven attention. Building on SDHA, we further analyze various spike-driven space-time attention designs and identify an optimal scheme that delivers appealing performance for video tasks, while maintaining only linear temporal complexity. The generalization ability and efficiency of our model are demonstrated across diverse downstream video tasks, including classification, human pose tracking, and semantic segmentation. Empirical results show our method achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance compared to existing SNN approaches, with over 15\% improvement on the latter two tasks. Additionally, it matches the performance of recent ANN-based methods while offering significant efficiency gains, achieving $\times 16$, $\times 10$ and $\times 5$ improvements on the three tasks. https://github.com/JimmyZou/SpikeVideoFormer
Constants of motion network revisited
Apr 13, 2025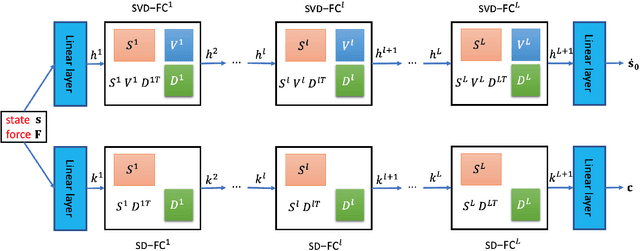
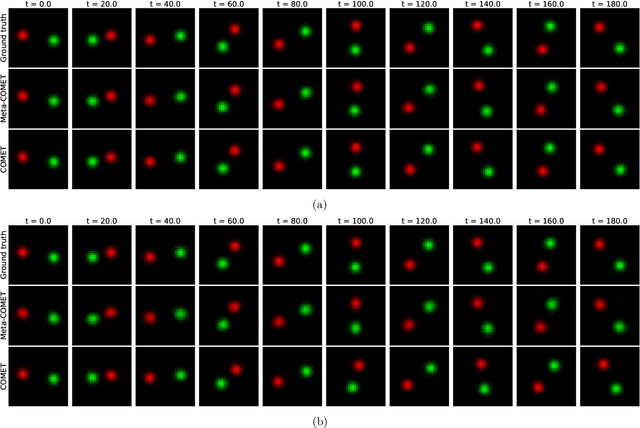

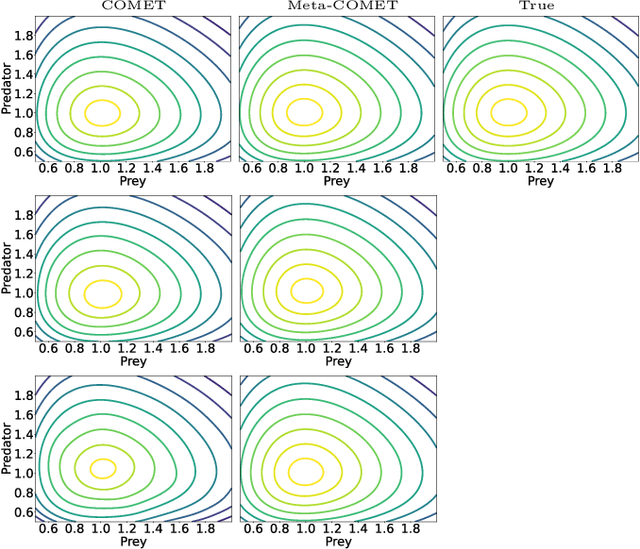
Abstract:Discovering constants of motion is meaningful in helping understand the dynamical systems, but inevitably needs proficient mathematical skills and keen analytical capabilities. With the prevalence of deep learning, methods employing neural networks, such as Constant Of Motion nETwork (COMET), are promising in handling this scientific problem. Although the COMET method can produce better predictions on dynamics by exploiting the discovered constants of motion, there is still plenty of room to sharpen it. In this paper, we propose a novel neural network architecture, built using the singular-value-decomposition (SVD) technique, and a two-phase training algorithm to improve the performance of COMET. Extensive experiments show that our approach not only retains the advantages of COMET, such as applying to non-Hamiltonian systems and indicating the number of constants of motion, but also can be more lightweight and noise-robust than COMET.
SpGesture: Source-Free Domain-adaptive sEMG-based Gesture Recognition with Jaccard Attentive Spiking Neural Network
May 23, 2024



Abstract:Surface electromyography (sEMG) based gesture recognition offers a natural and intuitive interaction modality for wearable devices. Despite significant advancements in sEMG-based gesture-recognition models, existing methods often suffer from high computational latency and increased energy consumption. Additionally, the inherent instability of sEMG signals, combined with their sensitivity to distribution shifts in real-world settings, compromises model robustness. To tackle these challenges, we propose a novel SpGesture framework based on Spiking Neural Networks, which possesses several unique merits compared with existing methods: (1) Robustness: By utilizing membrane potential as a memory list, we pioneer the introduction of Source-Free Domain Adaptation into SNN for the first time. This enables SpGesture to mitigate the accuracy degradation caused by distribution shifts. (2) High Accuracy: With a novel Spiking Jaccard Attention, SpGesture enhances the SNNs' ability to represent sEMG features, leading to a notable rise in system accuracy. To validate SpGesture's performance, we collected a new sEMG gesture dataset which has different forearm postures, where SpGesture achieved the highest accuracy among the baselines ($89.26\%$). Moreover, the actual deployment on the CPU demonstrated a system latency below 100ms, well within real-time requirements. This impressive performance showcases SpGesture's potential to enhance the applicability of sEMG in real-world scenarios. The code is available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/SpGesture.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge