Jingjing Li
AC^2-VLA: Action-Context-Aware Adaptive Computation in Vision-Language-Action Models for Efficient Robotic Manipulation
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models have demonstrated strong performance in robotic manipulation, yet their closed-loop deployment is hindered by the high latency and compute cost of repeatedly running large vision-language backbones at every timestep. We observe that VLA inference exhibits structured redundancies across temporal, spatial, and depth dimensions, and that most existing efficiency methods ignore action context, despite its central role in embodied tasks. To address this gap, we propose Action-Context-aware Adaptive Computation for VLA models (AC^2-VLA), a unified framework that conditions computation on current visual observations, language instructions, and previous action states. Based on this action-centric context, AC^2-VLA adaptively performs cognition reuse across timesteps, token pruning, and selective execution of model components within a unified mechanism. To train the adaptive policy, we introduce an action-guided self-distillation scheme that preserves the behavior of the dense VLA policy while enabling structured sparsification that transfers across tasks and settings. Extensive experiments on robotic manipulation benchmarks show that AC^2-VLA achieves up to a 1.79\times speedup while reducing FLOPs to 29.4% of the dense baseline, with comparable task success.
Learning ORDER-Aware Multimodal Representations for Composite Materials Design
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:Artificial intelligence (AI) has shown remarkable success in materials discovery and property prediction, particularly for crystalline and polymer systems where material properties and structures are dominated by discrete graph representations. Such graph-central paradigm breaks down on composite materials, which possess continuous and nonlinear design spaces that lack well-defined graph structures. General composite descriptors, e.g., fiber volume and misalignment angle, cannot fully capture the fiber distributions that fundamentally determine microstructural characteristics, necessitating the integration of heterogeneous data sources through multimodal learning. Existing alignment-oriented multimodal frameworks have proven effective on abundant crystal or polymer data under discrete, unique graph-property mapping assumptions, but fail to address the highly continuous composite design space under extreme data scarcity. In this work, we introduce ORDinal-aware imagE-tabulaR alignment (ORDER), a multimodal pretraining framework that establishes ordinality as a core principle for composite material representations. ORDER ensures that materials with similar target properties occupy nearby regions in the latent space, which effectively preserves the continuous nature of composite properties and enables meaningful interpolation between sparsely observed designs. We evaluate ORDER on a public Nanofiber-enforced composite dataset and an internally curated dataset that simulates the construction of carbon fiber T700 with diverse fiber distributions. ORDER achieves consistent improvements over state-of-the-art multimodal baselines across property prediction, cross-modal retrieval, and microstructure generation tasks.
Surgical Scene Segmentation using a Spike-Driven Video Transformer with Real-Time Potential
Dec 24, 2025Abstract:Modern surgical systems increasingly rely on intelligent scene understanding to provide timely situational awareness for enhanced intra-operative safety. Within this pipeline, surgical scene segmentation plays a central role in accurately perceiving operative events. Although recent deep learning models, particularly large-scale foundation models, achieve remarkable segmentation accuracy, their substantial computational demands and power consumption hinder real-time deployment in resource-constrained surgical environments. To address this limitation, we explore the emerging SNN as a promising paradigm for highly efficient surgical intelligence. However, their performance is still constrained by the scarcity of labeled surgical data and the inherently sparse nature of surgical video representations. To this end, we propose \textit{SpikeSurgSeg}, the first spike-driven video Transformer framework tailored for surgical scene segmentation with real-time potential on non-GPU platforms. To address the limited availability of surgical annotations, we introduce a surgical-scene masked autoencoding pretraining strategy for SNNs that enables robust spatiotemporal representation learning via layer-wise tube masking. Building on this pretrained backbone, we further adopt a lightweight spike-driven segmentation head that produces temporally consistent predictions while preserving the low-latency characteristics of SNNs. Extensive experiments on EndoVis18 and our in-house SurgBleed dataset demonstrate that SpikeSurgSeg achieves mIoU comparable to SOTA ANN-based models while reducing inference latency by at least $8\times$. Notably, it delivers over $20\times$ acceleration relative to most foundation-model baselines, underscoring its potential for time-critical surgical scene segmentation.
The Devil is in Attention Sharing: Improving Complex Non-rigid Image Editing Faithfulness via Attention Synergy
Dec 17, 2025Abstract:Training-free image editing with large diffusion models has become practical, yet faithfully performing complex non-rigid edits (e.g., pose or shape changes) remains highly challenging. We identify a key underlying cause: attention collapse in existing attention sharing mechanisms, where either positional embeddings or semantic features dominate visual content retrieval, leading to over-editing or under-editing. To address this issue, we introduce SynPS, a method that Synergistically leverages Positional embeddings and Semantic information for faithful non-rigid image editing. We first propose an editing measurement that quantifies the required editing magnitude at each denoising step. Based on this measurement, we design an attention synergy pipeline that dynamically modulates the influence of positional embeddings, enabling SynPS to balance semantic modifications and fidelity preservation. By adaptively integrating positional and semantic cues, SynPS effectively avoids both over- and under-editing. Extensive experiments on public and newly curated benchmarks demonstrate the superior performance and faithfulness of our approach.
Distributed Zero-Shot Learning for Visual Recognition
Nov 11, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we propose a Distributed Zero-Shot Learning (DistZSL) framework that can fully exploit decentralized data to learn an effective model for unseen classes. Considering the data heterogeneity issues across distributed nodes, we introduce two key components to ensure the effective learning of DistZSL: a cross-node attribute regularizer and a global attribute-to-visual consensus. Our proposed cross-node attribute regularizer enforces the distances between attribute features to be similar across different nodes. In this manner, the overall attribute feature space would be stable during learning, and thus facilitate the establishment of visual-to-attribute(V2A) relationships. Then, we introduce the global attribute-tovisual consensus to mitigate biased V2A mappings learned from individual nodes. Specifically, we enforce the bilateral mapping between the attribute and visual feature distributions to be consistent across different nodes. Thus, the learned consistent V2A mapping can significantly enhance zero-shot learning across different nodes. Extensive experiments demonstrate that DistZSL achieves superior performance to the state-of-the-art in learning from distributed data.
Acquiring Common Chinese Emotional Events Using Large Language Model
Nov 07, 2025Abstract:Knowledge about emotional events is an important kind of knowledge which has been applied to improve the effectiveness of different applications. However, emotional events cannot be easily acquired, especially common or generalized emotional events that are context-independent. The goal of this paper is to obtain common emotional events in Chinese language such as "win a prize" and "be criticized". Our approach begins by collecting a comprehensive list of Chinese emotional event indicators. Then, we generate emotional events by prompting a Chinese large language model (LLM) using these indicators. To ensure the quality of these emotional events, we train a filter to discard invalid generated results. We also classify these emotional events as being positive events and negative events using different techniques. Finally, we harvest a total of 102,218 high-quality common emotional events with sentiment polarity labels, which is the only large-scale commonsense knowledge base of emotional events in Chinese language. Intrinsic evaluation results show that the proposed method in this paper can be effectively used to acquire common Chinese emotional events. An extrinsic use case also demonstrates the strong potential of common emotional events in the field of emotion cause extraction (ECE). Related resources including emotional event indicators and emotional events will be released after the publication of this paper.
FootFormer: Estimating Stability from Visual Input
Oct 22, 2025Abstract:We propose FootFormer, a cross-modality approach for jointly predicting human motion dynamics directly from visual input. On multiple datasets, FootFormer achieves statistically significantly better or equivalent estimates of foot pressure distributions, foot contact maps, and center of mass (CoM), as compared with existing methods that generate one or two of those measures. Furthermore, FootFormer achieves SOTA performance in estimating stability-predictive components (CoP, CoM, BoS) used in classic kinesiology metrics. Code and data are available at https://github.com/keatonkraiger/Vision-to-Stability.git.
ViTs: Teaching Machines to See Time Series Anomalies Like Human Experts
Oct 06, 2025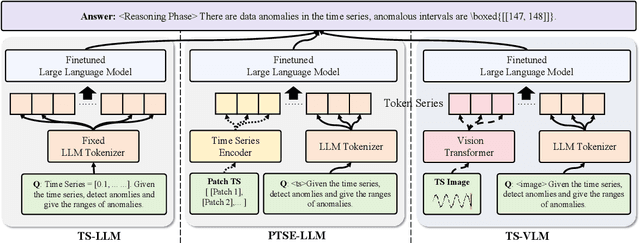
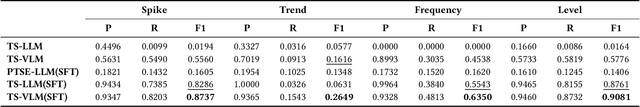
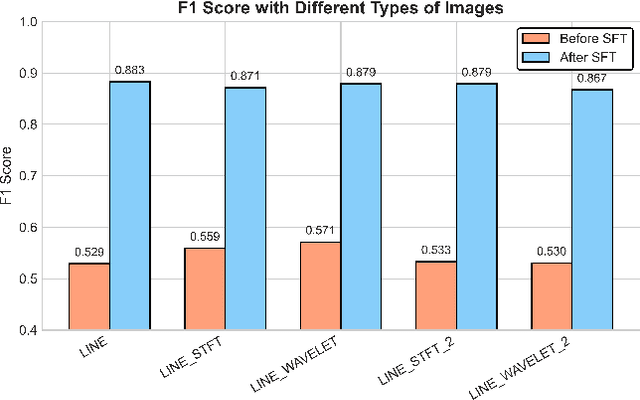
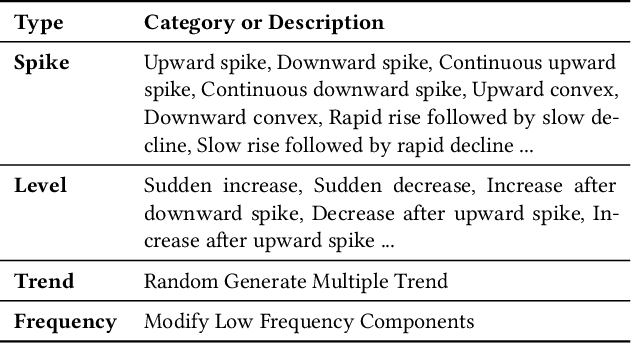
Abstract:Web service administrators must ensure the stability of multiple systems by promptly detecting anomalies in Key Performance Indicators (KPIs). Achieving the goal of "train once, infer across scenarios" remains a fundamental challenge for time series anomaly detection models. Beyond improving zero-shot generalization, such models must also flexibly handle sequences of varying lengths during inference, ranging from one hour to one week, without retraining. Conventional approaches rely on sliding-window encoding and self-supervised learning, which restrict inference to fixed-length inputs. Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable zero-shot capabilities across general domains. However, when applied to time series data, they face inherent limitations due to context length. To address this issue, we propose ViTs, a Vision-Language Model (VLM)-based framework that converts time series curves into visual representations. By rescaling time series images, temporal dependencies are preserved while maintaining a consistent input size, thereby enabling efficient processing of arbitrarily long sequences without context constraints. Training VLMs for this purpose introduces unique challenges, primarily due to the scarcity of aligned time series image-text data. To overcome this, we employ an evolutionary algorithm to automatically generate thousands of high-quality image-text pairs and design a three-stage training pipeline consisting of: (1) time series knowledge injection, (2) anomaly detection enhancement, and (3) anomaly reasoning refinement. Extensive experiments demonstrate that ViTs substantially enhance the ability of VLMs to understand and detect anomalies in time series data. All datasets and code will be publicly released at: https://anonymous.4open.science/r/ViTs-C484/.
Fast, Slow, and Tool-augmented Thinking for LLMs: A Review
Aug 17, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable progress in reasoning across diverse domains. However, effective reasoning in real-world tasks requires adapting the reasoning strategy to the demands of the problem, ranging from fast, intuitive responses to deliberate, step-by-step reasoning and tool-augmented thinking. Drawing inspiration from cognitive psychology, we propose a novel taxonomy of LLM reasoning strategies along two knowledge boundaries: a fast/slow boundary separating intuitive from deliberative processes, and an internal/external boundary distinguishing reasoning grounded in the model's parameters from reasoning augmented by external tools. We systematically survey recent work on adaptive reasoning in LLMs and categorize methods based on key decision factors. We conclude by highlighting open challenges and future directions toward more adaptive, efficient, and reliable LLMs.
Unified modality separation: A vision-language framework for unsupervised domain adaptation
Aug 07, 2025



Abstract:Unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA) enables models trained on a labeled source domain to handle new unlabeled domains. Recently, pre-trained vision-language models (VLMs) have demonstrated promising zero-shot performance by leveraging semantic information to facilitate target tasks. By aligning vision and text embeddings, VLMs have shown notable success in bridging domain gaps. However, inherent differences naturally exist between modalities, which is known as modality gap. Our findings reveal that direct UDA with the presence of modality gap only transfers modality-invariant knowledge, leading to suboptimal target performance. To address this limitation, we propose a unified modality separation framework that accommodates both modality-specific and modality-invariant components. During training, different modality components are disentangled from VLM features then handled separately in a unified manner. At test time, modality-adaptive ensemble weights are automatically determined to maximize the synergy of different components. To evaluate instance-level modality characteristics, we design a modality discrepancy metric to categorize samples into modality-invariant, modality-specific, and uncertain ones. The modality-invariant samples are exploited to facilitate cross-modal alignment, while uncertain ones are annotated to enhance model capabilities. Building upon prompt tuning techniques, our methods achieve up to 9% performance gain with 9 times of computational efficiencies. Extensive experiments and analysis across various backbones, baselines, datasets and adaptation settings demonstrate the efficacy of our design.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge