Heng Tao Shen
Beyond the Majority: Long-tail Imitation Learning for Robotic Manipulation
Feb 06, 2026Abstract:While generalist robot policies hold significant promise for learning diverse manipulation skills through imitation, their performance is often hindered by the long-tail distribution of training demonstrations. Policies learned on such data, which is heavily skewed towards a few data-rich head tasks, frequently exhibit poor generalization when confronted with the vast number of data-scarce tail tasks. In this work, we conduct a comprehensive analysis of the pervasive long-tail challenge inherent in policy learning. Our analysis begins by demonstrating the inefficacy of conventional long-tail learning strategies (e.g., re-sampling) for improving the policy's performance on tail tasks. We then uncover the underlying mechanism for this failure, revealing that data scarcity on tail tasks directly impairs the policy's spatial reasoning capability. To overcome this, we introduce Approaching-Phase Augmentation (APA), a simple yet effective scheme that transfers knowledge from data-rich head tasks to data-scarce tail tasks without requiring external demonstrations. Extensive experiments in both simulation and real-world manipulation tasks demonstrate the effectiveness of APA. Our code and demos are publicly available at: https://mldxy.github.io/Project-VLA-long-tail/.
Sim-and-Human Co-training for Data-Efficient and Generalizable Robotic Manipulation
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Synthetic simulation data and real-world human data provide scalable alternatives to circumvent the prohibitive costs of robot data collection. However, these sources suffer from the sim-to-real visual gap and the human-to-robot embodiment gap, respectively, which limits the policy's generalization to real-world scenarios. In this work, we identify a natural yet underexplored complementarity between these sources: simulation offers the robot action that human data lacks, while human data provides the real-world observation that simulation struggles to render. Motivated by this insight, we present SimHum, a co-training framework to simultaneously extract kinematic prior from simulated robot actions and visual prior from real-world human observations. Based on the two complementary priors, we achieve data-efficient and generalizable robotic manipulation in real-world tasks. Empirically, SimHum outperforms the baseline by up to $\mathbf{40\%}$ under the same data collection budget, and achieves a $\mathbf{62.5\%}$ OOD success with only 80 real data, outperforming the real only baseline by $7.1\times$. Videos and additional information can be found at \href{https://kaipengfang.github.io/sim-and-human}{project website}.
GRASP: Guided Region-Aware Sparse Prompting for Adapting MLLMs to Remote Sensing
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:In recent years, Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have made significant progress in visual question answering tasks. However, directly applying existing fine-tuning methods to remote sensing (RS) images often leads to issues such as overfitting on background noise or neglecting target details. This is primarily due to the large-scale variations, sparse target distributions, and complex regional semantic features inherent in RS images. These challenges limit the effectiveness of MLLMs in RS tasks. To address these challenges, we propose a parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) strategy called Guided Region-Aware Sparse Prompting (GRASP). GRASP introduces spatially structured soft prompts associated with spatial blocks extracted from a frozen visual token grid. Through a question-guided sparse fusion mechanism, GRASP dynamically aggregates task-specific context into a compact global prompt, enabling the model to focus on relevant regions while filtering out background noise. Extensive experiments on multiple RSVQA benchmarks show that GRASP achieves competitive performance compared to existing fine-tuning and prompt-based methods while maintaining high parameter efficiency.
RISER: Orchestrating Latent Reasoning Skills for Adaptive Activation Steering
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:Recent work on domain-specific reasoning with large language models (LLMs) often relies on training-intensive approaches that require parameter updates. While activation steering has emerged as a parameter efficient alternative, existing methods apply static, manual interventions that fail to adapt to the dynamic nature of complex reasoning. To address this limitation, we propose RISER (Router-based Intervention for Steerable Enhancement of Reasoning), a plug-and-play intervention framework that adaptively steers LLM reasoning in activation space. RISER constructs a library of reusable reasoning vectors and employs a lightweight Router to dynamically compose them for each input. The Router is optimized via reinforcement learning under task-level rewards, activating latent cognitive primitives in an emergent and compositional manner. Across seven diverse benchmarks, RISER yields 3.4-6.5% average zero-shot accuracy improvements over the base model while surpassing CoT-style reasoning with 2-3x higher token efficiency and robust accuracy gains. Further analysis shows that RISER autonomously combines multiple vectors into interpretable, precise control strategies, pointing toward more controllable and efficient LLM reasoning.
Unleashing the Potential of Neighbors: Diffusion-based Latent Neighbor Generation for Session-based Recommendation
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Session-based recommendation aims to predict the next item that anonymous users may be interested in, based on their current session interactions. Recent studies have demonstrated that retrieving neighbor sessions to augment the current session can effectively alleviate the data sparsity issue and improve recommendation performance. However, existing methods typically rely on explicitly observed session data, neglecting latent neighbors - not directly observed but potentially relevant within the interest space - thereby failing to fully exploit the potential of neighbor sessions in recommendation. To address the above limitation, we propose a novel model of diffusion-based latent neighbor generation for session-based recommendation, named DiffSBR. Specifically, DiffSBR leverages two diffusion modules, including retrieval-augmented diffusion and self-augmented diffusion, to generate high-quality latent neighbors. In the retrieval-augmented diffusion module, we leverage retrieved neighbors as guiding signals to constrain and reconstruct the distribution of latent neighbors. Meanwhile, we adopt a training strategy that enables the retriever to learn from the feedback provided by the generator. In the self-augmented diffusion module, we explicitly guide the generation of latent neighbors by injecting the current session's multi-modal signals through contrastive learning. After obtaining the generated latent neighbors, we utilize them to enhance session representations for improving session-based recommendation. Extensive experiments on four public datasets show that DiffSBR generates effective latent neighbors and improves recommendation performance against state-of-the-art baselines.
Fast SAM2 with Text-Driven Token Pruning
Dec 24, 2025Abstract:Segment Anything Model 2 (SAM2), a vision foundation model has significantly advanced in prompt-driven video object segmentation, yet their practical deployment remains limited by the high computational and memory cost of processing dense visual tokens across time. The SAM2 pipelines typically propagate all visual tokens produced by the image encoder through downstream temporal reasoning modules, regardless of their relevance to the target object, resulting in reduced scalability due to quadratic memory attention overhead. In this work, we introduce a text-guided token pruning framework that improves inference efficiency by selectively reducing token density prior to temporal propagation, without modifying the underlying segmentation architecture. Operating after visual encoding and before memory based propagation, our method ranks tokens using a lightweight routing mechanism that integrates local visual context, semantic relevance derived from object-centric textual descriptions (either user-provided or automatically generated), and uncertainty cues that help preserve ambiguous or boundary critical regions. By retaining only the most informative tokens for downstream processing, the proposed approach reduces redundant computation while maintaining segmentation fidelity. Extensive experiments across multiple challenging video segmentation benchmarks demonstrate that post-encoder token pruning provides a practical and effective pathway to efficient, prompt-aware video segmentation, achieving up to 42.50 percent faster inference and 37.41 percent lower GPU memory usage compared to the unpruned baseline SAM2, while preserving competitive J and F performance. These results highlight the potential of early token selection to improve the scalability of transformer-based video segmentation systems for real-time and resource-constrained applications.
MiVLA: Towards Generalizable Vision-Language-Action Model with Human-Robot Mutual Imitation Pre-training
Dec 19, 2025Abstract:While leveraging abundant human videos and simulated robot data poses a scalable solution to the scarcity of real-world robot data, the generalization capability of existing vision-language-action models (VLAs) remains limited by mismatches in camera views, visual appearance, and embodiment morphologies. To overcome this limitation, we propose MiVLA, a generalizable VLA empowered by human-robot mutual imitation pre-training, which leverages inherent behavioral similarity between human hands and robotic arms to build a foundation of strong behavioral priors for both human actions and robotic control. Specifically, our method utilizes kinematic rules with left/right hand coordinate systems for bidirectional alignment between human and robot action spaces. Given human or simulated robot demonstrations, MiVLA is trained to forecast behavior trajectories for one embodiment, and imitate behaviors for another one unseen in the demonstration. Based on this mutual imitation, it integrates the behavioral fidelity of real-world human data with the manipulative diversity of simulated robot data into a unified model, thereby enhancing the generalization capability for downstream tasks. Extensive experiments conducted on both simulation and real-world platforms with three robots (ARX, PiPer and LocoMan), demonstrate that MiVLA achieves strong improved generalization capability, outperforming state-of-the-art VLAs (e.g., $\boldsymbolπ_{0}$, $\boldsymbolπ_{0.5}$ and H-RDT) by 25% in simulation, and 14% in real-world robot control tasks.
A Semantically Enhanced Generative Foundation Model Improves Pathological Image Synthesis
Dec 16, 2025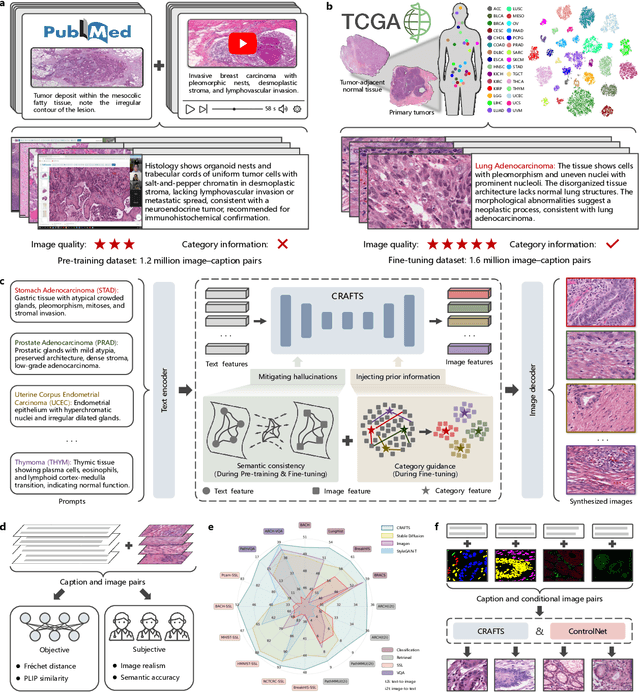
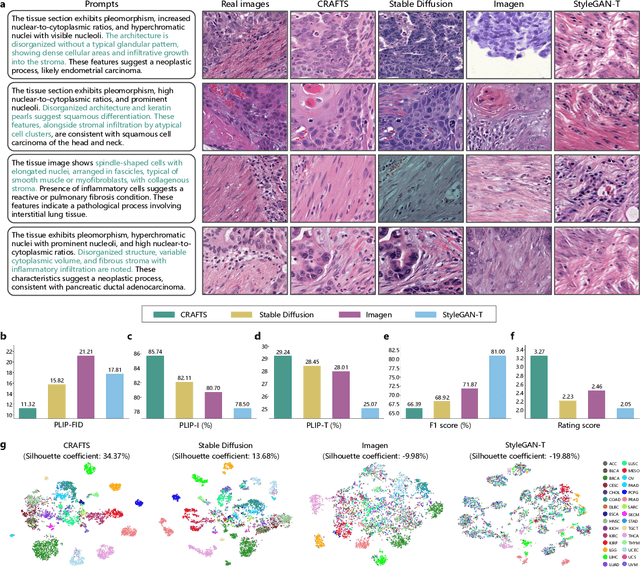
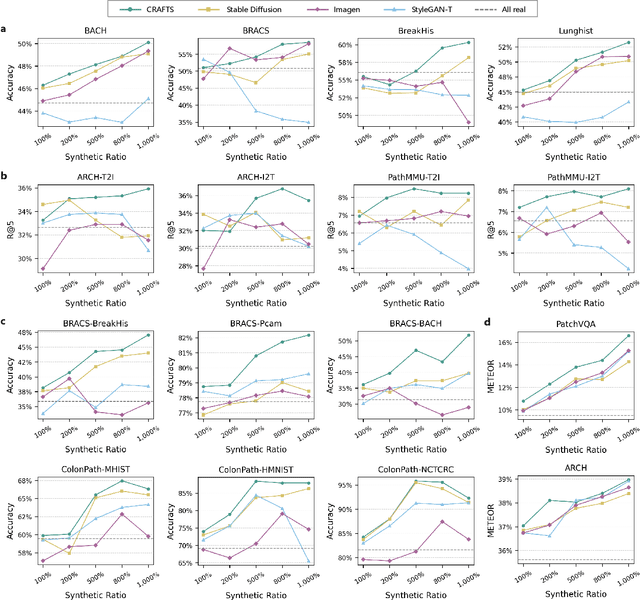
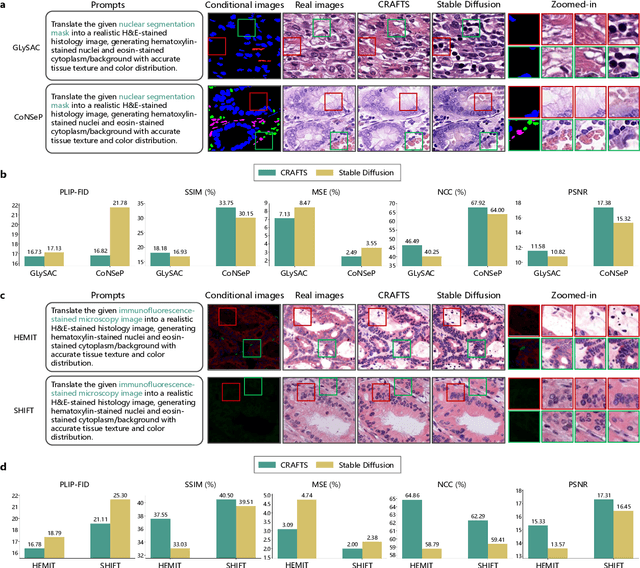
Abstract:The development of clinical-grade artificial intelligence in pathology is limited by the scarcity of diverse, high-quality annotated datasets. Generative models offer a potential solution but suffer from semantic instability and morphological hallucinations that compromise diagnostic reliability. To address this challenge, we introduce a Correlation-Regulated Alignment Framework for Tissue Synthesis (CRAFTS), the first generative foundation model for pathology-specific text-to-image synthesis. By leveraging a dual-stage training strategy on approximately 2.8 million image-caption pairs, CRAFTS incorporates a novel alignment mechanism that suppresses semantic drift to ensure biological accuracy. This model generates diverse pathological images spanning 30 cancer types, with quality rigorously validated by objective metrics and pathologist evaluations. Furthermore, CRAFTS-augmented datasets enhance the performance across various clinical tasks, including classification, cross-modal retrieval, self-supervised learning, and visual question answering. In addition, coupling CRAFTS with ControlNet enables precise control over tissue architecture from inputs such as nuclear segmentation masks and fluorescence images. By overcoming the critical barriers of data scarcity and privacy concerns, CRAFTS provides a limitless source of diverse, annotated histology data, effectively unlocking the creation of robust diagnostic tools for rare and complex cancer phenotypes.
Explore Briefly, Then Decide: Mitigating LLM Overthinking via Cumulative Entropy Regulation
Oct 02, 2025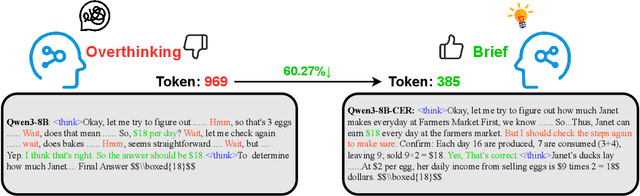
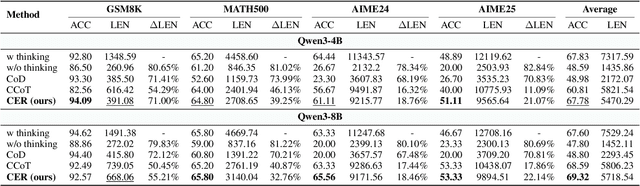
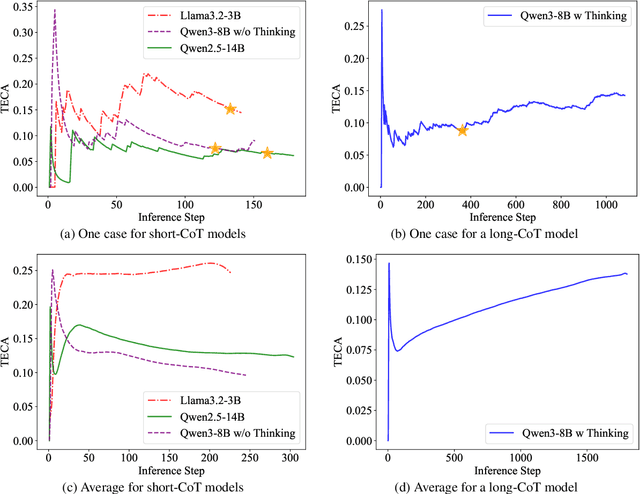
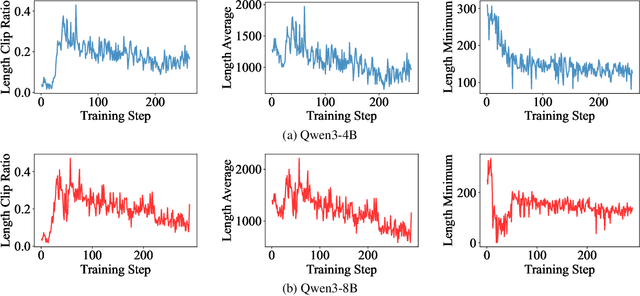
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable reasoning abilities on complex problems using long Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning. However, they often suffer from overthinking, meaning generating unnecessarily lengthy reasoning steps for simpler problems. This issue may degrade the efficiency of the models and make them difficult to adapt the reasoning depth to the complexity of problems. To address this, we introduce a novel metric Token Entropy Cumulative Average (TECA), which measures the extent of exploration throughout the reasoning process. We further propose a novel reasoning paradigm -- Explore Briefly, Then Decide -- with an associated Cumulative Entropy Regulation (CER) mechanism. This paradigm leverages TECA to help the model dynamically determine the optimal point to conclude its thought process and provide a final answer, thus achieving efficient reasoning. Experimental results across diverse mathematical benchmarks show that our approach substantially mitigates overthinking without sacrificing problem-solving ability. With our thinking paradigm, the average response length decreases by up to 71% on simpler datasets, demonstrating the effectiveness of our method in creating a more efficient and adaptive reasoning process.
GeoPurify: A Data-Efficient Geometric Distillation Framework for Open-Vocabulary 3D Segmentation
Oct 02, 2025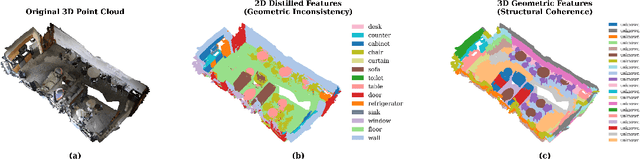
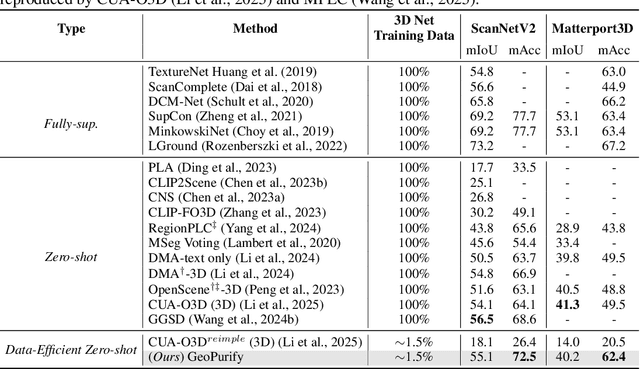
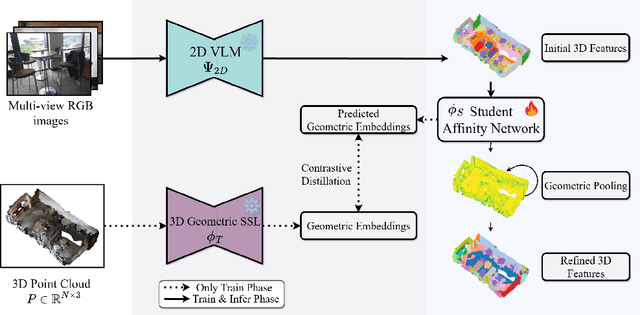
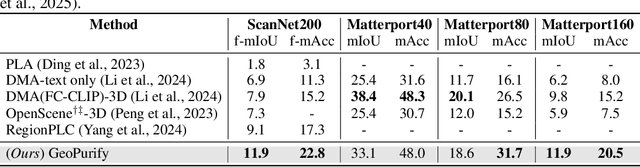
Abstract:Recent attempts to transfer features from 2D Vision-Language Models (VLMs) to 3D semantic segmentation expose a persistent trade-off. Directly projecting 2D features into 3D yields noisy and fragmented predictions, whereas enforcing geometric coherence necessitates costly training pipelines and large-scale annotated 3D data. We argue that this limitation stems from the dominant segmentation-and-matching paradigm, which fails to reconcile 2D semantics with 3D geometric structure. The geometric cues are not eliminated during the 2D-to-3D transfer but remain latent within the noisy and view-aggregated features. To exploit this property, we propose GeoPurify that applies a small Student Affinity Network to purify 2D VLM-generated 3D point features using geometric priors distilled from a 3D self-supervised teacher model. During inference, we devise a Geometry-Guided Pooling module to further denoise the point cloud and ensure the semantic and structural consistency. Benefiting from latent geometric information and the learned affinity network, GeoPurify effectively mitigates the trade-off and achieves superior data efficiency. Extensive experiments on major 3D benchmarks demonstrate that GeoPurify achieves or surpasses state-of-the-art performance while utilizing only about 1.5% of the training data. Our codes and checkpoints are available at [https://github.com/tj12323/GeoPurify](https://github.com/tj12323/GeoPurify).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge