Sheng Zheng
LLaVA-FA: Learning Fourier Approximation for Compressing Large Multimodal Models
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Large multimodal models (LMMs) have achieved impressive performance on various vision-language tasks, but their substantial computational and memory costs hinder their practical deployment. Existing compression methods often decouple low-rank decomposition and quantization, leading to compounded reconstruction errors, especially in multimodal architectures with cross-modal redundancy. To address this issue, we propose LLaVA-FA, a novel efficient LMM that performs joint low-rank plus quantization approximation in the frequency domain. By leveraging the de-correlation and conjugate symmetry properties of Fourier transform, LLaVA-FA achieves more compact and accurate weight representations. Furthermore, we introduce PolarQuant, a polar-coordinate quantization method tailored for complex matrices, and an optional diagonal calibration (ODC) scheme that eliminates the need for large-scale calibration data. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that our proposed LLaVA-FA outperforms existing efficient multimodal models across multiple benchmarks while maintaining minimal activated parameters and low computational costs, validating its effectiveness as a powerful solution for compressing LMMs.
Exploring Kernel Transformations for Implicit Neural Representations
Apr 07, 2025Abstract:Implicit neural representations (INRs), which leverage neural networks to represent signals by mapping coordinates to their corresponding attributes, have garnered significant attention. They are extensively utilized for image representation, with pixel coordinates as input and pixel values as output. In contrast to prior works focusing on investigating the effect of the model's inside components (activation function, for instance), this work pioneers the exploration of the effect of kernel transformation of input/output while keeping the model itself unchanged. A byproduct of our findings is a simple yet effective method that combines scale and shift to significantly boost INR with negligible computation overhead. Moreover, we present two perspectives, depth and normalization, to interpret the performance benefits caused by scale and shift transformation. Overall, our work provides a new avenue for future works to understand and improve INR through the lens of kernel transformation.
Sora as an AGI World Model? A Complete Survey on Text-to-Video Generation
Mar 08, 2024


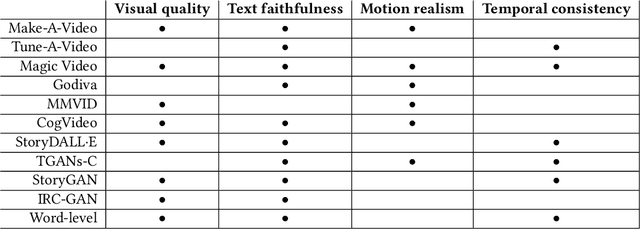
Abstract:Text-to-video generation marks a significant frontier in the rapidly evolving domain of generative AI, integrating advancements in text-to-image synthesis, video captioning, and text-guided editing. This survey critically examines the progression of text-to-video technologies, focusing on the shift from traditional generative models to the cutting-edge Sora model, highlighting developments in scalability and generalizability. Distinguishing our analysis from prior works, we offer an in-depth exploration of the technological frameworks and evolutionary pathways of these models. Additionally, we delve into practical applications and address ethical and technological challenges such as the inability to perform multiple entity handling, comprehend causal-effect learning, understand physical interaction, perceive object scaling and proportioning, and combat object hallucination which is also a long-standing problem in generative models. Our comprehensive discussion covers the topic of enablement of text-to-video generation models as human-assistive tools and world models, as well as eliciting model's shortcomings and summarizing future improvement direction that mainly centers around training datasets and evaluation metrics (both automatic and human-centered). Aimed at both newcomers and seasoned researchers, this survey seeks to catalyze further innovation and discussion in the growing field of text-to-video generation, paving the way for more reliable and practical generative artificial intelligence technologies.
MobileSAMv2: Faster Segment Anything to Everything
Dec 15, 2023Abstract:Segment anything model (SAM) addresses two practical yet challenging segmentation tasks: \textbf{segment anything (SegAny)}, which utilizes a certain point to predict the mask for a single object of interest, and \textbf{segment everything (SegEvery)}, which predicts the masks for all objects on the image. What makes SegAny slow for SAM is its heavyweight image encoder, which has been addressed by MobileSAM via decoupled knowledge distillation. The efficiency bottleneck of SegEvery with SAM, however, lies in its mask decoder because it needs to first generate numerous masks with redundant grid-search prompts and then perform filtering to obtain the final valid masks. We propose to improve its efficiency by directly generating the final masks with only valid prompts, which can be obtained through object discovery. Our proposed approach not only helps reduce the total time on the mask decoder by at least 16 times but also achieves superior performance. Specifically, our approach yields an average performance boost of 3.6\% (42.5\% \textit{v.s.} 38.9\%) for zero-shot object proposal on the LVIS dataset with the mask AR@$K$ metric. Qualitative results show that our approach generates fine-grained masks while avoiding over-segmenting things. This project targeting faster SegEvery than the original SAM is termed MobileSAMv2 to differentiate from MobileSAM which targets faster SegAny. Moreover, we demonstrate that our new prompt sampling is also compatible with the distilled image encoders in MobileSAM, contributing to a unified framework for efficient SegAny and SegEvery. The code is available at the same link as MobileSAM Project \href{https://github.com/ChaoningZhang/MobileSAM}{\textcolor{red}{https://github.com/ChaoningZhang/MobileSAM}}. \end{abstract}
Segment Anything Meets Universal Adversarial Perturbation
Oct 19, 2023



Abstract:As Segment Anything Model (SAM) becomes a popular foundation model in computer vision, its adversarial robustness has become a concern that cannot be ignored. This works investigates whether it is possible to attack SAM with image-agnostic Universal Adversarial Perturbation (UAP). In other words, we seek a single perturbation that can fool the SAM to predict invalid masks for most (if not all) images. We demonstrate convetional image-centric attack framework is effective for image-independent attacks but fails for universal adversarial attack. To this end, we propose a novel perturbation-centric framework that results in a UAP generation method based on self-supervised contrastive learning (CL), where the UAP is set to the anchor sample and the positive sample is augmented from the UAP. The representations of negative samples are obtained from the image encoder in advance and saved in a memory bank. The effectiveness of our proposed CL-based UAP generation method is validated by both quantitative and qualitative results. On top of the ablation study to understand various components in our proposed method, we shed light on the roles of positive and negative samples in making the generated UAP effective for attacking SAM.
Black-box Targeted Adversarial Attack on Segment Anything (SAM)
Oct 16, 2023



Abstract:Deep recognition models are widely vulnerable to adversarial examples, which change the model output by adding quasi-imperceptible perturbation to the image input. Recently, Segment Anything Model (SAM) has emerged to become a popular foundation model in computer vision due to its impressive generalization to unseen data and tasks. Realizing flexible attacks on SAM is beneficial for understanding the robustness of SAM in the adversarial context. To this end, this work aims to achieve a targeted adversarial attack (TAA) on SAM. Specifically, under a certain prompt, the goal is to make the predicted mask of an adversarial example resemble that of a given target image. The task of TAA on SAM has been realized in a recent arXiv work in the white-box setup by assuming access to prompt and model, which is thus less practical. To address the issue of prompt dependence, we propose a simple yet effective approach by only attacking the image encoder. Moreover, we propose a novel regularization loss to enhance the cross-model transferability by increasing the feature dominance of adversarial images over random natural images. Extensive experiments verify the effectiveness of our proposed simple techniques to conduct a successful black-box TAA on SAM.
One Small Step for Generative AI, One Giant Leap for AGI: A Complete Survey on ChatGPT in AIGC Era
Apr 04, 2023Abstract:OpenAI has recently released GPT-4 (a.k.a. ChatGPT plus), which is demonstrated to be one small step for generative AI (GAI), but one giant leap for artificial general intelligence (AGI). Since its official release in November 2022, ChatGPT has quickly attracted numerous users with extensive media coverage. Such unprecedented attention has also motivated numerous researchers to investigate ChatGPT from various aspects. According to Google scholar, there are more than 500 articles with ChatGPT in their titles or mentioning it in their abstracts. Considering this, a review is urgently needed, and our work fills this gap. Overall, this work is the first to survey ChatGPT with a comprehensive review of its underlying technology, applications, and challenges. Moreover, we present an outlook on how ChatGPT might evolve to realize general-purpose AIGC (a.k.a. AI-generated content), which will be a significant milestone for the development of AGI.
A Survey on Audio Diffusion Models: Text To Speech Synthesis and Enhancement in Generative AI
Apr 02, 2023



Abstract:Generative AI has demonstrated impressive performance in various fields, among which speech synthesis is an interesting direction. With the diffusion model as the most popular generative model, numerous works have attempted two active tasks: text to speech and speech enhancement. This work conducts a survey on audio diffusion model, which is complementary to existing surveys that either lack the recent progress of diffusion-based speech synthesis or highlight an overall picture of applying diffusion model in multiple fields. Specifically, this work first briefly introduces the background of audio and diffusion model. As for the text-to-speech task, we divide the methods into three categories based on the stage where diffusion model is adopted: acoustic model, vocoder and end-to-end framework. Moreover, we categorize various speech enhancement tasks by either certain signals are removed or added into the input speech. Comparisons of experimental results and discussions are also covered in this survey.
A Complete Survey on Generative AI : Is ChatGPT from GPT-4 to GPT-5 All You Need?
Mar 21, 2023



Abstract:As ChatGPT goes viral, generative AI (AIGC, a.k.a AI-generated content) has made headlines everywhere because of its ability to analyze and create text, images, and beyond. With such overwhelming media coverage, it is almost impossible for us to miss the opportunity to glimpse AIGC from a certain angle. In the era of AI transitioning from pure analysis to creation, it is worth noting that ChatGPT, with its most recent language model GPT-4, is just a tool out of numerous AIGC tasks. Impressed by the capability of the ChatGPT, many people are wondering about its limits: can GPT-5 (or other future GPT variants) help ChatGPT unify all AIGC tasks for diversified content creation? Toward answering this question, a comprehensive review of existing AIGC tasks is needed. As such, our work comes to fill this gap promptly by offering a first look at AIGC, ranging from its techniques to applications. Modern generative AI relies on various technical foundations, ranging from model architecture and self-supervised pretraining to generative modeling methods (like GAN and diffusion models). After introducing the fundamental techniques, this work focuses on the technological development of various AIGC tasks based on their output type, including text, images, videos, 3D content, etc., which depicts the full potential of ChatGPT's future. Moreover, we summarize their significant applications in some mainstream industries, such as education and creativity content. Finally, we discuss the challenges currently faced and present an outlook on how generative AI might evolve in the near future.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge