Maryam Qamar
I-INR: Iterative Implicit Neural Representations
Apr 24, 2025Abstract:Implicit Neural Representations (INRs) have revolutionized signal processing and computer vision by modeling signals as continuous, differentiable functions parameterized by neural networks. However, their inherent formulation as a regression problem makes them prone to regression to the mean, limiting their ability to capture fine details, retain high-frequency information, and handle noise effectively. To address these challenges, we propose Iterative Implicit Neural Representations (I-INRs) a novel plug-and-play framework that enhances signal reconstruction through an iterative refinement process. I-INRs effectively recover high-frequency details, improve robustness to noise, and achieve superior reconstruction quality. Our framework seamlessly integrates with existing INR architectures, delivering substantial performance gains across various tasks. Extensive experiments show that I-INRs outperform baseline methods, including WIRE, SIREN, and Gauss, in diverse computer vision applications such as image restoration, image denoising, and object occupancy prediction.
Trimming the Fat: Efficient Compression of 3D Gaussian Splats through Pruning
Jun 26, 2024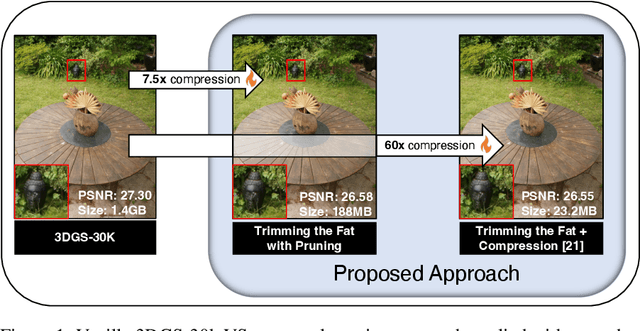
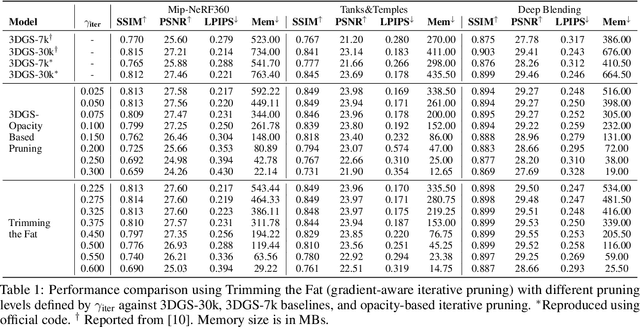
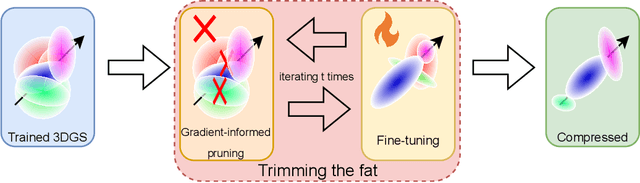
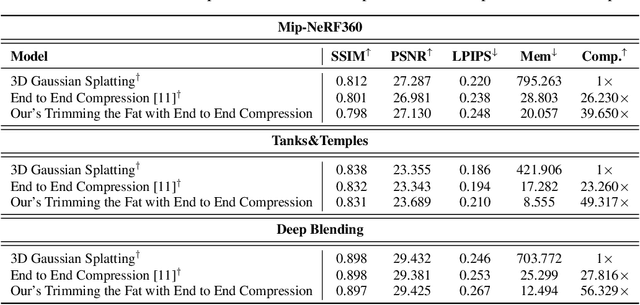
Abstract:In recent times, the utilization of 3D models has gained traction, owing to the capacity for end-to-end training initially offered by Neural Radiance Fields and more recently by 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) models. The latter holds a significant advantage by inherently easing rapid convergence during training and offering extensive editability. However, despite rapid advancements, the literature still lives in its infancy regarding the scalability of these models. In this study, we take some initial steps in addressing this gap, showing an approach that enables both the memory and computational scalability of such models. Specifically, we propose "Trimming the fat", a post-hoc gradient-informed iterative pruning technique to eliminate redundant information encoded in the model. Our experimental findings on widely acknowledged benchmarks attest to the effectiveness of our approach, revealing that up to 75% of the Gaussians can be removed while maintaining or even improving upon baseline performance. Our approach achieves around 50$\times$ compression while preserving performance similar to the baseline model, and is able to speed-up computation up to 600~FPS.
Segment Anything Model Meets Glass: Mirror and Transparent Objects Cannot Be Easily Detected
Apr 29, 2023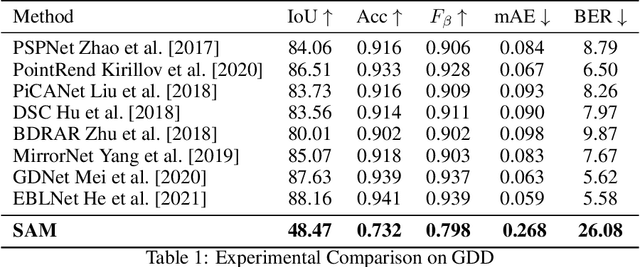
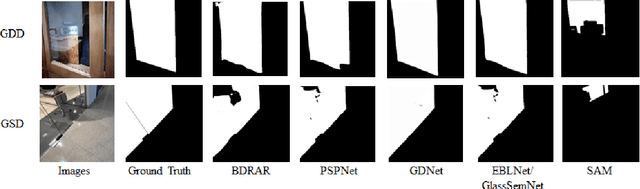
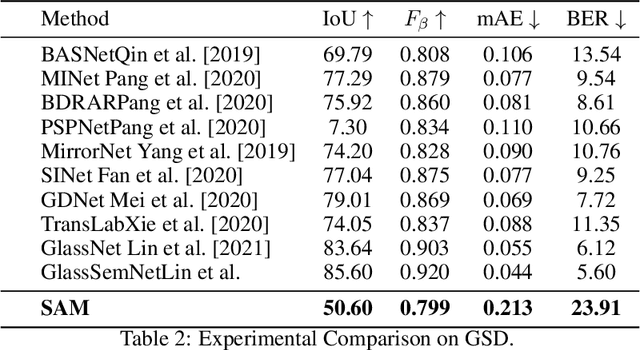

Abstract:Meta AI Research has recently released SAM (Segment Anything Model) which is trained on a large segmentation dataset of over 1 billion masks. As a foundation model in the field of computer vision, SAM (Segment Anything Model) has gained attention for its impressive performance in generic object segmentation. Despite its strong capability in a wide range of zero-shot transfer tasks, it remains unknown whether SAM can detect things in challenging setups like transparent objects. In this work, we perform an empirical evaluation of two glass-related challenging scenarios: mirror and transparent objects. We found that SAM often fails to detect the glass in both scenarios, which raises concern for deploying the SAM in safety-critical situations that have various forms of glass.
A Survey on Graph Diffusion Models: Generative AI in Science for Molecule, Protein and Material
Apr 04, 2023



Abstract:Diffusion models have become a new SOTA generative modeling method in various fields, for which there are multiple survey works that provide an overall survey. With the number of articles on diffusion models increasing exponentially in the past few years, there is an increasing need for surveys of diffusion models on specific fields. In this work, we are committed to conducting a survey on the graph diffusion models. Even though our focus is to cover the progress of diffusion models in graphs, we first briefly summarize how other generative modeling methods are used for graphs. After that, we introduce the mechanism of diffusion models in various forms, which facilitates the discussion on the graph diffusion models. The applications of graph diffusion models mainly fall into the category of AI-generated content (AIGC) in science, for which we mainly focus on how graph diffusion models are utilized for generating molecules and proteins but also cover other cases, including materials design. Moreover, we discuss the issue of evaluating diffusion models in the graph domain and the existing challenges.
A Survey on Audio Diffusion Models: Text To Speech Synthesis and Enhancement in Generative AI
Apr 02, 2023



Abstract:Generative AI has demonstrated impressive performance in various fields, among which speech synthesis is an interesting direction. With the diffusion model as the most popular generative model, numerous works have attempted two active tasks: text to speech and speech enhancement. This work conducts a survey on audio diffusion model, which is complementary to existing surveys that either lack the recent progress of diffusion-based speech synthesis or highlight an overall picture of applying diffusion model in multiple fields. Specifically, this work first briefly introduces the background of audio and diffusion model. As for the text-to-speech task, we divide the methods into three categories based on the stage where diffusion model is adopted: acoustic model, vocoder and end-to-end framework. Moreover, we categorize various speech enhancement tasks by either certain signals are removed or added into the input speech. Comparisons of experimental results and discussions are also covered in this survey.
Autonomous Drone Swarm Navigation and Multi-target Tracking in 3D Environments with Dynamic Obstacles
Feb 13, 2022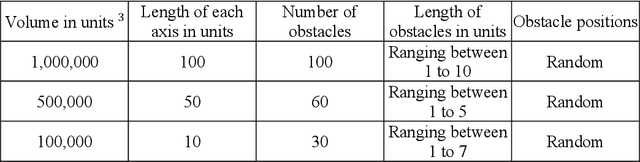
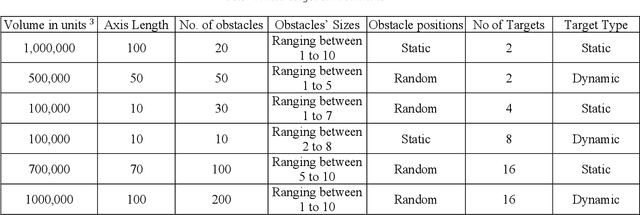

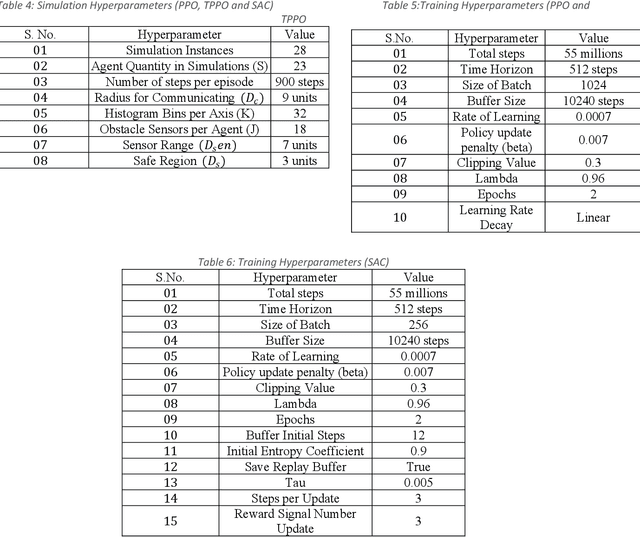
Abstract:Autonomous modeling of artificial swarms is necessary because manual creation is a time intensive and complicated procedure which makes it impractical. An autonomous approach employing deep reinforcement learning is presented in this study for swarm navigation. In this approach, complex 3D environments with static and dynamic obstacles and resistive forces (like linear drag, angular drag, and gravity) are modeled to track multiple dynamic targets. Moreover, reward functions for robust swarm formation and target tracking are devised for learning complex swarm behaviors. Since the number of agents is not fixed and has only the partial observance of the environment, swarm formation and navigation become challenging. In this regard, the proposed strategy consists of three main phases to tackle the aforementioned challenges: 1) A methodology for dynamic swarm management, 2) Avoiding obstacles, Finding the shortest path towards the targets, 3) Tracking the targets and Island modeling. The dynamic swarm management phase translates basic sensory input to high level commands to enhance swarm navigation and decentralized setup while maintaining the swarms size fluctuations. While, in the island modeling, the swarm can split into individual subswarms according to the number of targets, conversely, these subswarms may join to form a single huge swarm, giving the swarm ability to track multiple targets. Customized state of the art policy based deep reinforcement learning algorithms are employed to achieve significant results. The promising results show that our proposed strategy enhances swarm navigation and can track multiple static and dynamic targets in complex dynamic environments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge