Soo Ye Kim
G2P: Gaussian-to-Point Attribute Alignment for Boundary-Aware 3D Semantic Segmentation
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Semantic segmentation on point clouds is critical for 3D scene understanding. However, sparse and irregular point distributions provide limited appearance evidence, making geometry-only features insufficient to distinguish objects with similar shapes but distinct appearances (e.g., color, texture, material). We propose Gaussian-to-Point (G2P), which transfers appearance-aware attributes from 3D Gaussian Splatting to point clouds for more discriminative and appearance-consistent segmentation. Our G2P address the misalignment between optimized Gaussians and original point geometry by establishing point-wise correspondences. By leveraging Gaussian opacity attributes, we resolve the geometric ambiguity that limits existing models. Additionally, Gaussian scale attributes enable precise boundary localization in complex 3D scenes. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach achieves superior performance on standard benchmarks and shows significant improvements on geometrically challenging classes, all without any 2D or language supervision.
Both Semantics and Reconstruction Matter: Making Representation Encoders Ready for Text-to-Image Generation and Editing
Dec 19, 2025Abstract:Modern Latent Diffusion Models (LDMs) typically operate in low-level Variational Autoencoder (VAE) latent spaces that are primarily optimized for pixel-level reconstruction. To unify vision generation and understanding, a burgeoning trend is to adopt high-dimensional features from representation encoders as generative latents. However, we empirically identify two fundamental obstacles in this paradigm: (1) the discriminative feature space lacks compact regularization, making diffusion models prone to off-manifold latents that lead to inaccurate object structures; and (2) the encoder's inherently weak pixel-level reconstruction hinders the generator from learning accurate fine-grained geometry and texture. In this paper, we propose a systematic framework to adapt understanding-oriented encoder features for generative tasks. We introduce a semantic-pixel reconstruction objective to regularize the latent space, enabling the compression of both semantic information and fine-grained details into a highly compact representation (96 channels with 16x16 spatial downsampling). This design ensures that the latent space remains semantically rich and achieves state-of-the-art image reconstruction, while remaining compact enough for accurate generation. Leveraging this representation, we design a unified Text-to-Image (T2I) and image editing model. Benchmarking against various feature spaces, we demonstrate that our approach achieves state-of-the-art reconstruction, faster convergence, and substantial performance gains in both T2I and editing tasks, validating that representation encoders can be effectively adapted into robust generative components.
Frame Guidance: Training-Free Guidance for Frame-Level Control in Video Diffusion Models
Jun 08, 2025Abstract:Advancements in diffusion models have significantly improved video quality, directing attention to fine-grained controllability. However, many existing methods depend on fine-tuning large-scale video models for specific tasks, which becomes increasingly impractical as model sizes continue to grow. In this work, we present Frame Guidance, a training-free guidance for controllable video generation based on frame-level signals, such as keyframes, style reference images, sketches, or depth maps. For practical training-free guidance, we propose a simple latent processing method that dramatically reduces memory usage, and apply a novel latent optimization strategy designed for globally coherent video generation. Frame Guidance enables effective control across diverse tasks, including keyframe guidance, stylization, and looping, without any training, compatible with any video models. Experimental results show that Frame Guidance can produce high-quality controlled videos for a wide range of tasks and input signals.
I-INR: Iterative Implicit Neural Representations
Apr 24, 2025Abstract:Implicit Neural Representations (INRs) have revolutionized signal processing and computer vision by modeling signals as continuous, differentiable functions parameterized by neural networks. However, their inherent formulation as a regression problem makes them prone to regression to the mean, limiting their ability to capture fine details, retain high-frequency information, and handle noise effectively. To address these challenges, we propose Iterative Implicit Neural Representations (I-INRs) a novel plug-and-play framework that enhances signal reconstruction through an iterative refinement process. I-INRs effectively recover high-frequency details, improve robustness to noise, and achieve superior reconstruction quality. Our framework seamlessly integrates with existing INR architectures, delivering substantial performance gains across various tasks. Extensive experiments show that I-INRs outperform baseline methods, including WIRE, SIREN, and Gauss, in diverse computer vision applications such as image restoration, image denoising, and object occupancy prediction.
ObjectMover: Generative Object Movement with Video Prior
Mar 11, 2025Abstract:Simple as it seems, moving an object to another location within an image is, in fact, a challenging image-editing task that requires re-harmonizing the lighting, adjusting the pose based on perspective, accurately filling occluded regions, and ensuring coherent synchronization of shadows and reflections while maintaining the object identity. In this paper, we present ObjectMover, a generative model that can perform object movement in highly challenging scenes. Our key insight is that we model this task as a sequence-to-sequence problem and fine-tune a video generation model to leverage its knowledge of consistent object generation across video frames. We show that with this approach, our model is able to adjust to complex real-world scenarios, handling extreme lighting harmonization and object effect movement. As large-scale data for object movement are unavailable, we construct a data generation pipeline using a modern game engine to synthesize high-quality data pairs. We further propose a multi-task learning strategy that enables training on real-world video data to improve the model generalization. Through extensive experiments, we demonstrate that ObjectMover achieves outstanding results and adapts well to real-world scenarios.
Multitwine: Multi-Object Compositing with Text and Layout Control
Feb 07, 2025



Abstract:We introduce the first generative model capable of simultaneous multi-object compositing, guided by both text and layout. Our model allows for the addition of multiple objects within a scene, capturing a range of interactions from simple positional relations (e.g., next to, in front of) to complex actions requiring reposing (e.g., hugging, playing guitar). When an interaction implies additional props, like `taking a selfie', our model autonomously generates these supporting objects. By jointly training for compositing and subject-driven generation, also known as customization, we achieve a more balanced integration of textual and visual inputs for text-driven object compositing. As a result, we obtain a versatile model with state-of-the-art performance in both tasks. We further present a data generation pipeline leveraging visual and language models to effortlessly synthesize multimodal, aligned training data.
Generative Video Propagation
Dec 27, 2024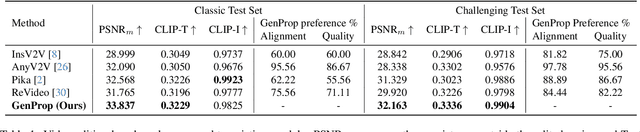
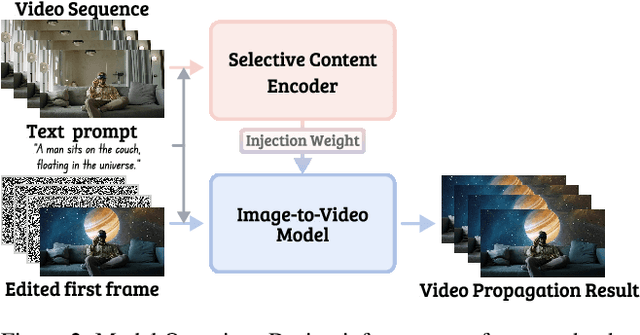
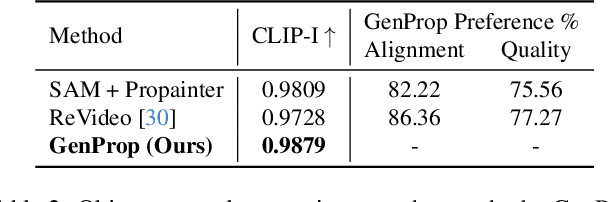
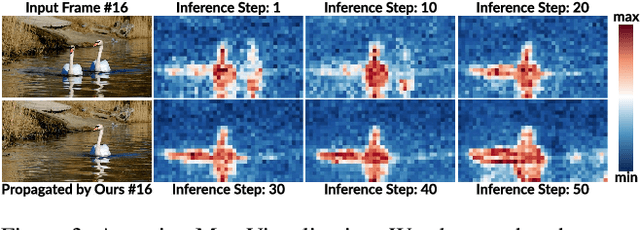
Abstract:Large-scale video generation models have the inherent ability to realistically model natural scenes. In this paper, we demonstrate that through a careful design of a generative video propagation framework, various video tasks can be addressed in a unified way by leveraging the generative power of such models. Specifically, our framework, GenProp, encodes the original video with a selective content encoder and propagates the changes made to the first frame using an image-to-video generation model. We propose a data generation scheme to cover multiple video tasks based on instance-level video segmentation datasets. Our model is trained by incorporating a mask prediction decoder head and optimizing a region-aware loss to aid the encoder to preserve the original content while the generation model propagates the modified region. This novel design opens up new possibilities: In editing scenarios, GenProp allows substantial changes to an object's shape; for insertion, the inserted objects can exhibit independent motion; for removal, GenProp effectively removes effects like shadows and reflections from the whole video; for tracking, GenProp is capable of tracking objects and their associated effects together. Experiment results demonstrate the leading performance of our model in various video tasks, and we further provide in-depth analyses of the proposed framework.
MIVE: New Design and Benchmark for Multi-Instance Video Editing
Dec 17, 2024



Abstract:Recent AI-based video editing has enabled users to edit videos through simple text prompts, significantly simplifying the editing process. However, recent zero-shot video editing techniques primarily focus on global or single-object edits, which can lead to unintended changes in other parts of the video. When multiple objects require localized edits, existing methods face challenges, such as unfaithful editing, editing leakage, and lack of suitable evaluation datasets and metrics. To overcome these limitations, we propose a zero-shot $\textbf{M}$ulti-$\textbf{I}$nstance $\textbf{V}$ideo $\textbf{E}$diting framework, called MIVE. MIVE is a general-purpose mask-based framework, not dedicated to specific objects (e.g., people). MIVE introduces two key modules: (i) Disentangled Multi-instance Sampling (DMS) to prevent editing leakage and (ii) Instance-centric Probability Redistribution (IPR) to ensure precise localization and faithful editing. Additionally, we present our new MIVE Dataset featuring diverse video scenarios and introduce the Cross-Instance Accuracy (CIA) Score to evaluate editing leakage in multi-instance video editing tasks. Our extensive qualitative, quantitative, and user study evaluations demonstrate that MIVE significantly outperforms recent state-of-the-art methods in terms of editing faithfulness, accuracy, and leakage prevention, setting a new benchmark for multi-instance video editing. The project page is available at https://kaist-viclab.github.io/mive-site/
UniReal: Universal Image Generation and Editing via Learning Real-world Dynamics
Dec 10, 2024



Abstract:We introduce UniReal, a unified framework designed to address various image generation and editing tasks. Existing solutions often vary by tasks, yet share fundamental principles: preserving consistency between inputs and outputs while capturing visual variations. Inspired by recent video generation models that effectively balance consistency and variation across frames, we propose a unifying approach that treats image-level tasks as discontinuous video generation. Specifically, we treat varying numbers of input and output images as frames, enabling seamless support for tasks such as image generation, editing, customization, composition, etc. Although designed for image-level tasks, we leverage videos as a scalable source for universal supervision. UniReal learns world dynamics from large-scale videos, demonstrating advanced capability in handling shadows, reflections, pose variation, and object interaction, while also exhibiting emergent capability for novel applications.
MetaShadow: Object-Centered Shadow Detection, Removal, and Synthesis
Dec 03, 2024



Abstract:Shadows are often under-considered or even ignored in image editing applications, limiting the realism of the edited results. In this paper, we introduce MetaShadow, a three-in-one versatile framework that enables detection, removal, and controllable synthesis of shadows in natural images in an object-centered fashion. MetaShadow combines the strengths of two cooperative components: Shadow Analyzer, for object-centered shadow detection and removal, and Shadow Synthesizer, for reference-based controllable shadow synthesis. Notably, we optimize the learning of the intermediate features from Shadow Analyzer to guide Shadow Synthesizer to generate more realistic shadows that blend seamlessly with the scene. Extensive evaluations on multiple shadow benchmark datasets show significant improvements of MetaShadow over the existing state-of-the-art methods on object-centered shadow detection, removal, and synthesis. MetaShadow excels in image-editing tasks such as object removal, relocation, and insertion, pushing the boundaries of object-centered image editing.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge