Wei Xiong
Gene regulatory network inference algorithm based on spectral signed directed graph convolution
Dec 12, 2025Abstract:Accurately reconstructing Gene Regulatory Networks (GRNs) is crucial for understanding gene functions and disease mechanisms. Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) technology provides vast data for computational GRN reconstruction. Since GRNs are ideally modeled as signed directed graphs to capture activation/inhibition relationships, the most intuitive and reasonable approach is to design feature extractors based on the topological structure of GRNs to extract structural features, then combine them with biological characteristics for research. However, traditional spectral graph convolution struggles with this representation. Thus, we propose MSGRNLink, a novel framework that explicitly models GRNs as signed directed graphs and employs magnetic signed Laplacian convolution. Experiments across simulated and real datasets demonstrate that MSGRNLink outperforms all baseline models in AUROC. Parameter sensitivity analysis and ablation studies confirmed its robustness and the importance of each module. In a bladder cancer case study, MSGRNLink predicted more known edges and edge signs than benchmark models, further validating its biological relevance.
Reinforce-Ada: An Adaptive Sampling Framework for Reinforce-Style LLM Training
Oct 06, 2025Abstract:Reinforcement learning applied to large language models (LLMs) for reasoning tasks is often bottlenecked by unstable gradient estimates due to fixed and uniform sampling of responses across prompts. Prior work such as GVM-RAFT addresses this by dynamically allocating inference budget per prompt to minimize stochastic gradient variance under a budget constraint. Inspired by this insight, we propose Reinforce-Ada, an adaptive sampling framework for online RL post-training of LLMs that continuously reallocates sampling effort to the prompts with the greatest uncertainty or learning potential. Unlike conventional two-stage allocation methods, Reinforce-Ada interleaves estimation and sampling in an online successive elimination process, and automatically stops sampling for a prompt once sufficient signal is collected. To stabilize updates, we form fixed-size groups with enforced reward diversity and compute advantage baselines using global statistics aggregated over the adaptive sampling phase. Empirical results across multiple model architectures and reasoning benchmarks show that Reinforce-Ada accelerates convergence and improves final performance compared to GRPO, especially when using the balanced sampling variant. Our work highlights the central role of variance-aware, adaptive data curation in enabling efficient and reliable reinforcement learning for reasoning-capable LLMs. Code is available at https://github.com/RLHFlow/Reinforce-Ada.
StepWiser: Stepwise Generative Judges for Wiser Reasoning
Aug 27, 2025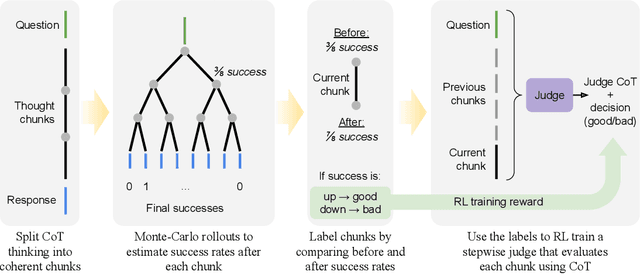


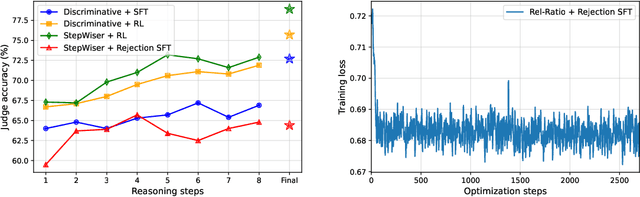
Abstract:As models increasingly leverage multi-step reasoning strategies to solve complex problems, supervising the logical validity of these intermediate steps has become a critical research challenge. Process reward models address this by providing step-by-step feedback, but current approaches have two major drawbacks: they typically function as classifiers without providing explanations, and their reliance on supervised fine-tuning with static datasets limits generalization. Inspired by recent advances, we reframe stepwise reward modeling from a classification task to a reasoning task itself. We thus propose a generative judge that reasons about the policy model's reasoning steps (i.e., meta-reasons), outputting thinking tokens before delivering a final verdict. Our model, StepWiser, is trained by reinforcement learning using relative outcomes of rollouts. We show it provides (i) better judgment accuracy on intermediate steps than existing methods; (ii) can be used to improve the policy model at training time; and (iii) improves inference-time search.
EEG-FM-Bench: A Comprehensive Benchmark for the Systematic Evaluation of EEG Foundation Models
Aug 25, 2025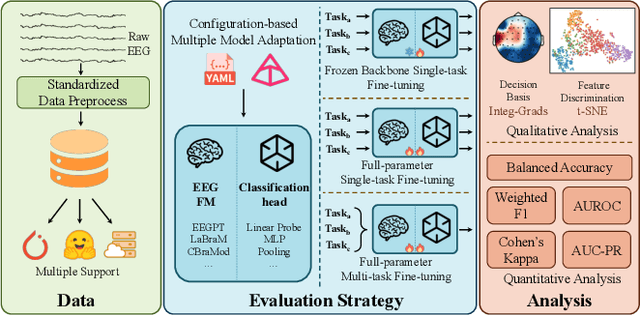
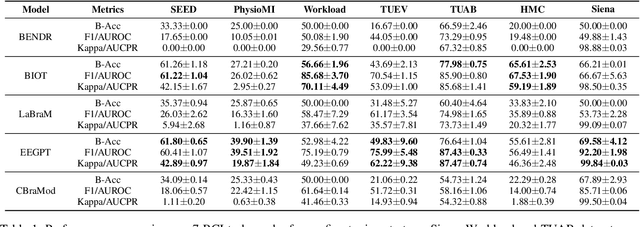
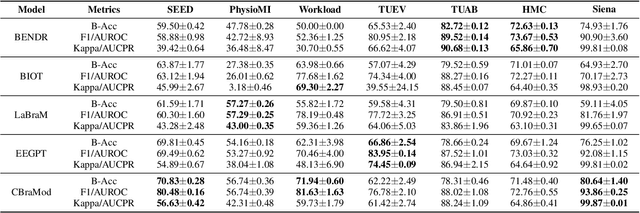
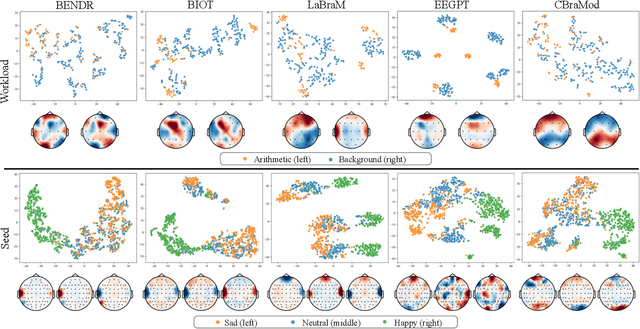
Abstract:Electroencephalography (EEG) foundation models are poised to significantly advance brain signal analysis by learning robust representations from large-scale, unlabeled datasets. However, their rapid proliferation has outpaced the development of standardized evaluation benchmarks, which complicates direct model comparisons and hinders systematic scientific progress. This fragmentation fosters scientific inefficiency and obscures genuine architectural advancements. To address this critical gap, we introduce EEG-FM-Bench, the first comprehensive benchmark for the systematic and standardized evaluation of EEG foundation models (EEG-FMs). Our contributions are threefold: (1) we curate a diverse suite of downstream tasks and datasets from canonical EEG paradigms, implementing standardized processing and evaluation protocols within a unified open-source framework; (2) we benchmark prominent state-of-the-art foundation models to establish comprehensive baseline results for a clear comparison of the current landscape; (3) we perform qualitative analyses of the learned representations to provide insights into model behavior and inform future architectural design. Through extensive experiments, we find that fine-grained spatio-temporal feature interaction, multitask unified training and neuropsychological priors would contribute to enhancing model performance and generalization capabilities. By offering a unified platform for fair comparison and reproducible research, EEG-FM-Bench seeks to catalyze progress and guide the community toward the development of more robust and generalizable EEG-FMs. Code is released at https://github.com/xw1216/EEG-FM-Bench.
MMIG-Bench: Towards Comprehensive and Explainable Evaluation of Multi-Modal Image Generation Models
May 26, 2025Abstract:Recent multimodal image generators such as GPT-4o, Gemini 2.0 Flash, and Gemini 2.5 Pro excel at following complex instructions, editing images and maintaining concept consistency. However, they are still evaluated by disjoint toolkits: text-to-image (T2I) benchmarks that lacks multi-modal conditioning, and customized image generation benchmarks that overlook compositional semantics and common knowledge. We propose MMIG-Bench, a comprehensive Multi-Modal Image Generation Benchmark that unifies these tasks by pairing 4,850 richly annotated text prompts with 1,750 multi-view reference images across 380 subjects, spanning humans, animals, objects, and artistic styles. MMIG-Bench is equipped with a three-level evaluation framework: (1) low-level metrics for visual artifacts and identity preservation of objects; (2) novel Aspect Matching Score (AMS): a VQA-based mid-level metric that delivers fine-grained prompt-image alignment and shows strong correlation with human judgments; and (3) high-level metrics for aesthetics and human preference. Using MMIG-Bench, we benchmark 17 state-of-the-art models, including Gemini 2.5 Pro, FLUX, DreamBooth, and IP-Adapter, and validate our metrics with 32k human ratings, yielding in-depth insights into architecture and data design. We will release the dataset and evaluation code to foster rigorous, unified evaluation and accelerate future innovations in multi-modal image generation.
ALFEE: Adaptive Large Foundation Model for EEG Representation
May 07, 2025Abstract:While foundation models excel in text, image, and video domains, the critical biological signals, particularly electroencephalography(EEG), remain underexplored. EEG benefits neurological research with its high temporal resolution, operational practicality, and safety profile. However, low signal-to-noise ratio, inter-subject variability, and cross-paradigm differences hinder the generalization of current models. Existing methods often employ simplified strategies, such as a single loss function or a channel-temporal joint representation module, and suffer from a domain gap between pretraining and evaluation tasks that compromises efficiency and adaptability. To address these limitations, we propose the Adaptive Large Foundation model for EEG signal representation(ALFEE) framework, a novel hybrid transformer architecture with two learning stages for robust EEG representation learning. ALFEE employs a hybrid attention that separates channel-wise feature aggregation from temporal dynamics modeling, enabling robust EEG representation with variable channel configurations. A channel encoder adaptively compresses variable channel information, a temporal encoder captures task-guided evolution, and a hybrid decoder reconstructs signals in both temporal and frequency domains. During pretraining, ALFEE optimizes task prediction, channel and temporal mask reconstruction, and temporal forecasting to enhance multi-scale and multi-channel representation. During fine-tuning, a full-model adaptation with a task-specific token dictionary and a cross-attention layer boosts performance across multiple tasks. After 25,000 hours of pretraining, extensive experimental results on six downstream EEG tasks demonstrate the superior performance of ALFEE over existing models. Our ALFEE framework establishes a scalable foundation for biological signal analysis with implementation at https://github.com/xw1216/ALFEE.
Optimizing Chain-of-Thought Reasoners via Gradient Variance Minimization in Rejection Sampling and RL
May 05, 2025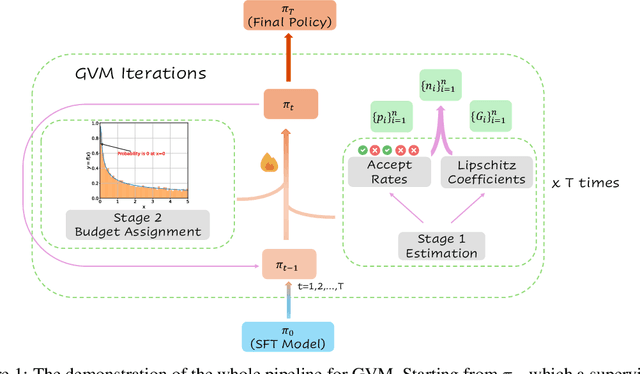
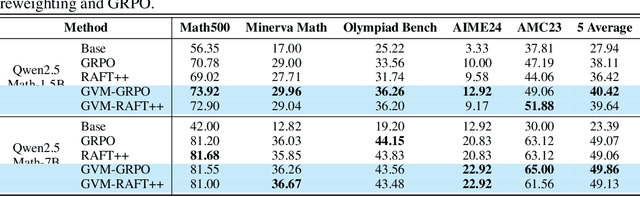
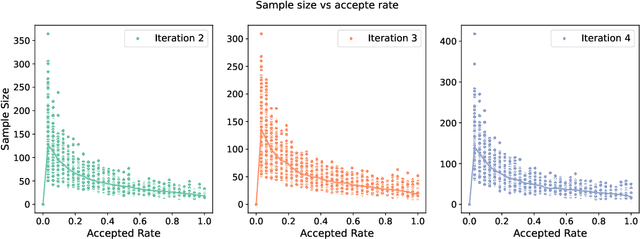
Abstract:Chain-of-thought (CoT) reasoning in large language models (LLMs) can be formalized as a latent variable problem, where the model needs to generate intermediate reasoning steps. While prior approaches such as iterative reward-ranked fine-tuning (RAFT) have relied on such formulations, they typically apply uniform inference budgets across prompts, which fails to account for variability in difficulty and convergence behavior. This work identifies the main bottleneck in CoT training as inefficient stochastic gradient estimation due to static sampling strategies. We propose GVM-RAFT, a prompt-specific Dynamic Sample Allocation Strategy designed to minimize stochastic gradient variance under a computational budget constraint. The method dynamically allocates computational resources by monitoring prompt acceptance rates and stochastic gradient norms, ensuring that the resulting gradient variance is minimized. Our theoretical analysis shows that the proposed dynamic sampling strategy leads to accelerated convergence guarantees under suitable conditions. Experiments on mathematical reasoning show that GVM-RAFT achieves a 2-4x speedup and considerable accuracy improvements over vanilla RAFT. The proposed dynamic sampling strategy is general and can be incorporated into other reinforcement learning algorithms, such as GRPO, leading to similar improvements in convergence and test accuracy. Our code is available at https://github.com/RLHFlow/GVM.
A Minimalist Approach to LLM Reasoning: from Rejection Sampling to Reinforce
Apr 15, 2025



Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL) has become a prevailing approach for fine-tuning large language models (LLMs) on complex reasoning tasks. Among recent methods, GRPO stands out for its empirical success in training models such as DeepSeek-R1, yet the sources of its effectiveness remain poorly understood. In this work, we revisit GRPO from a reinforce-like algorithm perspective and analyze its core components. Surprisingly, we find that a simple rejection sampling baseline, RAFT, which trains only on positively rewarded samples, yields competitive performance than GRPO and PPO. Our ablation studies reveal that GRPO's main advantage arises from discarding prompts with entirely incorrect responses, rather than from its reward normalization. Motivated by this insight, we propose Reinforce-Rej, a minimal extension of policy gradient that filters both entirely incorrect and entirely correct samples. Reinforce-Rej improves KL efficiency and stability, serving as a lightweight yet effective alternative to more complex RL algorithms. We advocate RAFT as a robust and interpretable baseline, and suggest that future advances should focus on more principled designs for incorporating negative samples, rather than relying on them indiscriminately. Our findings provide guidance for future work in reward-based LLM post-training.
ZipIR: Latent Pyramid Diffusion Transformer for High-Resolution Image Restoration
Apr 11, 2025Abstract:Recent progress in generative models has significantly improved image restoration capabilities, particularly through powerful diffusion models that offer remarkable recovery of semantic details and local fidelity. However, deploying these models at ultra-high resolutions faces a critical trade-off between quality and efficiency due to the computational demands of long-range attention mechanisms. To address this, we introduce ZipIR, a novel framework that enhances efficiency, scalability, and long-range modeling for high-res image restoration. ZipIR employs a highly compressed latent representation that compresses image 32x, effectively reducing the number of spatial tokens, and enabling the use of high-capacity models like the Diffusion Transformer (DiT). Toward this goal, we propose a Latent Pyramid VAE (LP-VAE) design that structures the latent space into sub-bands to ease diffusion training. Trained on full images up to 2K resolution, ZipIR surpasses existing diffusion-based methods, offering unmatched speed and quality in restoring high-resolution images from severely degraded inputs.
Self-rewarding correction for mathematical reasoning
Feb 26, 2025Abstract:We study self-rewarding reasoning large language models (LLMs), which can simultaneously generate step-by-step reasoning and evaluate the correctness of their outputs during the inference time-without external feedback. This integrated approach allows a single model to independently guide its reasoning process, offering computational advantages for model deployment. We particularly focus on the representative task of self-correction, where models autonomously detect errors in their responses, revise outputs, and decide when to terminate iterative refinement loops. To enable this, we propose a two-staged algorithmic framework for constructing self-rewarding reasoning models using only self-generated data. In the first stage, we employ sequential rejection sampling to synthesize long chain-of-thought trajectories that incorporate both self-rewarding and self-correction mechanisms. Fine-tuning models on these curated data allows them to learn the patterns of self-rewarding and self-correction. In the second stage, we further enhance the models' ability to assess response accuracy and refine outputs through reinforcement learning with rule-based signals. Experiments with Llama-3 and Qwen-2.5 demonstrate that our approach surpasses intrinsic self-correction capabilities and achieves performance comparable to systems that rely on external reward models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge