Hanjia Lyu
Assessing Historical Structural Oppression Worldwide via Rule-Guided Prompting of Large Language Models
Sep 18, 2025



Abstract:Traditional efforts to measure historical structural oppression struggle with cross-national validity due to the unique, locally specified histories of exclusion, colonization, and social status in each country, and often have relied on structured indices that privilege material resources while overlooking lived, identity-based exclusion. We introduce a novel framework for oppression measurement that leverages Large Language Models (LLMs) to generate context-sensitive scores of lived historical disadvantage across diverse geopolitical settings. Using unstructured self-identified ethnicity utterances from a multilingual COVID-19 global study, we design rule-guided prompting strategies that encourage models to produce interpretable, theoretically grounded estimations of oppression. We systematically evaluate these strategies across multiple state-of-the-art LLMs. Our results demonstrate that LLMs, when guided by explicit rules, can capture nuanced forms of identity-based historical oppression within nations. This approach provides a complementary measurement tool that highlights dimensions of systemic exclusion, offering a scalable, cross-cultural lens for understanding how oppression manifests in data-driven research and public health contexts. To support reproducible evaluation, we release an open-sourced benchmark dataset for assessing LLMs on oppression measurement (https://github.com/chattergpt/llm-oppression-benchmark).
Characterizing Bias: Benchmarking Large Language Models in Simplified versus Traditional Chinese
May 28, 2025



Abstract:While the capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) have been studied in both Simplified and Traditional Chinese, it is yet unclear whether LLMs exhibit differential performance when prompted in these two variants of written Chinese. This understanding is critical, as disparities in the quality of LLM responses can perpetuate representational harms by ignoring the different cultural contexts underlying Simplified versus Traditional Chinese, and can exacerbate downstream harms in LLM-facilitated decision-making in domains such as education or hiring. To investigate potential LLM performance disparities, we design two benchmark tasks that reflect real-world scenarios: regional term choice (prompting the LLM to name a described item which is referred to differently in Mainland China and Taiwan), and regional name choice (prompting the LLM to choose who to hire from a list of names in both Simplified and Traditional Chinese). For both tasks, we audit the performance of 11 leading commercial LLM services and open-sourced models -- spanning those primarily trained on English, Simplified Chinese, or Traditional Chinese. Our analyses indicate that biases in LLM responses are dependent on both the task and prompting language: while most LLMs disproportionately favored Simplified Chinese responses in the regional term choice task, they surprisingly favored Traditional Chinese names in the regional name choice task. We find that these disparities may arise from differences in training data representation, written character preferences, and tokenization of Simplified and Traditional Chinese. These findings highlight the need for further analysis of LLM biases; as such, we provide an open-sourced benchmark dataset to foster reproducible evaluations of future LLM behavior across Chinese language variants (https://github.com/brucelyu17/SC-TC-Bench).
SocioVerse: A World Model for Social Simulation Powered by LLM Agents and A Pool of 10 Million Real-World Users
Apr 14, 2025


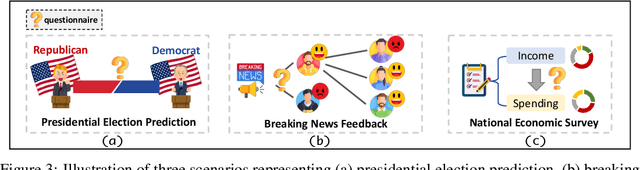
Abstract:Social simulation is transforming traditional social science research by modeling human behavior through interactions between virtual individuals and their environments. With recent advances in large language models (LLMs), this approach has shown growing potential in capturing individual differences and predicting group behaviors. However, existing methods face alignment challenges related to the environment, target users, interaction mechanisms, and behavioral patterns. To this end, we introduce SocioVerse, an LLM-agent-driven world model for social simulation. Our framework features four powerful alignment components and a user pool of 10 million real individuals. To validate its effectiveness, we conducted large-scale simulation experiments across three distinct domains: politics, news, and economics. Results demonstrate that SocioVerse can reflect large-scale population dynamics while ensuring diversity, credibility, and representativeness through standardized procedures and minimal manual adjustments.
Can LLMs Simulate Social Media Engagement? A Study on Action-Guided Response Generation
Feb 17, 2025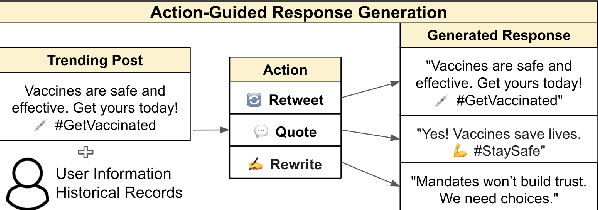



Abstract:Social media enables dynamic user engagement with trending topics, and recent research has explored the potential of large language models (LLMs) for response generation. While some studies investigate LLMs as agents for simulating user behavior on social media, their focus remains on practical viability and scalability rather than a deeper understanding of how well LLM aligns with human behavior. This paper analyzes LLMs' ability to simulate social media engagement through action guided response generation, where a model first predicts a user's most likely engagement action-retweet, quote, or rewrite-towards a trending post before generating a personalized response conditioned on the predicted action. We benchmark GPT-4o-mini, O1-mini, and DeepSeek-R1 in social media engagement simulation regarding a major societal event discussed on X. Our findings reveal that zero-shot LLMs underperform BERT in action prediction, while few-shot prompting initially degrades the prediction accuracy of LLMs with limited examples. However, in response generation, few-shot LLMs achieve stronger semantic alignment with ground truth posts.
From Selection to Generation: A Survey of LLM-based Active Learning
Feb 17, 2025Abstract:Active Learning (AL) has been a powerful paradigm for improving model efficiency and performance by selecting the most informative data points for labeling and training. In recent active learning frameworks, Large Language Models (LLMs) have been employed not only for selection but also for generating entirely new data instances and providing more cost-effective annotations. Motivated by the increasing importance of high-quality data and efficient model training in the era of LLMs, we present a comprehensive survey on LLM-based Active Learning. We introduce an intuitive taxonomy that categorizes these techniques and discuss the transformative roles LLMs can play in the active learning loop. We further examine the impact of AL on LLM learning paradigms and its applications across various domains. Finally, we identify open challenges and propose future research directions. This survey aims to serve as an up-to-date resource for researchers and practitioners seeking to gain an intuitive understanding of LLM-based AL techniques and deploy them to new applications.
Irony in Emojis: A Comparative Study of Human and LLM Interpretation
Jan 20, 2025Abstract:Emojis have become a universal language in online communication, often carrying nuanced and context-dependent meanings. Among these, irony poses a significant challenge for Large Language Models (LLMs) due to its inherent incongruity between appearance and intent. This study examines the ability of GPT-4o to interpret irony in emojis. By prompting GPT-4o to evaluate the likelihood of specific emojis being used to express irony on social media and comparing its interpretations with human perceptions, we aim to bridge the gap between machine and human understanding. Our findings reveal nuanced insights into GPT-4o's interpretive capabilities, highlighting areas of alignment with and divergence from human behavior. Additionally, this research underscores the importance of demographic factors, such as age and gender, in shaping emoji interpretation and evaluates how these factors influence GPT-4o's performance.
GUI Agents: A Survey
Dec 18, 2024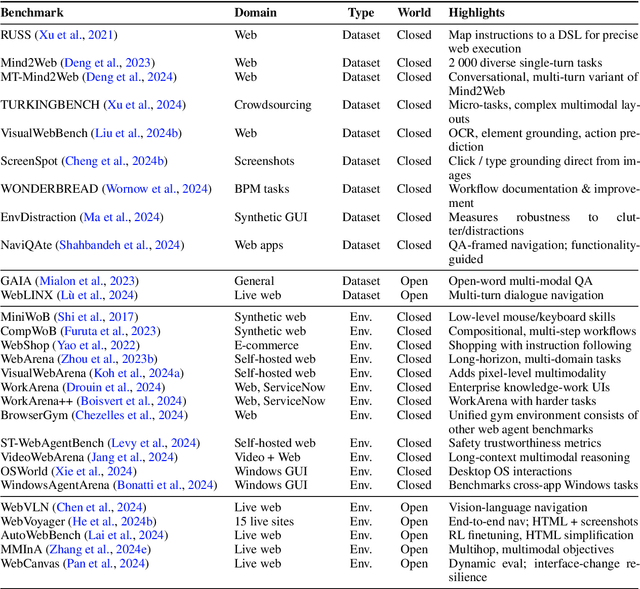
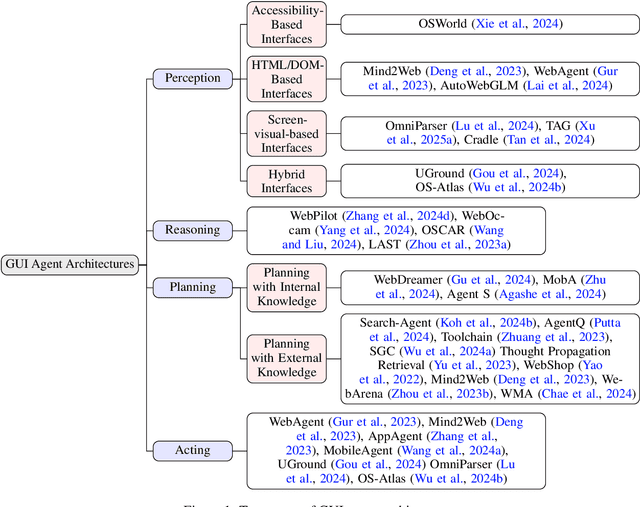

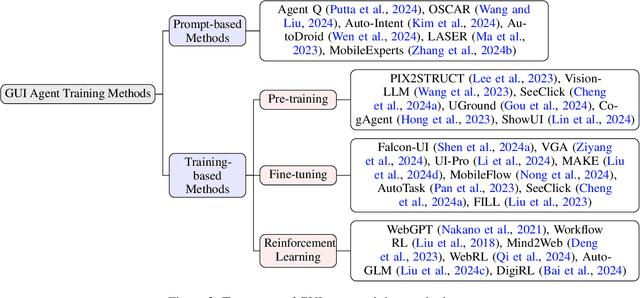
Abstract:Graphical User Interface (GUI) agents, powered by Large Foundation Models, have emerged as a transformative approach to automating human-computer interaction. These agents autonomously interact with digital systems or software applications via GUIs, emulating human actions such as clicking, typing, and navigating visual elements across diverse platforms. Motivated by the growing interest and fundamental importance of GUI agents, we provide a comprehensive survey that categorizes their benchmarks, evaluation metrics, architectures, and training methods. We propose a unified framework that delineates their perception, reasoning, planning, and acting capabilities. Furthermore, we identify important open challenges and discuss key future directions. Finally, this work serves as a basis for practitioners and researchers to gain an intuitive understanding of current progress, techniques, benchmarks, and critical open problems that remain to be addressed.
Personalized Multimodal Large Language Models: A Survey
Dec 03, 2024Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have become increasingly important due to their state-of-the-art performance and ability to integrate multiple data modalities, such as text, images, and audio, to perform complex tasks with high accuracy. This paper presents a comprehensive survey on personalized multimodal large language models, focusing on their architecture, training methods, and applications. We propose an intuitive taxonomy for categorizing the techniques used to personalize MLLMs to individual users, and discuss the techniques accordingly. Furthermore, we discuss how such techniques can be combined or adapted when appropriate, highlighting their advantages and underlying rationale. We also provide a succinct summary of personalization tasks investigated in existing research, along with the evaluation metrics commonly used. Additionally, we summarize the datasets that are useful for benchmarking personalized MLLMs. Finally, we outline critical open challenges. This survey aims to serve as a valuable resource for researchers and practitioners seeking to understand and advance the development of personalized multimodal large language models.
CRTRE: Causal Rule Generation with Target Trial Emulation Framework
Nov 10, 2024

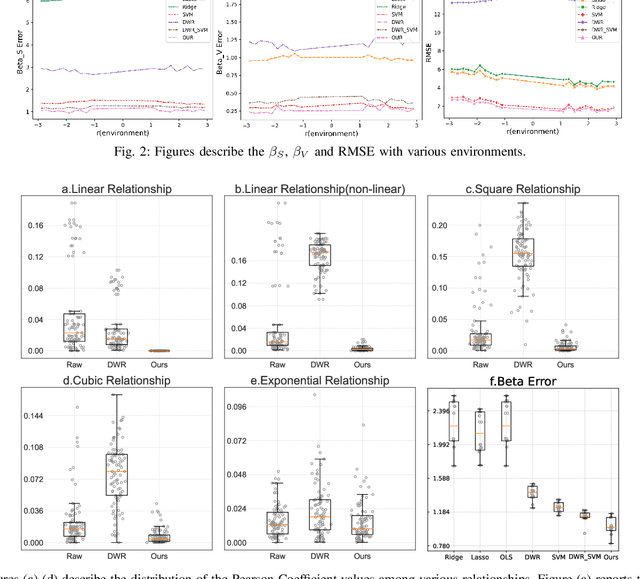

Abstract:Causal inference and model interpretability are gaining increasing attention, particularly in the biomedical domain. Despite recent advance, decorrelating features in nonlinear environments with human-interpretable representations remains underexplored. In this study, we introduce a novel method called causal rule generation with target trial emulation framework (CRTRE), which applies randomize trial design principles to estimate the causal effect of association rules. We then incorporate such association rules for the downstream applications such as prediction of disease onsets. Extensive experiments on six healthcare datasets, including synthetic data, real-world disease collections, and MIMIC-III/IV, demonstrate the model's superior performance. Specifically, our method achieved a $\beta$ error of 0.907, outperforming DWR (1.024) and SVM (1.141). On real-world datasets, our model achieved accuracies of 0.789, 0.920, and 0.300 for Esophageal Cancer, Heart Disease, and Cauda Equina Syndrome prediction task, respectively, consistently surpassing baseline models. On the ICD code prediction tasks, it achieved AUC Macro scores of 92.8 on MIMIC-III and 96.7 on MIMIC-IV, outperforming the state-of-the-art models KEPT and MSMN. Expert evaluations further validate the model's effectiveness, causality, and interpretability.
ElectionSim: Massive Population Election Simulation Powered by Large Language Model Driven Agents
Oct 28, 2024



Abstract:The massive population election simulation aims to model the preferences of specific groups in particular election scenarios. It has garnered significant attention for its potential to forecast real-world social trends. Traditional agent-based modeling (ABM) methods are constrained by their ability to incorporate complex individual background information and provide interactive prediction results. In this paper, we introduce ElectionSim, an innovative election simulation framework based on large language models, designed to support accurate voter simulations and customized distributions, together with an interactive platform to dialogue with simulated voters. We present a million-level voter pool sampled from social media platforms to support accurate individual simulation. We also introduce PPE, a poll-based presidential election benchmark to assess the performance of our framework under the U.S. presidential election scenario. Through extensive experiments and analyses, we demonstrate the effectiveness and robustness of our framework in U.S. presidential election simulations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge