Bowen Jin
Learning Query-Aware Budget-Tier Routing for Runtime Agent Memory
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Memory is increasingly central to Large Language Model (LLM) agents operating beyond a single context window, yet most existing systems rely on offline, query-agnostic memory construction that can be inefficient and may discard query-critical information. Although runtime memory utilization is a natural alternative, prior work often incurs substantial overhead and offers limited explicit control over the performance-cost trade-off. In this work, we present \textbf{BudgetMem}, a runtime agent memory framework for explicit, query-aware performance-cost control. BudgetMem structures memory processing as a set of memory modules, each offered in three budget tiers (i.e., \textsc{Low}/\textsc{Mid}/\textsc{High}). A lightweight router performs budget-tier routing across modules to balance task performance and memory construction cost, which is implemented as a compact neural policy trained with reinforcement learning. Using BudgetMem as a unified testbed, we study three complementary strategies for realizing budget tiers: implementation (method complexity), reasoning (inference behavior), and capacity (module model size). Across LoCoMo, LongMemEval, and HotpotQA, BudgetMem surpasses strong baselines when performance is prioritized (i.e., high-budget setting), and delivers better accuracy-cost frontiers under tighter budgets. Moreover, our analysis disentangles the strengths and weaknesses of different tiering strategies, clarifying when each axis delivers the most favorable trade-offs under varying budget regimes.
Improving Scientific Document Retrieval with Academic Concept Index
Jan 02, 2026Abstract:Adapting general-domain retrievers to scientific domains is challenging due to the scarcity of large-scale domain-specific relevance annotations and the substantial mismatch in vocabulary and information needs. Recent approaches address these issues through two independent directions that leverage large language models (LLMs): (1) generating synthetic queries for fine-tuning, and (2) generating auxiliary contexts to support relevance matching. However, both directions overlook the diverse academic concepts embedded within scientific documents, often producing redundant or conceptually narrow queries and contexts. To address this limitation, we introduce an academic concept index, which extracts key concepts from papers and organizes them guided by an academic taxonomy. This structured index serves as a foundation for improving both directions. First, we enhance the synthetic query generation with concept coverage-based generation (CCQGen), which adaptively conditions LLMs on uncovered concepts to generate complementary queries with broader concept coverage. Second, we strengthen the context augmentation with concept-focused auxiliary contexts (CCExpand), which leverages a set of document snippets that serve as concise responses to the concept-aware CCQGen queries. Extensive experiments show that incorporating the academic concept index into both query generation and context augmentation leads to higher-quality queries, better conceptual alignment, and improved retrieval performance.
COMPASS: A Multi-Turn Benchmark for Tool-Mediated Planning & Preference Optimization
Oct 08, 2025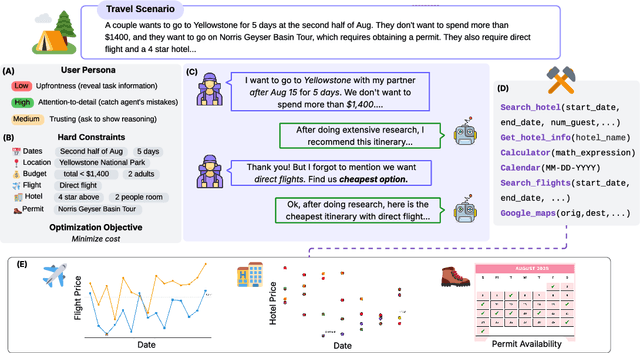
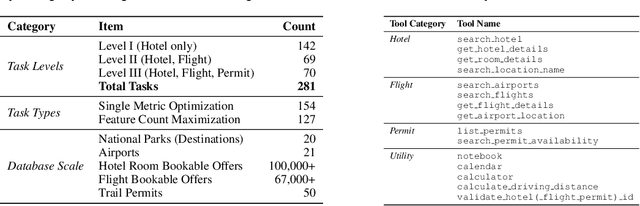
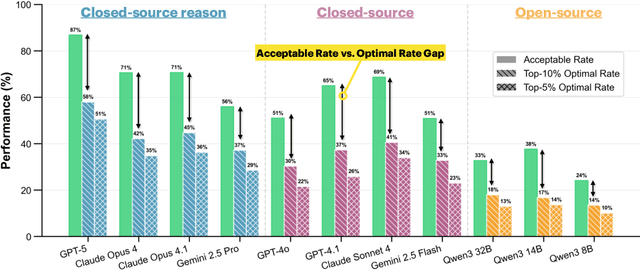
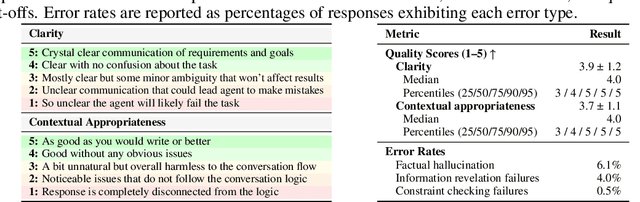
Abstract:Real-world large language model (LLM) agents must master strategic tool use and user preference optimization through multi-turn interactions to assist users with complex planning tasks. We introduce COMPASS (Constrained Optimization through Multi-turn Planning and Strategic Solutions), a benchmark that evaluates agents on realistic travel-planning scenarios. We cast travel planning as a constrained preference optimization problem, where agents must satisfy hard constraints while simultaneously optimizing soft user preferences. To support this, we build a realistic travel database covering transportation, accommodation, and ticketing for 20 U.S. National Parks, along with a comprehensive tool ecosystem that mirrors commercial booking platforms. Evaluating state-of-the-art models, we uncover two critical gaps: (i) an acceptable-optimal gap, where agents reliably meet constraints but fail to optimize preferences, and (ii) a plan-coordination gap, where performance collapses on multi-service (flight and hotel) coordination tasks, especially for open-source models. By grounding reasoning and planning in a practical, user-facing domain, COMPASS provides a benchmark that directly measures an agent's ability to optimize user preferences in realistic tasks, bridging theoretical advances with real-world impact.
GRACE: Generative Representation Learning via Contrastive Policy Optimization
Oct 06, 2025Abstract:Prevailing methods for training Large Language Models (LLMs) as text encoders rely on contrastive losses that treat the model as a black box function, discarding its generative and reasoning capabilities in favor of static embeddings. We introduce GRACE (Generative Representation Learning via Contrastive Policy Optimization), a novel framework that reimagines contrastive signals not as losses to be minimized, but as rewards that guide a generative policy. In GRACE, the LLM acts as a policy that produces explicit, human-interpretable rationales--structured natural language explanations of its semantic understanding. These rationales are then encoded into high-quality embeddings via mean pooling. Using policy gradient optimization, we train the model with a multi-component reward function that maximizes similarity between query positive pairs and minimizes similarity with negatives. This transforms the LLM from an opaque encoder into an interpretable agent whose reasoning process is transparent and inspectable. On MTEB benchmark, GRACE yields broad cross category gains: averaged over four backbones, the supervised setting improves overall score by 11.5% over base models, and the unsupervised variant adds 6.9%, while preserving general capabilities. This work treats contrastive objectives as rewards over rationales, unifying representation learning with generation to produce stronger embeddings and transparent rationales. The model, data and code are available at https://github.com/GasolSun36/GRACE.
Hypercube-RAG: Hypercube-Based Retrieval-Augmented Generation for In-domain Scientific Question-Answering
May 25, 2025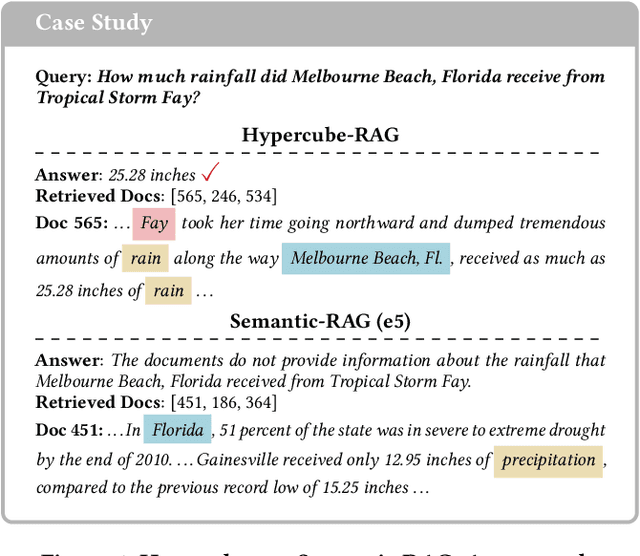

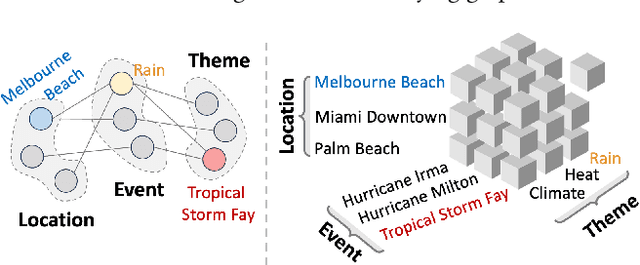
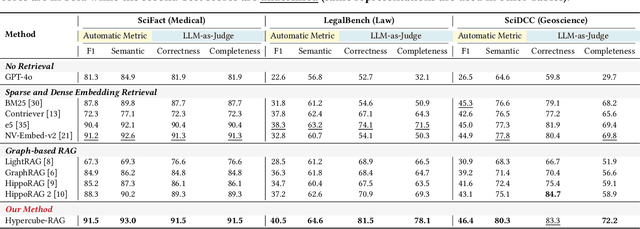
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) often need to incorporate external knowledge to solve theme-specific problems. Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), which empowers LLMs to generate more qualified responses with retrieved external data and knowledge, has shown its high promise. However, traditional semantic similarity-based RAGs struggle to return concise yet highly relevant information for domain knowledge-intensive tasks, such as scientific question-answering (QA). Built on a multi-dimensional (cube) structure called Hypercube, which can index documents in an application-driven, human-defined, multi-dimensional space, we introduce the Hypercube-RAG, a novel RAG framework for precise and efficient retrieval. Given a query, Hypercube-RAG first decomposes it based on its entities and topics and then retrieves relevant documents from cubes by aligning these decomposed components with hypercube dimensions. Experiments on three in-domain scientific QA datasets demonstrate that our method improves accuracy by 3.7% and boosts retrieval efficiency by 81.2%, measured as relative gains over the strongest RAG baseline. More importantly, our Hypercube-RAG inherently offers explainability by revealing the underlying predefined hypercube dimensions used for retrieval. The code and data sets are available at https://github.com/JimengShi/Hypercube-RAG.
Hybrid Latent Reasoning via Reinforcement Learning
May 24, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) have introduced latent reasoning as a promising alternative to autoregressive reasoning. By performing internal computation with hidden states from previous steps, latent reasoning benefit from more informative features rather than sampling a discrete chain-of-thought (CoT) path. Yet latent reasoning approaches are often incompatible with LLMs, as their continuous paradigm conflicts with the discrete nature of autoregressive generation. Moreover, these methods rely on CoT traces for training and thus fail to exploit the inherent reasoning patterns of LLMs. In this work, we explore latent reasoning by leveraging the intrinsic capabilities of LLMs via reinforcement learning (RL). To this end, we introduce hybrid reasoning policy optimization (HRPO), an RL-based hybrid latent reasoning approach that (1) integrates prior hidden states into sampled tokens with a learnable gating mechanism, and (2) initializes training with predominantly token embeddings while progressively incorporating more hidden features. This design maintains LLMs' generative capabilities and incentivizes hybrid reasoning using both discrete and continuous representations. In addition, the hybrid HRPO introduces stochasticity into latent reasoning via token sampling, thereby enabling RL-based optimization without requiring CoT trajectories. Extensive evaluations across diverse benchmarks show that HRPO outperforms prior methods in both knowledge- and reasoning-intensive tasks. Furthermore, HRPO-trained LLMs remain interpretable and exhibit intriguing behaviors like cross-lingual patterns and shorter completion lengths, highlighting the potential of our RL-based approach and offer insights for future work in latent reasoning.
An Empirical Study on Reinforcement Learning for Reasoning-Search Interleaved LLM Agents
May 21, 2025



Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL) has demonstrated strong potential in training large language models (LLMs) capable of complex reasoning for real-world problem solving. More recently, RL has been leveraged to create sophisticated LLM-based search agents that adeptly combine reasoning with search engine use. While the use of RL for training search agents is promising, the optimal design of such agents remains not fully understood. In particular, key factors -- such as (1) reward formulation, (2) the choice and characteristics of the underlying LLM, and (3) the role of the search engine in the RL process -- require further investigation. In this work, we conduct comprehensive empirical studies to systematically investigate these and offer actionable insights. We highlight several key findings: format rewards are effective in improving final performance, whereas intermediate retrieval rewards have limited impact; the scale and initialization of the LLM (general-purpose vs. reasoning-specialized) significantly influence RL outcomes; and the choice of search engine plays a critical role in shaping RL training dynamics and the robustness of the trained agent during inference. These establish important guidelines for successfully building and deploying LLM-based search agents in real-world applications. Code is available at https://github.com/PeterGriffinJin/Search-R1.
LLM-Based Compact Reranking with Document Features for Scientific Retrieval
May 19, 2025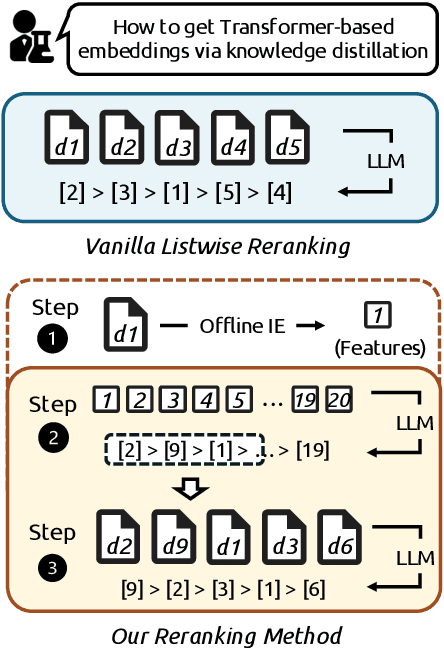
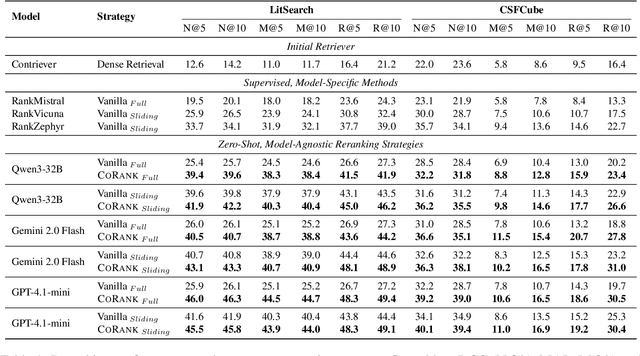
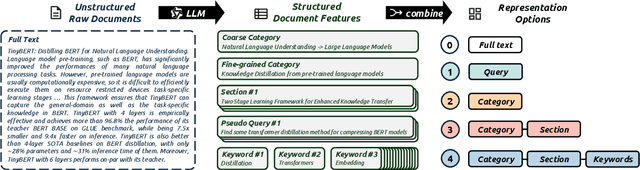
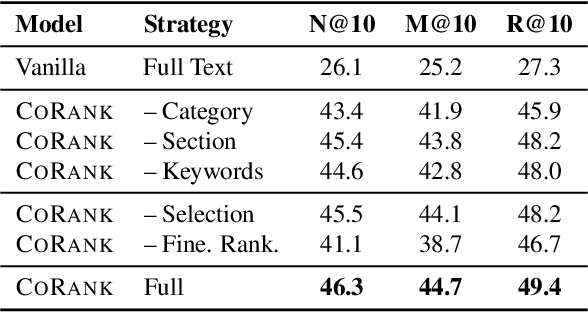
Abstract:Scientific retrieval is essential for advancing academic discovery. Within this process, document reranking plays a critical role by refining first-stage retrieval results. However, large language model (LLM) listwise reranking faces unique challenges in the scientific domain. First-stage retrieval is often suboptimal in the scientific domain, so relevant documents are ranked lower. Moreover, conventional listwise reranking uses the full text of candidate documents in the context window, limiting the number of candidates that can be considered. As a result, many relevant documents are excluded before reranking, which constrains overall retrieval performance. To address these challenges, we explore compact document representations based on semantic features such as categories, sections, and keywords, and propose a training-free, model-agnostic reranking framework for scientific retrieval called CoRank. The framework involves three stages: (i) offline extraction of document-level features, (ii) coarse reranking using these compact representations, and (iii) fine-grained reranking on full texts of the top candidates from stage (ii). This hybrid design provides a high-level abstraction of document semantics, expands candidate coverage, and retains critical details required for precise ranking. Experiments on LitSearch and CSFCube show that CoRank significantly improves reranking performance across different LLM backbones, increasing nDCG@10 from 32.0 to 39.7. Overall, these results highlight the value of information extraction for reranking in scientific retrieval.
mCLM: A Function-Infused and Synthesis-Friendly Modular Chemical Language Model
May 18, 2025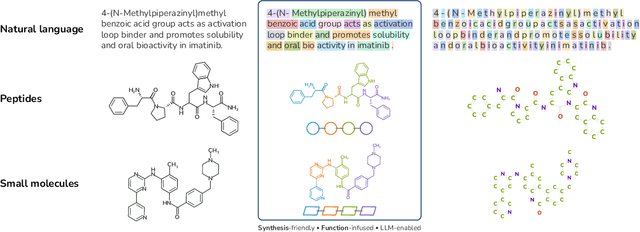
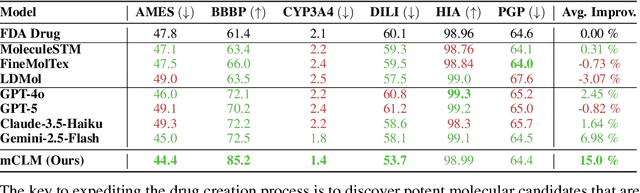
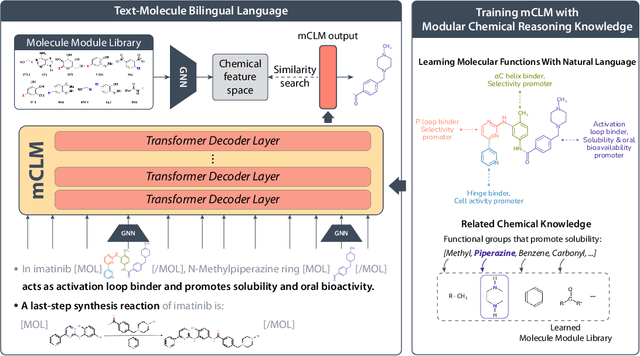
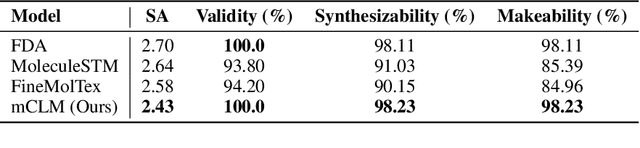
Abstract:Despite their ability to understand chemical knowledge and accurately generate sequential representations, large language models (LLMs) remain limited in their capacity to propose novel molecules with drug-like properties. In addition, the molecules that LLMs propose can often be challenging to make in the lab. To more effectively enable the discovery of functional small molecules, LLMs need to learn a molecular language. However, LLMs are currently limited by encoding molecules from atoms. In this paper, we argue that just like tokenizing texts into (sub-)word tokens instead of characters, molecules should be decomposed and reassembled at the level of functional building blocks, i.e., parts of molecules that bring unique functions and serve as effective building blocks for real-world automated laboratory synthesis. This motivates us to propose mCLM, a modular Chemical-Language Model tokenizing molecules into building blocks and learning a bilingual language model of both natural language descriptions of functions and molecule building blocks. By reasoning on such functional building blocks, mCLM guarantees to generate efficiently synthesizable molecules thanks to recent progress in block-based chemistry, while also improving the functions of molecules in a principled manner. In experiments on 430 FDA-approved drugs, we find mCLM capable of significantly improving 5 out of 6 chemical functions critical to determining drug potentials. More importantly, mCLM can reason on multiple functions and improve the FDA-rejected drugs (``fallen angels'') over multiple iterations to greatly improve their shortcomings.
Demystifying and Enhancing the Efficiency of Large Language Model Based Search Agents
May 17, 2025Abstract:Large Language Model (LLM)-based search agents have shown remarkable capabilities in solving complex tasks by dynamically decomposing problems and addressing them through interleaved reasoning and retrieval. However, this interleaved paradigm introduces substantial efficiency bottlenecks. First, we observe that both highly accurate and overly approximate retrieval methods degrade system efficiency: exact search incurs significant retrieval overhead, while coarse retrieval requires additional reasoning steps during generation. Second, we identify inefficiencies in system design, including improper scheduling and frequent retrieval stalls, which lead to cascading latency -- where even minor delays in retrieval amplify end-to-end inference time. To address these challenges, we introduce SearchAgent-X, a high-efficiency inference framework for LLM-based search agents. SearchAgent-X leverages high-recall approximate retrieval and incorporates two key techniques: priority-aware scheduling and non-stall retrieval. Extensive experiments demonstrate that SearchAgent-X consistently outperforms state-of-the-art systems such as vLLM and HNSW-based retrieval across diverse tasks, achieving up to 3.4$\times$ higher throughput and 5$\times$ lower latency, without compromising generation quality. SearchAgent-X is available at https://github.com/tiannuo-yang/SearchAgent-X.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge