Jinsung Yoon
PathCRF: Ball-Free Soccer Event Detection via Possession Path Inference from Player Trajectories
Feb 12, 2026Abstract:Despite recent advances in AI, event data collection in soccer still relies heavily on labor-intensive manual annotation. Although prior work has explored automatic event detection using player and ball trajectories, ball tracking also remains difficult to scale due to high infrastructural and operational costs. As a result, comprehensive data collection in soccer is largely confined to top-tier competitions, limiting the broader adoption of data-driven analysis in this domain. To address this challenge, this paper proposes PathCRF, a framework for detecting on-ball soccer events using only player tracking data. We model player trajectories as a fully connected dynamic graph and formulate event detection as the problem of selecting exactly one edge corresponding to the current possession state at each time step. To ensure logical consistency of the resulting edge sequence, we employ a Conditional Random Field (CRF) that forbids impossible transitions between consecutive edges. Both emission and transition scores dynamically computed from edge embeddings produced by a Set Attention-based backbone architecture. During inference, the most probable edge sequence is obtained via Viterbi decoding, and events such as ball controls or passes are detected whenever the selected edge changes between adjacent time steps. Experiments show that PathCRF produces accurate, logically consistent possession paths, enabling reliable downstream analyses while substantially reducing the need for manual event annotation. The source code is available at https://github.com/hyunsungkim-ds/pathcrf.git.
MARS: Modular Agent with Reflective Search for Automated AI Research
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Automating AI research differs from general software engineering due to computationally expensive evaluation (e.g., model training) and opaque performance attribution. Current LLM-based agents struggle here, often generating monolithic scripts that ignore execution costs and causal factors. We introduce MARS (Modular Agent with Reflective Search), a framework optimized for autonomous AI research. MARS relies on three pillars: (1) Budget-Aware Planning via cost-constrained Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) to explicitly balance performance with execution expense; (2) Modular Construction, employing a "Design-Decompose-Implement" pipeline to manage complex research repositories; and (3) Comparative Reflective Memory, which addresses credit assignment by analyzing solution differences to distill high-signal insights. MARS achieves state-of-the-art performance among open-source frameworks on MLE-Bench under comparable settings, maintaining competitiveness with the global leaderboard's top methods. Furthermore, the system exhibits qualitative "Aha!" moments, where 63% of all utilized lessons originate from cross-branch transfer, demonstrating that the agent effectively generalizes insights across search paths.
PaperBanana: Automating Academic Illustration for AI Scientists
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Despite rapid advances in autonomous AI scientists powered by language models, generating publication-ready illustrations remains a labor-intensive bottleneck in the research workflow. To lift this burden, we introduce PaperBanana, an agentic framework for automated generation of publication-ready academic illustrations. Powered by state-of-the-art VLMs and image generation models, PaperBanana orchestrates specialized agents to retrieve references, plan content and style, render images, and iteratively refine via self-critique. To rigorously evaluate our framework, we introduce PaperBananaBench, comprising 292 test cases for methodology diagrams curated from NeurIPS 2025 publications, covering diverse research domains and illustration styles. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that PaperBanana consistently outperforms leading baselines in faithfulness, conciseness, readability, and aesthetics. We further show that our method effectively extends to the generation of high-quality statistical plots. Collectively, PaperBanana paves the way for the automated generation of publication-ready illustrations.
ScholarPeer: A Context-Aware Multi-Agent Framework for Automated Peer Review
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Automated peer review has evolved from simple text classification to structured feedback generation. However, current state-of-the-art systems still struggle with "surface-level" critiques: they excel at summarizing content but often fail to accurately assess novelty and significance or identify deep methodological flaws because they evaluate papers in a vacuum, lacking the external context a human expert possesses. In this paper, we introduce ScholarPeer, a search-enabled multi-agent framework designed to emulate the cognitive processes of a senior researcher. ScholarPeer employs a dual-stream process of context acquisition and active verification. It dynamically constructs a domain narrative using a historian agent, identifies missing comparisons via a baseline scout, and verifies claims through a multi-aspect Q&A engine, grounding the critique in live web-scale literature. We evaluate ScholarPeer on DeepReview-13K and the results demonstrate that ScholarPeer achieves significant win-rates against state-of-the-art approaches in side-by-side evaluations and reduces the gap to human-level diversity.
Better Prevent than Tackle: Valuing Defense in Soccer Based on Graph Neural Networks
Dec 11, 2025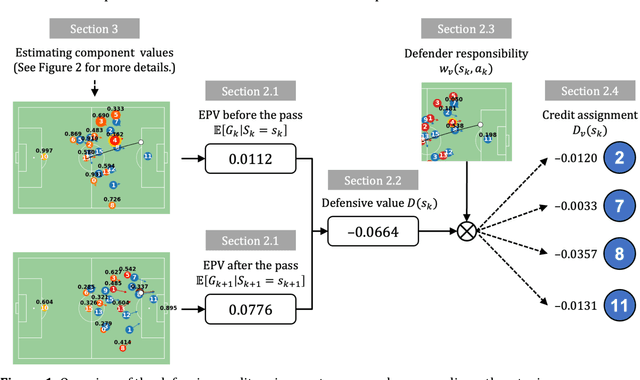
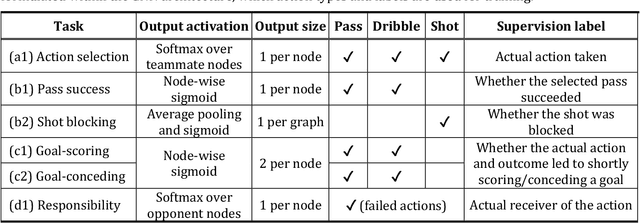
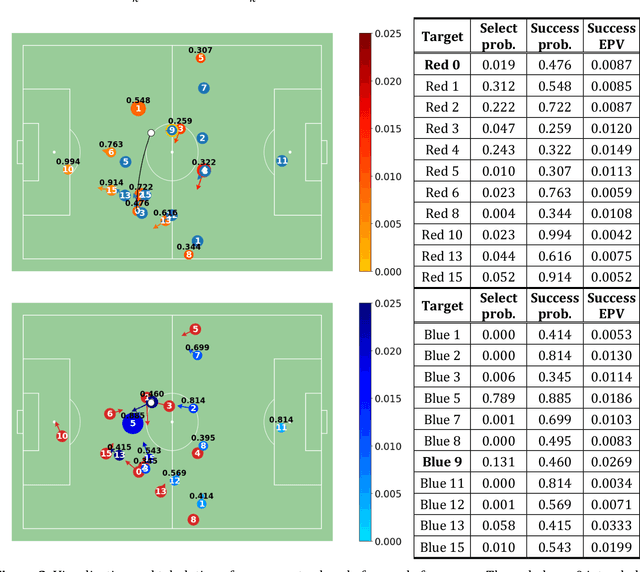
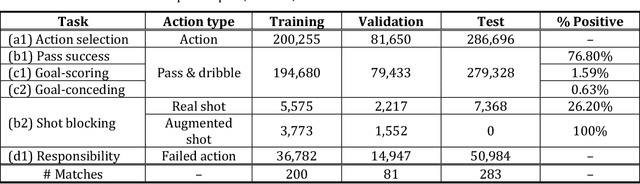
Abstract:Evaluating defensive performance in soccer remains challenging, as effective defending is often expressed not through visible on-ball actions such as interceptions and tackles, but through preventing dangerous opportunities before they arise. Existing approaches have largely focused on valuing on-ball actions, leaving much of defenders' true impact unmeasured. To address this gap, we propose DEFCON (DEFensive CONtribution evaluator), a comprehensive framework that quantifies player-level defensive contributions for every attacking situation in soccer. Leveraging Graph Attention Networks, DEFCON estimates the success probability and expected value of each attacking option, along with each defender's responsibility for stopping it. These components yield an Expected Possession Value (EPV) for the attacking team before and after each action, and DEFCON assigns positive or negative credits to defenders according to whether they reduced or increased the opponent's EPV. Trained on 2023-24 and evaluated on 2024-25 Eredivisie event and tracking data, DEFCON's aggregated player credits exhibit strong positive correlations with market valuations. Finally, we showcase several practical applications, including in-game timelines of defensive contributions, spatial analyses across pitch zones, and pairwise summaries of attacker-defender interactions.
TabFlash: Efficient Table Understanding with Progressive Question Conditioning and Token Focusing
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:Table images present unique challenges for effective and efficient understanding due to the need for question-specific focus and the presence of redundant background regions. Existing Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM) approaches often overlook these characteristics, resulting in uninformative and redundant visual representations. To address these issues, we aim to generate visual features that are both informative and compact to improve table understanding. We first propose progressive question conditioning, which injects the question into Vision Transformer layers with gradually increasing frequency, considering each layer's capacity to handle additional information, to generate question-aware visual features. To reduce redundancy, we introduce a pruning strategy that discards background tokens, thereby improving efficiency. To mitigate information loss from pruning, we further propose token focusing, a training strategy that encourages the model to concentrate essential information in the retained tokens. By combining these approaches, we present TabFlash, an efficient and effective MLLM for table understanding. TabFlash achieves state-of-the-art performance, outperforming both open-source and proprietary MLLMs, while requiring 27% less FLOPs and 30% less memory usage compared to the second-best MLLM.
DocLens : A Tool-Augmented Multi-Agent Framework for Long Visual Document Understanding
Nov 14, 2025Abstract:Comprehending long visual documents, where information is distributed across extensive pages of text and visual elements, is a critical but challenging task for modern Vision-Language Models (VLMs). Existing approaches falter on a fundamental challenge: evidence localization. They struggle to retrieve relevant pages and overlook fine-grained details within visual elements, leading to limited performance and model hallucination. To address this, we propose DocLens, a tool-augmented multi-agent framework that effectively ``zooms in'' on evidence like a lens. It first navigates from the full document to specific visual elements on relevant pages, then employs a sampling-adjudication mechanism to generate a single, reliable answer. Paired with Gemini-2.5-Pro, DocLens achieves state-of-the-art performance on MMLongBench-Doc and FinRAGBench-V, surpassing even human experts. The framework's superiority is particularly evident on vision-centric and unanswerable queries, demonstrating the power of its enhanced localization capabilities.
One-Topic-Doesn't-Fit-All: Transcreating Reading Comprehension Test for Personalized Learning
Nov 12, 2025


Abstract:Personalized learning has gained attention in English as a Foreign Language (EFL) education, where engagement and motivation play crucial roles in reading comprehension. We propose a novel approach to generating personalized English reading comprehension tests tailored to students' interests. We develop a structured content transcreation pipeline using OpenAI's gpt-4o, where we start with the RACE-C dataset, and generate new passages and multiple-choice reading comprehension questions that are linguistically similar to the original passages but semantically aligned with individual learners' interests. Our methodology integrates topic extraction, question classification based on Bloom's taxonomy, linguistic feature analysis, and content transcreation to enhance student engagement. We conduct a controlled experiment with EFL learners in South Korea to examine the impact of interest-aligned reading materials on comprehension and motivation. Our results show students learning with personalized reading passages demonstrate improved comprehension and motivation retention compared to those learning with non-personalized materials.
Synapse: Adaptive Arbitration of Complementary Expertise in Time Series Foundational Models
Nov 07, 2025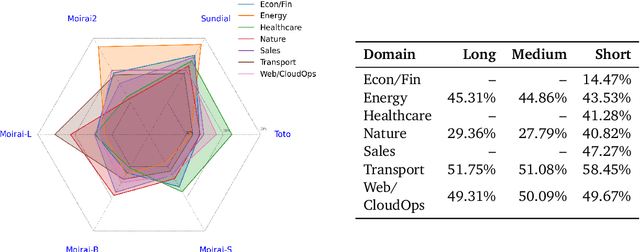
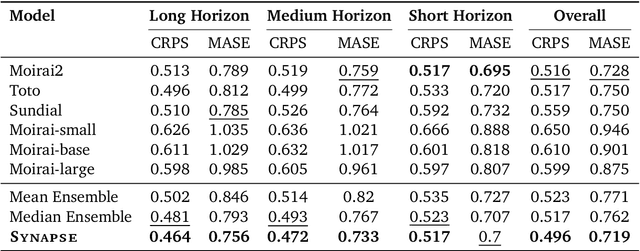
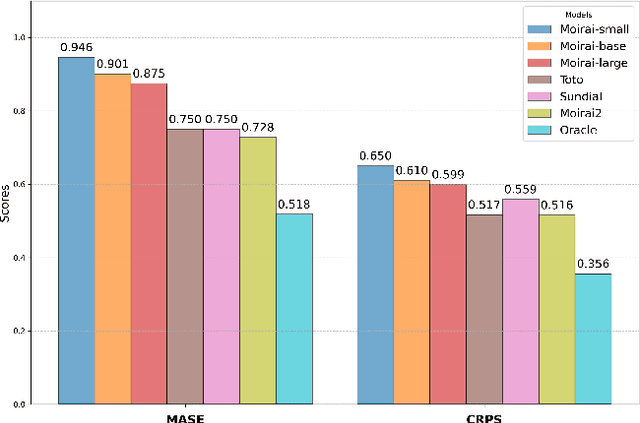
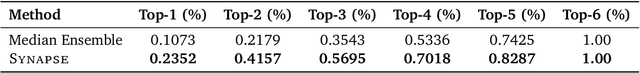
Abstract:Pre-trained Time Series Foundational Models (TSFMs) represent a significant advance, capable of forecasting diverse time series with complex characteristics, including varied seasonalities, trends, and long-range dependencies. Despite their primary goal of universal time series forecasting, their efficacy is far from uniform; divergent training protocols and data sources cause individual TSFMs to exhibit highly variable performance across different forecasting tasks, domains, and horizons. Leveraging this complementary expertise by arbitrating existing TSFM outputs presents a compelling strategy, yet this remains a largely unexplored area of research. In this paper, we conduct a thorough examination of how different TSFMs exhibit specialized performance profiles across various forecasting settings, and how we can effectively leverage this behavior in arbitration between different time series models. We specifically analyze how factors such as model selection and forecast horizon distribution can influence the efficacy of arbitration strategies. Based on this analysis, we propose Synapse, a novel arbitration framework for TSFMs. Synapse is designed to dynamically leverage a pool of TSFMs, assign and adjust predictive weights based on their relative, context-dependent performance, and construct a robust forecast distribution by adaptively sampling from the output quantiles of constituent models. Experimental results demonstrate that Synapse consistently outperforms other popular ensembling techniques as well as individual TSFMs, demonstrating Synapse's efficacy in time series forecasting.
Maestro-EVC: Controllable Emotional Voice Conversion Guided by References and Explicit Prosody
Aug 09, 2025



Abstract:Emotional voice conversion (EVC) aims to modify the emotional style of speech while preserving its linguistic content. In practical EVC, controllability, the ability to independently control speaker identity and emotional style using distinct references, is crucial. However, existing methods often struggle to fully disentangle these attributes and lack the ability to model fine-grained emotional expressions such as temporal dynamics. We propose Maestro-EVC, a controllable EVC framework that enables independent control of content, speaker identity, and emotion by effectively disentangling each attribute from separate references. We further introduce a temporal emotion representation and an explicit prosody modeling with prosody augmentation to robustly capture and transfer the temporal dynamics of the target emotion, even under prosody-mismatched conditions. Experimental results confirm that Maestro-EVC achieves high-quality, controllable, and emotionally expressive speech synthesis.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge