Mengzhou Xia
Lost in the Maze: Overcoming Context Limitations in Long-Horizon Agentic Search
Oct 21, 2025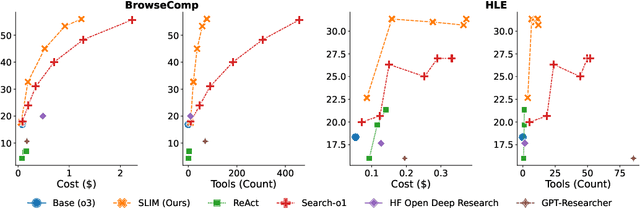



Abstract:Long-horizon agentic search requires iteratively exploring the web over long trajectories and synthesizing information across many sources, and is the foundation for enabling powerful applications like deep research systems. In this work, we show that popular agentic search frameworks struggle to scale to long trajectories primarily due to context limitations-they accumulate long, noisy content, hit context window and tool budgets, or stop early. Then, we introduce SLIM (Simple Lightweight Information Management), a simple framework that separates retrieval into distinct search and browse tools, and periodically summarizes the trajectory, keeping context concise while enabling longer, more focused searches. On long-horizon tasks, SLIM achieves comparable performance at substantially lower cost and with far fewer tool calls than strong open-source baselines across multiple base models. Specifically, with o3 as the base model, SLIM achieves 56% on BrowseComp and 31% on HLE, outperforming all open-source frameworks by 8 and 4 absolute points, respectively, while incurring 4-6x fewer tool calls. Finally, we release an automated fine-grained trajectory analysis pipeline and error taxonomy for characterizing long-horizon agentic search frameworks; SLIM exhibits fewer hallucinations than prior systems. We hope our analysis framework and simple tool design inform future long-horizon agents.
MoDoMoDo: Multi-Domain Data Mixtures for Multimodal LLM Reinforcement Learning
May 30, 2025



Abstract:Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR) has recently emerged as a powerful paradigm for post-training large language models (LLMs), achieving state-of-the-art performance on tasks with structured, verifiable answers. Applying RLVR to Multimodal LLMs (MLLMs) presents significant opportunities but is complicated by the broader, heterogeneous nature of vision-language tasks that demand nuanced visual, logical, and spatial capabilities. As such, training MLLMs using RLVR on multiple datasets could be beneficial but creates challenges with conflicting objectives from interaction among diverse datasets, highlighting the need for optimal dataset mixture strategies to improve generalization and reasoning. We introduce a systematic post-training framework for Multimodal LLM RLVR, featuring a rigorous data mixture problem formulation and benchmark implementation. Specifically, (1) We developed a multimodal RLVR framework for multi-dataset post-training by curating a dataset that contains different verifiable vision-language problems and enabling multi-domain online RL learning with different verifiable rewards; (2) We proposed a data mixture strategy that learns to predict the RL fine-tuning outcome from the data mixture distribution, and consequently optimizes the best mixture. Comprehensive experiments showcase that multi-domain RLVR training, when combined with mixture prediction strategies, can significantly boost MLLM general reasoning capacities. Our best mixture improves the post-trained model's accuracy on out-of-distribution benchmarks by an average of 5.24% compared to the same model post-trained with uniform data mixture, and by a total of 20.74% compared to the pre-finetuning baseline.
MMTEB: Massive Multilingual Text Embedding Benchmark
Feb 19, 2025Abstract:Text embeddings are typically evaluated on a limited set of tasks, which are constrained by language, domain, and task diversity. To address these limitations and provide a more comprehensive evaluation, we introduce the Massive Multilingual Text Embedding Benchmark (MMTEB) - a large-scale, community-driven expansion of MTEB, covering over 500 quality-controlled evaluation tasks across 250+ languages. MMTEB includes a diverse set of challenging, novel tasks such as instruction following, long-document retrieval, and code retrieval, representing the largest multilingual collection of evaluation tasks for embedding models to date. Using this collection, we develop several highly multilingual benchmarks, which we use to evaluate a representative set of models. We find that while large language models (LLMs) with billions of parameters can achieve state-of-the-art performance on certain language subsets and task categories, the best-performing publicly available model is multilingual-e5-large-instruct with only 560 million parameters. To facilitate accessibility and reduce computational cost, we introduce a novel downsampling method based on inter-task correlation, ensuring a diverse selection while preserving relative model rankings. Furthermore, we optimize tasks such as retrieval by sampling hard negatives, creating smaller but effective splits. These optimizations allow us to introduce benchmarks that drastically reduce computational demands. For instance, our newly introduced zero-shot English benchmark maintains a ranking order similar to the full-scale version but at a fraction of the computational cost.
Goedel-Prover: A Frontier Model for Open-Source Automated Theorem Proving
Feb 11, 2025Abstract:We introduce Goedel-Prover, an open-source large language model (LLM) that achieves the state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance in automated formal proof generation for mathematical problems. The key challenge in this field is the scarcity of formalized math statements and proofs, which we tackle in the following ways. We train statement formalizers to translate the natural language math problems from Numina into formal language (Lean 4), creating a dataset of 1.64 million formal statements. LLMs are used to check that the formal statements accurately preserve the content of the original natural language problems. We then iteratively build a large dataset of formal proofs by training a series of provers. Each prover succeeds in proving many statements that the previous ones could not, and these new proofs are added to the training set for the next prover. The final prover outperforms all existing open-source models in whole-proof generation. On the miniF2F benchmark, it achieves a 57.6% success rate (Pass@32), exceeding the previous best open-source model by 7.6%. On PutnamBench, Goedel-Prover successfully solves 7 problems (Pass@512), ranking first on the leaderboard. Furthermore, it generates 29.7K formal proofs for Lean Workbook problems, nearly doubling the 15.7K produced by earlier works.
PDE-Controller: LLMs for Autoformalization and Reasoning of PDEs
Feb 03, 2025



Abstract:While recent AI-for-math has made strides in pure mathematics, areas of applied mathematics, particularly PDEs, remain underexplored despite their significant real-world applications. We present PDE-Controller, a framework that enables large language models (LLMs) to control systems governed by partial differential equations (PDEs). Our approach enables LLMs to transform informal natural language instructions into formal specifications, and then execute reasoning and planning steps to improve the utility of PDE control. We build a holistic solution comprising datasets (both human-written cases and 2 million synthetic samples), math-reasoning models, and novel evaluation metrics, all of which require significant effort. Our PDE-Controller significantly outperforms prompting the latest open-source and GPT models in reasoning, autoformalization, and program synthesis, achieving up to a 62% improvement in utility gain for PDE control. By bridging the gap between language generation and PDE systems, we demonstrate the potential of LLMs in addressing complex scientific and engineering challenges. We will release all data, model checkpoints, and code at https://pde-controller.github.io/.
ICONS: Influence Consensus for Vision-Language Data Selection
Jan 06, 2025



Abstract:Visual Instruction Tuning typically requires a large amount of vision-language training data. This data often containing redundant information that increases computational costs without proportional performance gains. In this work, we introduce ICONS, a gradient-driven Influence CONsensus approach for vision-language data Selection that selects a compact training dataset for efficient multi-task training. The key element of our approach is cross-task influence consensus, which uses majority voting across task-specific influence matrices to identify samples that are consistently valuable across multiple tasks, allowing us to effectively prioritize data that optimizes for overall performance. Experiments show that models trained on our selected data (20% of LLaVA-665K) achieve 98.6% of the relative performance obtained using the full dataset. Additionally, we release this subset, LLaVA-ICONS-133K, a compact yet highly informative subset of LLaVA-665K visual instruction tuning data, preserving high impact training data for efficient vision-language model development.
BRIGHT: A Realistic and Challenging Benchmark for Reasoning-Intensive Retrieval
Jul 16, 2024



Abstract:Existing retrieval benchmarks primarily consist of information-seeking queries (e.g., aggregated questions from search engines) where keyword or semantic-based retrieval is usually sufficient. However, many complex real-world queries require in-depth reasoning to identify relevant documents that go beyond surface form matching. For example, finding documentation for a coding question requires understanding the logic and syntax of the functions involved. To better benchmark retrieval on such challenging queries, we introduce BRIGHT, the first text retrieval benchmark that requires intensive reasoning to retrieve relevant documents. BRIGHT is constructed from the 1,398 real-world queries collected from diverse domains (such as economics, psychology, robotics, software engineering, earth sciences, etc.), sourced from naturally occurring or carefully curated human data. Extensive evaluation reveals that even state-of-the-art retrieval models perform poorly on BRIGHT. The leading model on the MTEB leaderboard [38 ], which achieves a score of 59.0 nDCG@10,2 produces a score of nDCG@10 of 18.0 on BRIGHT. We further demonstrate that augmenting queries with Chain-of-Thought reasoning generated by large language models (LLMs) improves performance by up to 12.2 points. Moreover, BRIGHT is robust against data leakage during pretraining of the benchmarked models as we validate by showing similar performance even when documents from the benchmark are included in the training data. We believe that BRIGHT paves the way for future research on retrieval systems in more realistic and challenging settings. Our code and data are available at https://brightbenchmark.github.io.
CharXiv: Charting Gaps in Realistic Chart Understanding in Multimodal LLMs
Jun 26, 2024



Abstract:Chart understanding plays a pivotal role when applying Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) to real-world tasks such as analyzing scientific papers or financial reports. However, existing datasets often focus on oversimplified and homogeneous charts with template-based questions, leading to an over-optimistic measure of progress. We demonstrate that although open-source models can appear to outperform strong proprietary models on these benchmarks, a simple stress test with slightly different charts or questions can deteriorate performance by up to 34.5%. In this work, we propose CharXiv, a comprehensive evaluation suite involving 2,323 natural, challenging, and diverse charts from arXiv papers. CharXiv includes two types of questions: 1) descriptive questions about examining basic chart elements and 2) reasoning questions that require synthesizing information across complex visual elements in the chart. To ensure quality, all charts and questions are handpicked, curated, and verified by human experts. Our results reveal a substantial, previously underestimated gap between the reasoning skills of the strongest proprietary model (i.e., GPT-4o), which achieves 47.1% accuracy, and the strongest open-source model (i.e., InternVL Chat V1.5), which achieves 29.2%. All models lag far behind human performance of 80.5%, underscoring weaknesses in the chart understanding capabilities of existing MLLMs. We hope CharXiv facilitates future research on MLLM chart understanding by providing a more realistic and faithful measure of progress. Project page and leaderboard: https://charxiv.github.io/
SimPO: Simple Preference Optimization with a Reference-Free Reward
May 23, 2024Abstract:Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) is a widely used offline preference optimization algorithm that reparameterizes reward functions in reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) to enhance simplicity and training stability. In this work, we propose SimPO, a simpler yet more effective approach. The effectiveness of SimPO is attributed to a key design: using the average log probability of a sequence as the implicit reward. This reward formulation better aligns with model generation and eliminates the need for a reference model, making it more compute and memory efficient. Additionally, we introduce a target reward margin to the Bradley-Terry objective to encourage a larger margin between the winning and losing responses, further enhancing the algorithm's performance. We compare SimPO to DPO and its latest variants across various state-of-the-art training setups, including both base and instruction-tuned models like Mistral and Llama3. We evaluated on extensive instruction-following benchmarks, including AlpacaEval 2, MT-Bench, and the recent challenging Arena-Hard benchmark. Our results demonstrate that SimPO consistently and significantly outperforms existing approaches without substantially increasing response length. Specifically, SimPO outperforms DPO by up to 6.4 points on AlpacaEval 2 and by up to 7.5 points on Arena-Hard. Our top-performing model, built on Llama3-8B-Instruct, achieves a remarkable 44.7 length-controlled win rate on AlpacaEval 2 -- surpassing Claude 3 Opus on the leaderboard, and a 33.8 win rate on Arena-Hard -- making it the strongest 8B open-source model.
Lory: Fully Differentiable Mixture-of-Experts for Autoregressive Language Model Pre-training
May 06, 2024



Abstract:Mixture-of-experts (MoE) models facilitate efficient scaling; however, training the router network introduces the challenge of optimizing a non-differentiable, discrete objective. Recently, a fully-differentiable MoE architecture, SMEAR, was proposed (Muqeeth et al., 2023), which softly merges experts in the parameter space; nevertheless, its effectiveness was only demonstrated in downstream fine-tuning on classification tasks. In this paper, we present Lory, the first approach that scales such architectures to autoregressive language model pre-training. Lory introduces two key techniques: (1) a causal segment routing strategy that achieves high efficiency for expert merging operations while preserving the autoregressive nature of language models; (2) a similarity-based data batching method that encourages expert specialization by grouping similar documents in training instances. We pre-train a series of Lory models on 150B tokens from scratch, with up to 32 experts and 30B (1.5B active) parameters. Experimental results show significant performance gains over parameter-matched dense models on both perplexity (+13.9%) and a variety of downstream tasks (+1.5%-11.1%). Despite segment-level routing, Lory models achieve competitive performance compared to state-of-the-art MoE models with token-level routing. We further demonstrate that the trained experts in Lory capture domain-level specialization without supervision. Our work highlights the potential of fully-differentiable MoE architectures for language model pre-training and advocates future research in this area.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge