Jay Gala
LLMs Can Compensate for Deficiencies in Visual Representations
Jun 05, 2025



Abstract:Many vision-language models (VLMs) that prove very effective at a range of multimodal task, build on CLIP-based vision encoders, which are known to have various limitations. We investigate the hypothesis that the strong language backbone in VLMs compensates for possibly weak visual features by contextualizing or enriching them. Using three CLIP-based VLMs, we perform controlled self-attention ablations on a carefully designed probing task. Our findings show that despite known limitations, CLIP visual representations offer ready-to-read semantic information to the language decoder. However, in scenarios of reduced contextualization in the visual representations, the language decoder can largely compensate for the deficiency and recover performance. This suggests a dynamic division of labor in VLMs and motivates future architectures that offload more visual processing to the language decoder.
SG-Blend: Learning an Interpolation Between Improved Swish and GELU for Robust Neural Representations
May 29, 2025Abstract:The design of activation functions remains a pivotal component in optimizing deep neural networks. While prevailing choices like Swish and GELU demonstrate considerable efficacy, they often exhibit domain-specific optima. This work introduces SG-Blend, a novel activation function that blends our proposed SSwish, a first-order symmetric variant of Swish and the established GELU through dynamic interpolation. By adaptively blending these constituent functions via learnable parameters, SG-Blend aims to harness their complementary strengths: SSwish's controlled non-monotonicity and symmetry, and GELU's smooth, probabilistic profile, to achieve a more universally robust balance between model expressivity and gradient stability. We conduct comprehensive empirical evaluations across diverse modalities and architectures, showing performance improvements across all considered natural language and computer vision tasks and models. These results, achieved with negligible computational overhead, underscore SG-Blend's potential as a versatile, drop-in replacement that consistently outperforms strong contemporary baselines. The code is available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/SGBlend-6CBC.
MMTEB: Massive Multilingual Text Embedding Benchmark
Feb 19, 2025Abstract:Text embeddings are typically evaluated on a limited set of tasks, which are constrained by language, domain, and task diversity. To address these limitations and provide a more comprehensive evaluation, we introduce the Massive Multilingual Text Embedding Benchmark (MMTEB) - a large-scale, community-driven expansion of MTEB, covering over 500 quality-controlled evaluation tasks across 250+ languages. MMTEB includes a diverse set of challenging, novel tasks such as instruction following, long-document retrieval, and code retrieval, representing the largest multilingual collection of evaluation tasks for embedding models to date. Using this collection, we develop several highly multilingual benchmarks, which we use to evaluate a representative set of models. We find that while large language models (LLMs) with billions of parameters can achieve state-of-the-art performance on certain language subsets and task categories, the best-performing publicly available model is multilingual-e5-large-instruct with only 560 million parameters. To facilitate accessibility and reduce computational cost, we introduce a novel downsampling method based on inter-task correlation, ensuring a diverse selection while preserving relative model rankings. Furthermore, we optimize tasks such as retrieval by sampling hard negatives, creating smaller but effective splits. These optimizations allow us to introduce benchmarks that drastically reduce computational demands. For instance, our newly introduced zero-shot English benchmark maintains a ranking order similar to the full-scale version but at a fraction of the computational cost.
CVQA: Culturally-diverse Multilingual Visual Question Answering Benchmark
Jun 10, 2024



Abstract:Visual Question Answering (VQA) is an important task in multimodal AI, and it is often used to test the ability of vision-language models to understand and reason on knowledge present in both visual and textual data. However, most of the current VQA models use datasets that are primarily focused on English and a few major world languages, with images that are typically Western-centric. While recent efforts have tried to increase the number of languages covered on VQA datasets, they still lack diversity in low-resource languages. More importantly, although these datasets often extend their linguistic range via translation or some other approaches, they usually keep images the same, resulting in narrow cultural representation. To address these limitations, we construct CVQA, a new Culturally-diverse multilingual Visual Question Answering benchmark, designed to cover a rich set of languages and cultures, where we engage native speakers and cultural experts in the data collection process. As a result, CVQA includes culturally-driven images and questions from across 28 countries on four continents, covering 26 languages with 11 scripts, providing a total of 9k questions. We then benchmark several Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) on CVQA, and show that the dataset is challenging for the current state-of-the-art models. This benchmark can serve as a probing evaluation suite for assessing the cultural capability and bias of multimodal models and hopefully encourage more research efforts toward increasing cultural awareness and linguistic diversity in this field.
Critical Learning Periods: Leveraging Early Training Dynamics for Efficient Data Pruning
May 29, 2024
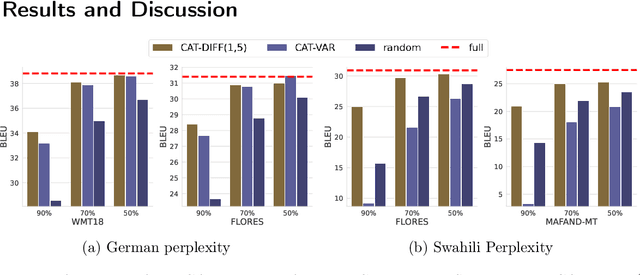
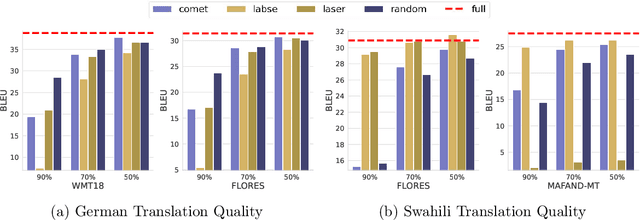
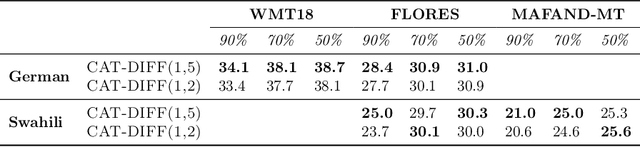
Abstract:Neural Machine Translation models are extremely data and compute-hungry. However, not all data points contribute equally to model training and generalization. Data pruning to remove the low-value data points has the benefit of drastically reducing the compute budget without significant drop in model performance. In this paper, we propose a new data pruning technique: Checkpoints Across Time (CAT), that leverages early model training dynamics to identify the most relevant data points for model performance. We benchmark CAT against several data pruning techniques including COMET-QE, LASER and LaBSE. We find that CAT outperforms the benchmarks on Indo-European languages on multiple test sets. When applied to English-German, English-French and English-Swahili translation tasks, CAT achieves comparable performance to using the full dataset, while pruning up to 50% of training data. We inspect the data points that CAT selects and find that it tends to favour longer sentences and sentences with unique or rare words.
On the low-shot transferability of -Mamba
Mar 15, 2024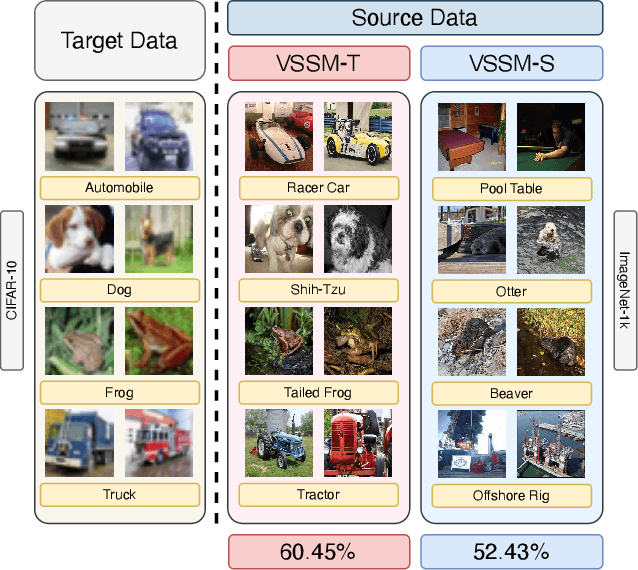
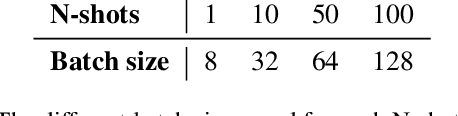
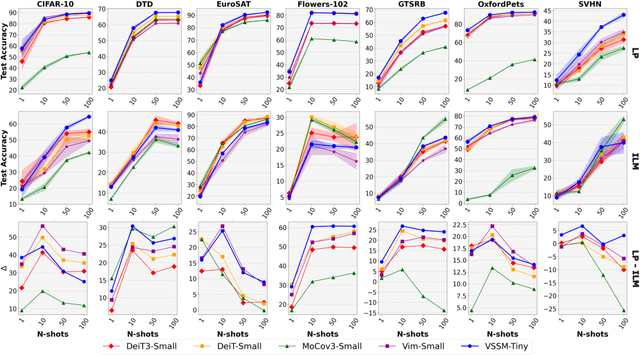
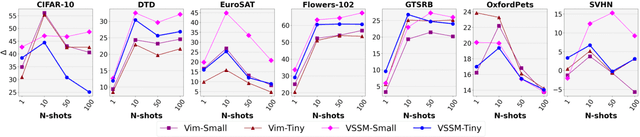
Abstract:The strength of modern large-scale neural networks lies in their ability to efficiently adapt to new tasks with few examples. Although extensive research has investigated the transferability of Vision Transformers (ViTs) to various downstream tasks under diverse constraints, this study shifts focus to explore the transfer learning potential of [V]-Mamba. We compare its performance with ViTs across different few-shot data budgets and efficient transfer methods. Our analysis yields three key insights into [V]-Mamba's few-shot transfer performance: (a) [V]-Mamba demonstrates superior or equivalent few-shot learning capabilities compared to ViTs when utilizing linear probing (LP) for transfer, (b) Conversely, [V]-Mamba exhibits weaker or similar few-shot learning performance compared to ViTs when employing visual prompting (VP) as the transfer method, and (c) We observe a weak positive correlation between the performance gap in transfer via LP and VP and the scale of the [V]-Mamba model. This preliminary analysis lays the foundation for more comprehensive studies aimed at furthering our understanding of the capabilities of [V]-Mamba variants and their distinctions from ViTs.
Airavata: Introducing Hindi Instruction-tuned LLM
Jan 26, 2024Abstract:We announce the initial release of "Airavata," an instruction-tuned LLM for Hindi. Airavata was created by fine-tuning OpenHathi with diverse, instruction-tuning Hindi datasets to make it better suited for assistive tasks. Along with the model, we also share the IndicInstruct dataset, which is a collection of diverse instruction-tuning datasets to enable further research for Indic LLMs. Additionally, we present evaluation benchmarks and a framework for assessing LLM performance across tasks in Hindi. Currently, Airavata supports Hindi, but we plan to expand this to all 22 scheduled Indic languages. You can access all artifacts at https://ai4bharat.github.io/airavata.
An Empirical Analysis of In-context Learning Abilities of LLMs for MT
Jan 22, 2024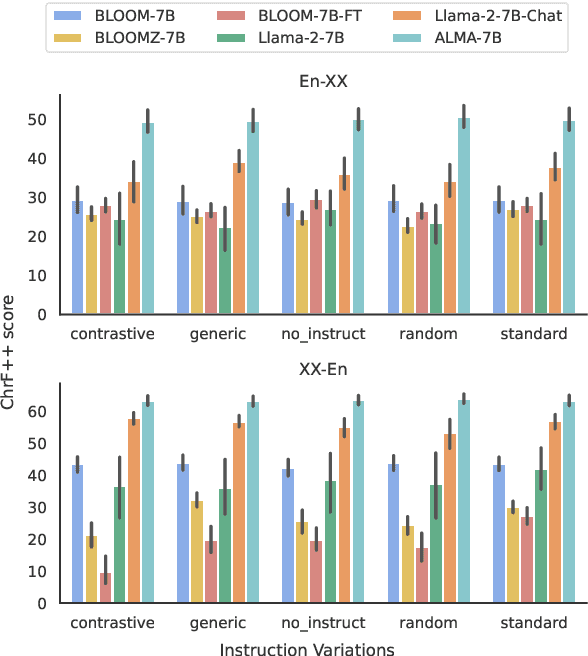
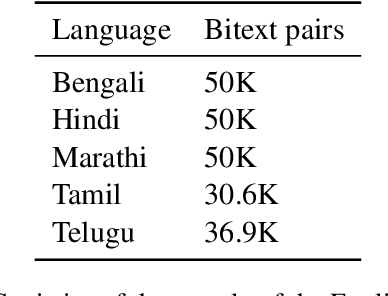
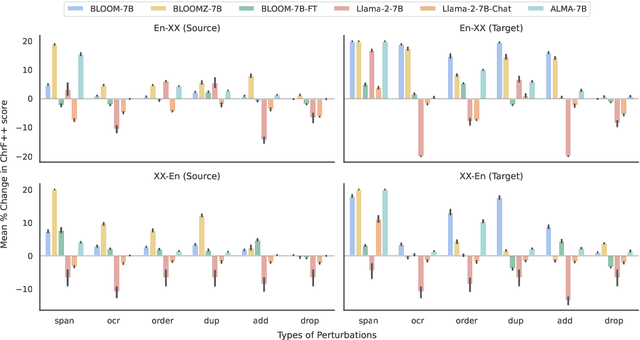
Abstract:In-context learning (ICL) has consistently demonstrated superior performance over zero-shot performance in large language models (LLMs). However, the understanding of the dynamics of ICL and the aspects that influence downstream performance remains limited, especially for natural language generation (NLG) tasks. This work aims to address this gap by investigating the ICL capabilities of LLMs and studying the impact of different aspects of the in-context demonstrations for the task of machine translation (MT). Our preliminary investigations aim to discern whether in-context learning (ICL) is predominantly influenced by demonstrations or instructions by applying diverse perturbations to in-context demonstrations while preserving the task instruction. We observe varying behavior to perturbed examples across different model families, notably with BLOOM-7B derivatives being severely influenced by noise, whereas Llama 2 derivatives not only exhibit robustness but also tend to show enhancements over the clean baseline when subject to perturbed demonstrations. This suggests that the robustness of ICL may be governed by several factors, including the type of noise, perturbation direction (source or target), the extent of pretraining of the specific model, and fine-tuning for downstream tasks if applicable. Further investigation is warranted to develop a comprehensive understanding of these factors in future research.
Adaptive-Labeling for Enhancing Remote Sensing Cloud Understanding
Nov 09, 2023Abstract:Cloud analysis is a critical component of weather and climate science, impacting various sectors like disaster management. However, achieving fine-grained cloud analysis, such as cloud segmentation, in remote sensing remains challenging due to the inherent difficulties in obtaining accurate labels, leading to significant labeling errors in training data. Existing methods often assume the availability of reliable segmentation annotations, limiting their overall performance. To address this inherent limitation, we introduce an innovative model-agnostic Cloud Adaptive-Labeling (CAL) approach, which operates iteratively to enhance the quality of training data annotations and consequently improve the performance of the learned model. Our methodology commences by training a cloud segmentation model using the original annotations. Subsequently, it introduces a trainable pixel intensity threshold for adaptively labeling the cloud training images on the fly. The newly generated labels are then employed to fine-tune the model. Extensive experiments conducted on multiple standard cloud segmentation benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach in significantly boosting the performance of existing segmentation models. Our CAL method establishes new state-of-the-art results when compared to a wide array of existing alternatives.
IndicTrans2: Towards High-Quality and Accessible Machine Translation Models for all 22 Scheduled Indian Languages
May 25, 2023Abstract:India has a rich linguistic landscape with languages from 4 major language families spoken by over a billion people. 22 of these languages are listed in the Constitution of India (referred to as scheduled languages) are the focus of this work. Given the linguistic diversity, high-quality and accessible Machine Translation (MT) systems are essential in a country like India. Prior to this work, there was (i) no parallel training data spanning all the 22 languages, (ii) no robust benchmarks covering all these languages and containing content relevant to India, and (iii) no existing translation models which support all the 22 scheduled languages of India. In this work, we aim to address this gap by focusing on the missing pieces required for enabling wide, easy, and open access to good machine translation systems for all 22 scheduled Indian languages. We identify four key areas of improvement: curating and creating larger training datasets, creating diverse and high-quality benchmarks, training multilingual models, and releasing models with open access. Our first contribution is the release of the Bharat Parallel Corpus Collection (BPCC), the largest publicly available parallel corpora for Indic languages. BPCC contains a total of 230M bitext pairs, of which a total of 126M were newly added, including 644K manually translated sentence pairs created as part of this work. Our second contribution is the release of the first n-way parallel benchmark covering all 22 Indian languages, featuring diverse domains, Indian-origin content, and source-original test sets. Next, we present IndicTrans2, the first model to support all 22 languages, surpassing existing models on multiple existing and new benchmarks created as a part of this work. Lastly, to promote accessibility and collaboration, we release our models and associated data with permissive licenses at https://github.com/ai4bharat/IndicTrans2.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge