Everlyn Asiko Chimoto
Calibrating Beyond English: Language Diversity for Better Quantized Multilingual LLM
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:Quantization is an effective technique for reducing the storage footprint and computational costs of Large Language Models (LLMs), but it often results in performance degradation. Existing post-training quantization methods typically use small, English-only calibration sets; however, their impact on multilingual models remains underexplored. We systematically evaluate eight calibration settings (five single-language and three multilingual mixes) on two quantizers (GPTQ, AWQ) on data from 10 languages. Our findings reveal a consistent trend: non-English and multilingual calibration sets significantly improve perplexity compared to English-only baselines. Specifically, we observe notable average perplexity gains across both quantizers on Llama3.1 8B and Qwen2.5 7B, with multilingual mixes achieving the largest overall reductions of up to 3.52 points in perplexity. Furthermore, our analysis indicates that tailoring calibration sets to the evaluation language yields the largest improvements for individual languages, underscoring the importance of linguistic alignment. We also identify specific failure cases where certain language-quantizer combinations degrade performance, which we trace to differences in activation range distributions across languages. These results highlight that static one-size-fits-all calibration is suboptimal and that tailoring calibration data, both in language and diversity, plays a crucial role in robustly quantizing multilingual LLMs.
The Esethu Framework: Reimagining Sustainable Dataset Governance and Curation for Low-Resource Languages
Feb 21, 2025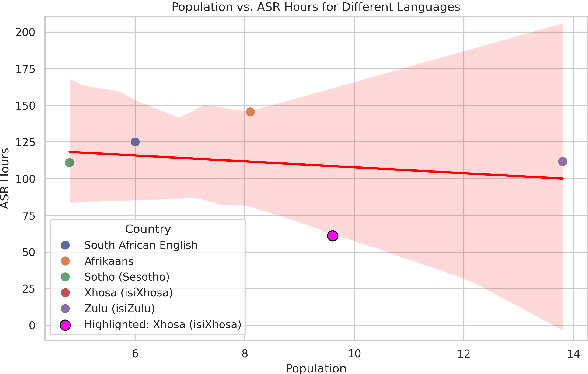

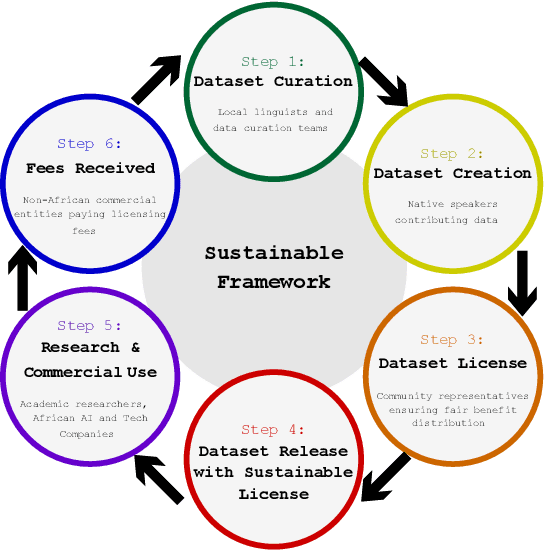
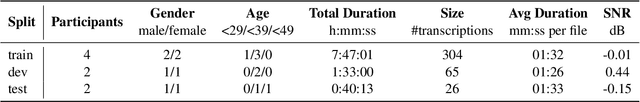
Abstract:This paper presents the Esethu Framework, a sustainable data curation framework specifically designed to empower local communities and ensure equitable benefit-sharing from their linguistic resources. This framework is supported by the Esethu license, a novel community-centric data license. As a proof of concept, we introduce the Vuk'uzenzele isiXhosa Speech Dataset (ViXSD), an open-source corpus developed under the Esethu Framework and License. The dataset, containing read speech from native isiXhosa speakers enriched with demographic and linguistic metadata, demonstrates how community-driven licensing and curation principles can bridge resource gaps in automatic speech recognition (ASR) for African languages while safeguarding the interests of data creators. We describe the framework guiding dataset development, outline the Esethu license provisions, present the methodology for ViXSD, and present ASR experiments validating ViXSD's usability in building and refining voice-driven applications for isiXhosa.
GrammaMT: Improving Machine Translation with Grammar-Informed In-Context Learning
Oct 24, 2024Abstract:We introduce GrammaMT, a grammatically-aware prompting approach for machine translation that uses Interlinear Glossed Text (IGT), a common form of linguistic description providing morphological and lexical annotations for source sentences. GrammaMT proposes three prompting strategies: gloss-shot, chain-gloss and model-gloss. All are training-free, requiring only a few examples that involve minimal effort to collect, and making them well-suited for low-resource setups. Experiments show that GrammaMT enhances translation performance on open-source instruction-tuned LLMs for various low- to high-resource languages across three benchmarks: (1) the largest IGT corpus, (2) the challenging 2023 SIGMORPHON Shared Task data over endangered languages, and (3) even in an out-of-domain setting with FLORES. Moreover, ablation studies reveal that leveraging gloss resources could substantially boost MT performance (by over 17 BLEU points) if LLMs accurately generate or access input sentence glosses.
State of NLP in Kenya: A Survey
Oct 13, 2024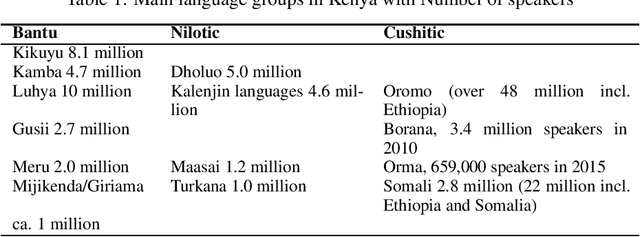
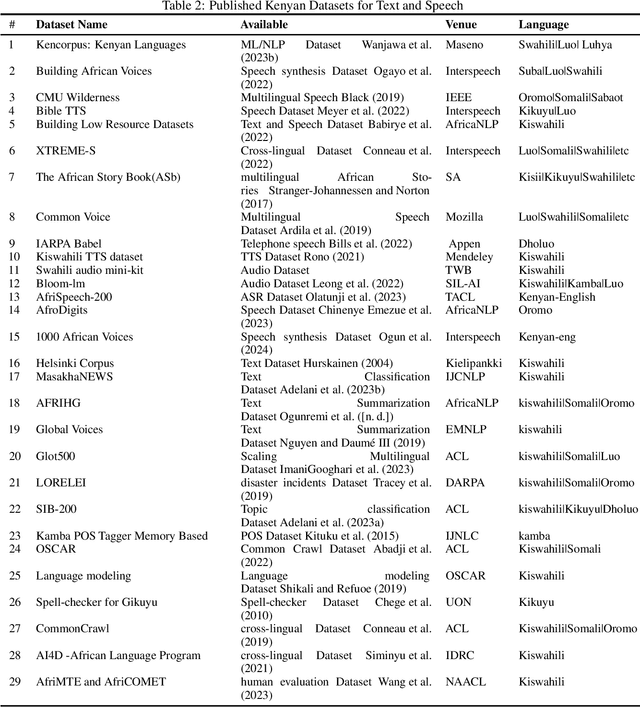
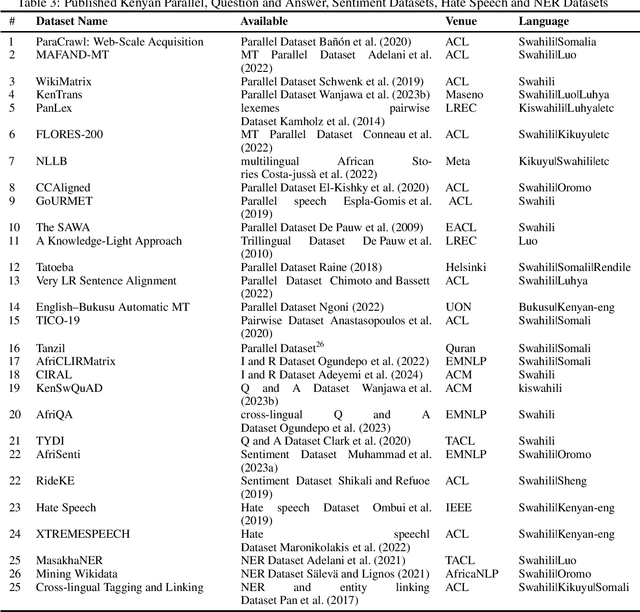
Abstract:Kenya, known for its linguistic diversity, faces unique challenges and promising opportunities in advancing Natural Language Processing (NLP) technologies, particularly for its underrepresented indigenous languages. This survey provides a detailed assessment of the current state of NLP in Kenya, emphasizing ongoing efforts in dataset creation, machine translation, sentiment analysis, and speech recognition for local dialects such as Kiswahili, Dholuo, Kikuyu, and Luhya. Despite these advancements, the development of NLP in Kenya remains constrained by limited resources and tools, resulting in the underrepresentation of most indigenous languages in digital spaces. This paper uncovers significant gaps by critically evaluating the available datasets and existing NLP models, most notably the need for large-scale language models and the insufficient digital representation of Indigenous languages. We also analyze key NLP applications: machine translation, information retrieval, and sentiment analysis-examining how they are tailored to address local linguistic needs. Furthermore, the paper explores the governance, policies, and regulations shaping the future of AI and NLP in Kenya and proposes a strategic roadmap to guide future research and development efforts. Our goal is to provide a foundation for accelerating the growth of NLP technologies that meet Kenya's diverse linguistic demands.
Critical Learning Periods: Leveraging Early Training Dynamics for Efficient Data Pruning
May 29, 2024
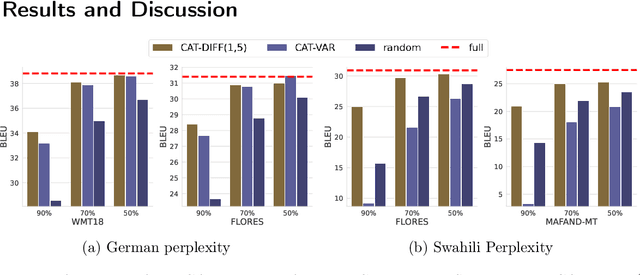
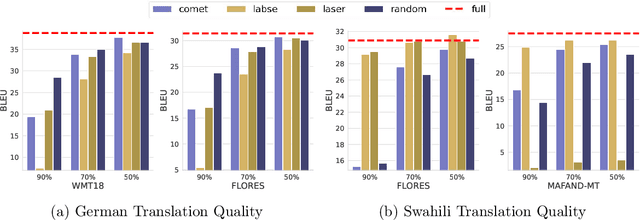
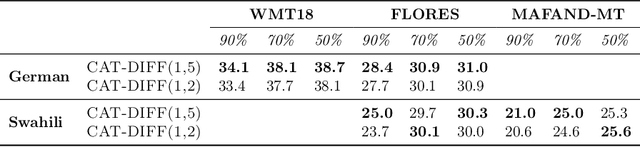
Abstract:Neural Machine Translation models are extremely data and compute-hungry. However, not all data points contribute equally to model training and generalization. Data pruning to remove the low-value data points has the benefit of drastically reducing the compute budget without significant drop in model performance. In this paper, we propose a new data pruning technique: Checkpoints Across Time (CAT), that leverages early model training dynamics to identify the most relevant data points for model performance. We benchmark CAT against several data pruning techniques including COMET-QE, LASER and LaBSE. We find that CAT outperforms the benchmarks on Indo-European languages on multiple test sets. When applied to English-German, English-French and English-Swahili translation tasks, CAT achieves comparable performance to using the full dataset, while pruning up to 50% of training data. We inspect the data points that CAT selects and find that it tends to favour longer sentences and sentences with unique or rare words.
Towards hate speech detection in low-resource languages: Comparing ASR to acoustic word embeddings on Wolof and Swahili
Jun 01, 2023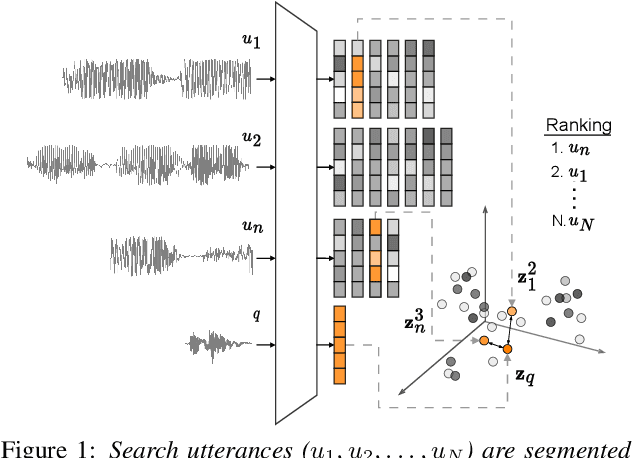

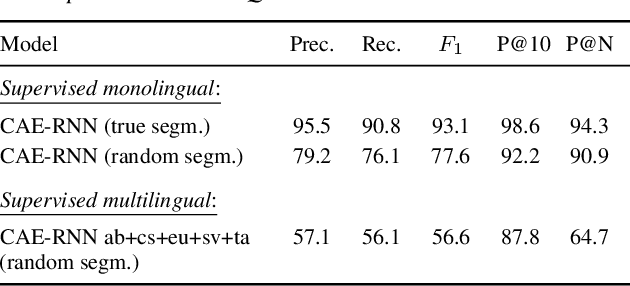
Abstract:We consider hate speech detection through keyword spotting on radio broadcasts. One approach is to build an automatic speech recognition (ASR) system for the target low-resource language. We compare this to using acoustic word embedding (AWE) models that map speech segments to a space where matching words have similar vectors. We specifically use a multilingual AWE model trained on labelled data from well-resourced languages to spot keywords in data in the unseen target language. In contrast to ASR, the AWE approach only requires a few keyword exemplars. In controlled experiments on Wolof and Swahili where training and test data are from the same domain, an ASR model trained on just five minutes of data outperforms the AWE approach. But in an in-the-wild test on Swahili radio broadcasts with actual hate speech keywords, the AWE model (using one minute of template data) is more robust, giving similar performance to an ASR system trained on 30 hours of labelled data.
Very Low Resource Sentence Alignment: Luhya and Swahili
Oct 31, 2022



Abstract:Language-agnostic sentence embeddings generated by pre-trained models such as LASER and LaBSE are attractive options for mining large datasets to produce parallel corpora for low-resource machine translation. We test LASER and LaBSE in extracting bitext for two related low-resource African languages: Luhya and Swahili. For this work, we created a new parallel set of nearly 8000 Luhya-English sentences which allows a new zero-shot test of LASER and LaBSE. We find that LaBSE significantly outperforms LASER on both languages. Both LASER and LaBSE however perform poorly at zero-shot alignment on Luhya, achieving just 1.5% and 22.0% successful alignments respectively (P@1 score). We fine-tune the embeddings on a small set of parallel Luhya sentences and show significant gains, improving the LaBSE alignment accuracy to 53.3%. Further, restricting the dataset to sentence embedding pairs with cosine similarity above 0.7 yielded alignments with over 85% accuracy.
COMET-QE and Active Learning for Low-Resource Machine Translation
Oct 27, 2022Abstract:Active learning aims to deliver maximum benefit when resources are scarce. We use COMET-QE, a reference-free evaluation metric, to select sentences for low-resource neural machine translation. Using Swahili, Kinyarwanda and Spanish for our experiments, we show that COMET-QE significantly outperforms two variants of Round Trip Translation Likelihood (RTTL) and random sentence selection by up to 5 BLEU points for 20k sentences selected by Active Learning on a 30k baseline. This suggests that COMET-QE is a powerful tool for sentence selection in the very low-resource limit.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge