Subarna Tripathi
Toward Scalable Video Narration: A Training-free Approach Using Multimodal Large Language Models
Jul 22, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we introduce VideoNarrator, a novel training-free pipeline designed to generate dense video captions that offer a structured snapshot of video content. These captions offer detailed narrations with precise timestamps, capturing the nuances present in each segment of the video. Despite advancements in multimodal large language models (MLLMs) for video comprehension, these models often struggle with temporally aligned narrations and tend to hallucinate, particularly in unfamiliar scenarios. VideoNarrator addresses these challenges by leveraging a flexible pipeline where off-the-shelf MLLMs and visual-language models (VLMs) can function as caption generators, context providers, or caption verifiers. Our experimental results demonstrate that the synergistic interaction of these components significantly enhances the quality and accuracy of video narrations, effectively reducing hallucinations and improving temporal alignment. This structured approach not only enhances video understanding but also facilitates downstream tasks such as video summarization and video question answering, and can be potentially extended for advertising and marketing applications.
EASG-Bench: Video Q&A Benchmark with Egocentric Action Scene Graphs
Jun 06, 2025Abstract:We introduce EASG-Bench, a question-answering benchmark for egocentric videos where the question-answering pairs are created from spatio-temporally grounded dynamic scene graphs capturing intricate relationships among actors, actions, and objects. We propose a systematic evaluation framework and evaluate several language-only and video large language models (video-LLMs) on this benchmark. We observe a performance gap in language-only and video-LLMs, especially on questions focusing on temporal ordering, thus identifying a research gap in the area of long-context video understanding. To promote the reproducibility of our findings and facilitate further research, the benchmark and accompanying code are available at the following GitHub page: https://github.com/fpv-iplab/EASG-bench.
SG-Blend: Learning an Interpolation Between Improved Swish and GELU for Robust Neural Representations
May 29, 2025Abstract:The design of activation functions remains a pivotal component in optimizing deep neural networks. While prevailing choices like Swish and GELU demonstrate considerable efficacy, they often exhibit domain-specific optima. This work introduces SG-Blend, a novel activation function that blends our proposed SSwish, a first-order symmetric variant of Swish and the established GELU through dynamic interpolation. By adaptively blending these constituent functions via learnable parameters, SG-Blend aims to harness their complementary strengths: SSwish's controlled non-monotonicity and symmetry, and GELU's smooth, probabilistic profile, to achieve a more universally robust balance between model expressivity and gradient stability. We conduct comprehensive empirical evaluations across diverse modalities and architectures, showing performance improvements across all considered natural language and computer vision tasks and models. These results, achieved with negligible computational overhead, underscore SG-Blend's potential as a versatile, drop-in replacement that consistently outperforms strong contemporary baselines. The code is available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/SGBlend-6CBC.
Graph-Based Multimodal and Multi-view Alignment for Keystep Recognition
Jan 07, 2025Abstract:Egocentric videos capture scenes from a wearer's viewpoint, resulting in dynamic backgrounds, frequent motion, and occlusions, posing challenges to accurate keystep recognition. We propose a flexible graph-learning framework for fine-grained keystep recognition that is able to effectively leverage long-term dependencies in egocentric videos, and leverage alignment between egocentric and exocentric videos during training for improved inference on egocentric videos. Our approach consists of constructing a graph where each video clip of the egocentric video corresponds to a node. During training, we consider each clip of each exocentric video (if available) as additional nodes. We examine several strategies to define connections across these nodes and pose keystep recognition as a node classification task on the constructed graphs. We perform extensive experiments on the Ego-Exo4D dataset and show that our proposed flexible graph-based framework notably outperforms existing methods by more than 12 points in accuracy. Furthermore, the constructed graphs are sparse and compute efficient. We also present a study examining on harnessing several multimodal features, including narrations, depth, and object class labels, on a heterogeneous graph and discuss their corresponding contribution to the keystep recognition performance.
Ego-VPA: Egocentric Video Understanding with Parameter-efficient Adaptation
Jul 28, 2024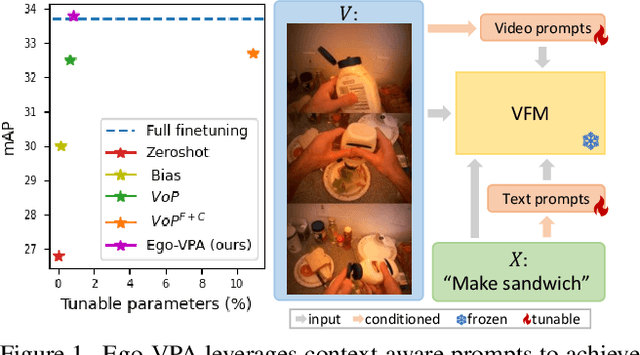
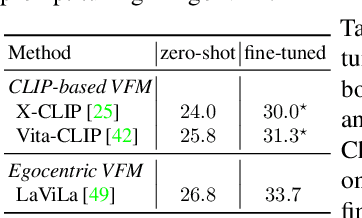
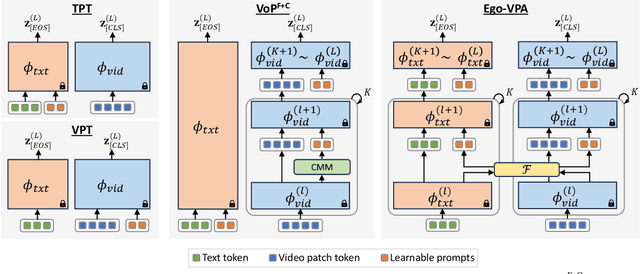
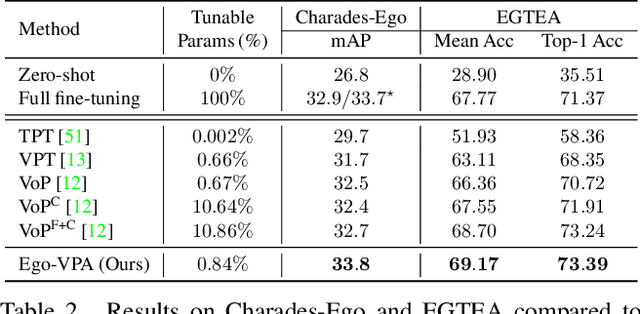
Abstract:Video understanding typically requires fine-tuning the large backbone when adapting to new domains. In this paper, we leverage the egocentric video foundation models (Ego-VFMs) based on video-language pre-training and propose a parameter-efficient adaptation for egocentric video tasks, namely Ego-VPA. It employs a local sparse approximation for each video frame/text feature using the basis prompts, and the selected basis prompts are used to synthesize video/text prompts. Since the basis prompts are shared across frames and modalities, it models context fusion and cross-modal transfer in an efficient fashion. Experiments show that Ego-VPA excels in lightweight adaptation (with only 0.84% learnable parameters), largely improving over baselines and reaching the performance of full fine-tuning.
SViTT-Ego: A Sparse Video-Text Transformer for Egocentric Video
Jun 13, 2024Abstract:Pretraining egocentric vision-language models has become essential to improving downstream egocentric video-text tasks. These egocentric foundation models commonly use the transformer architecture. The memory footprint of these models during pretraining can be substantial. Therefore, we pretrain SViTT-Ego, the first sparse egocentric video-text transformer model integrating edge and node sparsification. We pretrain on the EgoClip dataset and incorporate the egocentric-friendly objective EgoNCE, instead of the frequently used InfoNCE. Most notably, SViTT-Ego obtains a +2.8% gain on EgoMCQ (intra-video) accuracy compared to LAVILA large, with no additional data augmentation techniques other than standard image augmentations, yet pretrainable on memory-limited devices.
Contrastive Language Video Time Pre-training
Jun 04, 2024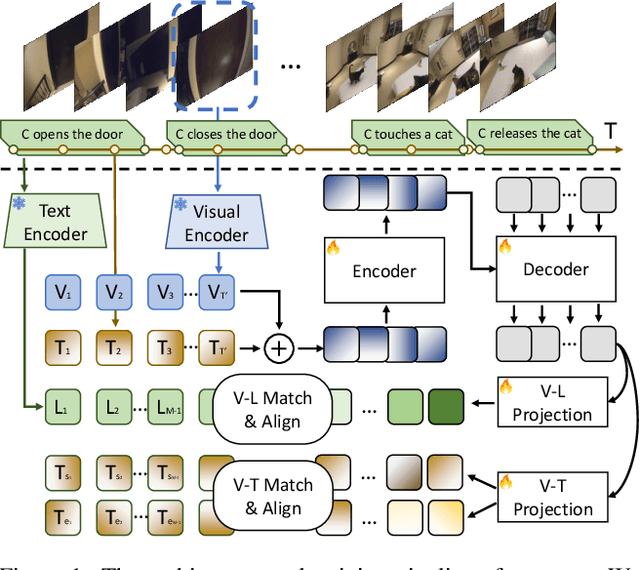
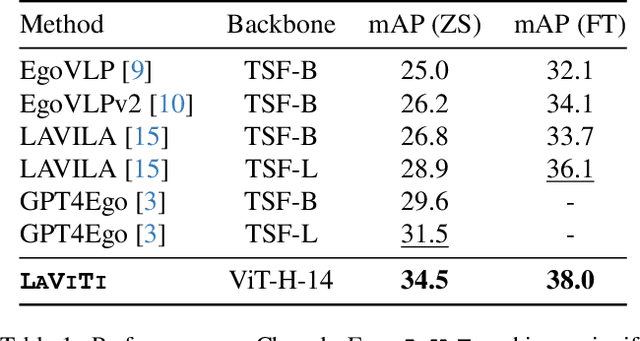

Abstract:We introduce LAVITI, a novel approach to learning language, video, and temporal representations in long-form videos via contrastive learning. Different from pre-training on video-text pairs like EgoVLP, LAVITI aims to align language, video, and temporal features by extracting meaningful moments in untrimmed videos. Our model employs a set of learnable moment queries to decode clip-level visual, language, and temporal features. In addition to vision and language alignment, we introduce relative temporal embeddings (TE) to represent timestamps in videos, which enables contrastive learning of time. Significantly different from traditional approaches, the prediction of a particular timestamp is transformed by computing the similarity score between the predicted TE and all TEs. Furthermore, existing approaches for video understanding are mainly designed for short videos due to high computational complexity and memory footprint. Our method can be trained on the Ego4D dataset with only 8 NVIDIA RTX-3090 GPUs in a day. We validated our method on CharadesEgo action recognition, achieving state-of-the-art results.
VideoSAGE: Video Summarization with Graph Representation Learning
Apr 14, 2024Abstract:We propose a graph-based representation learning framework for video summarization. First, we convert an input video to a graph where nodes correspond to each of the video frames. Then, we impose sparsity on the graph by connecting only those pairs of nodes that are within a specified temporal distance. We then formulate the video summarization task as a binary node classification problem, precisely classifying video frames whether they should belong to the output summary video. A graph constructed this way aims to capture long-range interactions among video frames, and the sparsity ensures the model trains without hitting the memory and compute bottleneck. Experiments on two datasets(SumMe and TVSum) demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed nimble model compared to existing state-of-the-art summarization approaches while being one order of magnitude more efficient in compute time and memory
Action Scene Graphs for Long-Form Understanding of Egocentric Videos
Dec 06, 2023Abstract:We present Egocentric Action Scene Graphs (EASGs), a new representation for long-form understanding of egocentric videos. EASGs extend standard manually-annotated representations of egocentric videos, such as verb-noun action labels, by providing a temporally evolving graph-based description of the actions performed by the camera wearer, including interacted objects, their relationships, and how actions unfold in time. Through a novel annotation procedure, we extend the Ego4D dataset by adding manually labeled Egocentric Action Scene Graphs offering a rich set of annotations designed for long-from egocentric video understanding. We hence define the EASG generation task and provide a baseline approach, establishing preliminary benchmarks. Experiments on two downstream tasks, egocentric action anticipation and egocentric activity summarization, highlight the effectiveness of EASGs for long-form egocentric video understanding. We will release the dataset and the code to replicate experiments and annotations.
Single-Stage Visual Relationship Learning using Conditional Queries
Jun 09, 2023Abstract:Research in scene graph generation (SGG) usually considers two-stage models, that is, detecting a set of entities, followed by combining them and labeling all possible relationships. While showing promising results, the pipeline structure induces large parameter and computation overhead, and typically hinders end-to-end optimizations. To address this, recent research attempts to train single-stage models that are computationally efficient. With the advent of DETR, a set based detection model, one-stage models attempt to predict a set of subject-predicate-object triplets directly in a single shot. However, SGG is inherently a multi-task learning problem that requires modeling entity and predicate distributions simultaneously. In this paper, we propose Transformers with conditional queries for SGG, namely, TraCQ with a new formulation for SGG that avoids the multi-task learning problem and the combinatorial entity pair distribution. We employ a DETR-based encoder-decoder design and leverage conditional queries to significantly reduce the entity label space as well, which leads to 20% fewer parameters compared to state-of-the-art single-stage models. Experimental results show that TraCQ not only outperforms existing single-stage scene graph generation methods, it also beats many state-of-the-art two-stage methods on the Visual Genome dataset, yet is capable of end-to-end training and faster inference.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge