Giovanni Maria Farinella
FPV@IPLAB - Department of Mathematics and Computer Science - University of Catania - Italy, Cognitive Robotics and Social Sensing Laboratory - ICAR-CNR - Palermo - Italy, Next Vision s.r.l. - Catania - Italy
ProSkill: Segment-Level Skill Assessment in Procedural Videos
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Skill assessment in procedural videos is crucial for the objective evaluation of human performance in settings such as manufacturing and procedural daily tasks. Current research on skill assessment has predominantly focused on sports and lacks large-scale datasets for complex procedural activities. Existing studies typically involve only a limited number of actions, focus on either pairwise assessments (e.g., A is better than B) or on binary labels (e.g., good execution vs needs improvement). In response to these shortcomings, we introduce ProSkill, the first benchmark dataset for action-level skill assessment in procedural tasks. ProSkill provides absolute skill assessment annotations, along with pairwise ones. This is enabled by a novel and scalable annotation protocol that allows for the creation of an absolute skill assessment ranking starting from pairwise assessments. This protocol leverages a Swiss Tournament scheme for efficient pairwise comparisons, which are then aggregated into consistent, continuous global scores using an ELO-based rating system. We use our dataset to benchmark the main state-of-the-art skill assessment algorithms, including both ranking-based and pairwise paradigms. The suboptimal results achieved by the current state-of-the-art highlight the challenges and thus the value of ProSkill in the context of skill assessment for procedural videos. All data and code are available at https://fpv-iplab.github.io/ProSkill/
GlovEgo-HOI: Bridging the Synthetic-to-Real Gap for Industrial Egocentric Human-Object Interaction Detection
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:Egocentric Human-Object Interaction (EHOI) analysis is crucial for industrial safety, yet the development of robust models is hindered by the scarcity of annotated domain-specific data. We address this challenge by introducing a data generation framework that combines synthetic data with a diffusion-based process to augment real-world images with realistic Personal Protective Equipment (PPE). We present GlovEgo-HOI, a new benchmark dataset for industrial EHOI, and GlovEgo-Net, a model integrating Glove-Head and Keypoint- Head modules to leverage hand pose information for enhanced interaction detection. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed data generation framework and GlovEgo-Net. To foster further research, we release the GlovEgo-HOI dataset, augmentation pipeline, and pre-trained models at: GitHub project.
SignIT: A Comprehensive Dataset and Multimodal Analysis for Italian Sign Language Recognition
Dec 16, 2025Abstract:In this work we present SignIT, a new dataset to study the task of Italian Sign Language (LIS) recognition. The dataset is composed of 644 videos covering 3.33 hours. We manually annotated videos considering a taxonomy of 94 distinct sign classes belonging to 5 macro-categories: Animals, Food, Colors, Emotions and Family. We also extracted 2D keypoints related to the hands, face and body of the users. With the dataset, we propose a benchmark for the sign recognition task, adopting several state-of-the-art models showing how temporal information, 2D keypoints and RGB frames can be influence the performance of these models. Results show the limitations of these models on this challenging LIS dataset. We release data and annotations at the following link: https://fpv-iplab.github.io/SignIT/.
Ego-EXTRA: video-language Egocentric Dataset for EXpert-TRAinee assistance
Dec 15, 2025Abstract:We present Ego-EXTRA, a video-language Egocentric Dataset for EXpert-TRAinee assistance. Ego-EXTRA features 50 hours of unscripted egocentric videos of subjects performing procedural activities (the trainees) while guided by real-world experts who provide guidance and answer specific questions using natural language. Following a ``Wizard of OZ'' data collection paradigm, the expert enacts a wearable intelligent assistant, looking at the activities performed by the trainee exclusively from their egocentric point of view, answering questions when asked by the trainee, or proactively interacting with suggestions during the procedures. This unique data collection protocol enables Ego-EXTRA to capture a high-quality dialogue in which expert-level feedback is provided to the trainee. Two-way dialogues between experts and trainees are recorded, transcribed, and used to create a novel benchmark comprising more than 15k high-quality Visual Question Answer sets, which we use to evaluate Multimodal Large Language Models. The results show that Ego-EXTRA is challenging and highlight the limitations of current models when used to provide expert-level assistance to the user. The Ego-EXTRA dataset is publicly available to support the benchmark of egocentric video-language assistants: https://fpv-iplab.github.io/Ego-EXTRA/.
A Real-Time System for Egocentric Hand-Object Interaction Detection in Industrial Domains
Jul 17, 2025Abstract:Hand-object interaction detection remains an open challenge in real-time applications, where intuitive user experiences depend on fast and accurate detection of interactions with surrounding objects. We propose an efficient approach for detecting hand-objects interactions from streaming egocentric vision that operates in real time. Our approach consists of an action recognition module and an object detection module for identifying active objects upon confirmed interaction. Our Mamba model with EfficientNetV2 as backbone for action recognition achieves 38.52% p-AP on the ENIGMA-51 benchmark at 30fps, while our fine-tuned YOLOWorld reaches 85.13% AP for hand and object. We implement our models in a cascaded architecture where the action recognition and object detection modules operate sequentially. When the action recognition predicts a contact state, it activates the object detection module, which in turn performs inference on the relevant frame to detect and classify the active object.
Efficient Calisthenics Skills Classification through Foreground Instance Selection and Depth Estimation
Jul 16, 2025
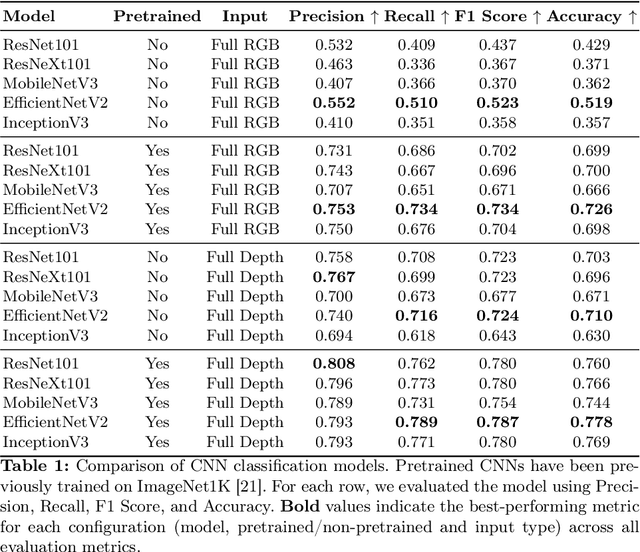
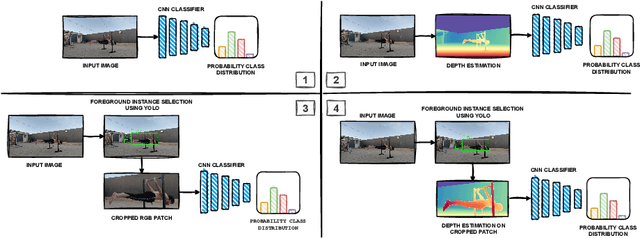
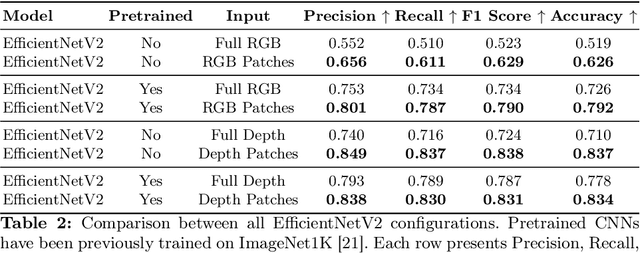
Abstract:Calisthenics skill classification is the computer vision task of inferring the skill performed by an athlete from images, enabling automatic performance assessment and personalized analytics. Traditional methods for calisthenics skill recognition are based on pose estimation methods to determine the position of skeletal data from images, which is later fed to a classification algorithm to infer the performed skill. Despite the progress in human pose estimation algorithms, they still involve high computational costs, long inference times, and complex setups, which limit the applicability of such approaches in real-time applications or mobile devices. This work proposes a direct approach to calisthenics skill recognition, which leverages depth estimation and athlete patch retrieval to avoid the computationally expensive human pose estimation module. Using Depth Anything V2 for depth estimation and YOLOv10 for athlete localization, we segment the subject from the background rather than relying on traditional pose estimation techniques. This strategy increases efficiency, reduces inference time, and improves classification accuracy. Our approach significantly outperforms skeleton-based methods, achieving 38.3x faster inference with RGB image patches and improved classification accuracy with depth patches (0.837 vs. 0.815). Beyond these performance gains, the modular design of our pipeline allows for flexible replacement of components, enabling future enhancements and adaptation to real-world applications.
Calisthenics Skills Temporal Video Segmentation
Jul 16, 2025
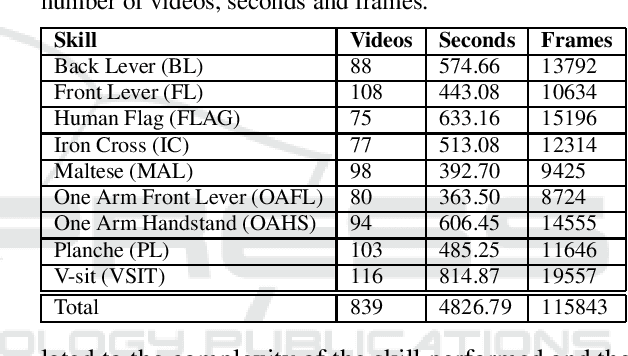

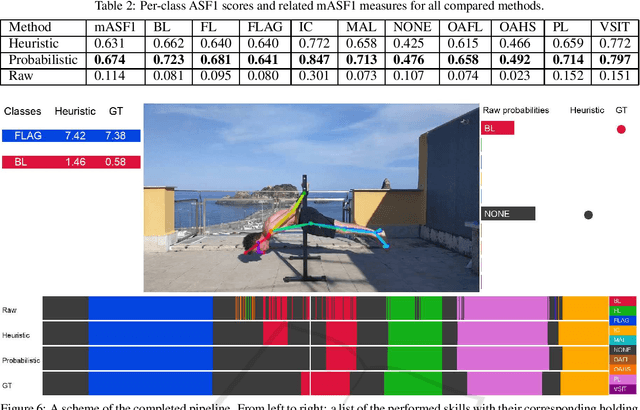
Abstract:Calisthenics is a fast-growing bodyweight discipline that consists of different categories, one of which is focused on skills. Skills in calisthenics encompass both static and dynamic elements performed by athletes. The evaluation of static skills is based on their difficulty level and the duration of the hold. Automated tools able to recognize isometric skills from a video by segmenting them to estimate their duration would be desirable to assist athletes in their training and judges during competitions. Although the video understanding literature on action recognition through body pose analysis is rich, no previous work has specifically addressed the problem of calisthenics skill temporal video segmentation. This study aims to provide an initial step towards the implementation of automated tools within the field of Calisthenics. To advance knowledge in this context, we propose a dataset of video footage of static calisthenics skills performed by athletes. Each video is annotated with a temporal segmentation which determines the extent of each skill. We hence report the results of a baseline approach to address the problem of skill temporal segmentation on the proposed dataset. The results highlight the feasibility of the proposed problem, while there is still room for improvement.
EASG-Bench: Video Q&A Benchmark with Egocentric Action Scene Graphs
Jun 06, 2025Abstract:We introduce EASG-Bench, a question-answering benchmark for egocentric videos where the question-answering pairs are created from spatio-temporally grounded dynamic scene graphs capturing intricate relationships among actors, actions, and objects. We propose a systematic evaluation framework and evaluate several language-only and video large language models (video-LLMs) on this benchmark. We observe a performance gap in language-only and video-LLMs, especially on questions focusing on temporal ordering, thus identifying a research gap in the area of long-context video understanding. To promote the reproducibility of our findings and facilitate further research, the benchmark and accompanying code are available at the following GitHub page: https://github.com/fpv-iplab/EASG-bench.
Task Graph Maximum Likelihood Estimation for Procedural Activity Understanding in Egocentric Videos
Feb 26, 2025Abstract:We introduce a gradient-based approach for learning task graphs from procedural activities, improving over hand-crafted methods. Our method directly optimizes edge weights via maximum likelihood, enabling integration into neural architectures. We validate our approach on CaptainCook4D, EgoPER, and EgoProceL, achieving +14.5%, +10.2%, and +13.6% F1-score improvements. Our feature-based approach for predicting task graphs from textual/video embeddings demonstrates emerging video understanding abilities. We also achieved top performance on the procedure understanding benchmark on Ego-Exo4D and significantly improved online mistake detection (+19.8% on Assembly101-O, +6.4% on EPIC-Tent-O). Code: https://github.com/fpv-iplab/Differentiable-Task-Graph-Learning.
Online Episodic Memory Visual Query Localization with Egocentric Streaming Object Memory
Nov 25, 2024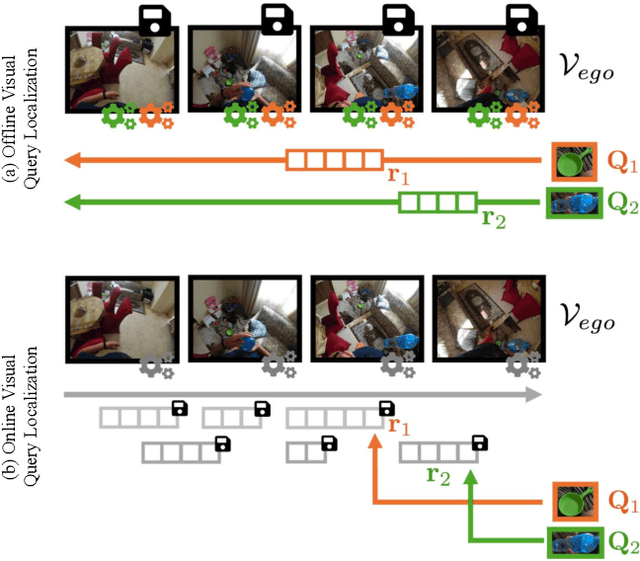
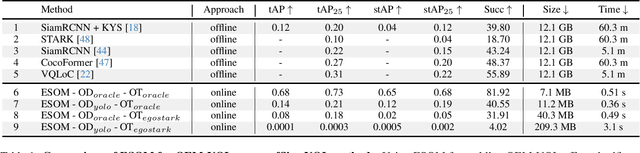
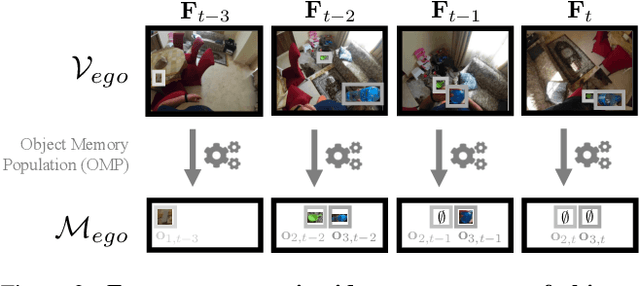
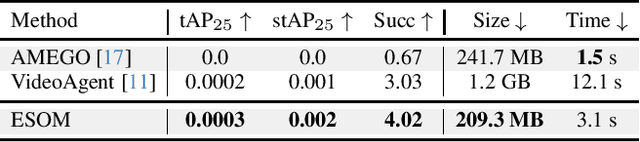
Abstract:Episodic memory retrieval aims to enable wearable devices with the ability to recollect from past video observations objects or events that have been observed (e.g., "where did I last see my smartphone?"). Despite the clear relevance of the task for a wide range of assistive systems, current task formulations are based on the "offline" assumption that the full video history can be accessed when the user makes a query, which is unrealistic in real settings, where wearable devices are limited in power and storage capacity. We introduce the novel task of Online Episodic Memory Visual Queries Localization (OEM-VQL), in which models are required to work in an online fashion, observing video frames only once and relying on past computations to answer user queries. To tackle this challenging task, we propose ESOM - Egocentric Streaming Object Memory, a novel framework based on an object discovery module to detect potentially interesting objects, a visual object tracker to track their position through the video in an online fashion, and a memory module to store spatio-temporal object coordinates and image representations, which can be queried efficiently at any moment. Comparisons with different baselines and offline methods show that OEM-VQL is challenging and ESOM is a viable approach to tackle the task, with results outperforming offline methods (81.92 vs 55.89 success rate %) when oracular object discovery and tracking are considered. Our analysis also sheds light on the limited performance of object detection and tracking in egocentric vision, providing a principled benchmark based on the OEM-VQL downstream task to assess progress in these areas.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge