Sauradip Nag
Advances in 4D Representation: Geometry, Motion, and Interaction
Oct 22, 2025Abstract:We present a survey on 4D generation and reconstruction, a fast-evolving subfield of computer graphics whose developments have been propelled by recent advances in neural fields, geometric and motion deep learning, as well 3D generative artificial intelligence (GenAI). While our survey is not the first of its kind, we build our coverage of the domain from a unique and distinctive perspective of 4D representations\/}, to model 3D geometry evolving over time while exhibiting motion and interaction. Specifically, instead of offering an exhaustive enumeration of many works, we take a more selective approach by focusing on representative works to highlight both the desirable properties and ensuing challenges of each representation under different computation, application, and data scenarios. The main take-away message we aim to convey to the readers is on how to select and then customize the appropriate 4D representations for their tasks. Organizationally, we separate the 4D representations based on three key pillars: geometry, motion, and interaction. Our discourse will not only encompass the most popular representations of today, such as neural radiance fields (NeRFs) and 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS), but also bring attention to relatively under-explored representations in the 4D context, such as structured models and long-range motions. Throughout our survey, we will reprise the role of large language models (LLMs) and video foundational models (VFMs) in a variety of 4D applications, while steering our discussion towards their current limitations and how they can be addressed. We also provide a dedicated coverage on what 4D datasets are currently available, as well as what is lacking, in driving the subfield forward. Project page:https://mingrui-zhao.github.io/4DRep-GMI/
RespoDiff: Dual-Module Bottleneck Transformation for Responsible & Faithful T2I Generation
Sep 18, 2025Abstract:The rapid advancement of diffusion models has enabled high-fidelity and semantically rich text-to-image generation; however, ensuring fairness and safety remains an open challenge. Existing methods typically improve fairness and safety at the expense of semantic fidelity and image quality. In this work, we propose RespoDiff, a novel framework for responsible text-to-image generation that incorporates a dual-module transformation on the intermediate bottleneck representations of diffusion models. Our approach introduces two distinct learnable modules: one focused on capturing and enforcing responsible concepts, such as fairness and safety, and the other dedicated to maintaining semantic alignment with neutral prompts. To facilitate the dual learning process, we introduce a novel score-matching objective that enables effective coordination between the modules. Our method outperforms state-of-the-art methods in responsible generation by ensuring semantic alignment while optimizing both objectives without compromising image fidelity. Our approach improves responsible and semantically coherent generation by 20% across diverse, unseen prompts. Moreover, it integrates seamlessly into large-scale models like SDXL, enhancing fairness and safety. Code will be released upon acceptance.
Cora: Correspondence-aware image editing using few step diffusion
May 29, 2025Abstract:Image editing is an important task in computer graphics, vision, and VFX, with recent diffusion-based methods achieving fast and high-quality results. However, edits requiring significant structural changes, such as non-rigid deformations, object modifications, or content generation, remain challenging. Existing few step editing approaches produce artifacts such as irrelevant texture or struggle to preserve key attributes of the source image (e.g., pose). We introduce Cora, a novel editing framework that addresses these limitations by introducing correspondence-aware noise correction and interpolated attention maps. Our method aligns textures and structures between the source and target images through semantic correspondence, enabling accurate texture transfer while generating new content when necessary. Cora offers control over the balance between content generation and preservation. Extensive experiments demonstrate that, quantitatively and qualitatively, Cora excels in maintaining structure, textures, and identity across diverse edits, including pose changes, object addition, and texture refinements. User studies confirm that Cora delivers superior results, outperforming alternatives.
In-2-4D: Inbetweening from Two Single-View Images to 4D Generation
Apr 11, 2025
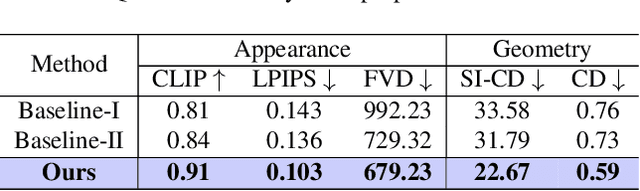
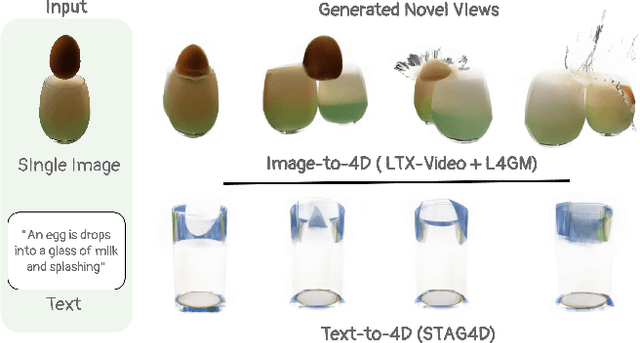
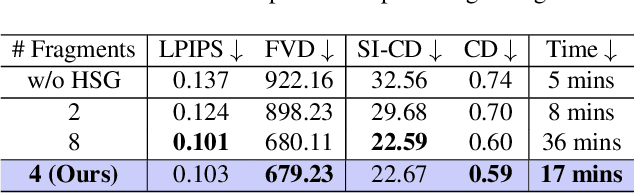
Abstract:We propose a new problem, In-2-4D, for generative 4D (i.e., 3D + motion) inbetweening from a minimalistic input setting: two single-view images capturing an object in two distinct motion states. Given two images representing the start and end states of an object in motion, our goal is to generate and reconstruct the motion in 4D. We utilize a video interpolation model to predict the motion, but large frame-to-frame motions can lead to ambiguous interpretations. To overcome this, we employ a hierarchical approach to identify keyframes that are visually close to the input states and show significant motion, then generate smooth fragments between them. For each fragment, we construct the 3D representation of the keyframe using Gaussian Splatting. The temporal frames within the fragment guide the motion, enabling their transformation into dynamic Gaussians through a deformation field. To improve temporal consistency and refine 3D motion, we expand the self-attention of multi-view diffusion across timesteps and apply rigid transformation regularization. Finally, we merge the independently generated 3D motion segments by interpolating boundary deformation fields and optimizing them to align with the guiding video, ensuring smooth and flicker-free transitions. Through extensive qualitative and quantitiave experiments as well as a user study, we show the effectiveness of our method and its components. The project page is available at https://in-2-4d.github.io/
Articulate That Object Part (ATOP): 3D Part Articulation from Text and Motion Personalization
Feb 11, 2025Abstract:We present ATOP (Articulate That Object Part), a novel method based on motion personalization to articulate a 3D object with respect to a part and its motion as prescribed in a text prompt. Specifically, the text input allows us to tap into the power of modern-day video diffusion to generate plausible motion samples for the right object category and part. In turn, the input 3D object provides image prompting to personalize the generated video to that very object we wish to articulate. Our method starts with a few-shot finetuning for category-specific motion generation, a key first step to compensate for the lack of articulation awareness by current video diffusion models. For this, we finetune a pre-trained multi-view image generation model for controllable multi-view video generation, using a small collection of video samples obtained for the target object category. This is followed by motion video personalization that is realized by multi-view rendered images of the target 3D object. At last, we transfer the personalized video motion to the target 3D object via differentiable rendering to optimize part motion parameters by a score distillation sampling loss. We show that our method is capable of generating realistic motion videos and predict 3D motion parameters in a more accurate and generalizable way, compared to prior works.
SMITE: Segment Me In TimE
Oct 24, 2024
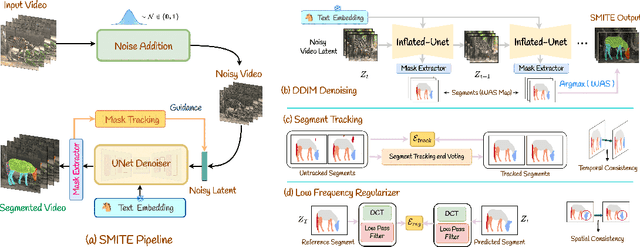
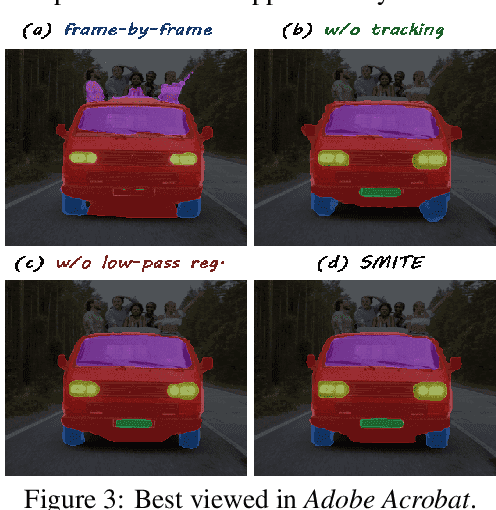
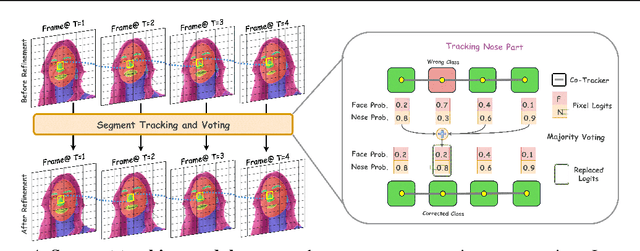
Abstract:Segmenting an object in a video presents significant challenges. Each pixel must be accurately labelled, and these labels must remain consistent across frames. The difficulty increases when the segmentation is with arbitrary granularity, meaning the number of segments can vary arbitrarily, and masks are defined based on only one or a few sample images. In this paper, we address this issue by employing a pre-trained text to image diffusion model supplemented with an additional tracking mechanism. We demonstrate that our approach can effectively manage various segmentation scenarios and outperforms state-of-the-art alternatives.
OmniCount: Multi-label Object Counting with Semantic-Geometric Priors
Mar 14, 2024Abstract:Object counting is pivotal for understanding the composition of scenes. Previously, this task was dominated by class-specific methods, which have gradually evolved into more adaptable class-agnostic strategies. However, these strategies come with their own set of limitations, such as the need for manual exemplar input and multiple passes for multiple categories, resulting in significant inefficiencies. This paper introduces a new, more practical approach enabling simultaneous counting of multiple object categories using an open vocabulary framework. Our solution, OmniCount, stands out by using semantic and geometric insights from pre-trained models to count multiple categories of objects as specified by users, all without additional training. OmniCount distinguishes itself by generating precise object masks and leveraging point prompts via the Segment Anything Model for efficient counting. To evaluate OmniCount, we created the OmniCount-191 benchmark, a first-of-its-kind dataset with multi-label object counts, including points, bounding boxes, and VQA annotations. Our comprehensive evaluation in OmniCount-191, alongside other leading benchmarks, demonstrates OmniCount's exceptional performance, significantly outpacing existing solutions and heralding a new era in object counting technology.
Adaptive-Labeling for Enhancing Remote Sensing Cloud Understanding
Nov 09, 2023Abstract:Cloud analysis is a critical component of weather and climate science, impacting various sectors like disaster management. However, achieving fine-grained cloud analysis, such as cloud segmentation, in remote sensing remains challenging due to the inherent difficulties in obtaining accurate labels, leading to significant labeling errors in training data. Existing methods often assume the availability of reliable segmentation annotations, limiting their overall performance. To address this inherent limitation, we introduce an innovative model-agnostic Cloud Adaptive-Labeling (CAL) approach, which operates iteratively to enhance the quality of training data annotations and consequently improve the performance of the learned model. Our methodology commences by training a cloud segmentation model using the original annotations. Subsequently, it introduces a trainable pixel intensity threshold for adaptively labeling the cloud training images on the fly. The newly generated labels are then employed to fine-tune the model. Extensive experiments conducted on multiple standard cloud segmentation benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach in significantly boosting the performance of existing segmentation models. Our CAL method establishes new state-of-the-art results when compared to a wide array of existing alternatives.
DiffSED: Sound Event Detection with Denoising Diffusion
Aug 16, 2023Abstract:Sound Event Detection (SED) aims to predict the temporal boundaries of all the events of interest and their class labels, given an unconstrained audio sample. Taking either the splitand-classify (i.e., frame-level) strategy or the more principled event-level modeling approach, all existing methods consider the SED problem from the discriminative learning perspective. In this work, we reformulate the SED problem by taking a generative learning perspective. Specifically, we aim to generate sound temporal boundaries from noisy proposals in a denoising diffusion process, conditioned on a target audio sample. During training, our model learns to reverse the noising process by converting noisy latent queries to the groundtruth versions in the elegant Transformer decoder framework. Doing so enables the model generate accurate event boundaries from even noisy queries during inference. Extensive experiments on the Urban-SED and EPIC-Sounds datasets demonstrate that our model significantly outperforms existing alternatives, with 40+% faster convergence in training.
Actor-agnostic Multi-label Action Recognition with Multi-modal Query
Aug 08, 2023



Abstract:Existing action recognition methods are typically actor-specific due to the intrinsic topological and apparent differences among the actors. This requires actor-specific pose estimation (e.g., humans vs. animals), leading to cumbersome model design complexity and high maintenance costs. Moreover, they often focus on learning the visual modality alone and single-label classification whilst neglecting other available information sources (e.g., class name text) and the concurrent occurrence of multiple actions. To overcome these limitations, we propose a new approach called 'actor-agnostic multi-modal multi-label action recognition,' which offers a unified solution for various types of actors, including humans and animals. We further formulate a novel Multi-modal Semantic Query Network (MSQNet) model in a transformer-based object detection framework (e.g., DETR), characterized by leveraging visual and textual modalities to represent the action classes better. The elimination of actor-specific model designs is a key advantage, as it removes the need for actor pose estimation altogether. Extensive experiments on five publicly available benchmarks show that our MSQNet consistently outperforms the prior arts of actor-specific alternatives on human and animal single- and multi-label action recognition tasks by up to 50%. Code will be released at https://github.com/mondalanindya/MSQNet.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge