Zihao Li
TSAQA: Time Series Analysis Question And Answering Benchmark
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Time series data are integral to critical applications across domains such as finance, healthcare, transportation, and environmental science. While recent work has begun to explore multi-task time series question answering (QA), current benchmarks remain limited to forecasting and anomaly detection tasks. We introduce TSAQA, a novel unified benchmark designed to broaden task coverage and evaluate diverse temporal analysis capabilities. TSAQA integrates six diverse tasks under a single framework ranging from conventional analysis, including anomaly detection and classification, to advanced analysis, such as characterization, comparison, data transformation, and temporal relationship analysis. Spanning 210k samples across 13 domains, the dataset employs diverse formats, including true-or-false (TF), multiple-choice (MC), and a novel puzzling (PZ), to comprehensively assess time series analysis. Zero-shot evaluation demonstrates that these tasks are challenging for current Large Language Models (LLMs): the best-performing commercial LLM, Gemini-2.5-Flash, achieves an average score of only 65.08. Although instruction tuning boosts open-source performance: the best-performing open-source model, LLaMA-3.1-8B, shows significant room for improvement, highlighting the complexity of temporal analysis for LLMs.
OWLEYE: Zero-Shot Learner for Cross-Domain Graph Data Anomaly Detection
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Graph data is informative to represent complex relationships such as transactions between accounts, communications between devices, and dependencies among machines or processes. Correspondingly, graph anomaly detection (GAD) plays a critical role in identifying anomalies across various domains, including finance, cybersecurity, manufacturing, etc. Facing the large-volume and multi-domain graph data, nascent efforts attempt to develop foundational generalist models capable of detecting anomalies in unseen graphs without retraining. To the best of our knowledge, the different feature semantics and dimensions of cross-domain graph data heavily hinder the development of the graph foundation model, leaving further in-depth continual learning and inference capabilities a quite open problem. Hence, we propose OWLEYE, a novel zero-shot GAD framework that learns transferable patterns of normal behavior from multiple graphs, with a threefold contribution. First, OWLEYE proposes a cross-domain feature alignment module to harmonize feature distributions, which preserves domain-specific semantics during alignment. Second, with aligned features, to enable continuous learning capabilities, OWLEYE designs the multi-domain multi-pattern dictionary learning to encode shared structural and attribute-based patterns. Third, for achieving the in-context learning ability, OWLEYE develops a truncated attention-based reconstruction module to robustly detect anomalies without requiring labeled data for unseen graph-structured data. Extensive experiments on real-world datasets demonstrate that OWLEYE achieves superior performance and generalizability compared to state-of-the-art baselines, establishing a strong foundation for scalable and label-efficient anomaly detection.
SpatialV2A: Visual-Guided High-fidelity Spatial Audio Generation
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:While video-to-audio generation has achieved remarkable progress in semantic and temporal alignment, most existing studies focus solely on these aspects, paying limited attention to the spatial perception and immersive quality of the synthesized audio. This limitation stems largely from current models' reliance on mono audio datasets, which lack the binaural spatial information needed to learn visual-to-spatial audio mappings. To address this gap, we introduce two key contributions: we construct BinauralVGGSound, the first large-scale video-binaural audio dataset designed to support spatially aware video-to-audio generation; and we propose a end-to-end spatial audio generation framework guided by visual cues, which explicitly models spatial features. Our framework incorporates a visual-guided audio spatialization module that ensures the generated audio exhibits realistic spatial attributes and layered spatial depth while maintaining semantic and temporal alignment. Experiments show that our approach substantially outperforms state-of-the-art models in spatial fidelity and delivers a more immersive auditory experience, without sacrificing temporal or semantic consistency. All datasets, code, and model checkpoints will be publicly released to facilitate future research.
Agentic Reasoning for Large Language Models
Jan 18, 2026Abstract:Reasoning is a fundamental cognitive process underlying inference, problem-solving, and decision-making. While large language models (LLMs) demonstrate strong reasoning capabilities in closed-world settings, they struggle in open-ended and dynamic environments. Agentic reasoning marks a paradigm shift by reframing LLMs as autonomous agents that plan, act, and learn through continual interaction. In this survey, we organize agentic reasoning along three complementary dimensions. First, we characterize environmental dynamics through three layers: foundational agentic reasoning, which establishes core single-agent capabilities including planning, tool use, and search in stable environments; self-evolving agentic reasoning, which studies how agents refine these capabilities through feedback, memory, and adaptation; and collective multi-agent reasoning, which extends intelligence to collaborative settings involving coordination, knowledge sharing, and shared goals. Across these layers, we distinguish in-context reasoning, which scales test-time interaction through structured orchestration, from post-training reasoning, which optimizes behaviors via reinforcement learning and supervised fine-tuning. We further review representative agentic reasoning frameworks across real-world applications and benchmarks, including science, robotics, healthcare, autonomous research, and mathematics. This survey synthesizes agentic reasoning methods into a unified roadmap bridging thought and action, and outlines open challenges and future directions, including personalization, long-horizon interaction, world modeling, scalable multi-agent training, and governance for real-world deployment.
Knowledge-Grounded Agentic Large Language Models for Multi-Hazard Understanding from Reconnaissance Reports
Nov 19, 2025Abstract:Post-disaster reconnaissance reports contain critical evidence for understanding multi-hazard interactions, yet their unstructured narratives make systematic knowledge transfer difficult. Large language models (LLMs) offer new potential for analyzing these reports, but often generate unreliable or hallucinated outputs when domain grounding is absent. This study introduces the Mixture-of-Retrieval Agentic RAG (MoRA-RAG), a knowledge-grounded LLM framework that transforms reconnaissance reports into a structured foundation for multi-hazard reasoning. The framework integrates a Mixture-of-Retrieval mechanism that dynamically routes queries across hazard-specific databases while using agentic chunking to preserve contextual coherence during retrieval. It also includes a verification loop that assesses evidence sufficiency, refines queries, and initiates targeted searches when information remains incomplete. We construct HazardRecQA by deriving question-answer pairs from GEER reconnaissance reports, which document 90 global events across seven major hazard types. MoRA-RAG achieves up to 94.5 percent accuracy, outperforming zero-shot LLMs by 30 percent and state-of-the-art RAG systems by 10 percent, while reducing hallucinations across diverse LLM architectures. MoRA-RAG also enables open-weight LLMs to achieve performance comparable to proprietary models. It establishes a new paradigm for transforming post-disaster documentation into actionable, trustworthy intelligence for hazard resilience.
TAPOM: Task-Space Topology-Guided Motion Planning for Manipulating Elongated Object in Cluttered Environments
Nov 07, 2025Abstract:Robotic manipulation in complex, constrained spaces is vital for widespread applications but challenging, particularly when navigating narrow passages with elongated objects. Existing planning methods often fail in these low-clearance scenarios due to the sampling difficulties or the local minima. This work proposes Topology-Aware Planning for Object Manipulation (TAPOM), which explicitly incorporates task-space topological analysis to enable efficient planning. TAPOM uses a high-level analysis to identify critical pathways and generate guiding keyframes, which are utilized in a low-level planner to find feasible configuration space trajectories. Experimental validation demonstrates significantly high success rates and improved efficiency over state-of-the-art methods on low-clearance manipulation tasks. This approach offers broad implications for enhancing manipulation capabilities of robots in complex real-world environments.
A Comprehensive Survey of Self-Evolving AI Agents: A New Paradigm Bridging Foundation Models and Lifelong Agentic Systems
Aug 10, 2025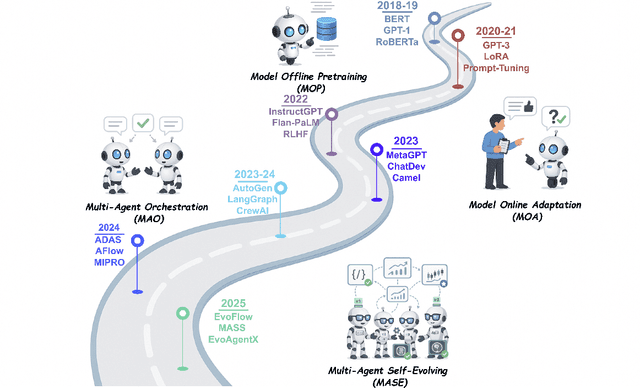
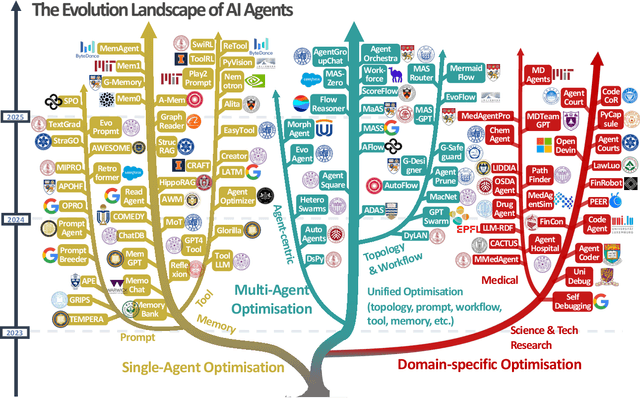
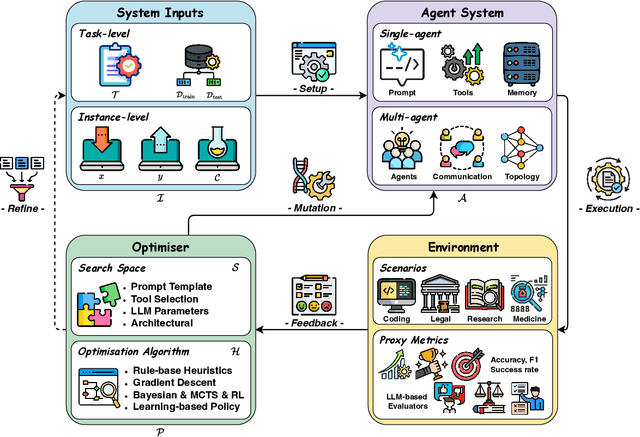
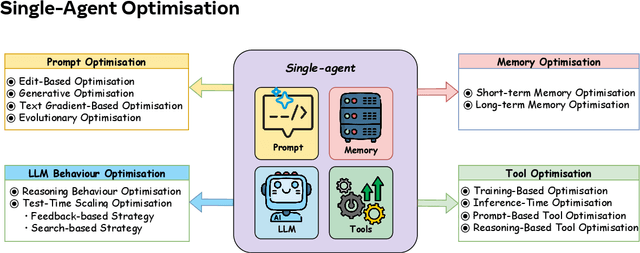
Abstract:Recent advances in large language models have sparked growing interest in AI agents capable of solving complex, real-world tasks. However, most existing agent systems rely on manually crafted configurations that remain static after deployment, limiting their ability to adapt to dynamic and evolving environments. To this end, recent research has explored agent evolution techniques that aim to automatically enhance agent systems based on interaction data and environmental feedback. This emerging direction lays the foundation for self-evolving AI agents, which bridge the static capabilities of foundation models with the continuous adaptability required by lifelong agentic systems. In this survey, we provide a comprehensive review of existing techniques for self-evolving agentic systems. Specifically, we first introduce a unified conceptual framework that abstracts the feedback loop underlying the design of self-evolving agentic systems. The framework highlights four key components: System Inputs, Agent System, Environment, and Optimisers, serving as a foundation for understanding and comparing different strategies. Based on this framework, we systematically review a wide range of self-evolving techniques that target different components of the agent system. We also investigate domain-specific evolution strategies developed for specialised fields such as biomedicine, programming, and finance, where optimisation objectives are tightly coupled with domain constraints. In addition, we provide a dedicated discussion on the evaluation, safety, and ethical considerations for self-evolving agentic systems, which are critical to ensuring their effectiveness and reliability. This survey aims to provide researchers and practitioners with a systematic understanding of self-evolving AI agents, laying the foundation for the development of more adaptive, autonomous, and lifelong agentic systems.
Flow Matching Meets Biology and Life Science: A Survey
Jul 23, 2025Abstract:Over the past decade, advances in generative modeling, such as generative adversarial networks, masked autoencoders, and diffusion models, have significantly transformed biological research and discovery, enabling breakthroughs in molecule design, protein generation, drug discovery, and beyond. At the same time, biological applications have served as valuable testbeds for evaluating the capabilities of generative models. Recently, flow matching has emerged as a powerful and efficient alternative to diffusion-based generative modeling, with growing interest in its application to problems in biology and life sciences. This paper presents the first comprehensive survey of recent developments in flow matching and its applications in biological domains. We begin by systematically reviewing the foundations and variants of flow matching, and then categorize its applications into three major areas: biological sequence modeling, molecule generation and design, and peptide and protein generation. For each, we provide an in-depth review of recent progress. We also summarize commonly used datasets and software tools, and conclude with a discussion of potential future directions. The corresponding curated resources are available at https://github.com/Violet24K/Awesome-Flow-Matching-Meets-Biology.
Listwise Preference Alignment Optimization for Tail Item Recommendation
Jul 03, 2025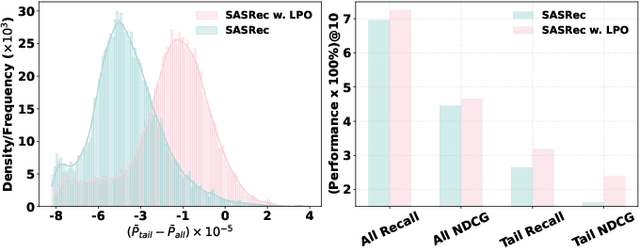
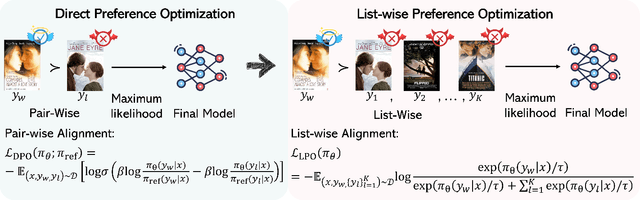
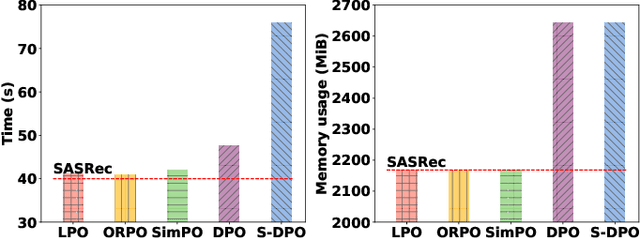
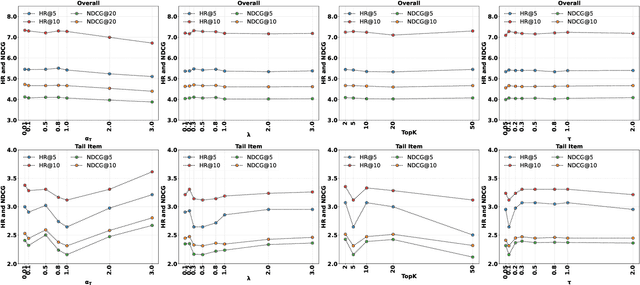
Abstract:Preference alignment has achieved greater success on Large Language Models (LLMs) and drawn broad interest in recommendation research. Existing preference alignment methods for recommendation either require explicit reward modeling or only support pairwise preference comparison. The former directly increases substantial computational costs, while the latter hinders training efficiency on negative samples. Moreover, no existing effort has explored preference alignment solutions for tail-item recommendation. To bridge the above gaps, we propose LPO4Rec, which extends the Bradley-Terry model from pairwise comparison to listwise comparison, to improve the efficiency of model training. Specifically, we derive a closed form optimal policy to enable more efficient and effective training without explicit reward modeling. We also present an adaptive negative sampling and reweighting strategy to prioritize tail items during optimization and enhance performance in tail-item recommendations. Besides, we theoretically prove that optimizing the listwise preference optimization (LPO) loss is equivalent to maximizing the upper bound of the optimal reward. Our experiments on three public datasets show that our method outperforms 10 baselines by a large margin, achieving up to 50% performance improvement while reducing 17.9% GPU memory usage when compared with direct preference optimization (DPO) in tail-item recommendation. Our code is available at https://github.com/Yuhanleeee/LPO4Rec.
Multi-Interest Recommendation: A Survey
Jun 18, 2025Abstract:Existing recommendation methods often struggle to model users' multifaceted preferences due to the diversity and volatility of user behavior, as well as the inherent uncertainty and ambiguity of item attributes in practical scenarios. Multi-interest recommendation addresses this challenge by extracting multiple interest representations from users' historical interactions, enabling fine-grained preference modeling and more accurate recommendations. It has drawn broad interest in recommendation research. However, current recommendation surveys have either specialized in frontier recommendation methods or delved into specific tasks and downstream applications. In this work, we systematically review the progress, solutions, challenges, and future directions of multi-interest recommendation by answering the following three questions: (1) Why is multi-interest modeling significantly important for recommendation? (2) What aspects are focused on by multi-interest modeling in recommendation? and (3) How can multi-interest modeling be applied, along with the technical details of the representative modules? We hope that this survey establishes a fundamental framework and delivers a preliminary overview for researchers interested in this field and committed to further exploration. The implementation of multi-interest recommendation summarized in this survey is maintained at https://github.com/WHUIR/Multi-Interest-Recommendation-A-Survey.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge