Benyou Wang
Towards Fair and Comprehensive Evaluation of Routers in Collaborative LLM Systems
Feb 12, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have achieved success, but cost and privacy constraints necessitate deploying smaller models locally while offloading complex queries to cloud-based models. Existing router evaluations are unsystematic, overlooking scenario-specific requirements and out-of-distribution robustness. We propose RouterXBench, a principled evaluation framework with three dimensions: router ability, scenario alignment, and cross-domain robustness. Unlike prior work that relies on output probabilities or external embeddings, we utilize internal hidden states that capture model uncertainty before answer generation. We introduce ProbeDirichlet, a lightweight router that aggregates cross-layer hidden states via learnable Dirichlet distributions with probabilistic training. Trained on multi-domain data, it generalizes robustly across in-domain and out-of-distribution scenarios. Our results show ProbeDirichlet achieves 16.68% and 18.86% relative improvements over the best baselines in router ability and high-accuracy scenarios, with consistent performance across model families, model scales, heterogeneous tasks, and agentic workflows.
ClinAlign: Scaling Healthcare Alignment from Clinician Preference
Feb 11, 2026Abstract:Although large language models (LLMs) demonstrate expert-level medical knowledge, aligning their open-ended outputs with fine-grained clinician preferences remains challenging. Existing methods often rely on coarse objectives or unreliable automated judges that are weakly grounded in professional guidelines. We propose a two-stage framework to address this gap. First, we introduce HealthRubrics, a dataset of 7,034 physician-verified preference examples in which clinicians refine LLM-drafted rubrics to meet rigorous medical standards. Second, we distill these rubrics into HealthPrinciples: 119 broadly reusable, clinically grounded principles organized by clinical dimensions, enabling scalable supervision beyond manual annotation. We use HealthPrinciples for (1) offline alignment by synthesizing rubrics for unlabeled queries and (2) an inference-time tool for guided self-revision. A 30B-A3B model trained with our framework achieves 33.4% on HealthBench-Hard, outperforming much larger models including Deepseek-R1 and o3, establishing a resource-efficient baseline for clinical alignment.
To What Extent Do Token-Level Representations from Pathology Foundation Models Improve Dense Prediction?
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Pathology foundation models (PFMs) have rapidly advanced and are becoming a common backbone for downstream clinical tasks, offering strong transferability across tissues and institutions. However, for dense prediction (e.g., segmentation), practical deployment still lacks a clear, reproducible understanding of how different PFMs behave across datasets and how adaptation choices affect performance and stability. We present PFM-DenseBench, a large-scale benchmark for dense pathology prediction, evaluating 17 PFMs across 18 public segmentation datasets. Under a unified protocol, we systematically assess PFMs with multiple adaptation and fine-tuning strategies, and derive insightful, practice-oriented findings on when and why different PFMs and tuning choices succeed or fail across heterogeneous datasets. We release containers, configs, and dataset cards to enable reproducible evaluation and informed PFM selection for real-world dense pathology tasks. Project Website: https://m4a1tastegood.github.io/PFM-DenseBench
Character-R1: Enhancing Role-Aware Reasoning in Role-Playing Agents via RLVR
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Current role-playing agents (RPAs) are typically constructed by imitating surface-level behaviors, but this approach lacks internal cognitive consistency, often causing out-of-character errors in complex situations. To address this, we propose Character-R1, a framework designed to provide comprehensive verifiable reward signals for effective role-aware reasoning, which are missing in recent studies. Specifically, our framework comprises three core designs: (1) Cognitive Focus Reward, which enforces explicit label-based analysis of 10 character elements (e.g., worldview) to structure internal cognition; (2) Reference-Guided Reward, which utilizes overlap-based metrics with reference responses as optimization anchors to enhance exploration and performance; and (3) Character-Conditioned Reward Normalization, which adjusts reward distributions based on character categories to ensure robust optimization across heterogeneous roles. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Character-R1 significantly outperforms existing methods in knowledge, memory and others.
DentalGPT: Incentivizing Multimodal Complex Reasoning in Dentistry
Dec 12, 2025Abstract:Reliable interpretation of multimodal data in dentistry is essential for automated oral healthcare, yet current multimodal large language models (MLLMs) struggle to capture fine-grained dental visual details and lack sufficient reasoning ability for precise diagnosis. To address these limitations, we present DentalGPT, a specialized dental MLLM developed through high-quality domain knowledge injection and reinforcement learning. Specifically, the largest annotated multimodal dataset for dentistry to date was constructed by aggregating over 120k dental images paired with detailed descriptions that highlight diagnostically relevant visual features, making it the multimodal dataset with the most extensive collection of dental images to date. Training on this dataset significantly enhances the MLLM's visual understanding of dental conditions, while the subsequent reinforcement learning stage further strengthens its capability for multimodal complex reasoning. Comprehensive evaluations on intraoral and panoramic benchmarks, along with dental subsets of medical VQA benchmarks, show that DentalGPT achieves superior performance in disease classification and dental VQA tasks, outperforming many state-of-the-art MLLMs despite having only 7B parameters. These results demonstrate that high-quality dental data combined with staged adaptation provides an effective pathway for building capable and domain-specialized dental MLLMs.
Human or LLM as Standardized Patients? A Comparative Study for Medical Education
Nov 12, 2025Abstract:Standardized Patients (SP) are indispensable for clinical skills training but remain expensive, inflexible, and difficult to scale. Existing large-language-model (LLM)-based SP simulators promise lower cost yet show inconsistent behavior and lack rigorous comparison with human SP. We present EasyMED, a multi-agent framework combining a Patient Agent for realistic dialogue, an Auxiliary Agent for factual consistency, and an Evaluation Agent that delivers actionable feedback. To support systematic assessment, we introduce SPBench, a benchmark of real SP-doctor interactions spanning 14 specialties and eight expert-defined evaluation criteria. Experiments demonstrate that EasyMED matches human SP learning outcomes while producing greater skill gains for lower-baseline students and offering improved flexibility, psychological safety, and cost efficiency.
EchoMind: An Interrelated Multi-level Benchmark for Evaluating Empathetic Speech Language Models
Oct 26, 2025Abstract:Speech Language Models (SLMs) have made significant progress in spoken language understanding. Yet it remains unclear whether they can fully perceive non lexical vocal cues alongside spoken words, and respond with empathy that aligns with both emotional and contextual factors. Existing benchmarks typically evaluate linguistic, acoustic, reasoning, or dialogue abilities in isolation, overlooking the integration of these skills that is crucial for human-like, emotionally intelligent conversation. We present EchoMind, the first interrelated, multi-level benchmark that simulates the cognitive process of empathetic dialogue through sequential, context-linked tasks: spoken-content understanding, vocal-cue perception, integrated reasoning, and response generation. All tasks share identical and semantically neutral scripts that are free of explicit emotional or contextual cues, and controlled variations in vocal style are used to test the effect of delivery independent of the transcript. EchoMind is grounded in an empathy-oriented framework spanning 3 coarse and 12 fine-grained dimensions, encompassing 39 vocal attributes, and evaluated using both objective and subjective metrics. Testing 12 advanced SLMs reveals that even state-of-the-art models struggle with high-expressive vocal cues, limiting empathetic response quality. Analyses of prompt strength, speech source, and ideal vocal cue recognition reveal persistent weaknesses in instruction-following, resilience to natural speech variability, and effective use of vocal cues for empathy. These results underscore the need for SLMs that integrate linguistic content with diverse vocal cues to achieve truly empathetic conversational ability.
Decoding the Ear: A Framework for Objectifying Expressiveness from Human Preference Through Efficient Alignment
Oct 23, 2025Abstract:Recent speech-to-speech (S2S) models generate intelligible speech but still lack natural expressiveness, largely due to the absence of a reliable evaluation metric. Existing approaches, such as subjective MOS ratings, low-level acoustic features, and emotion recognition are costly, limited, or incomplete. To address this, we present DeEAR (Decoding the Expressive Preference of eAR), a framework that converts human preference for speech expressiveness into an objective score. Grounded in phonetics and psychology, DeEAR evaluates speech across three dimensions: Emotion, Prosody, and Spontaneity, achieving strong alignment with human perception (Spearman's Rank Correlation Coefficient, SRCC = 0.86) using fewer than 500 annotated samples. Beyond reliable scoring, DeEAR enables fair benchmarking and targeted data curation. It not only distinguishes expressiveness gaps across S2S models but also selects 14K expressive utterances to form ExpressiveSpeech, which improves the expressive score (from 2.0 to 23.4 on a 100-point scale) of S2S models. Demos and codes are available at https://github.com/FreedomIntelligence/ExpressiveSpeech
Can Multimodal LLMs See Materials Clearly? A Multimodal Benchmark on Materials Characterization
Sep 11, 2025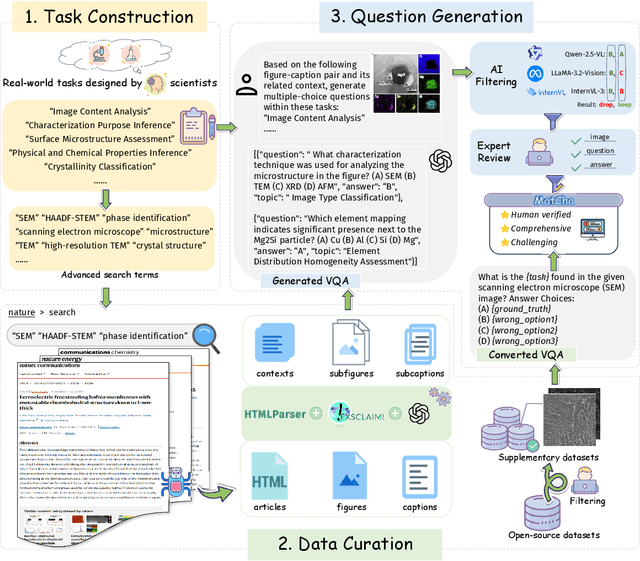
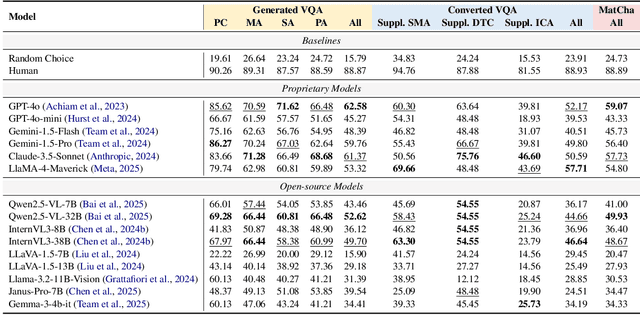
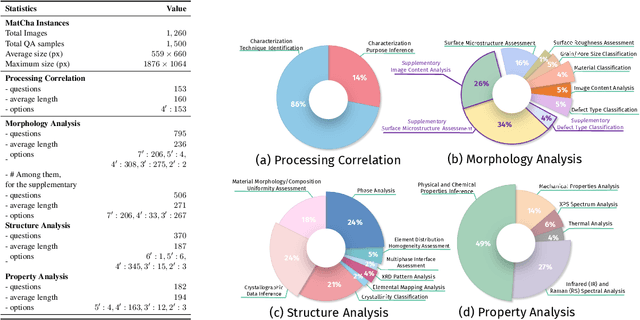
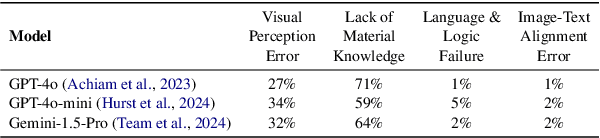
Abstract:Materials characterization is fundamental to acquiring materials information, revealing the processing-microstructure-property relationships that guide material design and optimization. While multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have recently shown promise in generative and predictive tasks within materials science, their capacity to understand real-world characterization imaging data remains underexplored. To bridge this gap, we present MatCha, the first benchmark for materials characterization image understanding, comprising 1,500 questions that demand expert-level domain expertise. MatCha encompasses four key stages of materials research comprising 21 distinct tasks, each designed to reflect authentic challenges faced by materials scientists. Our evaluation of state-of-the-art MLLMs on MatCha reveals a significant performance gap compared to human experts. These models exhibit degradation when addressing questions requiring higher-level expertise and sophisticated visual perception. Simple few-shot and chain-of-thought prompting struggle to alleviate these limitations. These findings highlight that existing MLLMs still exhibit limited adaptability to real-world materials characterization scenarios. We hope MatCha will facilitate future research in areas such as new material discovery and autonomous scientific agents. MatCha is available at https://github.com/FreedomIntelligence/MatCha.
EchoX: Towards Mitigating Acoustic-Semantic Gap via Echo Training for Speech-to-Speech LLMs
Sep 11, 2025Abstract:Speech-to-speech large language models (SLLMs) are attracting increasing attention. Derived from text-based large language models (LLMs), SLLMs often exhibit degradation in knowledge and reasoning capabilities. We hypothesize that this limitation arises because current training paradigms for SLLMs fail to bridge the acoustic-semantic gap in the feature representation space. To address this issue, we propose EchoX, which leverages semantic representations and dynamically generates speech training targets. This approach integrates both acoustic and semantic learning, enabling EchoX to preserve strong reasoning abilities as a speech LLM. Experimental results demonstrate that EchoX, with about six thousand hours of training data, achieves advanced performance on multiple knowledge-based question-answering benchmarks. The project is available at https://github.com/FreedomIntelligence/EchoX.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge