Junying Chen
DentalGPT: Incentivizing Multimodal Complex Reasoning in Dentistry
Dec 12, 2025Abstract:Reliable interpretation of multimodal data in dentistry is essential for automated oral healthcare, yet current multimodal large language models (MLLMs) struggle to capture fine-grained dental visual details and lack sufficient reasoning ability for precise diagnosis. To address these limitations, we present DentalGPT, a specialized dental MLLM developed through high-quality domain knowledge injection and reinforcement learning. Specifically, the largest annotated multimodal dataset for dentistry to date was constructed by aggregating over 120k dental images paired with detailed descriptions that highlight diagnostically relevant visual features, making it the multimodal dataset with the most extensive collection of dental images to date. Training on this dataset significantly enhances the MLLM's visual understanding of dental conditions, while the subsequent reinforcement learning stage further strengthens its capability for multimodal complex reasoning. Comprehensive evaluations on intraoral and panoramic benchmarks, along with dental subsets of medical VQA benchmarks, show that DentalGPT achieves superior performance in disease classification and dental VQA tasks, outperforming many state-of-the-art MLLMs despite having only 7B parameters. These results demonstrate that high-quality dental data combined with staged adaptation provides an effective pathway for building capable and domain-specialized dental MLLMs.
ShizhenGPT: Towards Multimodal LLMs for Traditional Chinese Medicine
Aug 20, 2025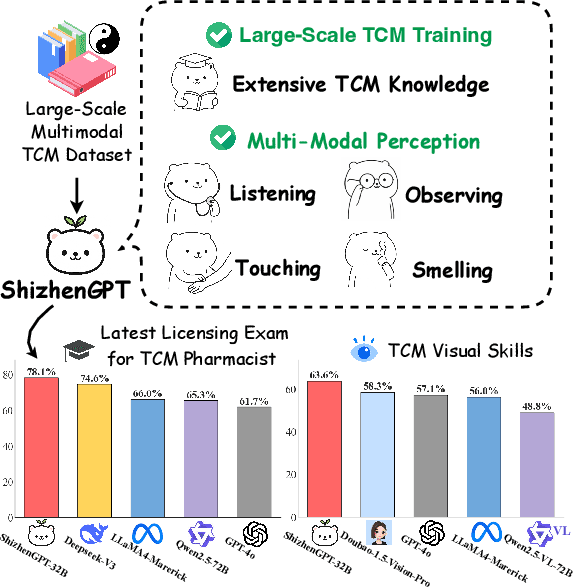
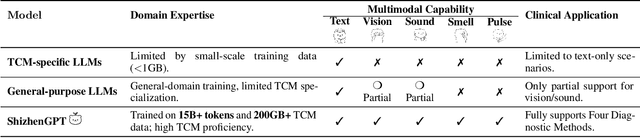
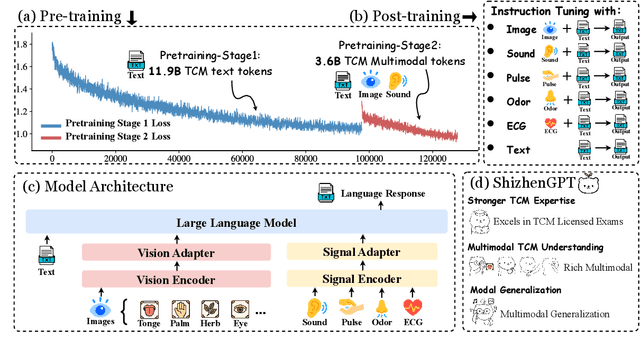
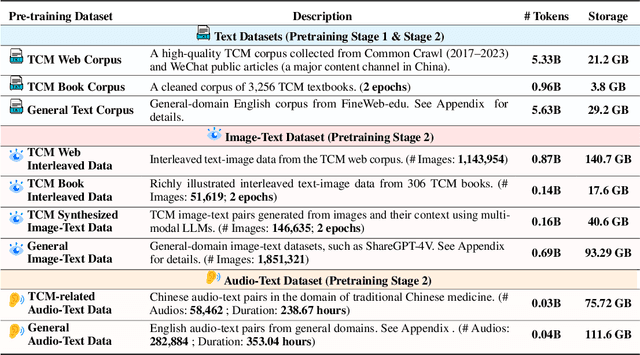
Abstract:Despite the success of large language models (LLMs) in various domains, their potential in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) remains largely underexplored due to two critical barriers: (1) the scarcity of high-quality TCM data and (2) the inherently multimodal nature of TCM diagnostics, which involve looking, listening, smelling, and pulse-taking. These sensory-rich modalities are beyond the scope of conventional LLMs. To address these challenges, we present ShizhenGPT, the first multimodal LLM tailored for TCM. To overcome data scarcity, we curate the largest TCM dataset to date, comprising 100GB+ of text and 200GB+ of multimodal data, including 1.2M images, 200 hours of audio, and physiological signals. ShizhenGPT is pretrained and instruction-tuned to achieve deep TCM knowledge and multimodal reasoning. For evaluation, we collect recent national TCM qualification exams and build a visual benchmark for Medicinal Recognition and Visual Diagnosis. Experiments demonstrate that ShizhenGPT outperforms comparable-scale LLMs and competes with larger proprietary models. Moreover, it leads in TCM visual understanding among existing multimodal LLMs and demonstrates unified perception across modalities like sound, pulse, smell, and vision, paving the way toward holistic multimodal perception and diagnosis in TCM. Datasets, models, and code are publicly available. We hope this work will inspire further exploration in this field.
Large Language Models for Outpatient Referral: Problem Definition, Benchmarking and Challenges
Mar 11, 2025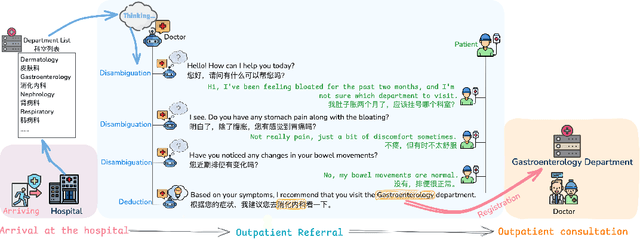
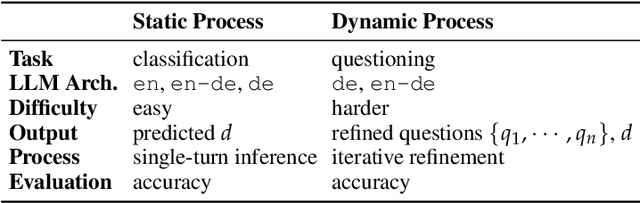
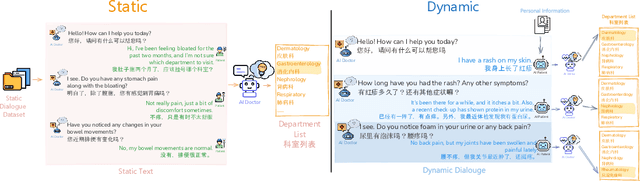
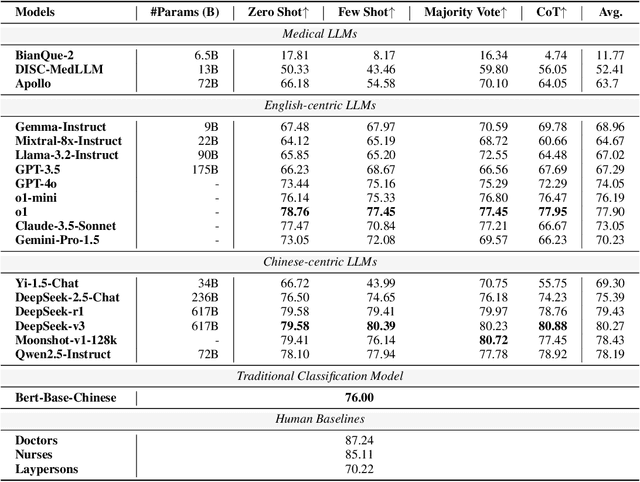
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly applied to outpatient referral tasks across healthcare systems. However, there is a lack of standardized evaluation criteria to assess their effectiveness, particularly in dynamic, interactive scenarios. In this study, we systematically examine the capabilities and limitations of LLMs in managing tasks within Intelligent Outpatient Referral (IOR) systems and propose a comprehensive evaluation framework specifically designed for such systems. This framework comprises two core tasks: static evaluation, which focuses on evaluating the ability of predefined outpatient referrals, and dynamic evaluation, which evaluates capabilities of refining outpatient referral recommendations through iterative dialogues. Our findings suggest that LLMs offer limited advantages over BERT-like models, but show promise in asking effective questions during interactive dialogues.
The First Few Tokens Are All You Need: An Efficient and Effective Unsupervised Prefix Fine-Tuning Method for Reasoning Models
Mar 04, 2025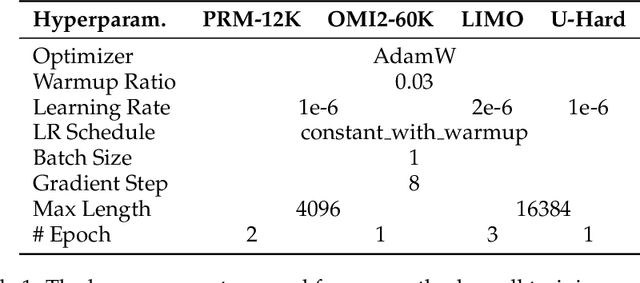
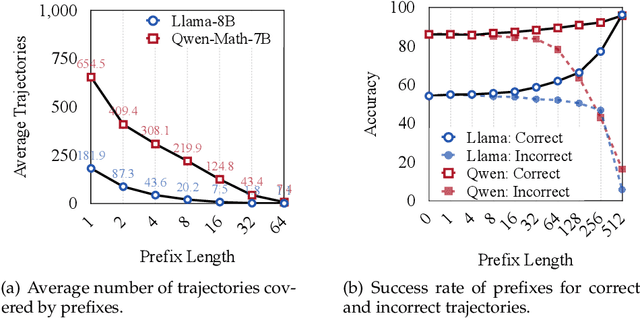
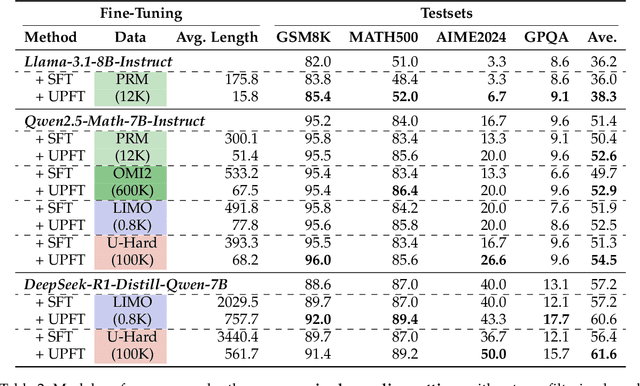

Abstract:Improving the reasoning capabilities of large language models (LLMs) typically requires supervised fine-tuning with labeled data or computationally expensive sampling. We introduce Unsupervised Prefix Fine-Tuning (UPFT), which leverages the observation of Prefix Self-Consistency -- the shared initial reasoning steps across diverse solution trajectories -- to enhance LLM reasoning efficiency. By training exclusively on the initial prefix substrings (as few as 8 tokens), UPFT removes the need for labeled data or exhaustive sampling. Experiments on reasoning benchmarks show that UPFT matches the performance of supervised methods such as Rejection Sampling Fine-Tuning, while reducing training time by 75% and sampling cost by 99%. Further analysis reveals that errors tend to appear in later stages of the reasoning process and that prefix-based training preserves the model's structural knowledge. This work demonstrates how minimal unsupervised fine-tuning can unlock substantial reasoning gains in LLMs, offering a scalable and resource-efficient alternative to conventional approaches.
RAG-Instruct: Boosting LLMs with Diverse Retrieval-Augmented Instructions
Dec 31, 2024



Abstract:Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) has emerged as a key paradigm for enhancing large language models (LLMs) by incorporating external knowledge. However, current RAG methods face two limitations: (1) they only cover limited RAG scenarios. (2) They suffer from limited task diversity due to the lack of a general RAG dataset. To address these limitations, we propose RAG-Instruct, a general method for synthesizing diverse and high-quality RAG instruction data based on any source corpus. Our approach leverages (1) five RAG paradigms, which encompass diverse query-document relationships, and (2) instruction simulation, which enhances instruction diversity and quality by utilizing the strengths of existing instruction datasets. Using this method, we construct a 40K instruction dataset from Wikipedia, comprehensively covering diverse RAG scenarios and tasks. Experiments demonstrate that RAG-Instruct effectively enhances LLMs' RAG capabilities, achieving strong zero-shot performance and significantly outperforming various RAG baselines across a diverse set of tasks. RAG-Instruct is publicly available at https://github.com/FreedomIntelligence/RAG-Instruct.
On the Compositional Generalization of Multimodal LLMs for Medical Imaging
Dec 28, 2024



Abstract:Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) hold significant potential in the medical field, but their capabilities are often limited by insufficient data in certain medical domains, highlighting the need for understanding what kinds of images can be used by MLLMs for generalization. Current research suggests that multi-task training outperforms single-task as different tasks can benefit each other, but they often overlook the internal relationships within these tasks, providing limited guidance on selecting datasets to enhance specific tasks. To analyze this phenomenon, we attempted to employ compositional generalization (CG)-the ability of models to understand novel combinations by recombining learned elements-as a guiding framework. Since medical images can be precisely defined by Modality, Anatomical area, and Task, naturally providing an environment for exploring CG. Therefore, we assembled 106 medical datasets to create Med-MAT for comprehensive experiments. The experiments confirmed that MLLMs can use CG to understand unseen medical images and identified CG as one of the main drivers of the generalization observed in multi-task training. Additionally, further studies demonstrated that CG effectively supports datasets with limited data and delivers consistent performance across different backbones, highlighting its versatility and broad applicability. Med-MAT is publicly available at https://github.com/FreedomIntelligence/Med-MAT.
HuatuoGPT-o1, Towards Medical Complex Reasoning with LLMs
Dec 25, 2024



Abstract:The breakthrough of OpenAI o1 highlights the potential of enhancing reasoning to improve LLM. Yet, most research in reasoning has focused on mathematical tasks, leaving domains like medicine underexplored. The medical domain, though distinct from mathematics, also demands robust reasoning to provide reliable answers, given the high standards of healthcare. However, verifying medical reasoning is challenging, unlike those in mathematics. To address this, we propose verifiable medical problems with a medical verifier to check the correctness of model outputs. This verifiable nature enables advancements in medical reasoning through a two-stage approach: (1) using the verifier to guide the search for a complex reasoning trajectory for fine-tuning LLMs, (2) applying reinforcement learning (RL) with verifier-based rewards to enhance complex reasoning further. Finally, we introduce HuatuoGPT-o1, a medical LLM capable of complex reasoning, which outperforms general and medical-specific baselines using only 40K verifiable problems. Experiments show complex reasoning improves medical problem-solving and benefits more from RL. We hope our approach inspires advancements in reasoning across medical and other specialized domains.
Second Language (Arabic) Acquisition of LLMs via Progressive Vocabulary Expansion
Dec 16, 2024



Abstract:This paper addresses the critical need for democratizing large language models (LLM) in the Arab world, a region that has seen slower progress in developing models comparable to state-of-the-art offerings like GPT-4 or ChatGPT 3.5, due to a predominant focus on mainstream languages (e.g., English and Chinese). One practical objective for an Arabic LLM is to utilize an Arabic-specific vocabulary for the tokenizer that could speed up decoding. However, using a different vocabulary often leads to a degradation of learned knowledge since many words are initially out-of-vocabulary (OOV) when training starts. Inspired by the vocabulary learning during Second Language (Arabic) Acquisition for humans, the released AraLLaMA employs progressive vocabulary expansion, which is implemented by a modified BPE algorithm that progressively extends the Arabic subwords in its dynamic vocabulary during training, thereby balancing the OOV ratio at every stage. The ablation study demonstrated the effectiveness of Progressive Vocabulary Expansion. Moreover, AraLLaMA achieves decent performance comparable to the best Arabic LLMs across a variety of Arabic benchmarks. Models, training data, benchmarks, and codes will be all open-sourced.
CoD, Towards an Interpretable Medical Agent using Chain of Diagnosis
Jul 18, 2024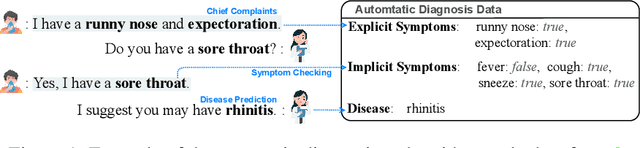
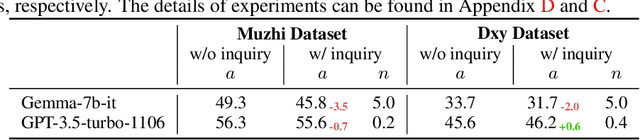
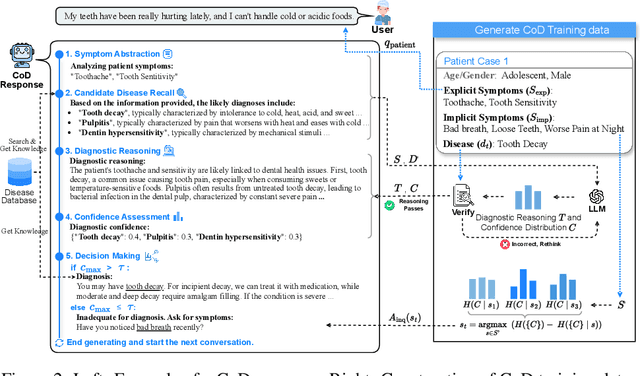
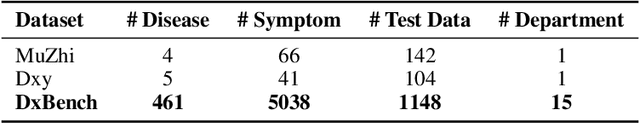
Abstract:The field of medical diagnosis has undergone a significant transformation with the advent of large language models (LLMs), yet the challenges of interpretability within these models remain largely unaddressed. This study introduces Chain-of-Diagnosis (CoD) to enhance the interpretability of LLM-based medical diagnostics. CoD transforms the diagnostic process into a diagnostic chain that mirrors a physician's thought process, providing a transparent reasoning pathway. Additionally, CoD outputs the disease confidence distribution to ensure transparency in decision-making. This interpretability makes model diagnostics controllable and aids in identifying critical symptoms for inquiry through the entropy reduction of confidences. With CoD, we developed DiagnosisGPT, capable of diagnosing 9604 diseases. Experimental results demonstrate that DiagnosisGPT outperforms other LLMs on diagnostic benchmarks. Moreover, DiagnosisGPT provides interpretability while ensuring controllability in diagnostic rigor.
HuatuoGPT-Vision, Towards Injecting Medical Visual Knowledge into Multimodal LLMs at Scale
Jun 27, 2024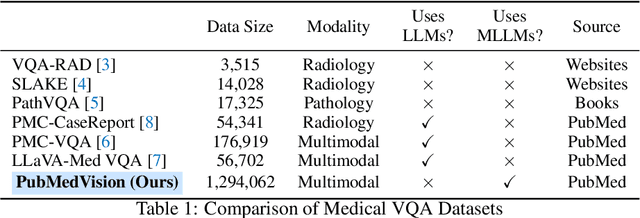
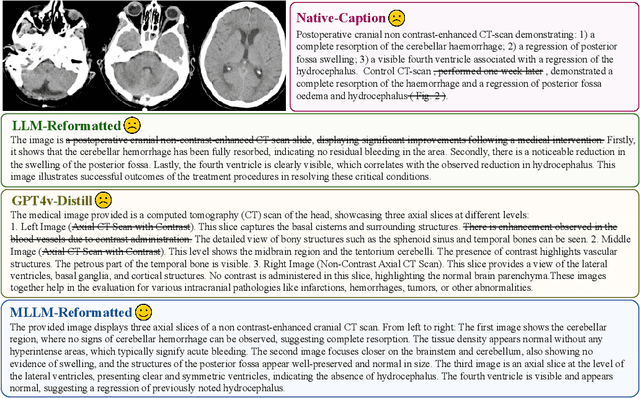
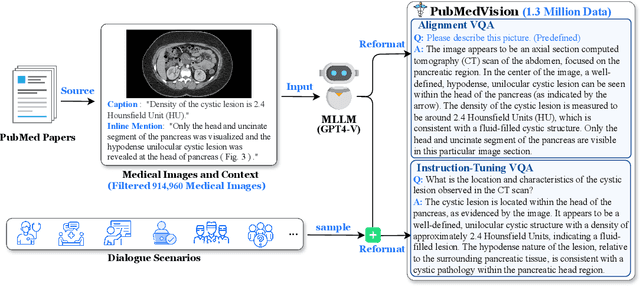
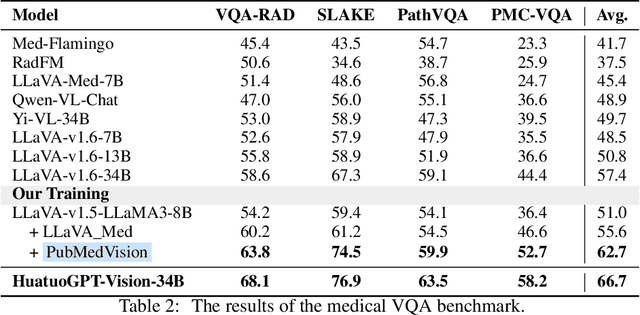
Abstract:The rapid development of multimodal large language models (MLLMs), such as GPT-4V, has led to significant advancements. However, these models still face challenges in medical multimodal capabilities due to limitations in the quantity and quality of medical vision-text data, stemming from data privacy concerns and high annotation costs. While pioneering approaches utilize PubMed's large-scale, de-identified medical image-text pairs to address these limitations, they still fall short due to inherent data noise. To tackle this, we refined medical image-text pairs from PubMed and employed MLLMs (GPT-4V) in an 'unblinded' capacity to denoise and reformat the data, resulting in the creation of the PubMedVision dataset with 1.3 million medical VQA samples. Our validation demonstrates that: (1) PubMedVision can significantly enhance the medical multimodal capabilities of current MLLMs, showing significant improvement in benchmarks including the MMMU Health & Medicine track; (2) manual checks by medical experts and empirical results validate the superior data quality of our dataset compared to other data construction methods. Using PubMedVision, we train a 34B medical MLLM HuatuoGPT-Vision, which shows superior performance in medical multimodal scenarios among open-source MLLMs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge