Wenya Xie
Reasoning While Asking: Transforming Reasoning Large Language Models from Passive Solvers to Proactive Inquirers
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Reasoning-oriented Large Language Models (LLMs) have achieved remarkable progress with Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting, yet they remain fundamentally limited by a \emph{blind self-thinking} paradigm: performing extensive internal reasoning even when critical information is missing or ambiguous. We propose Proactive Interactive Reasoning (PIR), a new reasoning paradigm that transforms LLMs from passive solvers into proactive inquirers that interleave reasoning with clarification. Unlike existing search- or tool-based frameworks that primarily address knowledge uncertainty by querying external environments, PIR targets premise- and intent-level uncertainty through direct interaction with the user. PIR is implemented via two core components: (1) an uncertainty-aware supervised fine-tuning procedure that equips models with interactive reasoning capability, and (2) a user-simulator-based policy optimization framework driven by a composite reward that aligns model behavior with user intent. Extensive experiments on mathematical reasoning, code generation, and document editing demonstrate that PIR consistently outperforms strong baselines, achieving up to 32.70\% higher accuracy, 22.90\% higher pass rate, and 41.36 BLEU improvement, while reducing nearly half of the reasoning computation and unnecessary interaction turns. Further reliability evaluations on factual knowledge, question answering, and missing-premise scenarios confirm the strong generalization and robustness of PIR. Model and code are publicly available at: \href{https://github.com/SUAT-AIRI/Proactive-Interactive-R1}
Automating Expert-Level Medical Reasoning Evaluation of Large Language Models
Jul 10, 2025Abstract:As large language models (LLMs) become increasingly integrated into clinical decision-making, ensuring transparent and trustworthy reasoning is essential. However, existing evaluation strategies of LLMs' medical reasoning capability either suffer from unsatisfactory assessment or poor scalability, and a rigorous benchmark remains lacking. To address this, we introduce MedThink-Bench, a benchmark designed for rigorous, explainable, and scalable assessment of LLMs' medical reasoning. MedThink-Bench comprises 500 challenging questions across ten medical domains, each annotated with expert-crafted step-by-step rationales. Building on this, we propose LLM-w-Ref, a novel evaluation framework that leverages fine-grained rationales and LLM-as-a-Judge mechanisms to assess intermediate reasoning with expert-level fidelity while maintaining scalability. Experiments show that LLM-w-Ref exhibits a strong positive correlation with expert judgments. Benchmarking twelve state-of-the-art LLMs, we find that smaller models (e.g., MedGemma-27B) can surpass larger proprietary counterparts (e.g., OpenAI-o3). Overall, MedThink-Bench offers a foundational tool for evaluating LLMs' medical reasoning, advancing their safe and responsible deployment in clinical practice.
Give Me FP32 or Give Me Death? Challenges and Solutions for Reproducible Reasoning
Jun 11, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are now integral across various domains and have demonstrated impressive performance. Progress, however, rests on the premise that benchmark scores are both accurate and reproducible. We demonstrate that the reproducibility of LLM performance is fragile: changing system configuration such as evaluation batch size, GPU count, and GPU version can introduce significant difference in the generated responses. This issue is especially pronounced in reasoning models, where minor rounding differences in early tokens can cascade into divergent chains of thought, ultimately affecting accuracy. For instance, under bfloat16 precision with greedy decoding, a reasoning model like DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-7B can exhibit up to 9% variation in accuracy and 9,000 tokens difference in response length due to differences in GPU count, type, and evaluation batch size. We trace the root cause of this variability to the non-associative nature of floating-point arithmetic under limited numerical precision. This work presents the first systematic investigation into how numerical precision affects reproducibility in LLM inference. Through carefully controlled experiments across various hardware, software, and precision settings, we quantify when and how model outputs diverge. Our analysis reveals that floating-point precision -- while critical for reproducibility -- is often neglected in evaluation practices. Inspired by this, we develop a lightweight inference pipeline, dubbed LayerCast, that stores weights in 16-bit precision but performs all computations in FP32, balancing memory efficiency with numerical stability. Code is available at https://github.com/nanomaoli/llm_reproducibility.
How Memory Management Impacts LLM Agents: An Empirical Study of Experience-Following Behavior
May 21, 2025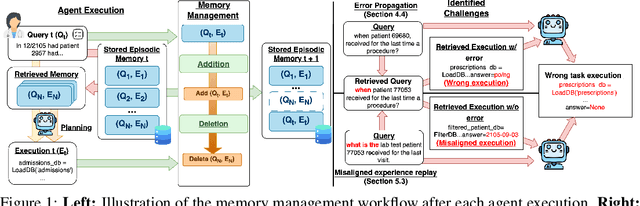
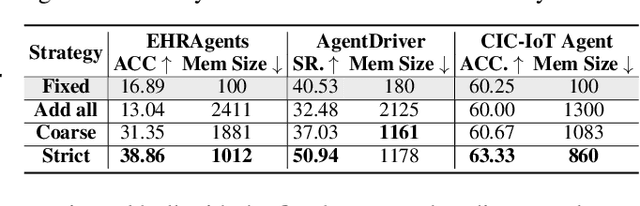
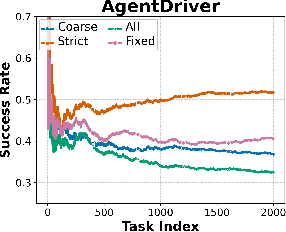
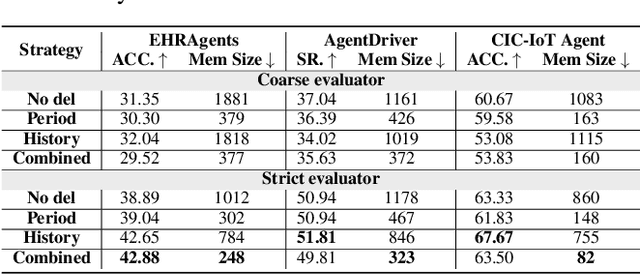
Abstract:Memory is a critical component in large language model (LLM)-based agents, enabling them to store and retrieve past executions to improve task performance over time. In this paper, we conduct an empirical study on how memory management choices impact the LLM agents' behavior, especially their long-term performance. Specifically, we focus on two fundamental memory operations that are widely used by many agent frameworks-addition, which incorporates new experiences into the memory base, and deletion, which selectively removes past experiences-to systematically study their impact on the agent behavior. Through our quantitative analysis, we find that LLM agents display an experience-following property: high similarity between a task input and the input in a retrieved memory record often results in highly similar agent outputs. Our analysis further reveals two significant challenges associated with this property: error propagation, where inaccuracies in past experiences compound and degrade future performance, and misaligned experience replay, where outdated or irrelevant experiences negatively influence current tasks. Through controlled experiments, we show that combining selective addition and deletion strategies can help mitigate these negative effects, yielding an average absolute performance gain of 10% compared to naive memory growth. Furthermore, we highlight how memory management choices affect agents' behavior under challenging conditions such as task distribution shifts and constrained memory resources. Our findings offer insights into the behavioral dynamics of LLM agent memory systems and provide practical guidance for designing memory components that support robust, long-term agent performance. We also release our code to facilitate further study.
Knowledge Boundary of Large Language Models: A Survey
Dec 17, 2024



Abstract:Although large language models (LLMs) store vast amount of knowledge in their parameters, they still have limitations in the memorization and utilization of certain knowledge, leading to undesired behaviors such as generating untruthful and inaccurate responses. This highlights the critical need to understand the knowledge boundary of LLMs, a concept that remains inadequately defined in existing research. In this survey, we propose a comprehensive definition of the LLM knowledge boundary and introduce a formalized taxonomy categorizing knowledge into four distinct types. Using this foundation, we systematically review the field through three key lenses: the motivation for studying LLM knowledge boundaries, methods for identifying these boundaries, and strategies for mitigating the challenges they present. Finally, we discuss open challenges and potential research directions in this area. We aim for this survey to offer the community a comprehensive overview, facilitate access to key issues, and inspire further advancements in LLM knowledge research.
LLMs for Doctors: Leveraging Medical LLMs to Assist Doctors, Not Replace Them
Jun 26, 2024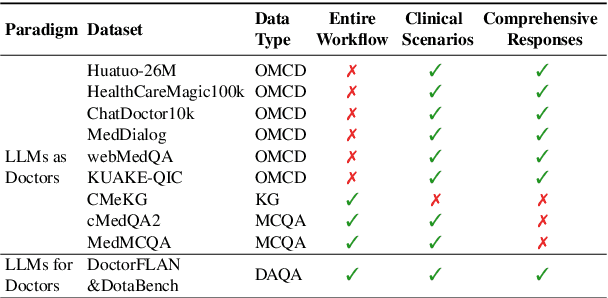
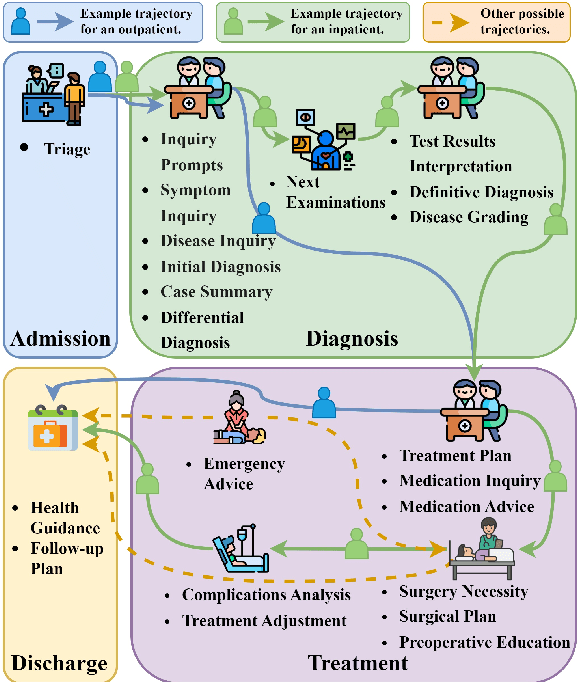
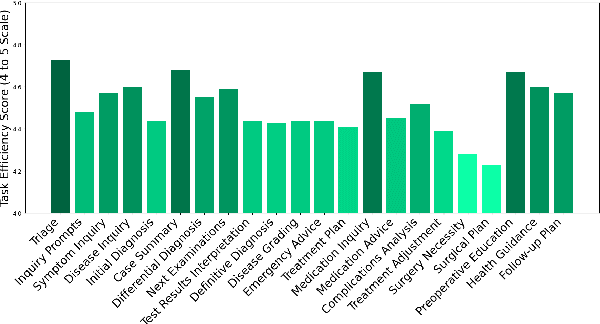
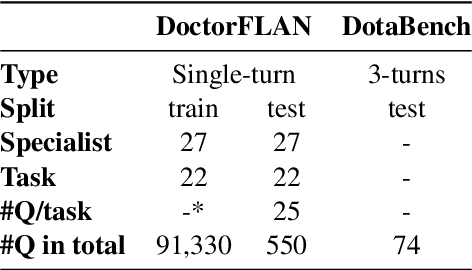
Abstract:The recent success of Large Language Models (LLMs) has had a significant impact on the healthcare field, providing patients with medical advice, diagnostic information, and more. However, due to a lack of professional medical knowledge, patients are easily misled by generated erroneous information from LLMs, which may result in serious medical problems. To address this issue, we focus on tuning the LLMs to be medical assistants who collaborate with more experienced doctors. We first conduct a two-stage survey by inspiration-feedback to gain a broad understanding of the real needs of doctors for medical assistants. Based on this, we construct a Chinese medical dataset called DoctorFLAN to support the entire workflow of doctors, which includes 92K Q\&A samples from 22 tasks and 27 specialists. Moreover, we evaluate LLMs in doctor-oriented scenarios by constructing the DoctorFLAN-\textit{test} containing 550 single-turn Q\&A and DotaBench containing 74 multi-turn conversations. The evaluation results indicate that being a medical assistant still poses challenges for existing open-source models, but DoctorFLAN can help them significantly. It demonstrates that the doctor-oriented dataset and benchmarks we construct can complement existing patient-oriented work and better promote medical LLMs research.
LLMs Could Autonomously Learn Without External Supervision
Jun 02, 2024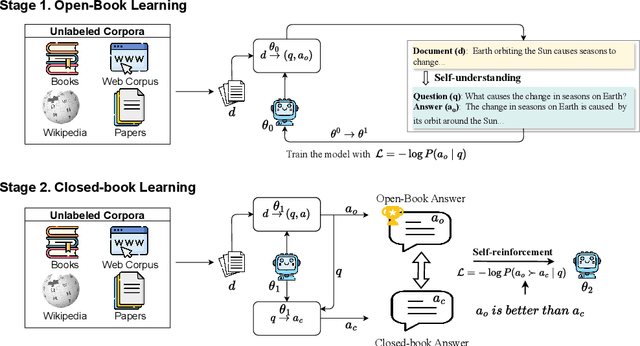
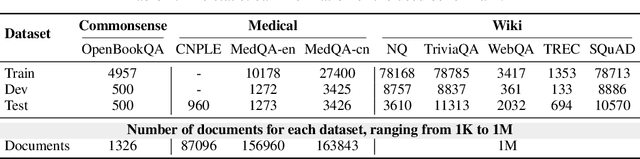

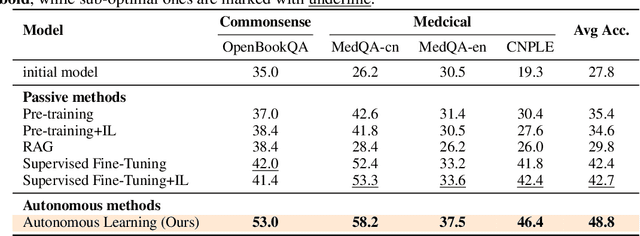
Abstract:In the quest for super-human performance, Large Language Models (LLMs) have traditionally been tethered to human-annotated datasets and predefined training objectives-a process that is both labor-intensive and inherently limited. This paper presents a transformative approach: Autonomous Learning for LLMs, a self-sufficient learning paradigm that frees models from the constraints of human supervision. This method endows LLMs with the ability to self-educate through direct interaction with text, akin to a human reading and comprehending literature. Our approach eliminates the reliance on annotated data, fostering an Autonomous Learning environment where the model independently identifies and reinforces its knowledge gaps. Empirical results from our comprehensive experiments, which utilized a diverse array of learning materials and were evaluated against standard public quizzes, reveal that Autonomous Learning outstrips the performance of both Pre-training and Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT), as well as retrieval-augmented methods. These findings underscore the potential of Autonomous Learning to not only enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of LLM training but also to pave the way for the development of more advanced, self-reliant AI systems.
MLLM-Bench, Evaluating Multi-modal LLMs using GPT-4V
Nov 23, 2023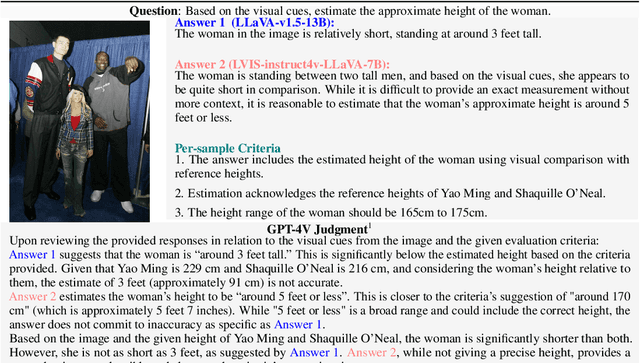
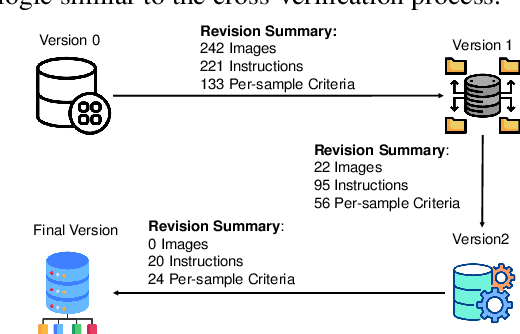

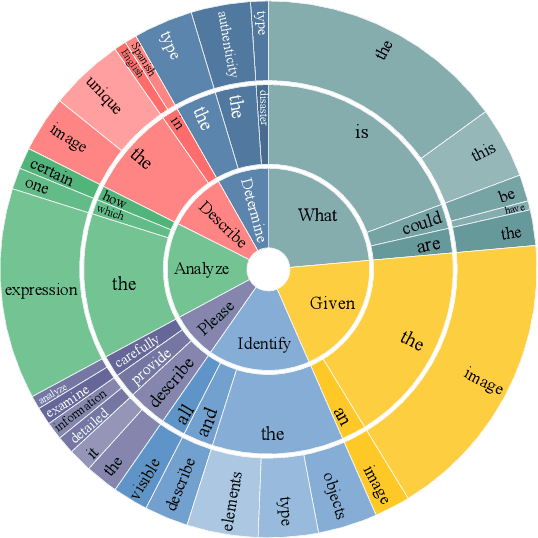
Abstract:In the pursuit of Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), the integration of vision in language models has marked a significant milestone. The advent of vision-language models (MLLMs) like GPT-4V have expanded AI applications, aligning with the multi-modal capabilities of the human brain. However, evaluating the efficacy of MLLMs poses a substantial challenge due to the subjective nature of tasks that lack definitive answers. Existing automatic evaluation methodologies on multi-modal large language models rely on objective queries that have standard answers, inadequately addressing the nuances of creative and associative multi-modal tasks. To address this, we introduce MLLM-Bench, an innovative benchmark inspired by Vicuna, spanning a diverse array of scenarios, including Perception, Understanding, Applying, Analyzing, Evaluating, and Creation along with the ethical consideration. MLLM-Bench is designed to reflect user experience more accurately and provide a more holistic assessment of model performance. Comparative evaluations indicate a significant performance gap between existing open-source models and GPT-4V. We posit that MLLM-Bench will catalyze progress in the open-source community towards developing user-centric vision-language models that meet a broad spectrum of real-world applications. See online leaderboard in \url{https://mllm-bench.llmzoo.com}.
HuatuoGPT-II, One-stage Training for Medical Adaption of LLMs
Nov 16, 2023Abstract:Adapting a language model into a specific domain, a.k.a `domain adaption', is a common practice when specialized knowledge, e.g. medicine, is not encapsulated in a general language model like Llama2. The challenge lies in the heterogeneity of data across the two training stages, as it varies in languages, genres, or formats. To tackle this and simplify the learning protocol, we propose to transform heterogeneous data, from the both pre-training and supervised stages, into a unified, simple input-output pair format. We validate the new protocol in the domains where proprietary LLMs like ChatGPT perform relatively poorly, such as Traditional Chinese Medicine. The developed model, HuatuoGPT-II, has shown state-of-the-art performance in Chinese medicine domain on a number of benchmarks, e.g. medical licensing exams. It even outperforms proprietary models like ChatGPT and GPT-4 in some aspects, especially in Traditional Chinese Medicine. Expert manual evaluations further validate HuatuoGPT-II's advantages over existing LLMs. Notably, HuatuoGPT-II was benchmarked in a fresh Chinese National Medical Licensing Examination where it achieved the best performance, showcasing not only its effectiveness but also its generalization capabilities.
Coarse-to-fine Hybrid 3D Mapping System with Co-calibrated Omnidirectional Camera and Non-repetitive LiDAR
Feb 08, 2023



Abstract:This paper presents a novel 3D mapping robot with an omnidirectional field-of-view (FoV) sensor suite composed of a non-repetitive LiDAR and an omnidirectional camera. Thanks to the non-repetitive scanning nature of the LiDAR, an automatic targetless co-calibration method is proposed to simultaneously calibrate the intrinsic parameters for the omnidirectional camera and the extrinsic parameters for the camera and LiDAR, which is crucial for the required step in bringing color and texture information to the point clouds in surveying and mapping tasks. Comparisons and analyses are made to target-based intrinsic calibration and mutual information (MI)-based extrinsic calibration, respectively. With this co-calibrated sensor suite, the hybrid mapping robot integrates both the odometry-based mapping mode and stationary mapping mode. Meanwhile, we proposed a new workflow to achieve coarse-to-fine mapping, including efficient and coarse mapping in a global environment with odometry-based mapping mode; planning for viewpoints in the region-of-interest (ROI) based on the coarse map (relies on the previous work); navigating to each viewpoint and performing finer and more precise stationary scanning and mapping of the ROI. The fine map is stitched with the global coarse map, which provides a more efficient and precise result than the conventional stationary approaches and the emerging odometry-based approaches, respectively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge