Zirui Liu
FlashSchNet: Fast and Accurate Coarse-Grained Neural Network Molecular Dynamics
Feb 13, 2026Abstract:Graph neural network (GNN) potentials such as SchNet improve the accuracy and transferability of molecular dynamics (MD) simulation by learning many-body interactions, but remain slower than classical force fields due to fragmented kernels and memory-bound pipelines that underutilize GPUs. We show that a missing principle is making GNN-MD IO-aware, carefully accounting for reads and writes between GPU high-bandwidth memory (HBM) and on-chip SRAM. We present FlashSchNet, an efficient and accurate IO-aware SchNet-style GNN-MD framework built on four techniques: (1) flash radial basis, which fuses pairwise distance computation, Gaussian basis expansion, and cosine envelope into a single tiled pass, computing each distance once and reusing it across all basis functions; (2) flash message passing, which fuses cutoff, neighbor gather, filter multiplication, and reduction to avoid materializing edge tensors in HBM; (3) flash aggregation, which reformulates scatter-add via CSR segment reduce, reducing atomic writes by a factor of feature dimension and enabling contention-free accumulation in both forward and backward passes; (4) channel-wise 16-bit quantization that exploits the low per-channel dynamic range in SchNet MLP weights to further improve throughput with negligible accuracy loss. On a single NVIDIA RTX PRO 6000, FlashSchNet achieves 1000 ns/day aggregate simulation throughput over 64 parallel replicas on coarse-grained (CG) protein containing 269 beads (6.5x faster than CGSchNet baseline with 80% reduction of peak memory), surpassing classical force fields (e.g. MARTINI) while retaining SchNet-level accuracy and transferability.
PaperScout: An Autonomous Agent for Academic Paper Search with Process-Aware Sequence-Level Policy Optimization
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Academic paper search is a fundamental task in scientific research, yet most existing approaches rely on rigid, predefined workflows that struggle with complex, conditional queries. To address this limitation, we propose PaperScout, an autonomous agent that reformulates paper search as a sequential decision-making process. Unlike static workflows, PaperScout dynamically decides whether, when, and how to invoke search and expand tools based on accumulated retrieval context. However, training such agents presents a fundamental challenge: standard reinforcement learning methods, typically designed for single-turn tasks, suffer from a granularity mismatch when applied to multi-turn agentic tasks, where token-level optimization diverges from the granularity of sequence-level interactions, leading to noisy credit assignment. We introduce Proximal Sequence Policy Optimization (PSPO), a process-aware, sequence-level policy optimization method that aligns optimization with agent-environment interaction. Comprehensive experiments on both synthetic and real-world benchmarks demonstrate that PaperScout significantly outperforms strong workflow-driven and RL baselines in both recall and relevance, validating the effectiveness of our adaptive agentic framework and optimization strategy.
EntroCoT: Enhancing Chain-of-Thought via Adaptive Entropy-Guided Segmentation
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting has significantly enhanced the mathematical reasoning capabilities of Large Language Models. We find existing fine-tuning datasets frequently suffer from the "answer right but reasoning wrong" probelm, where correct final answers are derived from hallucinated, redundant, or logically invalid intermediate steps. This paper proposes EntroCoT, a unified framework for automatically identifying and refining low-quality CoT supervision traces. EntroCoT first proposes an entropy-based mechanism to segment the reasoning trace into multiple steps at uncertain junctures, and then introduces a Monte Carlo rollout-based mechanism to evaluate the marginal contribution of each step. By accurately filtering deceptive reasoning samples, EntroCoT constructs a high-quality dataset where every intermediate step in each reasoning trace facilitates the final answer. Extensive experiments on mathematical benchmarks demonstrate that fine-tuning on the subset constructed by EntroCoT consistently outperforms the baseslines of full-dataset supervision.
Towards Stable and Structured Time Series Generation with Perturbation-Aware Flow Matching
Nov 18, 2025
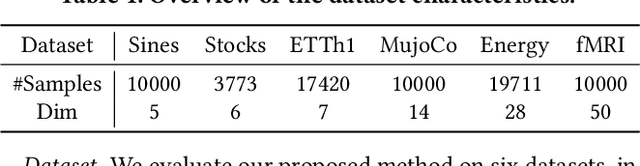
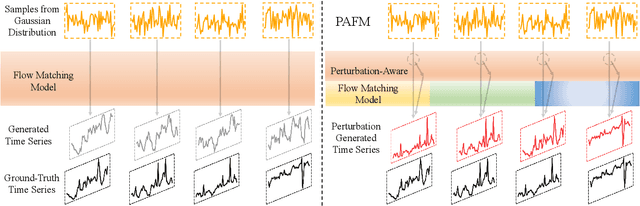
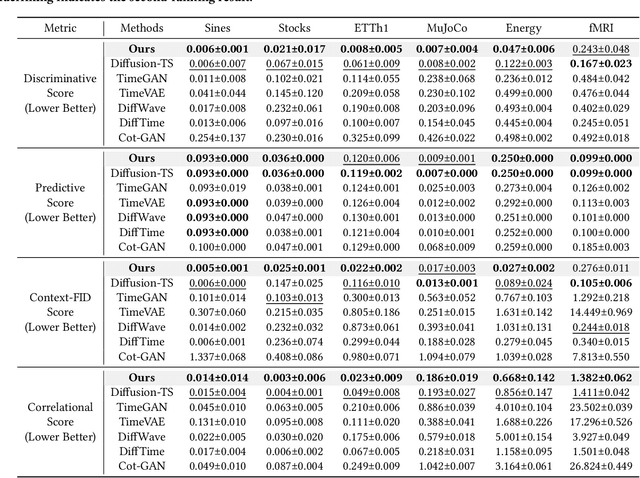
Abstract:Time series generation is critical for a wide range of applications, which greatly supports downstream analytical and decision-making tasks. However, the inherent temporal heterogeneous induced by localized perturbations present significant challenges for generating structurally consistent time series. While flow matching provides a promising paradigm by modeling temporal dynamics through trajectory-level supervision, it fails to adequately capture abrupt transitions in perturbed time series, as the use of globally shared parameters constrains the velocity field to a unified representation. To address these limitations, we introduce \textbf{PAFM}, a \textbf{P}erturbation-\textbf{A}ware \textbf{F}low \textbf{M}atching framework that models perturbed trajectories to ensure stable and structurally consistent time series generation. The framework incorporates perturbation-guided training to simulate localized disturbances and leverages a dual-path velocity field to capture trajectory deviations under perturbation, enabling refined modeling of perturbed behavior to enhance the structural coherence. In order to further improve sensitivity to trajectory perturbations while enhancing expressiveness, a mixture-of-experts decoder with flow routing dynamically allocates modeling capacity in response to different trajectory dynamics. Extensive experiments on both unconditional and conditional generation tasks demonstrate that PAFM consistently outperforms strong baselines. Code is available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/PAFM-03B2.
Agent-R1: Training Powerful LLM Agents with End-to-End Reinforcement Learning
Nov 18, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly being explored for building Agents capable of active environmental interaction (e.g., via tool use) to solve complex problems. Reinforcement Learning (RL) is considered a key technology with significant potential for training such Agents; however, the effective application of RL to LLM Agents is still in its nascent stages and faces considerable challenges. Currently, this emerging field lacks in-depth exploration into RL approaches specifically tailored for the LLM Agent context, alongside a scarcity of flexible and easily extensible training frameworks designed for this purpose. To help advance this area, this paper first revisits and clarifies Reinforcement Learning methodologies for LLM Agents by systematically extending the Markov Decision Process (MDP) framework to comprehensively define the key components of an LLM Agent. Secondly, we introduce Agent-R1, a modular, flexible, and user-friendly training framework for RL-based LLM Agents, designed for straightforward adaptation across diverse task scenarios and interactive environments. We conducted experiments on Multihop QA benchmark tasks, providing initial validation for the effectiveness of our proposed methods and framework.
MemWeaver: A Hierarchical Memory from Textual Interactive Behaviors for Personalized Generation
Oct 09, 2025
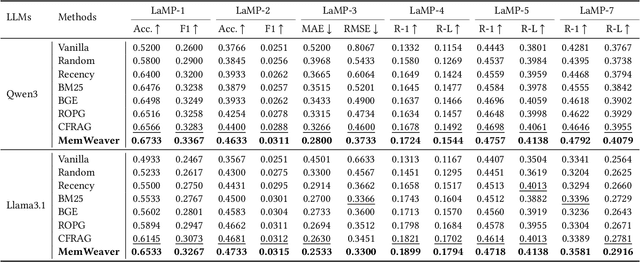
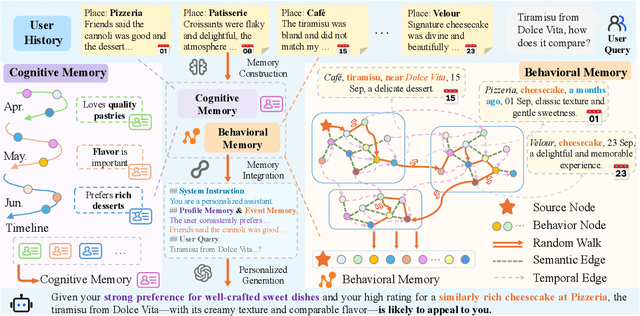
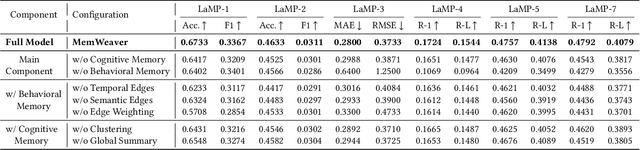
Abstract:The primary form of user-internet engagement is shifting from leveraging implicit feedback signals, such as browsing and clicks, to harnessing the rich explicit feedback provided by textual interactive behaviors. This shift unlocks a rich source of user textual history, presenting a profound opportunity for a deeper form of personalization. However, prevailing approaches offer only a shallow form of personalization, as they treat user history as a flat list of texts for retrieval and fail to model the rich temporal and semantic structures reflecting dynamic nature of user interests. In this work, we propose \textbf{MemWeaver}, a framework that weaves the user's entire textual history into a hierarchical memory to power deeply personalized generation. The core innovation of our memory lies in its ability to capture both the temporal evolution of interests and the semantic relationships between different activities. To achieve this, MemWeaver builds two complementary memory components that both integrate temporal and semantic information, but at different levels of abstraction: behavioral memory, which captures specific user actions, and cognitive memory, which represents long-term preferences. This dual-component memory serves as a unified representation of the user, allowing large language models (LLMs) to reason over both concrete behaviors and abstracted traits. Experiments on the Language Model Personalization (LaMP) benchmark validate the efficacy of MemWeaver. Our code is available\footnote{https://github.com/fishsure/MemWeaver}.
Systematic Evaluation of Optimization Techniques for Long-Context Language Models
Aug 01, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) excel across diverse natural language processing tasks but face resource demands and limited context windows. Although techniques like pruning, quantization, and token dropping can mitigate these issues, their efficacy in long-context scenarios and system evaluation remains underexplored. This paper systematically benchmarks these optimizations, characterizing memory usage, latency, and throughput, and studies how these methods impact the quality of text generation. We first analyze individual optimization methods for two LLM architectures supporting long context and then systematically evaluate combinations of these techniques to assess how this deeper analysis impacts performance metrics. We subsequently study the scalability of individual optimization methods on a larger variant with 70 billion-parameter model. Our novel insights reveal that naive combination inference optimization algorithms can adversely affect larger models due to compounded approximation errors, as compared to their smaller counterparts. Experiments show that relying solely on F1 obscures these effects by hiding precision-recall trade-offs in question answering tasks. By integrating system-level profiling with task-specific insights, this study helps LLM practitioners and researchers explore and balance efficiency, accuracy, and scalability across tasks and hardware configurations.
Automating Expert-Level Medical Reasoning Evaluation of Large Language Models
Jul 10, 2025Abstract:As large language models (LLMs) become increasingly integrated into clinical decision-making, ensuring transparent and trustworthy reasoning is essential. However, existing evaluation strategies of LLMs' medical reasoning capability either suffer from unsatisfactory assessment or poor scalability, and a rigorous benchmark remains lacking. To address this, we introduce MedThink-Bench, a benchmark designed for rigorous, explainable, and scalable assessment of LLMs' medical reasoning. MedThink-Bench comprises 500 challenging questions across ten medical domains, each annotated with expert-crafted step-by-step rationales. Building on this, we propose LLM-w-Ref, a novel evaluation framework that leverages fine-grained rationales and LLM-as-a-Judge mechanisms to assess intermediate reasoning with expert-level fidelity while maintaining scalability. Experiments show that LLM-w-Ref exhibits a strong positive correlation with expert judgments. Benchmarking twelve state-of-the-art LLMs, we find that smaller models (e.g., MedGemma-27B) can surpass larger proprietary counterparts (e.g., OpenAI-o3). Overall, MedThink-Bench offers a foundational tool for evaluating LLMs' medical reasoning, advancing their safe and responsible deployment in clinical practice.
Give Me FP32 or Give Me Death? Challenges and Solutions for Reproducible Reasoning
Jun 11, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are now integral across various domains and have demonstrated impressive performance. Progress, however, rests on the premise that benchmark scores are both accurate and reproducible. We demonstrate that the reproducibility of LLM performance is fragile: changing system configuration such as evaluation batch size, GPU count, and GPU version can introduce significant difference in the generated responses. This issue is especially pronounced in reasoning models, where minor rounding differences in early tokens can cascade into divergent chains of thought, ultimately affecting accuracy. For instance, under bfloat16 precision with greedy decoding, a reasoning model like DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-7B can exhibit up to 9% variation in accuracy and 9,000 tokens difference in response length due to differences in GPU count, type, and evaluation batch size. We trace the root cause of this variability to the non-associative nature of floating-point arithmetic under limited numerical precision. This work presents the first systematic investigation into how numerical precision affects reproducibility in LLM inference. Through carefully controlled experiments across various hardware, software, and precision settings, we quantify when and how model outputs diverge. Our analysis reveals that floating-point precision -- while critical for reproducibility -- is often neglected in evaluation practices. Inspired by this, we develop a lightweight inference pipeline, dubbed LayerCast, that stores weights in 16-bit precision but performs all computations in FP32, balancing memory efficiency with numerical stability. Code is available at https://github.com/nanomaoli/llm_reproducibility.
Are LLMs Reliable Translators of Logical Reasoning Across Lexically Diversified Contexts?
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:Neuro-symbolic approaches combining large language models (LLMs) with solvers excels in logical reasoning problems need long reasoning chains. In this paradigm, LLMs serve as translators, converting natural language reasoning problems into formal logic formulas. Then reliable symbolic solvers return correct solutions. Despite their success, we find that LLMs, as translators, struggle to handle lexical diversification, a common linguistic phenomenon, indicating that LLMs as logic translators are unreliable in real-world scenarios. Moreover, existing logical reasoning benchmarks lack lexical diversity, failing to challenge LLMs' ability to translate such text and thus obscuring this issue. In this work, we propose SCALe, a benchmark designed to address this significant gap through **logic-invariant lexical diversification**. By using LLMs to transform original benchmark datasets into lexically diversified but logically equivalent versions, we evaluate LLMs' ability to consistently map diverse expressions to uniform logical symbols on these new datasets. Experiments using SCALe further confirm that current LLMs exhibit deficiencies in this capability. Building directly on the deficiencies identified through our benchmark, we propose a new method, MenTaL, to address this limitation. This method guides LLMs to first construct a table unifying diverse expressions before performing translation. Applying MenTaL through in-context learning and supervised fine-tuning (SFT) significantly improves the performance of LLM translators on lexically diversified text. Our code is now available at https://github.com/wufeiwuwoshihua/LexicalDiver.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge