Wentian Zhao
HiPRAG: Hierarchical Process Rewards for Efficient Agentic Retrieval Augmented Generation
Oct 09, 2025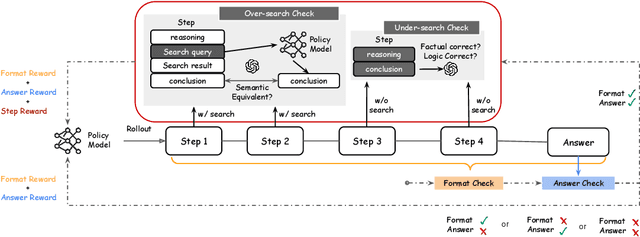
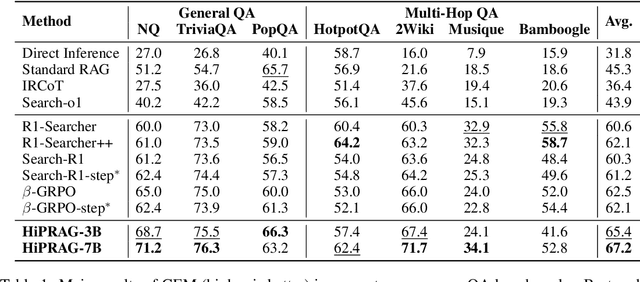
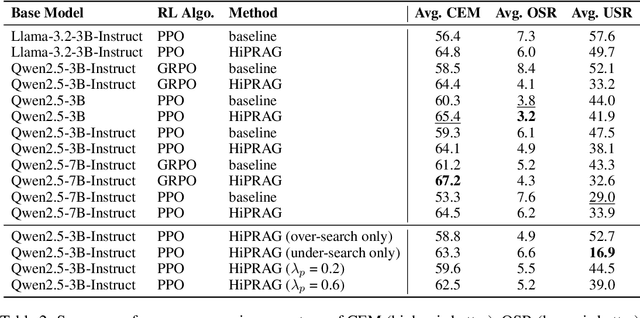
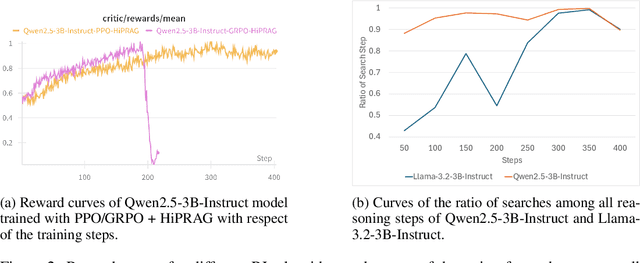
Abstract:Agentic RAG is a powerful technique for incorporating external information that LLMs lack, enabling better problem solving and question answering. However, suboptimal search behaviors exist widely, such as over-search (retrieving information already known) and under-search (failing to search when necessary), which leads to unnecessary overhead and unreliable outputs. Current training methods, which typically rely on outcome-based rewards in a RL framework, lack the fine-grained control needed to address these inefficiencies. To overcome this, we introduce Hierarchical Process Rewards for Efficient agentic RAG (HiPRAG), a training methodology that incorporates a fine-grained, knowledge-grounded process reward into the RL training. Our approach evaluates the necessity of each search decision on-the-fly by decomposing the agent's reasoning trajectory into discrete, parsable steps. We then apply a hierarchical reward function that provides an additional bonus based on the proportion of optimal search and non-search steps, on top of commonly used outcome and format rewards. Experiments on the Qwen2.5 and Llama-3.2 models across seven diverse QA benchmarks show that our method achieves average accuracies of 65.4% (3B) and 67.2% (7B). This is accomplished while improving search efficiency, reducing the over-search rate to just 2.3% and concurrently lowering the under-search rate. These results demonstrate the efficacy of optimizing the reasoning process itself, not just the final outcome. Further experiments and analysis demonstrate that HiPRAG shows good generalizability across a wide range of RL algorithms, model families, sizes, and types. This work demonstrates the importance and potential of fine-grained control through RL, for improving the efficiency and optimality of reasoning for search agents.
EPO: Entropy-regularized Policy Optimization for LLM Agents Reinforcement Learning
Sep 26, 2025



Abstract:Training LLM agents in multi-turn environments with sparse rewards, where completing a single task requires 30+ turns of interaction within an episode, presents a fundamental challenge for reinforcement learning. We identify a critical failure mode unique to this setting: the exploration-exploitation cascade failure. This cascade begins with early-stage policy premature convergence, where sparse feedback causes agents to commit to flawed, low-entropy strategies. Subsequently, agents enter late-stage policy collapse, where conventional entropy regularization becomes counterproductive, promoting chaotic exploration that destabilizes training. We propose Entropy-regularized Policy Optimization (EPO), a general framework that breaks this failure cycle through three synergistic mechanisms: (1) adopting entropy regularization in multi-turn settings to enhance exploration, (2) an entropy smoothing regularizer that bounds policy entropy within historical averages to prevent abrupt fluctuations, and (3) adaptive phase-based weighting that balances exploration and exploitation across training. Our analysis justifies that EPO guarantees monotonically decreasing entropy variance while maintaining convergence. EPO achieves up to 152% performance improvement on ScienceWorld and up to 19.8% on ALFWorld. Our work demonstrates that multi-turn sparse-reward settings require fundamentally different entropy control than traditional RL, with broad implications for LLM agent training.
Give Me FP32 or Give Me Death? Challenges and Solutions for Reproducible Reasoning
Jun 11, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are now integral across various domains and have demonstrated impressive performance. Progress, however, rests on the premise that benchmark scores are both accurate and reproducible. We demonstrate that the reproducibility of LLM performance is fragile: changing system configuration such as evaluation batch size, GPU count, and GPU version can introduce significant difference in the generated responses. This issue is especially pronounced in reasoning models, where minor rounding differences in early tokens can cascade into divergent chains of thought, ultimately affecting accuracy. For instance, under bfloat16 precision with greedy decoding, a reasoning model like DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-7B can exhibit up to 9% variation in accuracy and 9,000 tokens difference in response length due to differences in GPU count, type, and evaluation batch size. We trace the root cause of this variability to the non-associative nature of floating-point arithmetic under limited numerical precision. This work presents the first systematic investigation into how numerical precision affects reproducibility in LLM inference. Through carefully controlled experiments across various hardware, software, and precision settings, we quantify when and how model outputs diverge. Our analysis reveals that floating-point precision -- while critical for reproducibility -- is often neglected in evaluation practices. Inspired by this, we develop a lightweight inference pipeline, dubbed LayerCast, that stores weights in 16-bit precision but performs all computations in FP32, balancing memory efficiency with numerical stability. Code is available at https://github.com/nanomaoli/llm_reproducibility.
DUMP: Automated Distribution-Level Curriculum Learning for RL-based LLM Post-training
Apr 13, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in reinforcement learning (RL)-based post-training have led to notable improvements in large language models (LLMs), particularly in enhancing their reasoning capabilities to handle complex tasks. However, most existing methods treat the training data as a unified whole, overlooking the fact that modern LLM training often involves a mixture of data from diverse distributions-varying in both source and difficulty. This heterogeneity introduces a key challenge: how to adaptively schedule training across distributions to optimize learning efficiency. In this paper, we present a principled curriculum learning framework grounded in the notion of distribution-level learnability. Our core insight is that the magnitude of policy advantages reflects how much a model can still benefit from further training on a given distribution. Based on this, we propose a distribution-level curriculum learning framework for RL-based LLM post-training, which leverages the Upper Confidence Bound (UCB) principle to dynamically adjust sampling probabilities for different distrubutions. This approach prioritizes distributions with either high average advantage (exploitation) or low sample count (exploration), yielding an adaptive and theoretically grounded training schedule. We instantiate our curriculum learning framework with GRPO as the underlying RL algorithm and demonstrate its effectiveness on logic reasoning datasets with multiple difficulties and sources. Our experiments show that our framework significantly improves convergence speed and final performance, highlighting the value of distribution-aware curriculum strategies in LLM post-training. Code: https://github.com/ZhentingWang/DUMP.
Efficient Self-Improvement in Multimodal Large Language Models: A Model-Level Judge-Free Approach
Nov 26, 2024



Abstract:Self-improvement in multimodal large language models (MLLMs) is crucial for enhancing their reliability and robustness. However, current methods often rely heavily on MLLMs themselves as judges, leading to high computational costs and potential pitfalls like reward hacking and model collapse. This paper introduces a novel, model-level judge-free self-improvement framework. Our approach employs a controlled feedback mechanism while eliminating the need for MLLMs in the verification loop. We generate preference learning pairs using a controllable hallucination mechanism and optimize data quality by leveraging lightweight, contrastive language-image encoders to evaluate and reverse pairs when necessary. Evaluations across public benchmarks and our newly introduced IC dataset designed to challenge hallucination control demonstrate that our model outperforms conventional techniques. We achieve superior precision and recall with significantly lower computational demands. This method offers an efficient pathway to scalable self-improvement in MLLMs, balancing performance gains with reduced resource requirements.
Quadratic Is Not What You Need For Multimodal Large Language Models
Oct 08, 2024



Abstract:In the past year, the capabilities of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have significantly improved across various aspects. However, constrained by the quadratic growth of computation in LLMs as the number of tokens increases, efficiency has become a bottleneck for further scaling MLLMs. Although recent efforts have been made to prune visual tokens or use more lightweight LLMs to reduce computation, the problem of quadratic growth in computation with the increase of visual tokens still persists. To address this, we propose a novel approach: instead of reducing the input visual tokens for LLMs, we focus on pruning vision-related computations within the LLMs. After pruning, the computation growth in the LLM is no longer quadratic with the increase of visual tokens, but linear. Surprisingly, we found that after applying such extensive pruning, the capabilities of MLLMs are comparable with the original one and even superior on some benchmarks with only 25% of the computation. This finding opens up the possibility for MLLMs to incorporate much denser visual tokens. Additionally, based on this finding, we further analyzed some architectural design deficiencies in existing MLLMs and proposed promising improvements. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to investigate the computational redundancy in the LLM's vision component of MLLMs. Code and checkpoints will be released soon.
DL3DV-10K: A Large-Scale Scene Dataset for Deep Learning-based 3D Vision
Dec 29, 2023



Abstract:We have witnessed significant progress in deep learning-based 3D vision, ranging from neural radiance field (NeRF) based 3D representation learning to applications in novel view synthesis (NVS). However, existing scene-level datasets for deep learning-based 3D vision, limited to either synthetic environments or a narrow selection of real-world scenes, are quite insufficient. This insufficiency not only hinders a comprehensive benchmark of existing methods but also caps what could be explored in deep learning-based 3D analysis. To address this critical gap, we present DL3DV-10K, a large-scale scene dataset, featuring 51.2 million frames from 10,510 videos captured from 65 types of point-of-interest (POI) locations, covering both bounded and unbounded scenes, with different levels of reflection, transparency, and lighting. We conducted a comprehensive benchmark of recent NVS methods on DL3DV-10K, which revealed valuable insights for future research in NVS. In addition, we have obtained encouraging results in a pilot study to learn generalizable NeRF from DL3DV-10K, which manifests the necessity of a large-scale scene-level dataset to forge a path toward a foundation model for learning 3D representation. Our DL3DV-10K dataset, benchmark results, and models will be publicly accessible at https://dl3dv-10k.github.io/DL3DV-10K/.
Text2Layer: Layered Image Generation using Latent Diffusion Model
Jul 19, 2023Abstract:Layer compositing is one of the most popular image editing workflows among both amateurs and professionals. Motivated by the success of diffusion models, we explore layer compositing from a layered image generation perspective. Instead of generating an image, we propose to generate background, foreground, layer mask, and the composed image simultaneously. To achieve layered image generation, we train an autoencoder that is able to reconstruct layered images and train diffusion models on the latent representation. One benefit of the proposed problem is to enable better compositing workflows in addition to the high-quality image output. Another benefit is producing higher-quality layer masks compared to masks produced by a separate step of image segmentation. Experimental results show that the proposed method is able to generate high-quality layered images and initiates a benchmark for future work.
Boosting Entity-aware Image Captioning with Multi-modal Knowledge Graph
Jul 26, 2021
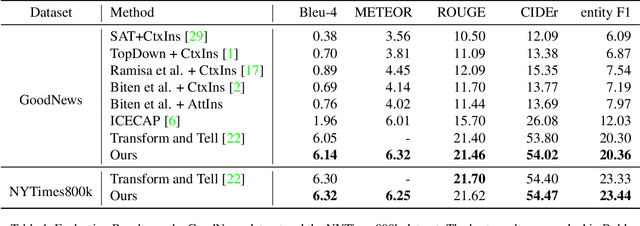
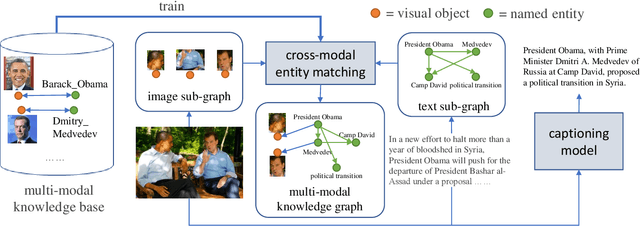
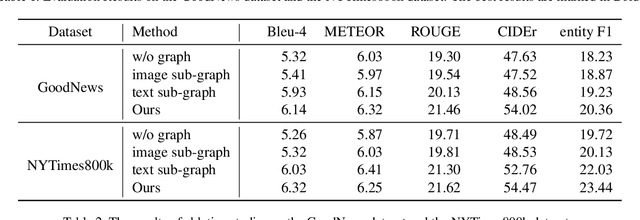
Abstract:Entity-aware image captioning aims to describe named entities and events related to the image by utilizing the background knowledge in the associated article. This task remains challenging as it is difficult to learn the association between named entities and visual cues due to the long-tail distribution of named entities. Furthermore, the complexity of the article brings difficulty in extracting fine-grained relationships between entities to generate informative event descriptions about the image. To tackle these challenges, we propose a novel approach that constructs a multi-modal knowledge graph to associate the visual objects with named entities and capture the relationship between entities simultaneously with the help of external knowledge collected from the web. Specifically, we build a text sub-graph by extracting named entities and their relationships from the article, and build an image sub-graph by detecting the objects in the image. To connect these two sub-graphs, we propose a cross-modal entity matching module trained using a knowledge base that contains Wikipedia entries and the corresponding images. Finally, the multi-modal knowledge graph is integrated into the captioning model via a graph attention mechanism. Extensive experiments on both GoodNews and NYTimes800k datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our method.
Video Question Answering on Screencast Tutorials
Aug 02, 2020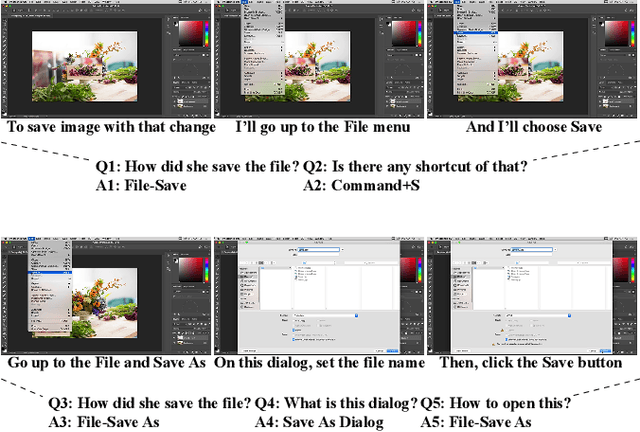
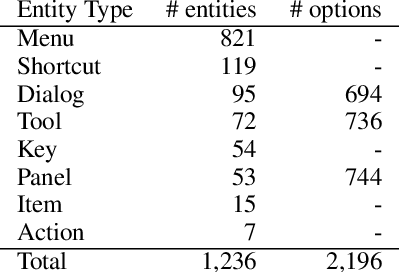
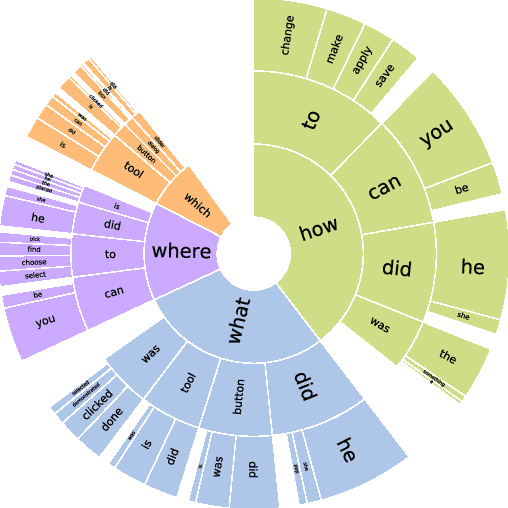
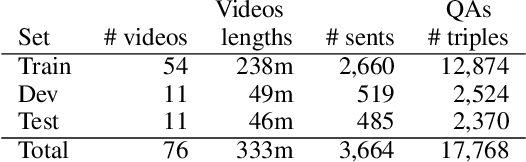
Abstract:This paper presents a new video question answering task on screencast tutorials. We introduce a dataset including question, answer and context triples from the tutorial videos for a software. Unlike other video question answering works, all the answers in our dataset are grounded to the domain knowledge base. An one-shot recognition algorithm is designed to extract the visual cues, which helps enhance the performance of video question answering. We also propose several baseline neural network architectures based on various aspects of video contexts from the dataset. The experimental results demonstrate that our proposed models significantly improve the question answering performances by incorporating multi-modal contexts and domain knowledge.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge