Shijian Deng
ARGaze: Autoregressive Transformers for Online Egocentric Gaze Estimation
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Online egocentric gaze estimation predicts where a camera wearer is looking from first-person video using only past and current frames, a task essential for augmented reality and assistive technologies. Unlike third-person gaze estimation, this setting lacks explicit head or eye signals, requiring models to infer current visual attention from sparse, indirect cues such as hand-object interactions and salient scene content. We observe that gaze exhibits strong temporal continuity during goal-directed activities: knowing where a person looked recently provides a powerful prior for predicting where they look next. Inspired by vision-conditioned autoregressive decoding in vision-language models, we propose ARGaze, which reformulates gaze estimation as sequential prediction: at each timestep, a transformer decoder predicts current gaze by conditioning on (i) current visual features and (ii) a fixed-length Gaze Context Window of recent gaze target estimates. This design enforces causality and enables bounded-resource streaming inference. We achieve state-of-the-art performance across multiple egocentric benchmarks under online evaluation, with extensive ablations validating that autoregressive modeling with bounded gaze history is critical for robust prediction. We will release our source code and pre-trained models.
Explainable AI-Generated Image Detection RewardBench
Nov 15, 2025Abstract:Conventional, classification-based AI-generated image detection methods cannot explain why an image is considered real or AI-generated in a way a human expert would, which reduces the trustworthiness and persuasiveness of these detection tools for real-world applications. Leveraging Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) has recently become a trending solution to this issue. Further, to evaluate the quality of generated explanations, a common approach is to adopt an "MLLM as a judge" methodology to evaluate explanations generated by other MLLMs. However, how well those MLLMs perform when judging explanations for AI-generated image detection generated by themselves or other MLLMs has not been well studied. We therefore propose \textbf{XAIGID-RewardBench}, the first benchmark designed to evaluate the ability of current MLLMs to judge the quality of explanations about whether an image is real or AI-generated. The benchmark consists of approximately 3,000 annotated triplets sourced from various image generation models and MLLMs as policy models (detectors) to assess the capabilities of current MLLMs as reward models (judges). Our results show that the current best reward model scored 88.76\% on this benchmark (while human inter-annotator agreement reaches 98.30\%), demonstrating that a visible gap remains between the reasoning abilities of today's MLLMs and human-level performance. In addition, we provide an analysis of common pitfalls that these models frequently encounter. Code and benchmark are available at https://github.com/RewardBench/XAIGID-RewardBench.
Toward Gaze Target Detection of Young Autistic Children
Nov 14, 2025Abstract:The automatic detection of gaze targets in autistic children through artificial intelligence can be impactful, especially for those who lack access to a sufficient number of professionals to improve their quality of life. This paper introduces a new, real-world AI application for gaze target detection in autistic children, which predicts a child's point of gaze from an activity image. This task is foundational for building automated systems that can measure joint attention-a core challenge in Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). To facilitate the study of this challenging application, we collected the first-ever Autism Gaze Target (AGT) dataset. We further propose a novel Socially Aware Coarse-to-Fine (SACF) gaze detection framework that explicitly leverages the social context of a scene to overcome the class imbalance common in autism datasets-a consequence of autistic children's tendency to show reduced gaze to faces. It utilizes a two-pathway architecture with expert models specialized in social and non-social gaze, guided by a context-awareness gate module. The results of our comprehensive experiments demonstrate that our framework achieves new state-of-the-art performance for gaze target detection in this population, significantly outperforming existing methods, especially on the critical minority class of face-directed gaze.
Towards Online Multi-Modal Social Interaction Understanding
Mar 25, 2025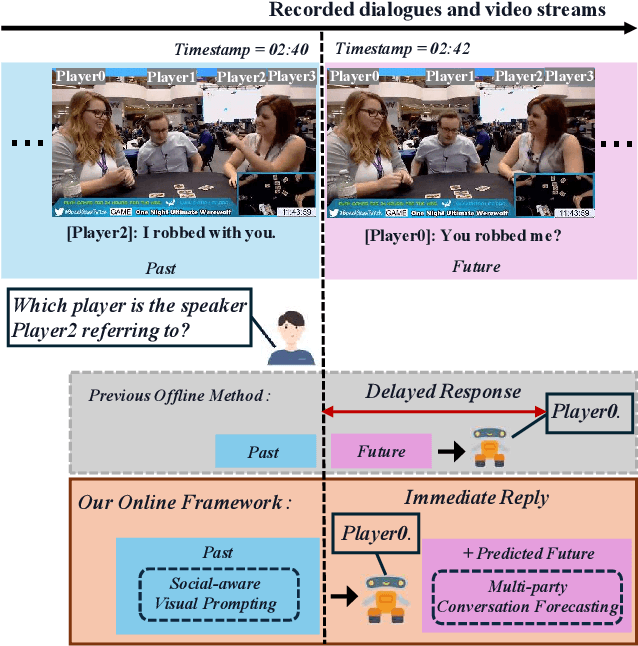
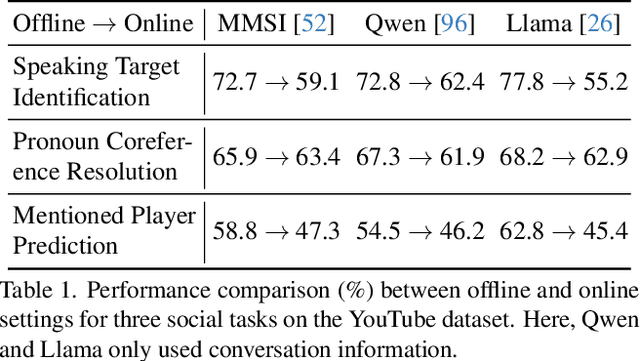
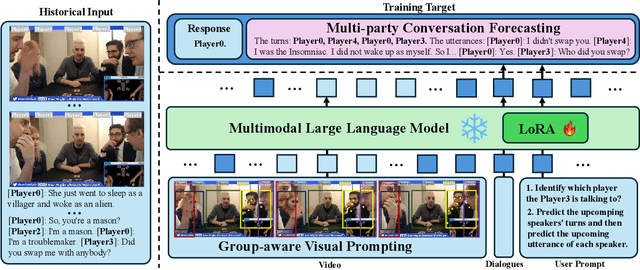
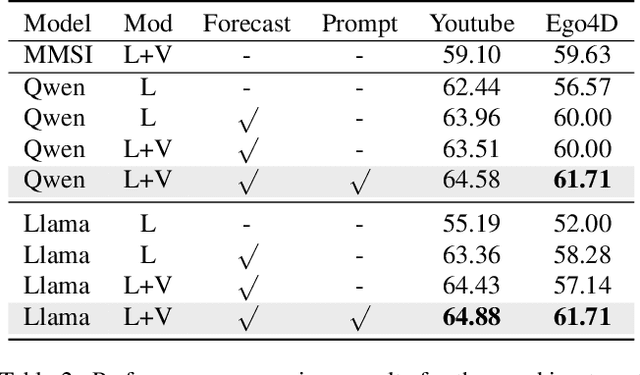
Abstract:Multimodal social interaction understanding (MMSI) is critical in human-robot interaction systems. In real-world scenarios, AI agents are required to provide real-time feedback. However, existing models often depend on both past and future contexts, which hinders them from applying to real-world problems. To bridge this gap, we propose an online MMSI setting, where the model must resolve MMSI tasks using only historical information, such as recorded dialogues and video streams. To address the challenges of missing the useful future context, we develop a novel framework, named Online-MMSI-VLM, that leverages two complementary strategies: multi-party conversation forecasting and social-aware visual prompting with multi-modal large language models. First, to enrich linguistic context, the multi-party conversation forecasting simulates potential future utterances in a coarse-to-fine manner, anticipating upcoming speaker turns and then generating fine-grained conversational details. Second, to effectively incorporate visual social cues like gaze and gesture, social-aware visual prompting highlights the social dynamics in video with bounding boxes and body keypoints for each person and frame. Extensive experiments on three tasks and two datasets demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance and significantly outperforms baseline models, indicating its effectiveness on Online-MMSI. The code and pre-trained models will be publicly released at: https://github.com/Sampson-Lee/OnlineMMSI.
Modality-Inconsistent Continual Learning of Multimodal Large Language Models
Dec 17, 2024


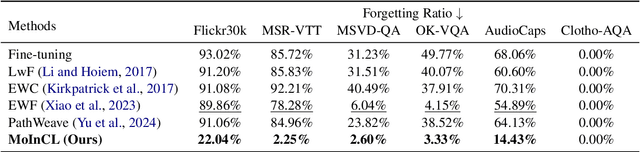
Abstract:In this paper, we introduce Modality-Inconsistent Continual Learning (MICL), a new continual learning scenario for Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) that involves tasks with inconsistent modalities (image, audio, or video) and varying task types (captioning or question-answering). Unlike existing vision-only or modality-incremental settings, MICL combines modality and task type shifts, both of which drive catastrophic forgetting. To address these challenges, we propose MoInCL, which employs a Pseudo Targets Generation Module to mitigate forgetting caused by task type shifts in previously seen modalities. It also incorporates Instruction-based Knowledge Distillation to preserve the model's ability to handle previously learned modalities when new ones are introduced. We benchmark MICL using a total of six tasks and conduct experiments to validate the effectiveness of our proposed MoInCL. The experimental results highlight the superiority of MoInCL, showing significant improvements over representative and state-of-the-art continual learning baselines.
Efficient Self-Improvement in Multimodal Large Language Models: A Model-Level Judge-Free Approach
Nov 26, 2024



Abstract:Self-improvement in multimodal large language models (MLLMs) is crucial for enhancing their reliability and robustness. However, current methods often rely heavily on MLLMs themselves as judges, leading to high computational costs and potential pitfalls like reward hacking and model collapse. This paper introduces a novel, model-level judge-free self-improvement framework. Our approach employs a controlled feedback mechanism while eliminating the need for MLLMs in the verification loop. We generate preference learning pairs using a controllable hallucination mechanism and optimize data quality by leveraging lightweight, contrastive language-image encoders to evaluate and reverse pairs when necessary. Evaluations across public benchmarks and our newly introduced IC dataset designed to challenge hallucination control demonstrate that our model outperforms conventional techniques. We achieve superior precision and recall with significantly lower computational demands. This method offers an efficient pathway to scalable self-improvement in MLLMs, balancing performance gains with reduced resource requirements.
Continual Audio-Visual Sound Separation
Nov 05, 2024



Abstract:In this paper, we introduce a novel continual audio-visual sound separation task, aiming to continuously separate sound sources for new classes while preserving performance on previously learned classes, with the aid of visual guidance. This problem is crucial for practical visually guided auditory perception as it can significantly enhance the adaptability and robustness of audio-visual sound separation models, making them more applicable for real-world scenarios where encountering new sound sources is commonplace. The task is inherently challenging as our models must not only effectively utilize information from both modalities in current tasks but also preserve their cross-modal association in old tasks to mitigate catastrophic forgetting during audio-visual continual learning. To address these challenges, we propose a novel approach named ContAV-Sep (\textbf{Cont}inual \textbf{A}udio-\textbf{V}isual Sound \textbf{Sep}aration). ContAV-Sep presents a novel Cross-modal Similarity Distillation Constraint (CrossSDC) to uphold the cross-modal semantic similarity through incremental tasks and retain previously acquired knowledge of semantic similarity in old models, mitigating the risk of catastrophic forgetting. The CrossSDC can seamlessly integrate into the training process of different audio-visual sound separation frameworks. Experiments demonstrate that ContAV-Sep can effectively mitigate catastrophic forgetting and achieve significantly better performance compared to other continual learning baselines for audio-visual sound separation. Code is available at: \url{https://github.com/weiguoPian/ContAV-Sep_NeurIPS2024}.
AV-DiT: Efficient Audio-Visual Diffusion Transformer for Joint Audio and Video Generation
Jun 11, 2024


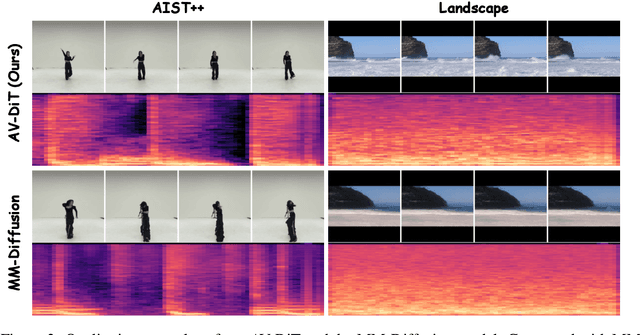
Abstract:Recent Diffusion Transformers (DiTs) have shown impressive capabilities in generating high-quality single-modality content, including images, videos, and audio. However, it is still under-explored whether the transformer-based diffuser can efficiently denoise the Gaussian noises towards superb multimodal content creation. To bridge this gap, we introduce AV-DiT, a novel and efficient audio-visual diffusion transformer designed to generate high-quality, realistic videos with both visual and audio tracks. To minimize model complexity and computational costs, AV-DiT utilizes a shared DiT backbone pre-trained on image-only data, with only lightweight, newly inserted adapters being trainable. This shared backbone facilitates both audio and video generation. Specifically, the video branch incorporates a trainable temporal attention layer into a frozen pre-trained DiT block for temporal consistency. Additionally, a small number of trainable parameters adapt the image-based DiT block for audio generation. An extra shared DiT block, equipped with lightweight parameters, facilitates feature interaction between audio and visual modalities, ensuring alignment. Extensive experiments on the AIST++ and Landscape datasets demonstrate that AV-DiT achieves state-of-the-art performance in joint audio-visual generation with significantly fewer tunable parameters. Furthermore, our results highlight that a single shared image generative backbone with modality-specific adaptations is sufficient for constructing a joint audio-video generator. Our source code and pre-trained models will be released.
Separating Invisible Sounds Toward Universal Audiovisual Scene-Aware Sound Separation
Oct 18, 2023



Abstract:The audio-visual sound separation field assumes visible sources in videos, but this excludes invisible sounds beyond the camera's view. Current methods struggle with such sounds lacking visible cues. This paper introduces a novel "Audio-Visual Scene-Aware Separation" (AVSA-Sep) framework. It includes a semantic parser for visible and invisible sounds and a separator for scene-informed separation. AVSA-Sep successfully separates both sound types, with joint training and cross-modal alignment enhancing effectiveness.
Unveiling Cross Modality Bias in Visual Question Answering: A Causal View with Possible Worlds VQA
May 31, 2023Abstract:To increase the generalization capability of VQA systems, many recent studies have tried to de-bias spurious language or vision associations that shortcut the question or image to the answer. Despite these efforts, the literature fails to address the confounding effect of vision and language simultaneously. As a result, when they reduce bias learned from one modality, they usually increase bias from the other. In this paper, we first model a confounding effect that causes language and vision bias simultaneously, then propose a counterfactual inference to remove the influence of this effect. The model trained in this strategy can concurrently and efficiently reduce vision and language bias. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work to reduce biases resulting from confounding effects of vision and language in VQA, leveraging causal explain-away relations. We accompany our method with an explain-away strategy, pushing the accuracy of the questions with numerical answers results compared to existing methods that have been an open problem. The proposed method outperforms the state-of-the-art methods in VQA-CP v2 datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge