Yapeng Tian
Vision Token Reduction via Attention-Driven Self-Compression for Efficient Multimodal Large Language Models
Feb 13, 2026Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) incur significant computational cost from processing numerous vision tokens through all LLM layers. Prior pruning methods operate either before the LLM, limiting generality due to diverse encoder-projector designs or within the LLM using heuristics that are incompatible with FlashAttention. We take a different approach: rather than identifying unimportant tokens, we treat the LLM itself as the optimal guide for compression. Observing that deeper layers naturally transmit vision-to-text information, we introduce Attention-Driven Self-Compression (ADSC), a simple, broadly applicable method that progressively reduces vision tokens using only the LLM's attention mechanism. Our method applies uniform token downsampling at selected layers, forming bottlenecks that encourage the model to reorganize and compress information into the remaining tokens. It requires no score computation, auxiliary modules, or attention modification, and remains fully compatible with FlashAttention. Applied to LLaVA-1.5, ADSC reduces FLOPs by 53.7% and peak KV-cache memory by 56.7%, while preserving 98.2% of the original model performance. Across multiple benchmarks, it outperforms prior pruning approaches in both efficiency and accuracy. Crucially, under high compression ratios, our method remains robust while heuristic-based techniques degrade sharply.
ARGaze: Autoregressive Transformers for Online Egocentric Gaze Estimation
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Online egocentric gaze estimation predicts where a camera wearer is looking from first-person video using only past and current frames, a task essential for augmented reality and assistive technologies. Unlike third-person gaze estimation, this setting lacks explicit head or eye signals, requiring models to infer current visual attention from sparse, indirect cues such as hand-object interactions and salient scene content. We observe that gaze exhibits strong temporal continuity during goal-directed activities: knowing where a person looked recently provides a powerful prior for predicting where they look next. Inspired by vision-conditioned autoregressive decoding in vision-language models, we propose ARGaze, which reformulates gaze estimation as sequential prediction: at each timestep, a transformer decoder predicts current gaze by conditioning on (i) current visual features and (ii) a fixed-length Gaze Context Window of recent gaze target estimates. This design enforces causality and enables bounded-resource streaming inference. We achieve state-of-the-art performance across multiple egocentric benchmarks under online evaluation, with extensive ablations validating that autoregressive modeling with bounded gaze history is critical for robust prediction. We will release our source code and pre-trained models.
TP-Blend: Textual-Prompt Attention Pairing for Precise Object-Style Blending in Diffusion Models
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Current text-conditioned diffusion editors handle single object replacement well but struggle when a new object and a new style must be introduced simultaneously. We present Twin-Prompt Attention Blend (TP-Blend), a lightweight training-free framework that receives two separate textual prompts, one specifying a blend object and the other defining a target style, and injects both into a single denoising trajectory. TP-Blend is driven by two complementary attention processors. Cross-Attention Object Fusion (CAOF) first averages head-wise attention to locate spatial tokens that respond strongly to either prompt, then solves an entropy-regularised optimal transport problem that reassigns complete multi-head feature vectors to those positions. CAOF updates feature vectors at the full combined dimensionality of all heads (e.g., 640 dimensions in SD-XL), preserving rich cross-head correlations while keeping memory low. Self-Attention Style Fusion (SASF) injects style at every self-attention layer through Detail-Sensitive Instance Normalization. A lightweight one-dimensional Gaussian filter separates low- and high-frequency components; only the high-frequency residual is blended back, imprinting brush-stroke-level texture without disrupting global geometry. SASF further swaps the Key and Value matrices with those derived from the style prompt, enforcing context-aware texture modulation that remains independent of object fusion. Extensive experiments show that TP-Blend produces high-resolution, photo-realistic edits with precise control over both content and appearance, surpassing recent baselines in quantitative fidelity, perceptual quality, and inference speed.
Object-WIPER : Training-Free Object and Associated Effect Removal in Videos
Jan 10, 2026Abstract:In this paper, we introduce Object-WIPER, a training-free framework for removing dynamic objects and their associated visual effects from videos, and inpainting them with semantically consistent and temporally coherent content. Our approach leverages a pre-trained text-to-video diffusion transformer (DiT). Given an input video, a user-provided object mask, and query tokens describing the target object and its effects, we localize relevant visual tokens via visual-text cross-attention and visual self-attention. This produces an intermediate effect mask that we fuse with the user mask to obtain a final foreground token mask to replace. We first invert the video through the DiT to obtain structured noise, then reinitialize the masked tokens with Gaussian noise while preserving background tokens. During denoising, we copy values for the background tokens saved during inversion to maintain scene fidelity. To address the lack of suitable evaluation, we introduce a new object removal metric that rewards temporal consistency among foreground tokens across consecutive frames, coherence between foreground and background tokens within each frame, and dissimilarity between the input and output foreground tokens. Experiments on DAVIS and a newly curated real-world associated effect benchmark (WIPER-Bench) show that Object-WIPER surpasses both training-based and training-free baselines in terms of the metric, achieving clean removal and temporally stable reconstruction without any retraining. Our new benchmark, source code, and pre-trained models will be publicly available.
Explainable AI-Generated Image Detection RewardBench
Nov 15, 2025Abstract:Conventional, classification-based AI-generated image detection methods cannot explain why an image is considered real or AI-generated in a way a human expert would, which reduces the trustworthiness and persuasiveness of these detection tools for real-world applications. Leveraging Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) has recently become a trending solution to this issue. Further, to evaluate the quality of generated explanations, a common approach is to adopt an "MLLM as a judge" methodology to evaluate explanations generated by other MLLMs. However, how well those MLLMs perform when judging explanations for AI-generated image detection generated by themselves or other MLLMs has not been well studied. We therefore propose \textbf{XAIGID-RewardBench}, the first benchmark designed to evaluate the ability of current MLLMs to judge the quality of explanations about whether an image is real or AI-generated. The benchmark consists of approximately 3,000 annotated triplets sourced from various image generation models and MLLMs as policy models (detectors) to assess the capabilities of current MLLMs as reward models (judges). Our results show that the current best reward model scored 88.76\% on this benchmark (while human inter-annotator agreement reaches 98.30\%), demonstrating that a visible gap remains between the reasoning abilities of today's MLLMs and human-level performance. In addition, we provide an analysis of common pitfalls that these models frequently encounter. Code and benchmark are available at https://github.com/RewardBench/XAIGID-RewardBench.
Toward Gaze Target Detection of Young Autistic Children
Nov 14, 2025Abstract:The automatic detection of gaze targets in autistic children through artificial intelligence can be impactful, especially for those who lack access to a sufficient number of professionals to improve their quality of life. This paper introduces a new, real-world AI application for gaze target detection in autistic children, which predicts a child's point of gaze from an activity image. This task is foundational for building automated systems that can measure joint attention-a core challenge in Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). To facilitate the study of this challenging application, we collected the first-ever Autism Gaze Target (AGT) dataset. We further propose a novel Socially Aware Coarse-to-Fine (SACF) gaze detection framework that explicitly leverages the social context of a scene to overcome the class imbalance common in autism datasets-a consequence of autistic children's tendency to show reduced gaze to faces. It utilizes a two-pathway architecture with expert models specialized in social and non-social gaze, guided by a context-awareness gate module. The results of our comprehensive experiments demonstrate that our framework achieves new state-of-the-art performance for gaze target detection in this population, significantly outperforming existing methods, especially on the critical minority class of face-directed gaze.
High-Quality Sound Separation Across Diverse Categories via Visually-Guided Generative Modeling
Sep 26, 2025Abstract:We propose DAVIS, a Diffusion-based Audio-VIsual Separation framework that solves the audio-visual sound source separation task through generative learning. Existing methods typically frame sound separation as a mask-based regression problem, achieving significant progress. However, they face limitations in capturing the complex data distribution required for high-quality separation of sounds from diverse categories. In contrast, DAVIS circumvents these issues by leveraging potent generative modeling paradigms, specifically Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models (DDPM) and the more recent Flow Matching (FM), integrated within a specialized Separation U-Net architecture. Our framework operates by synthesizing the desired separated sound spectrograms directly from a noise distribution, conditioned concurrently on the mixed audio input and associated visual information. The inherent nature of its generative objective makes DAVIS particularly adept at producing high-quality sound separations for diverse sound categories. We present comparative evaluations of DAVIS, encompassing both its DDPM and Flow Matching variants, against leading methods on the standard AVE and MUSIC datasets. The results affirm that both variants surpass existing approaches in separation quality, highlighting the efficacy of our generative framework for tackling the audio-visual source separation task.
ANNIE: Be Careful of Your Robots
Sep 03, 2025Abstract:The integration of vision-language-action (VLA) models into embodied AI (EAI) robots is rapidly advancing their ability to perform complex, long-horizon tasks in humancentric environments. However, EAI systems introduce critical security risks: a compromised VLA model can directly translate adversarial perturbations on sensory input into unsafe physical actions. Traditional safety definitions and methodologies from the machine learning community are no longer sufficient. EAI systems raise new questions, such as what constitutes safety, how to measure it, and how to design effective attack and defense mechanisms in physically grounded, interactive settings. In this work, we present the first systematic study of adversarial safety attacks on embodied AI systems, grounded in ISO standards for human-robot interactions. We (1) formalize a principled taxonomy of safety violations (critical, dangerous, risky) based on physical constraints such as separation distance, velocity, and collision boundaries; (2) introduce ANNIEBench, a benchmark of nine safety-critical scenarios with 2,400 video-action sequences for evaluating embodied safety; and (3) ANNIE-Attack, a task-aware adversarial framework with an attack leader model that decomposes long-horizon goals into frame-level perturbations. Our evaluation across representative EAI models shows attack success rates exceeding 50% across all safety categories. We further demonstrate sparse and adaptive attack strategies and validate the real-world impact through physical robot experiments. These results expose a previously underexplored but highly consequential attack surface in embodied AI systems, highlighting the urgent need for security-driven defenses in the physical AI era. Code is available at https://github.com/RLCLab/Annie.
FreSca: Unveiling the Scaling Space in Diffusion Models
Apr 02, 2025Abstract:Diffusion models offer impressive controllability for image tasks, primarily through noise predictions that encode task-specific information and classifier-free guidance enabling adjustable scaling. This scaling mechanism implicitly defines a ``scaling space'' whose potential for fine-grained semantic manipulation remains underexplored. We investigate this space, starting with inversion-based editing where the difference between conditional/unconditional noise predictions carries key semantic information. Our core contribution stems from a Fourier analysis of noise predictions, revealing that its low- and high-frequency components evolve differently throughout diffusion. Based on this insight, we introduce FreSca, a straightforward method that applies guidance scaling independently to different frequency bands in the Fourier domain. FreSca demonstrably enhances existing image editing methods without retraining. Excitingly, its effectiveness extends to image understanding tasks such as depth estimation, yielding quantitative gains across multiple datasets.
Towards Online Multi-Modal Social Interaction Understanding
Mar 25, 2025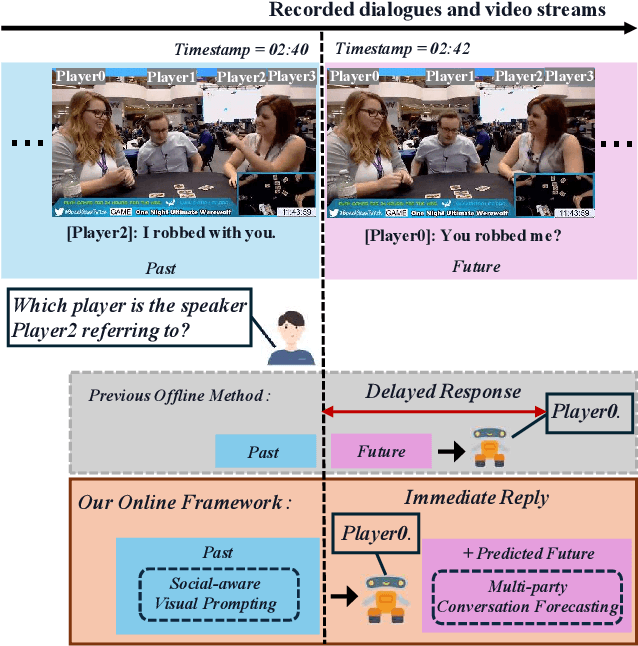
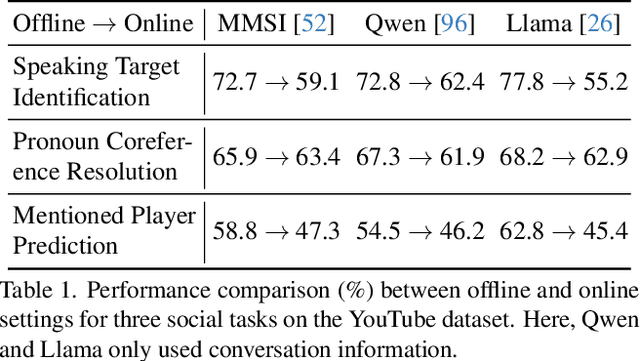
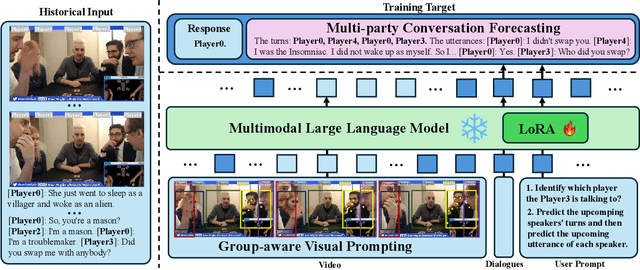
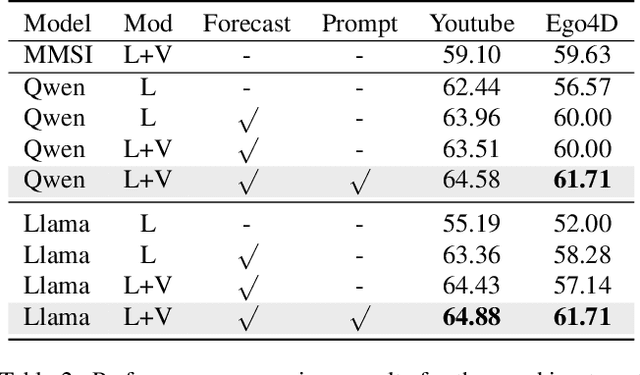
Abstract:Multimodal social interaction understanding (MMSI) is critical in human-robot interaction systems. In real-world scenarios, AI agents are required to provide real-time feedback. However, existing models often depend on both past and future contexts, which hinders them from applying to real-world problems. To bridge this gap, we propose an online MMSI setting, where the model must resolve MMSI tasks using only historical information, such as recorded dialogues and video streams. To address the challenges of missing the useful future context, we develop a novel framework, named Online-MMSI-VLM, that leverages two complementary strategies: multi-party conversation forecasting and social-aware visual prompting with multi-modal large language models. First, to enrich linguistic context, the multi-party conversation forecasting simulates potential future utterances in a coarse-to-fine manner, anticipating upcoming speaker turns and then generating fine-grained conversational details. Second, to effectively incorporate visual social cues like gaze and gesture, social-aware visual prompting highlights the social dynamics in video with bounding boxes and body keypoints for each person and frame. Extensive experiments on three tasks and two datasets demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance and significantly outperforms baseline models, indicating its effectiveness on Online-MMSI. The code and pre-trained models will be publicly released at: https://github.com/Sampson-Lee/OnlineMMSI.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge