Xu Li
Britton Chance Center for Biomedical Photonics, Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics-Huazhong University of Science and Technology, China
Wild-Drive: Off-Road Scene Captioning and Path Planning via Robust Multi-modal Routing and Efficient Large Language Model
Feb 28, 2026Abstract:Explainability and transparent decision-making are essential for the safe deployment of autonomous driving systems. Scene captioning summarizes environmental conditions and risk factors in natural language, improving transparency, safety, and human--robot interaction. However, most existing approaches target structured urban scenarios; in off-road environments, they are vulnerable to single-modality degradations caused by rain, fog, snow, and darkness, and they lack a unified framework that jointly models structured scene captioning and path planning. To bridge this gap, we propose Wild-Drive, an efficient framework for off-road scene captioning and path planning. Wild-Drive adopts modern multimodal encoders and introduces a task-conditioned modality-routing bridge, MoRo-Former, to adaptively aggregate reliable information under degraded sensing. It then integrates an efficient large language model (LLM), together with a planning token and a gate recurrent unit (GRU) decoder, to generate structured captions and predict future trajectories. We also build the OR-C2P Benchmark, which covers structured off-road scene captioning and path planning under diverse sensor corruption conditions. Experiments on OR-C2P dataset and a self-collected dataset show that Wild-Drive outperforms prior LLM-based methods and remains more stable under degraded sensing. The code and benchmark will be publicly available at https://github.com/wangzihanggg/Wild-Drive.
Unsafer in Many Turns: Benchmarking and Defending Multi-Turn Safety Risks in Tool-Using Agents
Feb 13, 2026Abstract:LLM-based agents are becoming increasingly capable, yet their safety lags behind. This creates a gap between what agents can do and should do. This gap widens as agents engage in multi-turn interactions and employ diverse tools, introducing new risks overlooked by existing benchmarks. To systematically scale safety testing into multi-turn, tool-realistic settings, we propose a principled taxonomy that transforms single-turn harmful tasks into multi-turn attack sequences. Using this taxonomy, we construct MT-AgentRisk (Multi-Turn Agent Risk Benchmark), the first benchmark to evaluate multi-turn tool-using agent safety. Our experiments reveal substantial safety degradation: the Attack Success Rate (ASR) increases by 16% on average across open and closed models in multi-turn settings. To close this gap, we propose ToolShield, a training-free, tool-agnostic, self-exploration defense: when encountering a new tool, the agent autonomously generates test cases, executes them to observe downstream effects, and distills safety experiences for deployment. Experiments show that ToolShield effectively reduces ASR by 30% on average in multi-turn interactions. Our code is available at https://github.com/CHATS-lab/ToolShield.
The RoboSense Challenge: Sense Anything, Navigate Anywhere, Adapt Across Platforms
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Autonomous systems are increasingly deployed in open and dynamic environments -- from city streets to aerial and indoor spaces -- where perception models must remain reliable under sensor noise, environmental variation, and platform shifts. However, even state-of-the-art methods often degrade under unseen conditions, highlighting the need for robust and generalizable robot sensing. The RoboSense 2025 Challenge is designed to advance robustness and adaptability in robot perception across diverse sensing scenarios. It unifies five complementary research tracks spanning language-grounded decision making, socially compliant navigation, sensor configuration generalization, cross-view and cross-modal correspondence, and cross-platform 3D perception. Together, these tasks form a comprehensive benchmark for evaluating real-world sensing reliability under domain shifts, sensor failures, and platform discrepancies. RoboSense 2025 provides standardized datasets, baseline models, and unified evaluation protocols, enabling large-scale and reproducible comparison of robust perception methods. The challenge attracted 143 teams from 85 institutions across 16 countries, reflecting broad community engagement. By consolidating insights from 23 winning solutions, this report highlights emerging methodological trends, shared design principles, and open challenges across all tracks, marking a step toward building robots that can sense reliably, act robustly, and adapt across platforms in real-world environments.
VLM-NCD:Novel Class Discovery with Vision-Based Large Language Models
Dec 11, 2025Abstract:Novel Class Discovery aims to utilise prior knowledge of known classes to classify and discover unknown classes from unlabelled data. Existing NCD methods for images primarily rely on visual features, which suffer from limitations such as insufficient feature discriminability and the long-tail distribution of data. We propose LLM-NCD, a multimodal framework that breaks this bottleneck by fusing visual-textual semantics and prototype guided clustering. Our key innovation lies in modelling cluster centres and semantic prototypes of known classes by jointly optimising known class image and text features, and a dualphase discovery mechanism that dynamically separates known or novel samples via semantic affinity thresholds and adaptive clustering. Experiments on the CIFAR-100 dataset show that compared to the current methods, this method achieves up to 25.3% improvement in accuracy for unknown classes. Notably, our method shows unique resilience to long tail distributions, a first in NCD literature.
LVD-GS: Gaussian Splatting SLAM for Dynamic Scenes via Hierarchical Explicit-Implicit Representation Collaboration Rendering
Oct 26, 2025Abstract:3D Gaussian Splatting SLAM has emerged as a widely used technique for high-fidelity mapping in spatial intelligence. However, existing methods often rely on a single representation scheme, which limits their performance in large-scale dynamic outdoor scenes and leads to cumulative pose errors and scale ambiguity. To address these challenges, we propose \textbf{LVD-GS}, a novel LiDAR-Visual 3D Gaussian Splatting SLAM system. Motivated by the human chain-of-thought process for information seeking, we introduce a hierarchical collaborative representation module that facilitates mutual reinforcement for mapping optimization, effectively mitigating scale drift and enhancing reconstruction robustness. Furthermore, to effectively eliminate the influence of dynamic objects, we propose a joint dynamic modeling module that generates fine-grained dynamic masks by fusing open-world segmentation with implicit residual constraints, guided by uncertainty estimates from DINO-Depth features. Extensive evaluations on KITTI, nuScenes, and self-collected datasets demonstrate that our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance compared to existing methods.
Text2Move: Text-to-moving sound generation via trajectory prediction and temporal alignment
Sep 26, 2025Abstract:Human auditory perception is shaped by moving sound sources in 3D space, yet prior work in generative sound modelling has largely been restricted to mono signals or static spatial audio. In this work, we introduce a framework for generating moving sounds given text prompts in a controllable fashion. To enable training, we construct a synthetic dataset that records moving sounds in binaural format, their spatial trajectories, and text captions about the sound event and spatial motion. Using this dataset, we train a text-to-trajectory prediction model that outputs the three-dimensional trajectory of a moving sound source given text prompts. To generate spatial audio, we first fine-tune a pre-trained text-to-audio generative model to output temporally aligned mono sound with the trajectory. The spatial audio is then simulated using the predicted temporally-aligned trajectory. Experimental evaluation demonstrates reasonable spatial understanding of the text-to-trajectory model. This approach could be easily integrated into existing text-to-audio generative workflow and extended to moving sound generation in other spatial audio formats.
Training-Free Pyramid Token Pruning for Efficient Large Vision-Language Models via Region, Token, and Instruction-Guided Importance
Sep 19, 2025Abstract:Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) have significantly advanced multimodal understanding but still struggle with efficiently processing high-resolution images. Recent approaches partition high-resolution images into multiple sub-images, dramatically increasing the number of visual tokens and causing exponential computational overhead during inference. To address these limitations, we propose a training-free token pruning strategy, Pyramid Token Pruning (PTP), that integrates bottom-up visual saliency at both region and token levels with top-down instruction-guided importance. Inspired by human visual attention mechanisms, PTP selectively retains more tokens from visually salient regions and further leverages textual instructions to pinpoint tokens most relevant to specific multimodal tasks. Extensive experiments across 13 diverse benchmarks demonstrate that our method substantially reduces computational overhead and inference latency with minimal performance loss.
HERO: Rethinking Visual Token Early Dropping in High-Resolution Large Vision-Language Models
Sep 16, 2025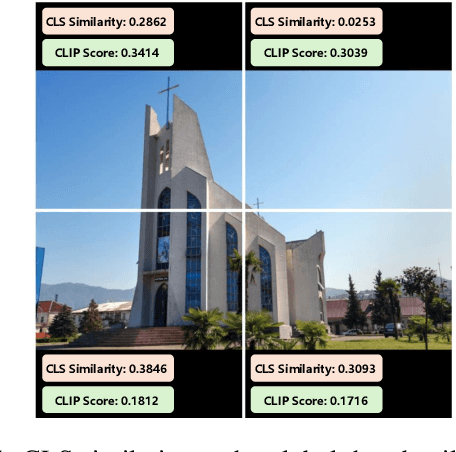
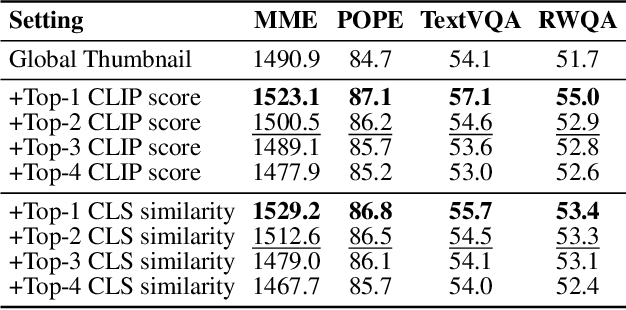
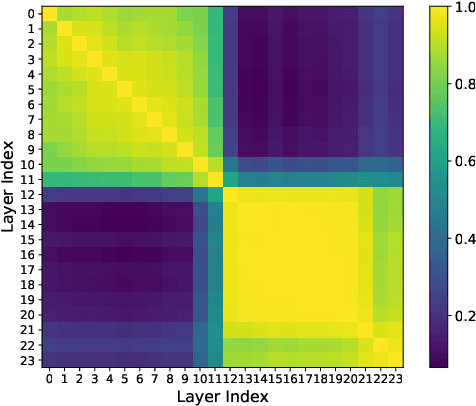
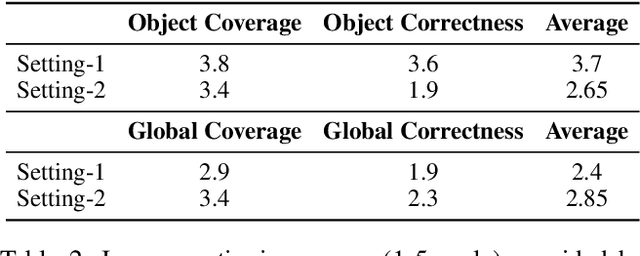
Abstract:By cropping high-resolution images into local tiles and encoding them independently, High-Resolution Large Vision-Language Models (HR-LVLMs) have demonstrated remarkable fine-grained visual understanding capabilities. However, this divide-and-conquer paradigm significantly increases the number of visual tokens, resulting in substantial computational and memory overhead. To better understand and address this challenge, we empirically investigate visual token utilization in HR-LVLMs and uncover three key findings: (1) the local tiles have varying importance, jointly determined by visual saliency and task relevance; (2) the CLS token in CLIP-based vision encoders exhibits a two-stage attention pattern across layers, with each stage attending to different types of visual tokens; (3) the visual tokens emphasized at different stages encode information at varying levels of granularity, playing complementary roles within LVLMs. Building on these insights, we propose HERO, a High-resolution visual token early dropping framework that integrates content-adaptive token budget allocation with function-aware token selection. By accurately estimating tile-level importance and selectively retaining visual tokens with complementary roles, HERO achieves superior efficiency-accuracy trade-offs across diverse benchmarks and model scales, all in a training-free manner. This study provides both empirical insights and practical solutions toward efficient inference in HR-LVLMs.
Joint decoding method for controllable contextual speech recognition based on Speech LLM
Aug 12, 2025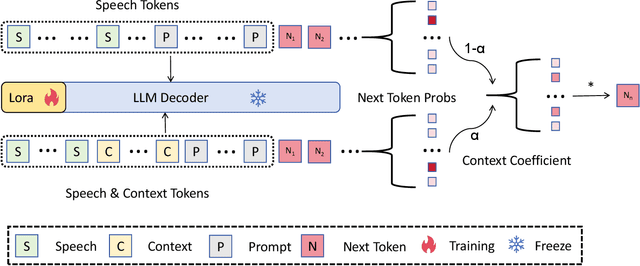
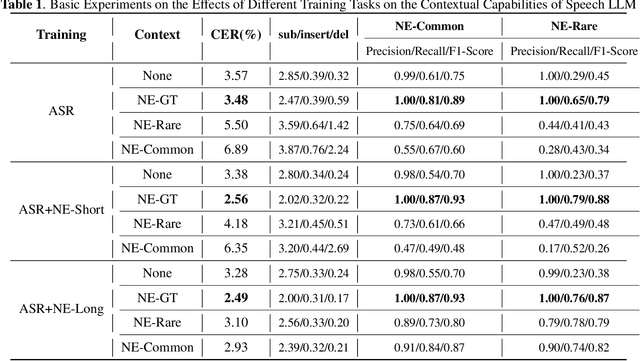
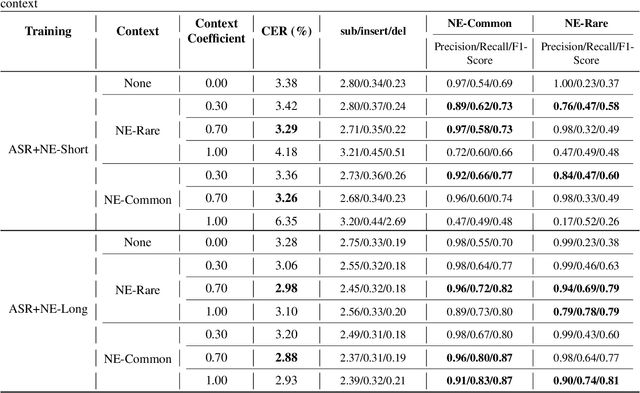
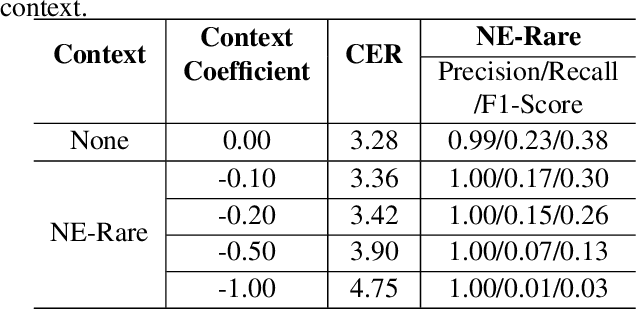
Abstract:Contextual speech recognition refers to the ability to identify preferences for specific content based on contextual information. Recently, leveraging the contextual understanding capabilities of Speech LLM to achieve contextual biasing by injecting contextual information through prompts have emerged as a research hotspot.However, the direct information injection method via prompts relies on the internal attention mechanism of the model, making it impossible to explicitly control the extent of information injection. To address this limitation, we propose a joint decoding method to control the contextual information. This approach enables explicit control over the injected contextual information and achieving superior recognition performance. Additionally, Our method can also be used for sensitive word suppression recognition.Furthermore, experimental results show that even Speech LLM not pre-trained on long contextual data can acquire long contextual capabilities through our method.
Large Language Models Enhanced by Plug and Play Syntactic Knowledge for Aspect-based Sentiment Analysis
Jun 15, 2025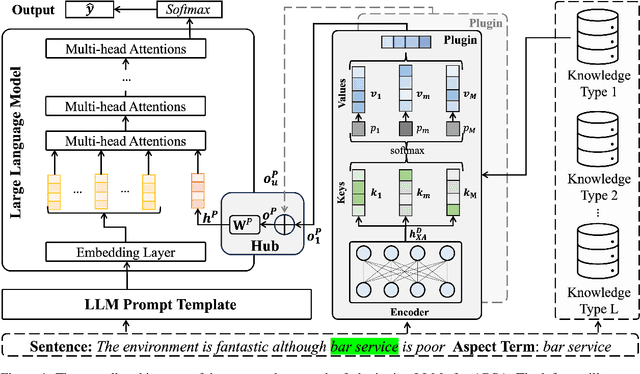
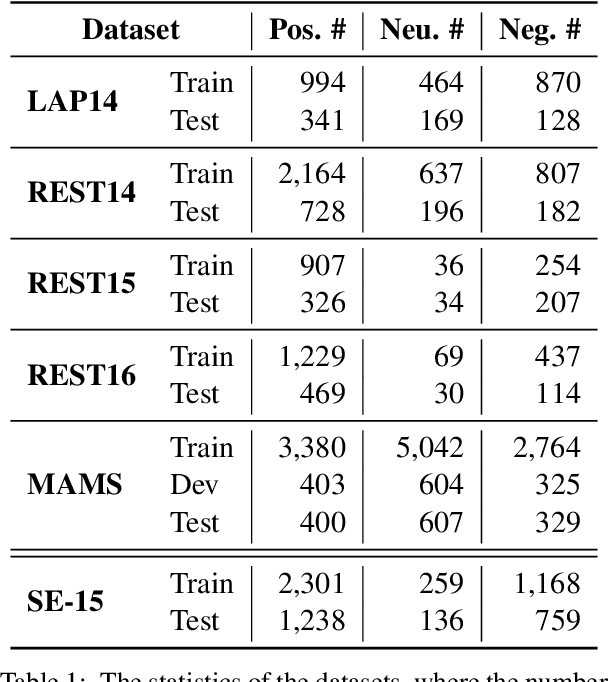
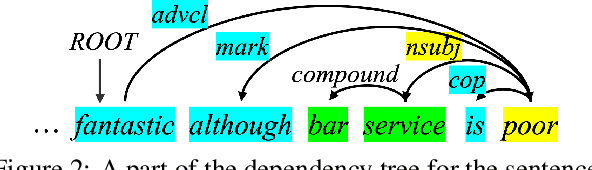
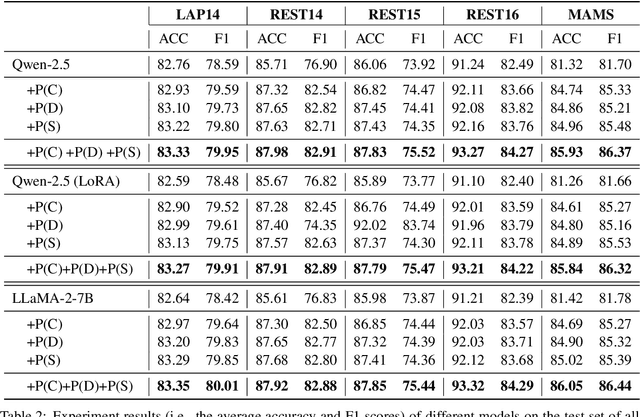
Abstract:Aspect-based sentiment analysis (ABSA) generally requires a deep understanding of the contextual information, including the words associated with the aspect terms and their syntactic dependencies. Most existing studies employ advanced encoders (e.g., pre-trained models) to capture such context, especially large language models (LLMs). However, training these encoders is resource-intensive, and in many cases, the available data is insufficient for necessary fine-tuning. Therefore it is challenging for learning LLMs within such restricted environments and computation efficiency requirement. As a result, it motivates the exploration of plug-and-play methods that adapt LLMs to ABSA with minimal effort. In this paper, we propose an approach that integrates extendable components capable of incorporating various types of syntactic knowledge, such as constituent syntax, word dependencies, and combinatory categorial grammar (CCG). Specifically, we propose a memory module that records syntactic information and is incorporated into LLMs to instruct the prediction of sentiment polarities. Importantly, this encoder acts as a versatile, detachable plugin that is trained independently of the LLM. We conduct experiments on benchmark datasets, which show that our approach outperforms strong baselines and previous approaches, thus demonstrates its effectiveness.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge