Guoqing Jin
Large Language Models Enhanced by Plug and Play Syntactic Knowledge for Aspect-based Sentiment Analysis
Jun 15, 2025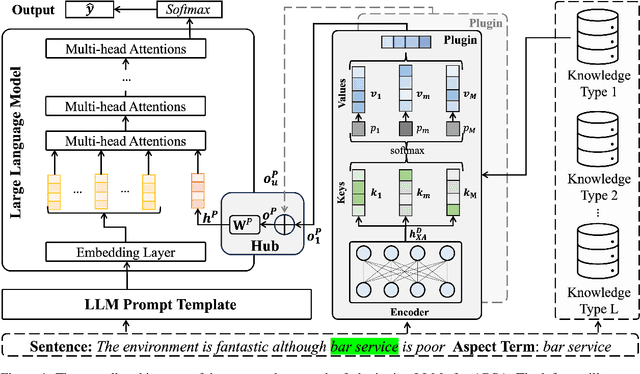
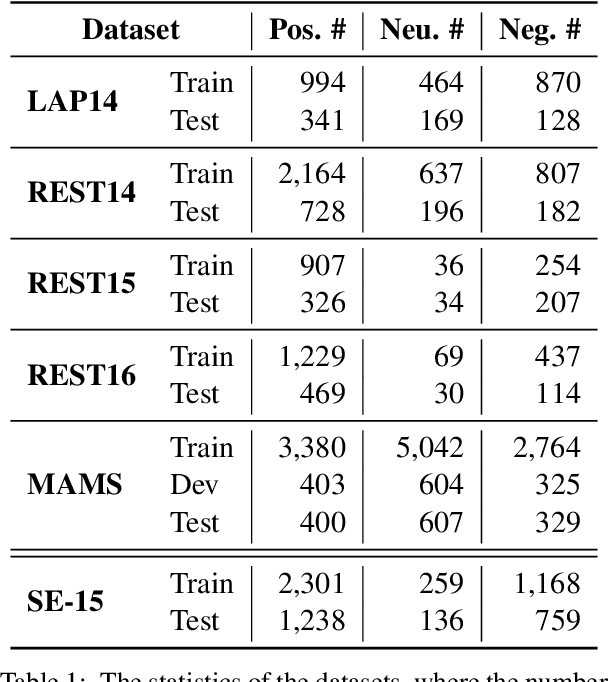
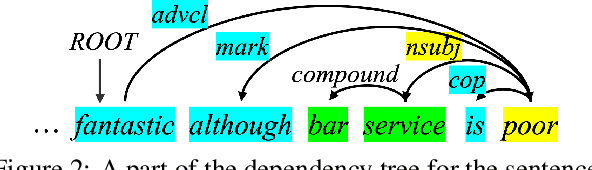
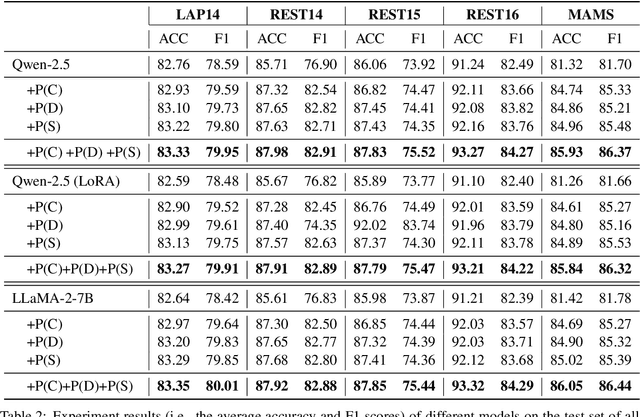
Abstract:Aspect-based sentiment analysis (ABSA) generally requires a deep understanding of the contextual information, including the words associated with the aspect terms and their syntactic dependencies. Most existing studies employ advanced encoders (e.g., pre-trained models) to capture such context, especially large language models (LLMs). However, training these encoders is resource-intensive, and in many cases, the available data is insufficient for necessary fine-tuning. Therefore it is challenging for learning LLMs within such restricted environments and computation efficiency requirement. As a result, it motivates the exploration of plug-and-play methods that adapt LLMs to ABSA with minimal effort. In this paper, we propose an approach that integrates extendable components capable of incorporating various types of syntactic knowledge, such as constituent syntax, word dependencies, and combinatory categorial grammar (CCG). Specifically, we propose a memory module that records syntactic information and is incorporated into LLMs to instruct the prediction of sentiment polarities. Importantly, this encoder acts as a versatile, detachable plugin that is trained independently of the LLM. We conduct experiments on benchmark datasets, which show that our approach outperforms strong baselines and previous approaches, thus demonstrates its effectiveness.
Representation Decomposition for Learning Similarity and Contrastness Across Modalities for Affective Computing
Jun 08, 2025



Abstract:Multi-modal affective computing aims to automatically recognize and interpret human attitudes from diverse data sources such as images and text, thereby enhancing human-computer interaction and emotion understanding. Existing approaches typically rely on unimodal analysis or straightforward fusion of cross-modal information that fail to capture complex and conflicting evidence presented across different modalities. In this paper, we propose a novel LLM-based approach for affective computing that explicitly deconstructs visual and textual representations into shared (modality-invariant) and modality-specific components. Specifically, our approach firstly encodes and aligns input modalities using pre-trained multi-modal encoders, then employs a representation decomposition framework to separate common emotional content from unique cues, and finally integrates these decomposed signals via an attention mechanism to form a dynamic soft prompt for a multi-modal LLM. Extensive experiments on three representative tasks for affective computing, namely, multi-modal aspect-based sentiment analysis, multi-modal emotion analysis, and hateful meme detection, demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach, which consistently outperforms strong baselines and state-of-the-art models.
OmniPrism: Learning Disentangled Visual Concept for Image Generation
Dec 16, 2024



Abstract:Creative visual concept generation often draws inspiration from specific concepts in a reference image to produce relevant outcomes. However, existing methods are typically constrained to single-aspect concept generation or are easily disrupted by irrelevant concepts in multi-aspect concept scenarios, leading to concept confusion and hindering creative generation. To address this, we propose OmniPrism, a visual concept disentangling approach for creative image generation. Our method learns disentangled concept representations guided by natural language and trains a diffusion model to incorporate these concepts. We utilize the rich semantic space of a multimodal extractor to achieve concept disentanglement from given images and concept guidance. To disentangle concepts with different semantics, we construct a paired concept disentangled dataset (PCD-200K), where each pair shares the same concept such as content, style, and composition. We learn disentangled concept representations through our contrastive orthogonal disentangled (COD) training pipeline, which are then injected into additional diffusion cross-attention layers for generation. A set of block embeddings is designed to adapt each block's concept domain in the diffusion models. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method can generate high-quality, concept-disentangled results with high fidelity to text prompts and desired concepts.
Feature-Adaptive and Data-Scalable In-Context Learning
May 17, 2024



Abstract:In-context learning (ICL), which promotes inference with several demonstrations, has become a widespread paradigm to stimulate LLM capabilities for downstream tasks. Due to context length constraints, it cannot be further improved in spite of more training data, and general features directly from LLMs in ICL are not adaptive to the specific downstream task. In this paper, we propose a feature-adaptive and data-scalable in-context learning framework (FADS-ICL), which can leverage task-adaptive features to promote inference on the downstream task, with the supervision of beyond-context samples. Specifically, it first extracts general features of beyond-context samples via the LLM with ICL input form one by one, and introduces a task-specific modulator to perform feature refinement and prediction after fitting a specific downstream task. We conduct extensive experiments on FADS-ICL under varying data settings (4$\sim$128 shots) and LLM scale (0.8$\sim$70B) settings. Experimental results show that FADS-ICL consistently outperforms previous state-of-the-art methods by a significant margin under all settings, verifying the effectiveness and superiority of FADS-ICL. For example, under the 1.5B and 32 shots setting, FADS-ICL can achieve \textbf{+14.3} average accuracy from feature adaptation over vanilla ICL on 10 datasets, with \textbf{+6.2} average accuracy over the previous state-of-the-art method, and the performance can further improve with increasing training data. Code and data are publicly available at \url{https://github.com/jiahaozhenbang/FADS-ICL}.
Towards Balanced Alignment: Modal-Enhanced Semantic Modeling for Video Moment Retrieval
Dec 19, 2023



Abstract:Video Moment Retrieval (VMR) aims to retrieve temporal segments in untrimmed videos corresponding to a given language query by constructing cross-modal alignment strategies. However, these existing strategies are often sub-optimal since they ignore the modality imbalance problem, \textit{i.e.}, the semantic richness inherent in videos far exceeds that of a given limited-length sentence. Therefore, in pursuit of better alignment, a natural idea is enhancing the video modality to filter out query-irrelevant semantics, and enhancing the text modality to capture more segment-relevant knowledge. In this paper, we introduce Modal-Enhanced Semantic Modeling (MESM), a novel framework for more balanced alignment through enhancing features at two levels. First, we enhance the video modality at the frame-word level through word reconstruction. This strategy emphasizes the portions associated with query words in frame-level features while suppressing irrelevant parts. Therefore, the enhanced video contains less redundant semantics and is more balanced with the textual modality. Second, we enhance the textual modality at the segment-sentence level by learning complementary knowledge from context sentences and ground-truth segments. With the knowledge added to the query, the textual modality thus maintains more meaningful semantics and is more balanced with the video modality. By implementing two levels of MESM, the semantic information from both modalities is more balanced to align, thereby bridging the modality gap. Experiments on three widely used benchmarks, including the out-of-distribution settings, show that the proposed framework achieves a new start-of-the-art performance with notable generalization ability (e.g., 4.42% and 7.69% average gains of R1@0.7 on Charades-STA and Charades-CG). The code will be available at https://github.com/lntzm/MESM.
APE-GAN: Adversarial Perturbation Elimination with GAN
Sep 26, 2017



Abstract:Although neural networks could achieve state-of-the-art performance while recongnizing images, they often suffer a tremendous defeat from adversarial examples--inputs generated by utilizing imperceptible but intentional perturbation to clean samples from the datasets. How to defense against adversarial examples is an important problem which is well worth researching. So far, very few methods have provided a significant defense to adversarial examples. In this paper, a novel idea is proposed and an effective framework based Generative Adversarial Nets named APE-GAN is implemented to defense against the adversarial examples. The experimental results on three benchmark datasets including MNIST, CIFAR10 and ImageNet indicate that APE-GAN is effective to resist adversarial examples generated from five attacks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge