Shiwei Shen
Human2Robot: Learning Robot Actions from Paired Human-Robot Videos
Feb 23, 2025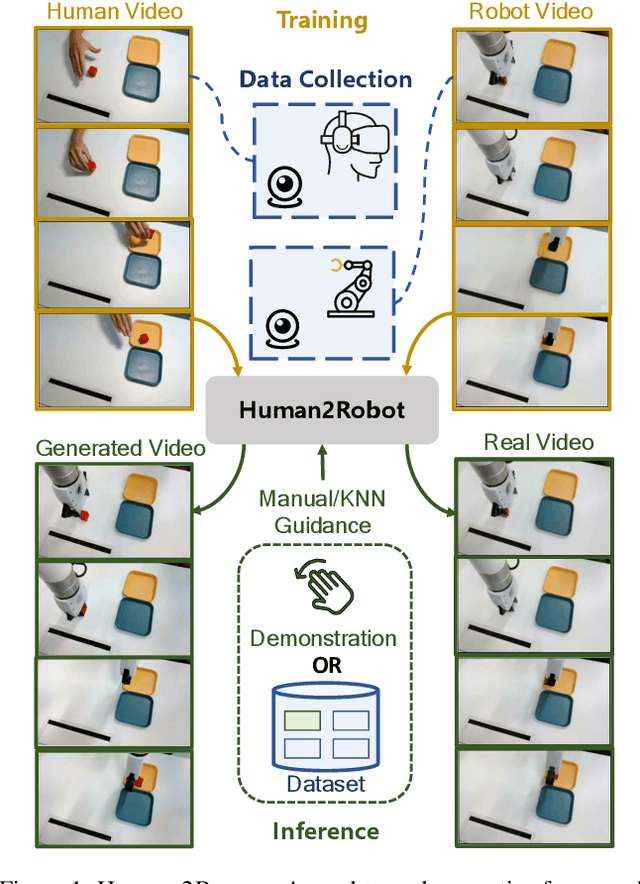
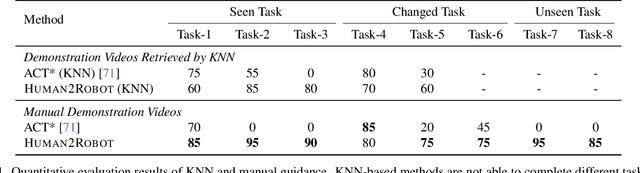
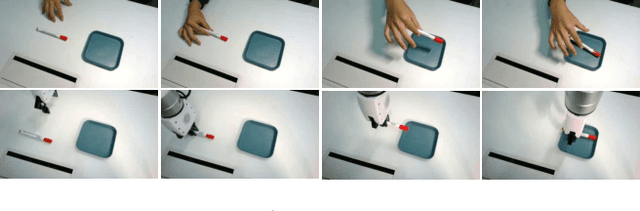
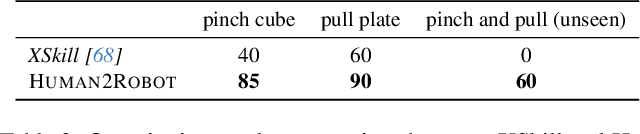
Abstract:Distilling knowledge from human demonstrations is a promising way for robots to learn and act. Existing work often overlooks the differences between humans and robots, producing unsatisfactory results. In this paper, we study how perfectly aligned human-robot pairs benefit robot learning. Capitalizing on VR-based teleportation, we introduce H\&R, a third-person dataset with 2,600 episodes, each of which captures the fine-grained correspondence between human hands and robot gripper. Inspired by the recent success of diffusion models, we introduce Human2Robot, an end-to-end diffusion framework that formulates learning from human demonstrates as a generative task. Human2Robot fully explores temporal dynamics in human videos to generate robot videos and predict actions at the same time. Through comprehensive evaluations of 8 seen, changed and unseen tasks in real-world settings, we demonstrate that Human2Robot can not only generate high-quality robot videos but also excel in seen tasks and generalize to unseen objects, backgrounds and even new tasks effortlessly.
APE-GAN: Adversarial Perturbation Elimination with GAN
Sep 26, 2017



Abstract:Although neural networks could achieve state-of-the-art performance while recongnizing images, they often suffer a tremendous defeat from adversarial examples--inputs generated by utilizing imperceptible but intentional perturbation to clean samples from the datasets. How to defense against adversarial examples is an important problem which is well worth researching. So far, very few methods have provided a significant defense to adversarial examples. In this paper, a novel idea is proposed and an effective framework based Generative Adversarial Nets named APE-GAN is implemented to defense against the adversarial examples. The experimental results on three benchmark datasets including MNIST, CIFAR10 and ImageNet indicate that APE-GAN is effective to resist adversarial examples generated from five attacks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge