Ke Gao
Meningioma Analysis and Diagnosis using Limited Labeled Samples
Feb 11, 2026Abstract:The biological behavior and treatment response of meningiomas depend on their grade, making an accurate diagnosis essential for treatment planning and prognosis assessment. We observed that the weighted fusion of spatial-frequency domain features significantly influences meningioma classification performance. Notably, the contribution of specific frequency bands obtained by discrete wavelet transform varies considerably across different images. A feature fusion architecture with adaptive weights of different frequency band information and spatial domain information is proposed for few-shot meningioma learning. To verify the effectiveness of the proposed method, a new MRI dataset of meningiomas is introduced. The experimental results demonstrate the superiority of the proposed method compared with existing state-of-the-art methods in three datasets. The code will be available at: https://github.com/ICL-SUST/AMSF-Net
QiMeng-Attention: SOTA Attention Operator is generated by SOTA Attention Algorithm
Jun 14, 2025Abstract:The attention operator remains a critical performance bottleneck in large language models (LLMs), particularly for long-context scenarios. While FlashAttention is the most widely used and effective GPU-aware acceleration algorithm, it must require time-consuming and hardware-specific manual implementation, limiting adaptability across GPU architectures. Existing LLMs have shown a lot of promise in code generation tasks, but struggle to generate high-performance attention code. The key challenge is it cannot comprehend the complex data flow and computation process of the attention operator and utilize low-level primitive to exploit GPU performance. To address the above challenge, we propose an LLM-friendly Thinking Language (LLM-TL) to help LLMs decouple the generation of high-level optimization logic and low-level implementation on GPU, and enhance LLMs' understanding of attention operator. Along with a 2-stage reasoning workflow, TL-Code generation and translation, the LLMs can automatically generate FlashAttention implementation on diverse GPUs, establishing a self-optimizing paradigm for generating high-performance attention operators in attention-centric algorithms. Verified on A100, RTX8000, and T4 GPUs, the performance of our methods significantly outshines that of vanilla LLMs, achieving a speed-up of up to 35.16x. Besides, our method not only surpasses human-optimized libraries (cuDNN and official library) in most scenarios but also extends support to unsupported hardware and data types, reducing development time from months to minutes compared with human experts.
QiMeng-TensorOp: Automatically Generating High-Performance Tensor Operators with Hardware Primitives
May 08, 2025Abstract:Computation-intensive tensor operators constitute over 90\% of the computations in Large Language Models (LLMs) and Deep Neural Networks.Automatically and efficiently generating high-performance tensor operators with hardware primitives is crucial for diverse and ever-evolving hardware architectures like RISC-V, ARM, and GPUs, as manually optimized implementation takes at least months and lacks portability.LLMs excel at generating high-level language codes, but they struggle to fully comprehend hardware characteristics and produce high-performance tensor operators. We introduce a tensor-operator auto-generation framework with a one-line user prompt (QiMeng-TensorOp), which enables LLMs to automatically exploit hardware characteristics to generate tensor operators with hardware primitives, and tune parameters for optimal performance across diverse hardware. Experimental results on various hardware platforms, SOTA LLMs, and typical tensor operators demonstrate that QiMeng-TensorOp effectively unleashes the computing capability of various hardware platforms, and automatically generates tensor operators of superior performance. Compared with vanilla LLMs, QiMeng-TensorOp achieves up to $1291 \times$ performance improvement. Even compared with human experts, QiMeng-TensorOp could reach $251 \%$ of OpenBLAS on RISC-V CPUs, and $124 \%$ of cuBLAS on NVIDIA GPUs. Additionally, QiMeng-TensorOp also significantly reduces development costs by $200 \times$ compared with human experts.
EasySpec: Layer-Parallel Speculative Decoding for Efficient Multi-GPU Utilization
Feb 04, 2025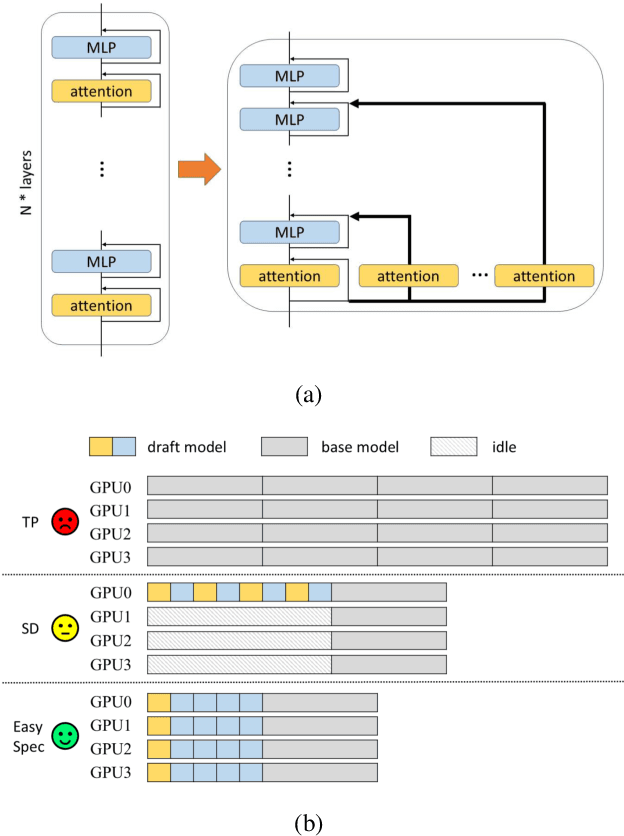
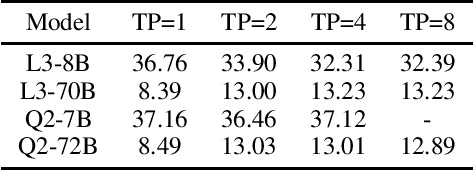
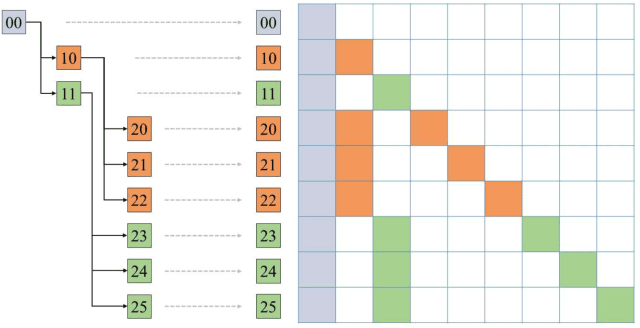
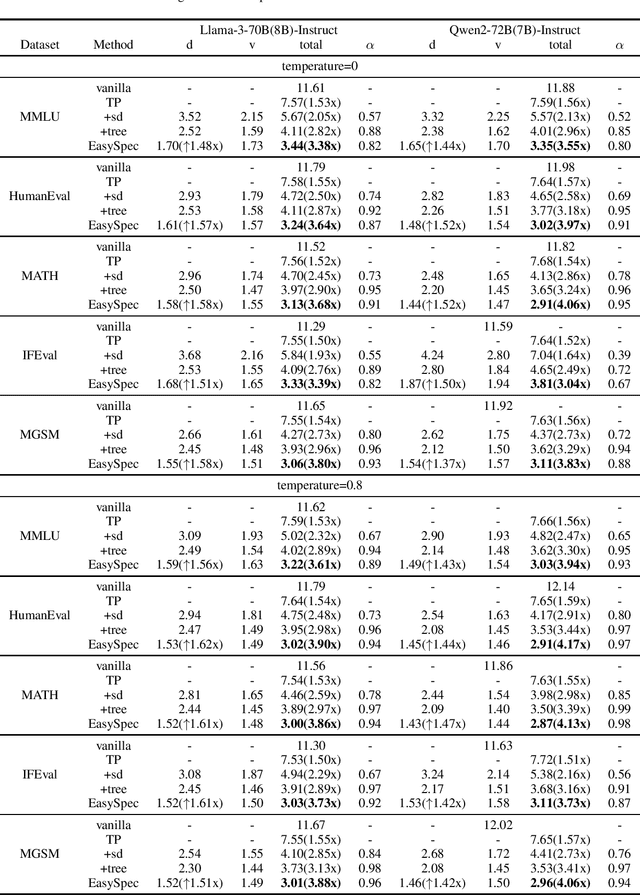
Abstract:Speculative decoding is an effective and lossless method for Large Language Model (LLM) inference acceleration. It employs a smaller model to generate a draft token sequence, which is then verified by the original base model. In multi-GPU systems, inference latency can be further reduced through tensor parallelism (TP), while the optimal TP size of the draft model is typically smaller than that of the base model, leading to GPU idling during the drafting stage. To solve this problem, we propose EasySpec, a layer-parallel speculation strategy that optimizes the efficiency of multi-GPU utilization.EasySpec breaks the sequential execution order of layers in the drafting model, enabling multi-layer parallelization across devices, albeit with some induced approximation errors. After each drafting-and-verification iteration, the draft model's key-value (KV) cache is calibrated in a single forward pass, preventing long-term error accumulation at minimal additional latency. We evaluated EasySpec on several mainstream open-source LLMs, using smaller versions of models from the same series as drafters. The results demonstrate that EasySpec can achieve a peak speedup of 4.17x compared to vanilla decoding, while preserving the original distribution of the base LLMs. Specifically, the drafting stage can be accelerated by up to 1.62x with a maximum accuracy drop of only 7%, requiring no training or fine-tuning on the draft models.
ITEM3D: Illumination-Aware Directional Texture Editing for 3D Models
Sep 27, 2023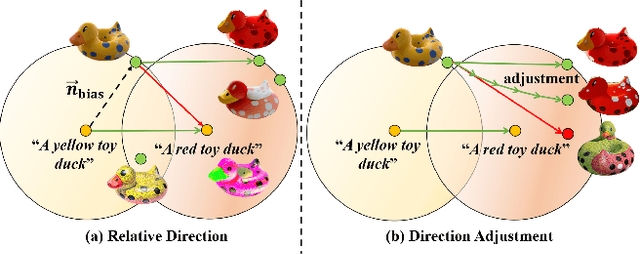
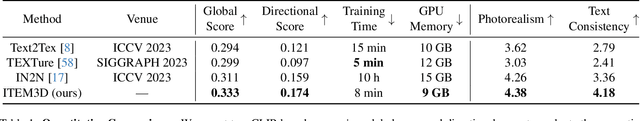
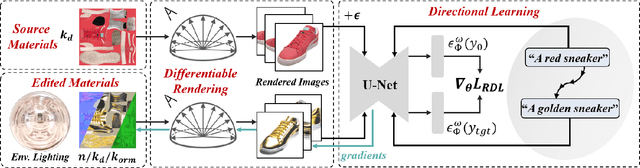

Abstract:Texture editing is a crucial task in 3D modeling that allows users to automatically manipulate the surface materials of 3D models. However, the inherent complexity of 3D models and the ambiguous text description lead to the challenge in this task. To address this challenge, we propose ITEM3D, an illumination-aware model for automatic 3D object editing according to the text prompts. Leveraging the diffusion models and the differentiable rendering, ITEM3D takes the rendered images as the bridge of text and 3D representation, and further optimizes the disentangled texture and environment map. Previous methods adopt the absolute editing direction namely score distillation sampling (SDS) as the optimization objective, which unfortunately results in the noisy appearance and text inconsistency. To solve the problem caused by the ambiguous text, we introduce a relative editing direction, an optimization objective defined by the noise difference between the source and target texts, to release the semantic ambiguity between the texts and images. Additionally, we gradually adjust the direction during optimization to further address the unexpected deviation in the texture domain. Qualitative and quantitative experiments show that our ITEM3D outperforms the state-of-the-art methods on various 3D objects. We also perform text-guided relighting to show explicit control over lighting.
GANHead: Towards Generative Animatable Neural Head Avatars
Apr 08, 2023



Abstract:To bring digital avatars into people's lives, it is highly demanded to efficiently generate complete, realistic, and animatable head avatars. This task is challenging, and it is difficult for existing methods to satisfy all the requirements at once. To achieve these goals, we propose GANHead (Generative Animatable Neural Head Avatar), a novel generative head model that takes advantages of both the fine-grained control over the explicit expression parameters and the realistic rendering results of implicit representations. Specifically, GANHead represents coarse geometry, fine-gained details and texture via three networks in canonical space to obtain the ability to generate complete and realistic head avatars. To achieve flexible animation, we define the deformation filed by standard linear blend skinning (LBS), with the learned continuous pose and expression bases and LBS weights. This allows the avatars to be directly animated by FLAME parameters and generalize well to unseen poses and expressions. Compared to state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods, GANHead achieves superior performance on head avatar generation and raw scan fitting.
Scenario-Adaptive and Self-Supervised Model for Multi-Scenario Personalized Recommendation
Aug 24, 2022
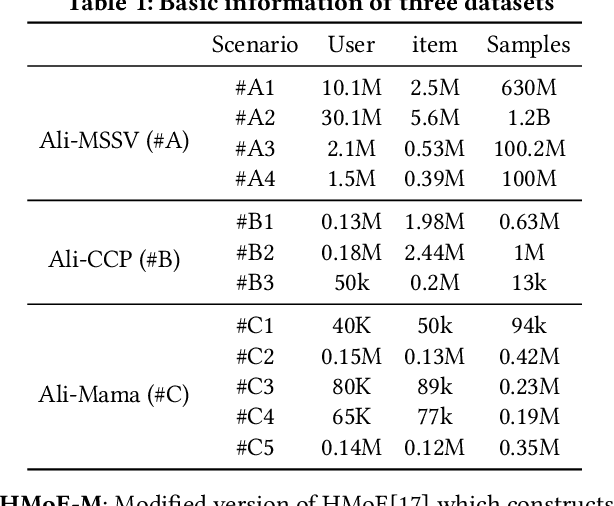
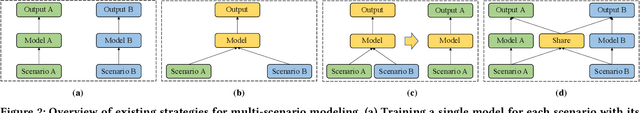
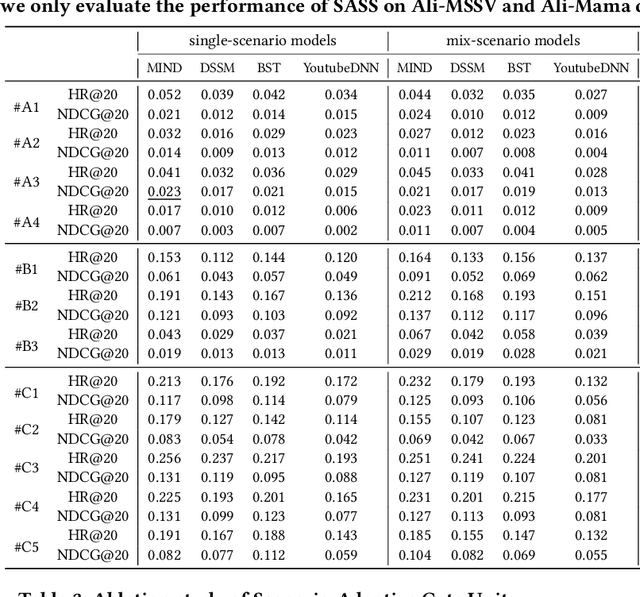
Abstract:Multi-scenario recommendation is dedicated to retrieve relevant items for users in multiple scenarios, which is ubiquitous in industrial recommendation systems. These scenarios enjoy portions of overlaps in users and items, while the distribution of different scenarios is different. The key point of multi-scenario modeling is to efficiently maximize the use of whole-scenario information and granularly generate adaptive representations both for users and items among multiple scenarios. we summarize three practical challenges which are not well solved for multi-scenario modeling: (1) Lacking of fine-grained and decoupled information transfer controls among multiple scenarios. (2) Insufficient exploitation of entire space samples. (3) Item's multi-scenario representation disentanglement problem. In this paper, we propose a Scenario-Adaptive and Self-Supervised (SASS) model to solve the three challenges mentioned above. Specifically, we design a Multi-Layer Scenario Adaptive Transfer (ML-SAT) module with scenario-adaptive gate units to select and fuse effective transfer information from whole scenario to individual scenario in a quite fine-grained and decoupled way. To sufficiently exploit the power of entire space samples, a two-stage training process including pre-training and fine-tune is introduced. The pre-training stage is based on a scenario-supervised contrastive learning task with the training samples drawn from labeled and unlabeled data spaces. The model is created symmetrically both in user side and item side, so that we can get distinguishing representations of items in different scenarios. Extensive experimental results on public and industrial datasets demonstrate the superiority of the SASS model over state-of-the-art methods. This model also achieves more than 8.0% improvement on Average Watching Time Per User in online A/B tests.
Multi-Granularity Network with Modal Attention for Dense Affective Understanding
Jun 18, 2021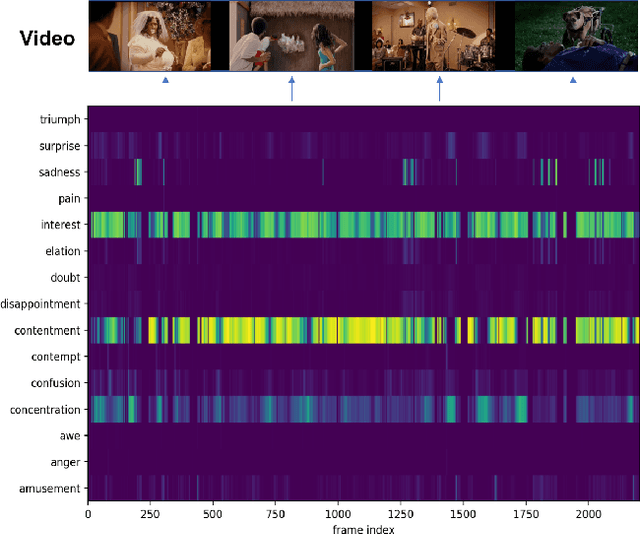

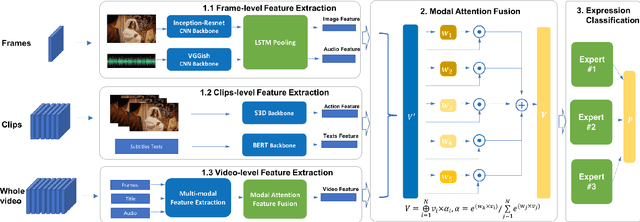
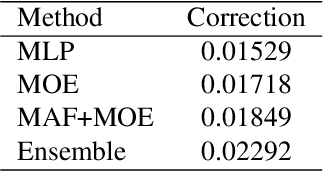
Abstract:Video affective understanding, which aims to predict the evoked expressions by the video content, is desired for video creation and recommendation. In the recent EEV challenge, a dense affective understanding task is proposed and requires frame-level affective prediction. In this paper, we propose a multi-granularity network with modal attention (MGN-MA), which employs multi-granularity features for better description of the target frame. Specifically, the multi-granularity features could be divided into frame-level, clips-level and video-level features, which corresponds to visual-salient content, semantic-context and video theme information. Then the modal attention fusion module is designed to fuse the multi-granularity features and emphasize more affection-relevant modals. Finally, the fused feature is fed into a Mixtures Of Experts (MOE) classifier to predict the expressions. Further employing model-ensemble post-processing, the proposed method achieves the correlation score of 0.02292 in the EEV challenge.
Progressive Domain Expansion Network for Single Domain Generalization
Mar 30, 2021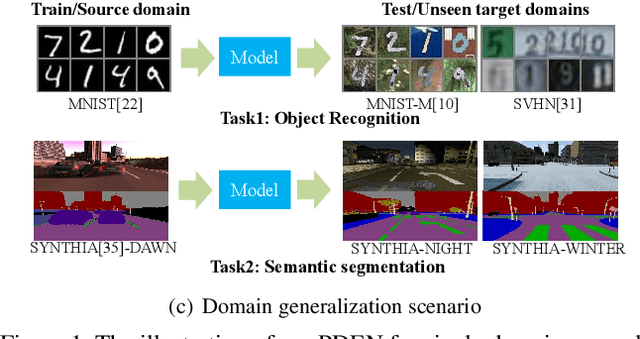
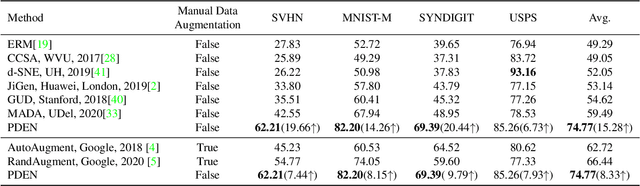
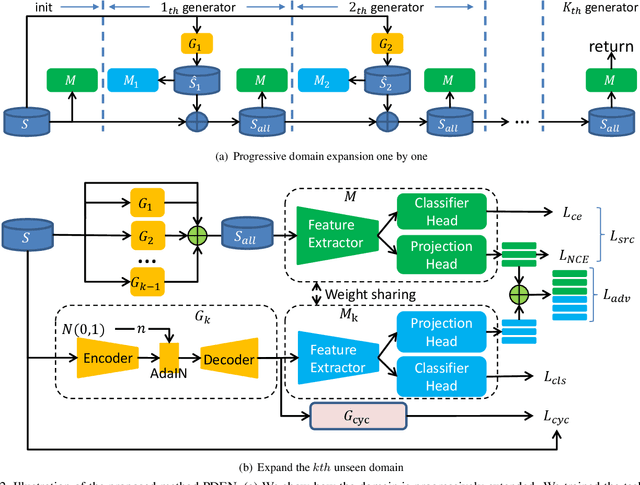
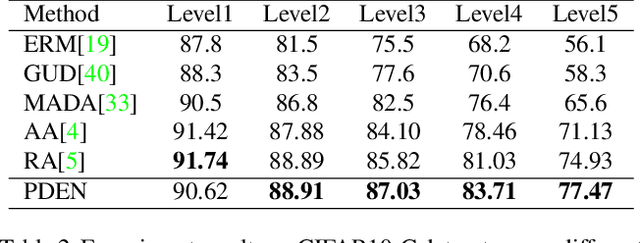
Abstract:Single domain generalization is a challenging case of model generalization, where the models are trained on a single domain and tested on other unseen domains. A promising solution is to learn cross-domain invariant representations by expanding the coverage of the training domain. These methods have limited generalization performance gains in practical applications due to the lack of appropriate safety and effectiveness constraints. In this paper, we propose a novel learning framework called progressive domain expansion network (PDEN) for single domain generalization. The domain expansion subnetwork and representation learning subnetwork in PDEN mutually benefit from each other by joint learning. For the domain expansion subnetwork, multiple domains are progressively generated in order to simulate various photometric and geometric transforms in unseen domains. A series of strategies are introduced to guarantee the safety and effectiveness of the expanded domains. For the domain invariant representation learning subnetwork, contrastive learning is introduced to learn the domain invariant representation in which each class is well clustered so that a better decision boundary can be learned to improve it's generalization. Extensive experiments on classification and segmentation have shown that PDEN can achieve up to 15.28% improvement compared with the state-of-the-art single-domain generalization methods.
Not All Words are Equal: Video-specific Information Loss for Video Captioning
Jan 01, 2019
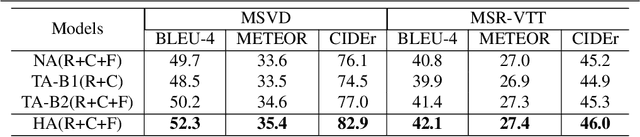
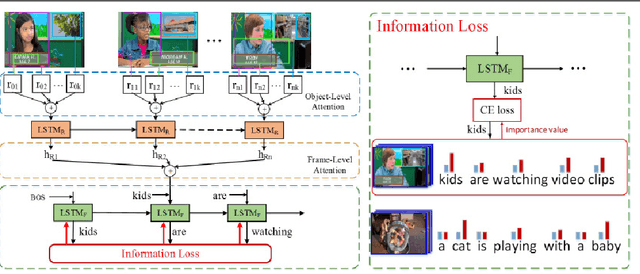
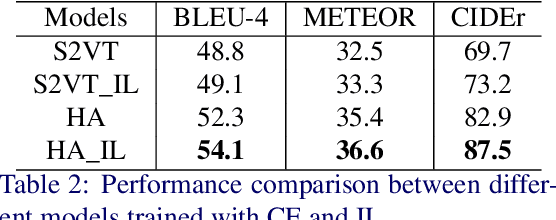
Abstract:An ideal description for a given video should fix its gaze on salient and representative content, which is capable of distinguishing this video from others. However, the distribution of different words is unbalanced in video captioning datasets, where distinctive words for describing video-specific salient objects are far less than common words such as 'a' 'the' and 'person'. The dataset bias often results in recognition error or detail deficiency of salient but unusual objects. To address this issue, we propose a novel learning strategy called Information Loss, which focuses on the relationship between the video-specific visual content and corresponding representative words. Moreover, a framework with hierarchical visual representations and an optimized hierarchical attention mechanism is established to capture the most salient spatial-temporal visual information, which fully exploits the potential strength of the proposed learning strategy. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the ingenious guidance strategy together with the optimized architecture outperforms state-of-the-art video captioning methods on MSVD with CIDEr score 87.5, and achieves superior CIDEr score 47.7 on MSR-VTT. We also show that our Information Loss is generic which improves various models by significant margins.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge